miR-125a-5p通过GSK-3β/Snail信号通路抑制乳腺癌细胞的上皮-间充质转化*
2018-06-30王照岩杨玉玲杨志一尹崇高李洪利刘雨清
王照岩,杨玉玲,杨志一,尹崇高,李洪利,刘雨清△
(潍坊医学院 1病理学教研室, 2医学研究实验中心, 3护理学院, 山东 潍坊 261053)
乳腺癌是全球女性肿瘤相关死亡的主要疾病,每年有超过150万的新确诊病例[1]。尽管通过手术、放疗和化疗的联合应用,已大大提高了早期乳腺癌患者的生存率,但晚期患者的临床生存率仍不容乐观[2]。因此,研究乳腺癌远处转移的分子机制,为提高病人的生存率提供新的理论依据。
微小RNA(microRNA,miRNA,miR)是一种非编码单链RNA分子,大约由22个核苷酸组成,可通过对靶基因的mRNA进行特异性碱基配对,调控靶基因的翻译过程,从而调节转录后基因表达[3]。上皮-间充质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)是上皮细胞获得间充质特征的一种现象,通过EMT,具有间质特征的肿瘤细胞明显增强了侵袭与迁移能力。新的研究表明,EMT在肿瘤细胞迁移的早期过程起着关键作用,并可通过多种信号通路促进癌细胞的侵袭转移[4]。miRNA在EMT中扮演着重要的角色,如miR-655[5]和miR-208[6]通过诱导EMT的发生促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭转移。生长因子受体结合蛋白2(growth factor receptor-bound protein 2,GRB2)相关结合蛋白2(GRB2-associated-binding protein 2,GAB2)是DOS/GAB家族的成员,通过整合多种信号通路,参与多种类型肿瘤的发生发展过程。本课题组先前研究发现,miR-125a-5p能够通过调控GAB2抑制乳腺癌细胞的侵袭与转移[7]。但miR-125a-5p能否通过其它机制对乳腺癌细胞EMT影响的研究尚不清楚。因此,本研究进一步探讨miR-125a-5p通过糖原合成酶激酶3β(glycogen synthase kinase-3β,GSK-3β)/Snail信号通路对乳腺癌细胞EMT的作用,为抑制乳腺癌细胞发生远处转移提供有价值的miRNA分子,同时也为乳腺癌治疗提供新的靶点。
材 料 和 方 法
1 主要材料
抗波形蛋白(vimentin)和上皮钙黏着蛋白(E-cadherin)单克隆抗体购自Santa Cruz;抗Snail、p-GSK-3β和GSK-3β抗体购自Cell Signaling Technology;表皮生长因子(epidermal growth factor,EGF)购自Peprotech;Lipofectamine 2000脂质体转染试剂购自Invitrogen;Transwell小室购自 Corning;Matrigel购自BD;胎牛血清和RPMI-1640培养基购自HyClone;MDA-MB-231、MCF-7和MCF-10A细胞购自ATCC。
2 主要方法
2.1细胞培养 细胞培养参照先前文献[8]。按文献[9]将细胞分组:(1)MDA-MB-231/NC组,转入空载质粒;(2)MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p组,转入miR-125a-5p过表达质粒;(3)MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+Con组,同时转入miR-125a-5p过表达质粒和GAB2过表达对照质粒;(4)MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+GAB2组,同时转入miR-125a-5p过表达质粒和GAB2过表达质粒。
2.2RT-qPCR实验 RNA提取及逆转录过程参照先前文献[10]。 PCR条件为95 ℃ 5 s、63 ℃ 30 s、72 ℃ 30 s进行35个循环。以U6作为内参照,U6的上游引物为5′-GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT-3′,下游引物为5′-CGCTTCACGAAT TTGCGTGTCAT-3′。miR-125a-5p的上游引物为5′-AGCGCGTCCCTGAGACCCTTTAAC-3′,下游引物为5′-ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG-3′,茎环结构序列为5′-GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTCACAG-3′。
2.3趋化运动实验 用EGF按4种不同浓度(0、1、10和100 μg/L)分别刺激MDA-MB-231细胞24 h,Transwell上室中加入细胞悬液,于5% CO2、37 ℃条件下培养24 h,固定、洗涤、Giemsa染色并拍照计数,所有实验均重复3次。
2.4Transwell侵袭实验 实验过程参照先前文献[11]。随机选取5个高倍镜视野拍照计数,计算平均值为实验的最终结果,所有实验均重复3次。
2.5核质分离 按核质分离试剂盒说明书对培养24 h后的各组细胞进行提取核蛋白,将所得的蛋白应用Western blot检测Snail蛋白在各组细胞中的表达。实验重复3次。
2.6Western blot实验 将转染后的细胞抽提蛋白。上样,电泳,转膜,封闭,滴加 I 抗4 ℃过夜,滴加 II 抗,TBST洗膜,曝光。抗体配制如下:β-actin(1∶1 000)、Snail(1∶500)、p-GSK-3β(1∶500)、GSK-3β(1∶500)、nucleolin(1∶500)、E-cadherin(1∶500)、vimentin(1∶500)。
3 统计学处理
采用SPSS 22.0进行统计学处理,实验数据均用均数±标准差(mean±SD),两组间定量资料采用独立样本t检验,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结 果
1 miR-125a-5p在人正常乳腺上皮细胞和乳腺癌细胞中的表达情况
RT-qPCR检测结果显示,与人正常乳腺上皮细胞MCF-10A相比,乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231和MCF-7中的miR-125a-5p表达明显降低(P<0.05)。结果表明,miR-125a-5p在MDA-MB-231和MCF-7细胞中低表达,见图1。

Figure 1. The expression of miR-125a-5p in normal breast epithelial cells and breast cancer cells. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vsMCF-10A group.
图1miR-125a-5p在人正常乳腺上皮细胞和乳腺癌细胞中的表达情况
2 miR-125a-5p在乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231中的转染效率
RT-qPCR检测结果显示,与MDA-MB-231/NC组细胞相比,MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p组细胞中miR-125a-5p的水平明显增高(P<0.05),提示转染成功,见图2。

Figure 2. The transfection efficiency of miR-125a-5p in MDA-MB-231 cells. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vsMDA-MB-231/NC group.
图2miR-125a-5p在乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231中的转染效率
3 EGF刺激乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231的最适浓度为10 μg/L
趋化运动实验结果显示,用0、1、10和100 μg/L的4种浓度的EGF刺激MDA-MB-231细胞后,与未用EGF刺激的MDA-MB-231细胞相比,其它3种浓度刺激的MDA-MB-231细胞趋化能力明显增强,其中,EGF浓度为10 μg/L时刺激趋化能力最强(P<0.05),见图3。
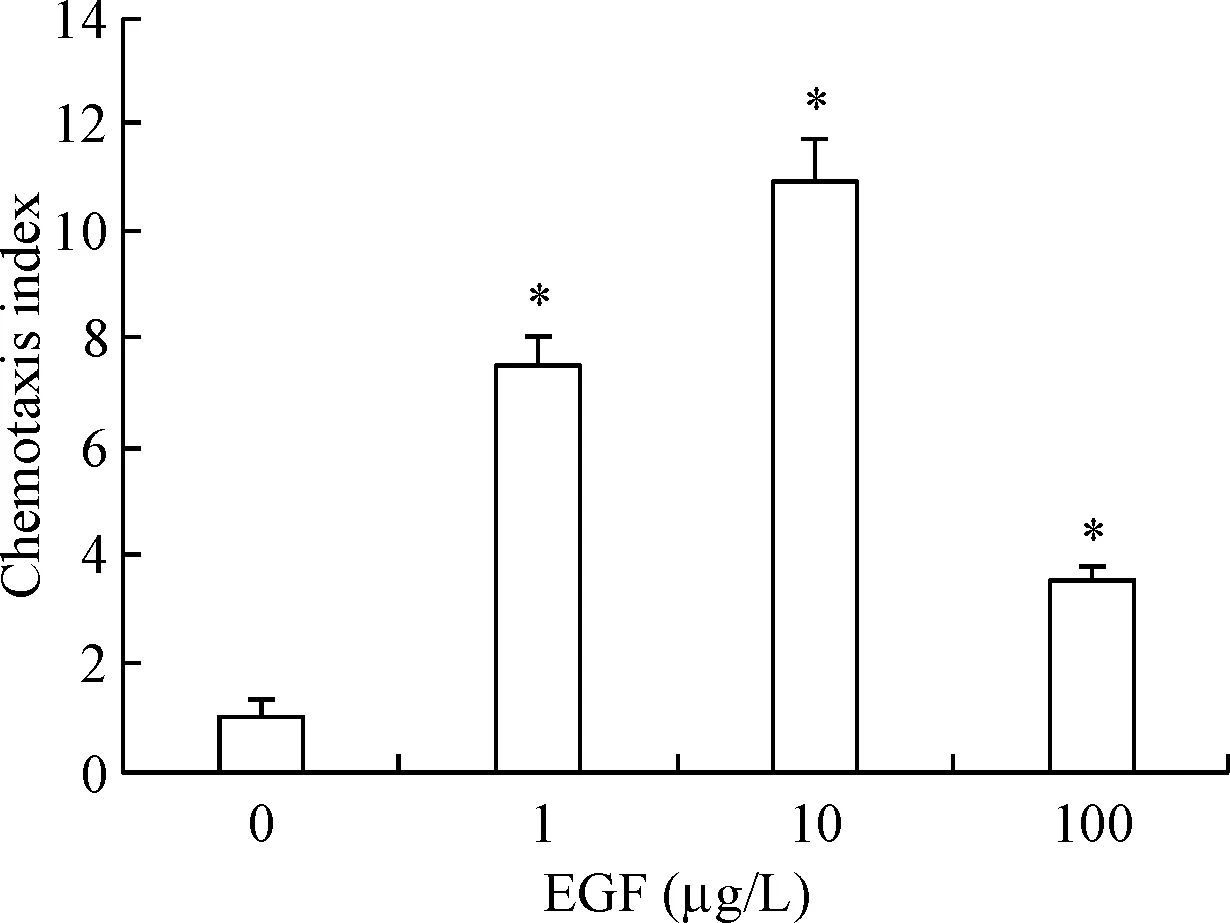
Figure 3. The optimal stimulation concentration of EGF in MDA-MB-231 cells was at 10 μg/L. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vs0 μg/L group.
图3EGF刺激乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231的最适浓度为10μg/L
4 miR-125a-5p抑制乳腺癌细胞的侵袭能力
Transwell侵袭实验结果显示,用EGF刺激24 h后,与MDA-MB-231/NC组细胞相比,MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p组细胞穿过基底膜的细胞数明显减少;而MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+GAB2组细胞穿过基底膜的细胞数比MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+Con组细胞明显增多(P<0.05),表明miR-125a-5p能明显降低MDA-MB-231细胞的侵袭能力,见图4。
5 miR-125a-5p抑制乳腺癌细胞的上皮-间质转化
Western blot检测EMT相关标志物的表达情况。结果显示,用EGF刺激后,在MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p组中,E-cadherin的表达量比MDA-MB-231/NC组细胞中的表达量明显上调,而vimentin的表达量显著下调(P<0.05);与MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+Con组相比,MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+GAB2组细胞中E-cadherin的表达量显著下调,vimentin的表达量明显上调(P<0.05),表明miR-125a-5p可有效抑制MDA-MB-231细胞的EMT,见图5。
6 miR-125a-5p对GSK-3β/Snail信号通路的影响
用10 μg/L EGF刺激乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231,Western blot检测结果显示,与MDA-MB-231/NC组细胞相比,MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p组细胞中的p-GSK-3β和Snail蛋白水平明显下调(P<0.05);而MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+GAB2组细胞中的p-GSK-3β和Snail蛋白水平与MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+Con组细胞相比明显上调(P<0.05),表明miR-125a-5p通过GSK-3β/Snail信号通路,抑制MDA-MB-231细胞中Snail的入核,见图6、7。
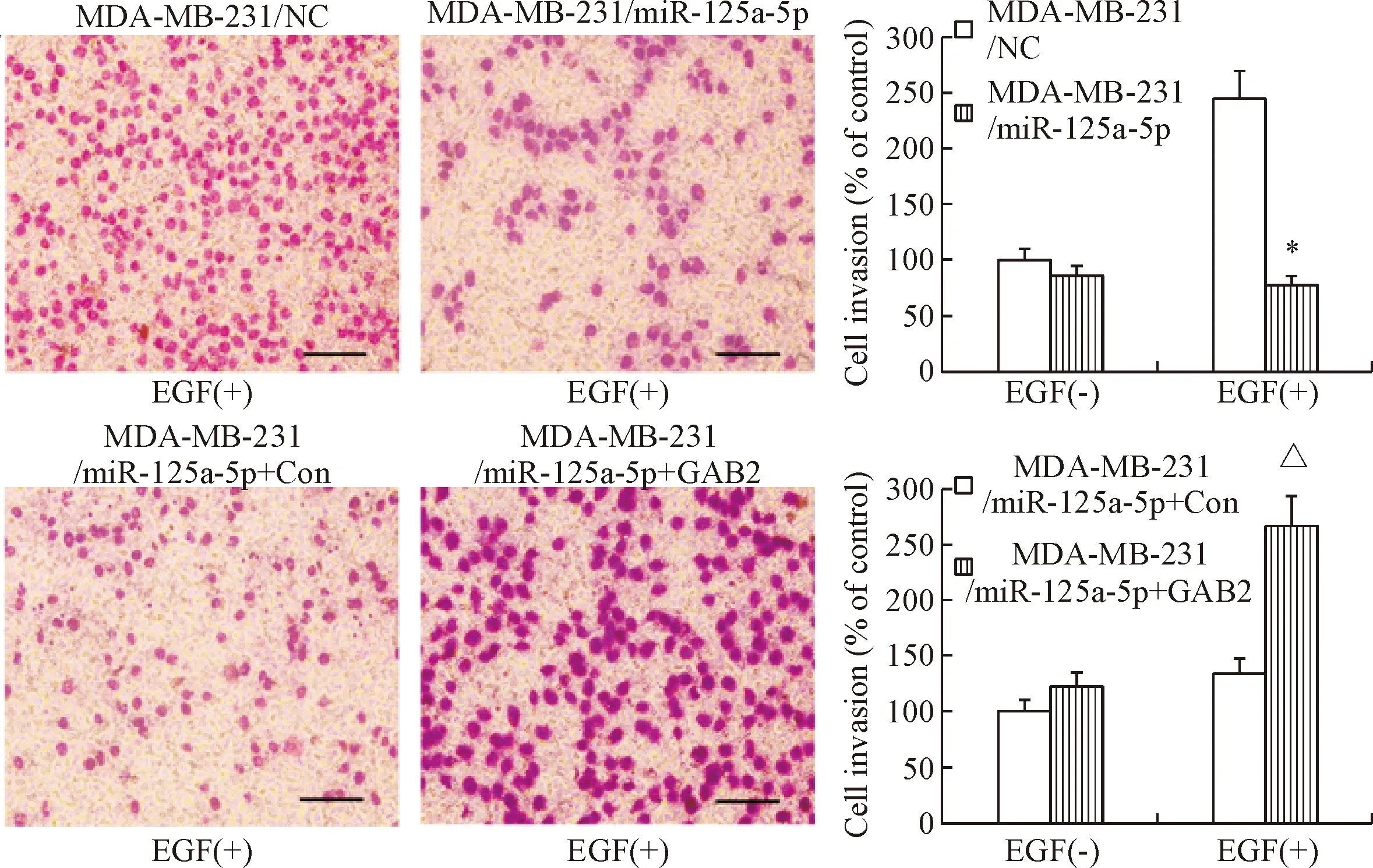
Figure 4. miR-125a-5p inhibited the invasion ability of breast cancer cells (Giemsa staining, scale bar=100 μm). Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vsMDA-MB-231/NC;△P<0.05vsMDA-MB-231/mir-125a-5p+Con.
图4miR-125a-5p抑制乳腺癌细胞的侵袭能力

Figure 5. miR-125a-5p inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vsMDA-MB-231/NC(+);△P<0.05vsMDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+Con(+).
图5miR-125a-5p抑制乳腺癌细胞的上皮-间充质转化
讨 论
乳腺癌是由多种复杂病因引起的异质性疾病,涉及到基因和环境因素,已对女性的生命和健康构成严重威胁[12]。远处转移是引起死亡率剧增的主要原因,其分子机制一直是肿瘤研究领域的热点。因此,研究乳腺癌细胞发生侵袭转移的潜在分子机制是治疗乳腺癌的重点与难点。
miRNA通过对下游靶基因进行靶向调控,间接发挥癌基因或抑癌基因的作用,从而参与肿瘤的发生、发展过程[13]。越来越多的证据表明,miRNA的失调在肿瘤恶性转化和进展中起着至关重要的作用[14]。
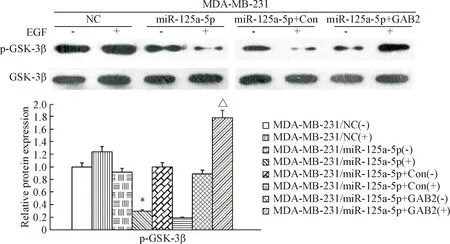
Figure 6. The phosphorylation of GSK-3β in MDA-MB-231 cells. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vsMDA-MB-231/NC(+);△P<0.05vsMDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+Con(+).
图6GSK-3β在MDA-MB-231细胞中的磷酸化水平

Figure 7. The expression levels of Snail protein in the nucleus of MDA-MB-231 cells. Mean±SD.n=3.*P<0.05vsMDA-MB-231/NC(+);△P<0.05vsMDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+Con(+).
图7Snail蛋白在MDA-MB-231细胞核中的表达水平
其中,miR-125是一个重要的miRNAs家族,其成员已被证实参与多种肿瘤类型,如肝癌[15]等。先前研究表明,miR-125a-5p可靶向调控BCL2、BCL2L12和MCL1,抑制结肠癌细胞的增殖[16]。同时miR-125a-5p 可负性调节GAB2的表达,抑制胶质瘤细胞的侵袭转移[9]。本研究中,将 miR-125a-5p质粒转染MDA-MB-231细胞,实现了miR-125a-5p的过表达,降低了MDA-MB-231细胞的体外侵袭能力;而在MDA-MB-231细胞中,与转染miR-125a-5p+Con质粒的细胞组相比,转染miR-125a-5p+GAB2质粒的细胞组体外侵袭能力明显增强。
新近研究表明,EMT的发生在肿瘤发生、发展过程中非常复杂,多条信号通路参与调控EMT过程,如Notch[17]、NF-κB[18]、ERK[19]和GSK-3β/Snail信号通路[20]等。其中,GSK-3β/Snail信号通路在EMT过程中至关重要。GSK-3β在许多参与EMT过程的信号通路中具有分子开关的功能,并参与调节多种生物功能,如细胞增殖[21]、分化[22]和迁移[23]等。Snail是EMT的一种重要的诱导物,是E-cadherin的关键转录调控器[24]。Zhou等[25]发现CXCR2/CXCL5可通过激活GSK-3β/Snail信号通路促进肝癌细胞的EMT发生。本研究中,与MDA-MB-231/NC细胞组相比,在MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p细胞组中GSK-3β的磷酸化水平和Snail转核明显降低,并引起E-cadherin表达上调,vimentin表达下调;与MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+Con细胞组相比,在MDA-MB-231/miR-125a-5p+GAB2细胞组中GSK-3β的磷酸化水平和Snail转核明显增加,E-cadherin表达下调,vimentin表达上调。
综上所述,miR-125a-5p可通过GSK-3β/Snail信号通路抑制乳腺癌细胞EMT的发生,进而抑制乳腺癌的侵袭与转移。因此,miR-125a-5p有望成为乳腺癌的独立预测因子,在乳腺癌的治疗和预后方面带来新的应用。
[参 考 文 献]
[1] Peng F, Xiong L, Tang H, et al. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through microRNAs: clinical and biological significance of microRNAs in breast cancer [J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(11):14463-14477.
[2] 刘清华, 于国华, 刘雨清. CCR7和VEGF-C蛋白与乳腺癌预后之间的关系[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2016, 32(8):1457-1461.
[3] Zhao M, Ang L, Huang J. MicroRNAs regulate the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and influence breast cancer invasion and metastasis[J]. Tumour Biol, 2017, 39(2):1010428317691682.
[4] Xue Y, Xu W, Zhao W, et al. miR-381 inhibited breast cancer cells proliferation, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting CXCR4[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 86:426-433.
[5] Lv ZD, Kong B, Liu XP, et al. miR-655 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting Prrx1 in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2016, 20(5):864-873.
[6] Liu A, Shao C, Jin G, et al. miR-208-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells promotes cell metastasis and invasion[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2014, 69(2):341-346.
[7] 徐新伟, 李佩瑞, 张增山, 等. miR-125a-5p通过靶向调控GAB2抑制乳腺癌细胞的迁移能力[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2017, 33(9):925-930.
[8] Li H, Zhang B, Liu Y, et al. EBP50 inhibits the migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells via LIMK/cofilin and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/MMP signaling pathway[J]. Med Oncol, 2014, 31:162.
[9] Sun L, Zhang B, Liu Y, et al. MiR125a-5p acting as a novel GAB2 suppressor inhibits invasion of glioma [J]. Mol Carcinog, 2016, 55(1):40-51.
[10] Zhang B, Li H, Yin C, et al. Dock1 promotes the mesenchymal transition of glioma and is modulated by miR-31[J]. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol, 2017, 43(5):419-432.
[11] Zhang B, Yin C, Li H, et al. Nir1 promotes invasion of breast cancer cells by binding to chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 through the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/Snail signalling pathway [J]. Eur J Cancer, 2013, 49(18):3900-3913.
[12] He H, Xu F, Huang W, et al. miR-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients[J]. Ge-net Mol Res, 2015, 14(4):17927-17933.
[13] Madhavan D, Peng C, Wallwiener M, et al. Circulating miRNAs with prognostic value in metastatic breast cancer and for early detection of metastasis [J]. Carcinogenesis, 2016, 37(5):461-470.
[14] Long J, Ou C, Xia H, et al. MiR-503 inhibited cell proliferation of human breast cancer cells by suppressing CCND1 expression[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(11): 8697-8702.
[15] Lu G, Ma Y, Jia C, et al. Reduced miR-125a levels associated with poor survival of patients with hepatocellular cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14(5):5952-5958.
[16] Tong Z, Liu N, Lin L, et al. miR-125a-5p inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in colon cancer via targeting BCL2, BCL2L12 and MCL1[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2015, 75:129-136.
[17] Yang Q, Cao X, Tao G, et al. Effects of FOXJ2 on TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Notch signaling pathway in non-small lung cancer [J]. Cell Biol Int, 2017, 41(1):79-83.
[18] Huang L, Li F, Deng P, et al. MicroRNA-223 promotes tumor progression in lung cancer A549 cells via activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Oncol Res, 2016, 24(6):405-413.
[19] Zhai L, Ma C, Li W, et al. miR-143 suppresses epithe-lial-mesenchymal transition and inhibits tumor growth of breast cancer through down-regulation of ERK5[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2016, 55(12):1990-2000.
[20] Liu L, Dai Y, Chen J, et al. Maelstrom promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition by way of Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signaling[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59(2):531-543.
[21] Wei R, Zhang C. MiR-155 affects renal carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion and apoptosis through regulating GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2017, 21(22):5034-5041.
[22] Chen S, Sun Y, Zhang Z, et al. Transcriptional suppression of microRNA-27a contributes to laryngeal cancer differentiation via GSK-3β-involved Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(9):14708-14718.
[23] Ma J, Guo X, Zhang J, et al.PTENgene induces cell invasion and migration via regulating Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway in human gastric cancer [J]. Digestive Dis Sci, 2017, 62(12):3415-3425.
[24] Li S, Lu J, Chen Y, et al. MCP-1-induced ERK/GSK-3β/Snail signaling facilitates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes the migration of MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2017, 14(7):621-630.
[25] Zhou S, Zhou Z, Hu Z, et al. CXCR2/CXCL5 axis contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HCC cells through activating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signaling[J]. Cancer Lett, 2015, 358(2):124-135.
