PDCD5通过Wnt/β-catenin通路抑制肾细胞癌侵袭转移及其机制研究
2018-06-13刘宏峰张彩虹张秀芳赵培庆
刘宏峰,张彩虹,张秀芳,赵培庆
PDCD5通过Wnt/β-catenin通路抑制肾细胞癌侵袭转移及其机制研究
刘宏峰,张彩虹,张秀芳,赵培庆
255036 山东省淄博市中心医院检验科
探讨肾细胞癌(RCC)患者 PDCD5 的表达水平及其参与调控 RCC 侵袭与转移的可能机制。
利用免疫组化检测 RCC 标本与癌旁组织中 PDCD5 的蛋白表达水平,同时分析 PDCD5 与疾病分期、预后的相关性;利用 transwell 及划痕实验检测 PDCD5 对肾癌细胞系 A498 侵袭与转移的影响;利用 Western blot 检测 A498 细胞转染 PDCD5 后 MMP2、MMP9、E-cadherin、N-cadherin 及 Wnt/β-catenin 通路的变化。
①与癌旁组织相比,RCC 标本中 PDCD5 明显下调(< 0.001),且与疾病分期及预后正相关;②PDCD5 明显抑制了肾癌细胞系 A498 的转移与侵袭能力(< 0.01);③PDCD5 通过抑制 A498 细胞系中 MMP2、MMP9 及 N-cadherin 的表达水平,增强 E-cadherin 的表达水平调控 EMT 转化,同时 Wnt/β-catenin 通路关键蛋白下调。
PDCD5 通过调控 Wnt/β-catenin 通路影响肾细胞癌 EMT 转化,负性调控了 RCC 病人的侵袭与转移进程。
癌,肾细胞;肿瘤侵润; 上皮-间质转化; 程序化细胞死亡因子 5; Wnt/β-catenin 通路
程序化细胞死亡因子 5(programmed cell death 5,PDCD5/TFAR19)是一种与凋亡密切相关的基因,于 1999 年从人类白血病细胞株 TF-1 细胞中克隆出来[1]。PDCD5 蛋白表达在多种细胞系中,其在乳腺癌[2]、胃癌[3]及肝细胞癌[4]等肿瘤中表达下调,表明其在多种肿瘤的发生发展中发挥重要作用。研究发现,在肾透明细胞癌中,PDCD5 可通过维持 p53 的稳定而起到抑癌的作用[5]。更为重要的是国内有学者发现,PDCD5 较正常对照在肾细胞癌中表达明显下调;同时其阳性表达率与肾细胞癌的临床分期及 TNM 分期呈明显正相关性,表明 PDCD5 可能在肾细胞的浸润与转移中发挥关键作用[6]。但到目前为止还没有文献报道PDCD5 在肾癌侵袭与转移中的确切机制。
肾癌中最常见的病理类型为肾细胞癌(renal cell carcinoma,RCC),25% ~ 30% 的肾细胞癌患者诊断时已经处于中晚期[7]。RCC 是一种异质性疾病,具有不同的临床、分子和病理特征。虽然早期手术治疗可以治愈,但已有转移的患者往往疗效极差。高剂量白细胞介素 2 和干扰素-α 是早期的主要治疗方案,但治疗反应率仅为 10% ~ 15%,且中位生存期仅为 10 ~ 12 个月[8]。近年来机制研究发现肾癌最常见的遗传病因是由 VHL 基因突变引起,约 50% 的 VHL 综合征患者将发展为肾癌,这种基因突变直接导致了肾癌中血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)和血小板衍生生长因子(PDGF)的高度表达,最终导致肿瘤细胞不断增生。阿昔替尼等靶向药物可有效抑制 VEGF 和 PDGF 的信号传导通路,抑制肾癌的进展,但在临床应用中也存在耐药问题[9]。因此,阐明 RCC 转移与侵袭新机制及新分子,将对 RCC 的转移与治疗产生深远影响。基于以上理论基础,本研究旨在探讨 PDCD5 如何影响 RCC 侵袭转移及其可能的机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 实验试剂和仪器 Transwell 试剂盒购自Corning 公司;WB 抗体 PDCD5、MMP2、MMP9、Wnt1 及 β-catenin 购自美国 Abcam 公司;E-cadherin、N-cadherin 购自 CST 公司;MEM-EBSS 培养基购自澳大利亚 Gibco 公司;多功能酶标仪为美国 Thermofisher 公司产品;PDCD5 慢病毒载体由上海吉凯基因构建;人肾癌细胞系 A498 购自中国科学院上海细胞生物研究所。
1.1.2 病例来源 皆来自淄博市中心医院泌尿外科且经病理确证为肾细胞癌患者,其中 I、II 期患者 35 例,III、IV 期 20 例。分析不同分期患者样本中 PDCD5 的表达水平,并根据其表达水平分析生存期并绘制 Kaplan-Meier 曲线。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 细胞培养 A498 于含10% 胎牛血清的 MEM-EBSS 培养基中,置于 37 ℃、5% CO2温箱中培养。
1.2.2 免疫组化检测 PDCD5 水平 60 ℃烤片 30 min,常规脱蜡水化;抗原修复以 1 mmol/L Tris-EDTA(pH 8.0)微波修复抗原,冷却至室温,三羟甲基氨基甲烷(Tris)盐缓冲液冲洗,PBS 洗3 次,每次洗 5 min;然后用 3%H2O2-甲醇封闭内源性过氧化物酶,室温 10 min,PBS 洗 3 次,每次洗 5 min;滴加一抗:PDCD5(1:200),4 ℃冰箱过夜;用 0.1% Tween-20 PBS 洗 3 次,每次洗5 min;滴加聚合物辅助剂,室温孵育 15 min;用 0.1% Tween-20 PBS 洗3 次,每次洗 5 min;滴加辣根酶标记抗山羊 IgG 多聚体,室温孵育 15 min;0.1% Tween-20 PBS 洗 3 次,每次洗 5 min;DAB 显色 5 ~ 10 min,蒸馏水洗终止显色;苏木素复染、水洗、分化后充分水洗返蓝;常规脱水透明,中性树胶封片,置光学显微镜下观察(× 100)。
1.2.3 Transwell 实验 细胞实验前转染含 PDCD5 慢病毒载体及空载体对照;实验采用8.0 μm 膜的小室,上室先用 50 mg/L Matrigel 基质胶 1:8 的稀释液包被、风干,并加入无血清培养液,37 ℃,30 min;制备细胞悬液前细胞血清饥饿 24 h,然后消化细胞,用 PBS 洗 1 ~ 2 遍,用含 BSA 的无血清培养基重悬细胞并调整细胞密度至合适范围;取细胞悬液 200 μl 加入 transwell 小室中;下室加入 500 μl 含 10% FBS 的培养基,每组设 3 个平行复孔。24 h 后 0.1% 结晶紫染色,200 倍正置光学显微镜下进行观察、拍照并进行统计学分析。
1.2.4 细胞划痕实验 细胞转染含 PDCD5 慢病毒载体及空载体对照后,常规种 6 孔板,每组 3 孔重复。待细胞融合度达 80% 后,用无菌枪头尽量垂直于背面划痕,用 PBS 洗细胞培养孔 3 次,去除漂浮细胞后,加入无血清培养基,放入 37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱培养 48 h,拍照并进行统计学分析。
1.2.5 蛋白印迹实验 细胞转染含 PDCD5 慢病毒载体及空载体对照后,RIPA 蛋白裂解液提取两组细胞总蛋白,酶标仪进行蛋白定量,最后分别与 PDCD5、MMP2、MMP9、E-cadherin、N-cadherin、Wnt1 及 β-catenin 抗体进行孵育,以 β-actin 为内参进行比照分析。
1.3 统计学处理
采用 Graphpad Prism5.0 软件进行统计学分析,数据采用检验进行分析,单变量分析对数秩检验分析肾癌患者生存率,以< 0.05 为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 RCC 患者 PDCD5 表达量明显下调且与生存期正相关
如图 1A、B 所示,RCC 患者 PDCD5 表达量较癌旁对照明显下调,有显著统计学意义(< 0.001);同时患者按 TNM 分期分为两组,A 组为 I、II 期患者共计 35 例,B 组为 III、IV 期患者共计 20 例。分析结果如图 1C 所示,A 组 PDCD5 表达量明显高于 B 组,差异有统计学意义(< 0.01),该结果提示 PDCD5 可能参与了 RCC 的转移与侵袭过程。为更进一步探讨 PDCD5 在 RCC 中的意义,收集了 35 例 RCC 患者 3 年总体生存率数据(其中 PDCD5 高表达组 15 例,低表达组 20 例),基于 Logrank 对数秩检验进行生存分析,检验两组终点的差异有无显著性,结果如图 1D 所示,表明 PDCD5 表达水平与生存率存在正相关(< 0.05),该结果进一步提示 PDCD5 可能参与 RCC 的转移过程。
2.2 PDCD5 明显抑制了肾癌细胞系 A498 的转移与侵袭能力
转染 PDCD5 慢病毒 48 h 后荧光显微镜观测 GFP 表达量达 80% 以上,表明转染目的蛋白成功,结果如图 2A 所示。Transwell 实验显示过表达 PDCD5 组较空载体组其侵袭能力显著下降(< 0.01),表明 PDCD5 对 RCC 细胞侵袭具有明显抑制作用。同时,采用划痕实验检测转染 PDCD5 后 A498 细胞转移能力,结果如图 2B 所示,发现其对细胞迁移也具有明显抑制作用,差异有统计学意义(< 0.01)。
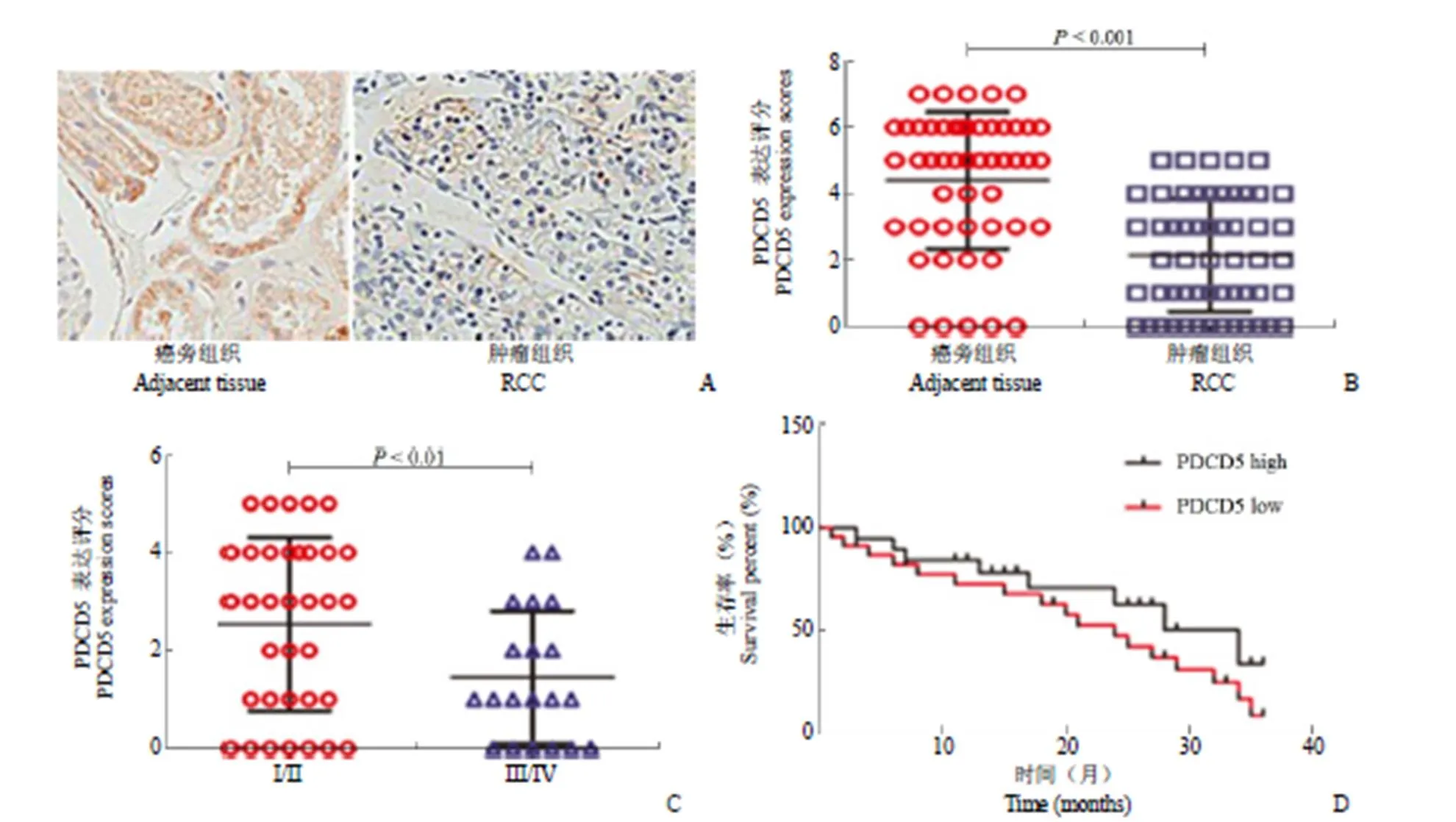
图 1 RCC 患者PDCD5 表达明显下调且与疾病分期、生存期正相关[A:肾细胞癌组织中 PDCD5 表达较癌旁组织明显降低;B:统计学分析表明肾细胞癌组织与癌旁组织中 PDCD5 表达有统计学意义(P < 0.001);C:I、II 期患者(35 例)较 III、IV 期患者(20 例)PDCD5 表达明显上调(P < 0.01);D:统计学分析表明35 例 RCC 患者(PDCD5 高表达组 15 例,低表达组 20 例)3 年总体生存率与 PDCD5 表达之间有统计学差异(P < 0.05)]
Figure 1 The levels of PDCD5 in RCC were significantly down-regulated and positively correlated with disease stage and survival rate [A: The expression of PDCD5 in renal cell carcinoma tissues was significantly lower than that in paracancerous tissues; B: Statistical analysis showed that the expression of PDCD5 in renal cell carcinoma tissues was decreased compared to paracancerous tissues (< 0.001); C: The expression of PDCD5 was increased in patients withstage I and II compared to stage III and IV (< 0.01); D: The 3-year overall survival was significantly higher in patients with PDCD5 high expression than the PDCD5 low expression (< 0.05)]
2.3 PDCD5 明显抑制 A498 细胞系中 MMP2、MMP9、N-cadherin、Wnt1 及 β-catenin 的表达水平,增强 E-cadherin 的表达水平
结果如图 3A 所示,过表达 PDCD5 组较正常对照组,A498 细胞中 MMP2、MMP9 及N-cadherin表达量明显下降,但 E-cadherin 表达量则上调。该结果提示 PDCD5 可通过降低 MMP2、MMP9、N-cadherin 表达及上调 E-cadherin 表达,抑制上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT),从而使肿瘤细胞转移与侵袭能力下降。同时,Wnt/β-catenin 通路中关键分子 Wnt1 及 β-catenin 表达下调,提示 PDCD5 通过下调 Wnt/β-catenin 通路影响 EMT 转化,进而导致 RCC 转移侵袭下降。
3 讨论
肾细胞癌(RCC)约占所有肾癌的 85%,虽然 RCC 可以完全通过手术切除,但复发率较高。最近数据统计表明美国近一年新发病例约 6.3 万例,死亡约 1.4 万人[10],转移与复发是导致病人高死亡率的重要原因之一。基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)和乙酰肝素酶主要降解细胞外基质(ECM)和基底膜(BM),在恶性肿瘤转移复发中起关键性作用[11],MMP家族是一类锌依赖性内肽酶,它们可以消化几乎所有组织的 BM 和 ECM,如胶原蛋白、蛋白聚糖、层黏连蛋白及纤连蛋白等;上皮-间质转化在维持癌细胞干性(CSC)方面起决定性作用,也被认为是恶性肿瘤转移与复发中的重要事件[12]。因此针对 MMPs 及 EMT 转化的靶向分子一般在肿瘤转移与复发中起抑制性生物学作用。
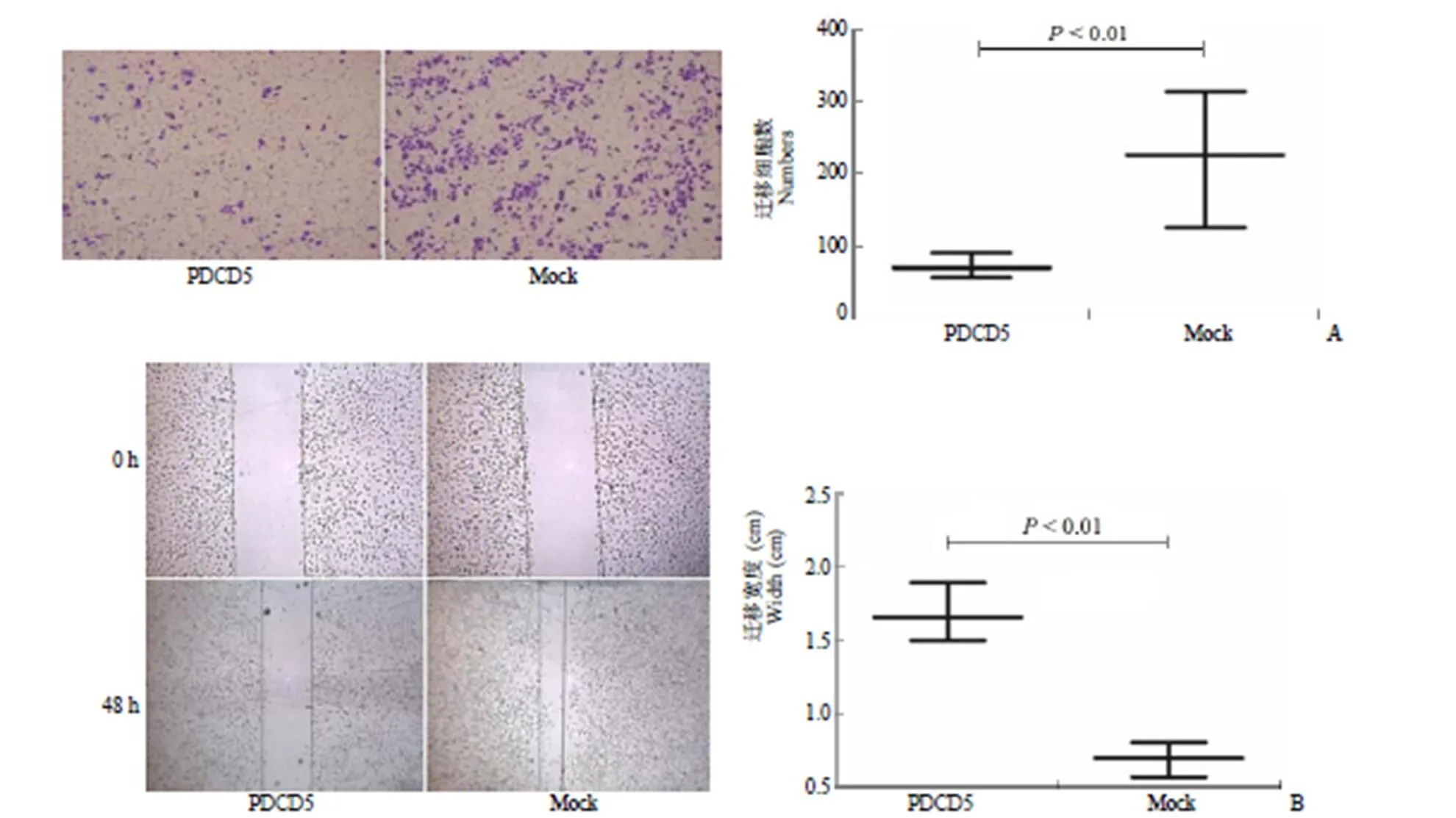
图 2 PDCD5 抑制肾癌细胞系 A498 的转移与侵袭能力[A:Transwell 结果提示肾细胞癌细胞系 A498 转染 PDCD5 后细胞迁移率明显低于对照组(P < 0.01);B:细胞划痕实验表明肾细胞癌细胞系 A498 转染 PDCD5 后,划痕宽度较对照组明显增宽(P < 0.01)]
Figure 2 PDCD5 significantly inhibited the metastasis and invasion of renal cancer cell line A498 [A: Transwell results showed that the cell migration rate of A498 cells transfected with PDCD5 was significantly lower than that of the control group (< 0.01); B: Cell scratch assay showed that the scratch width of A498 cells transfected with PDCD5 was wider than that of the control group (< 0.01)]
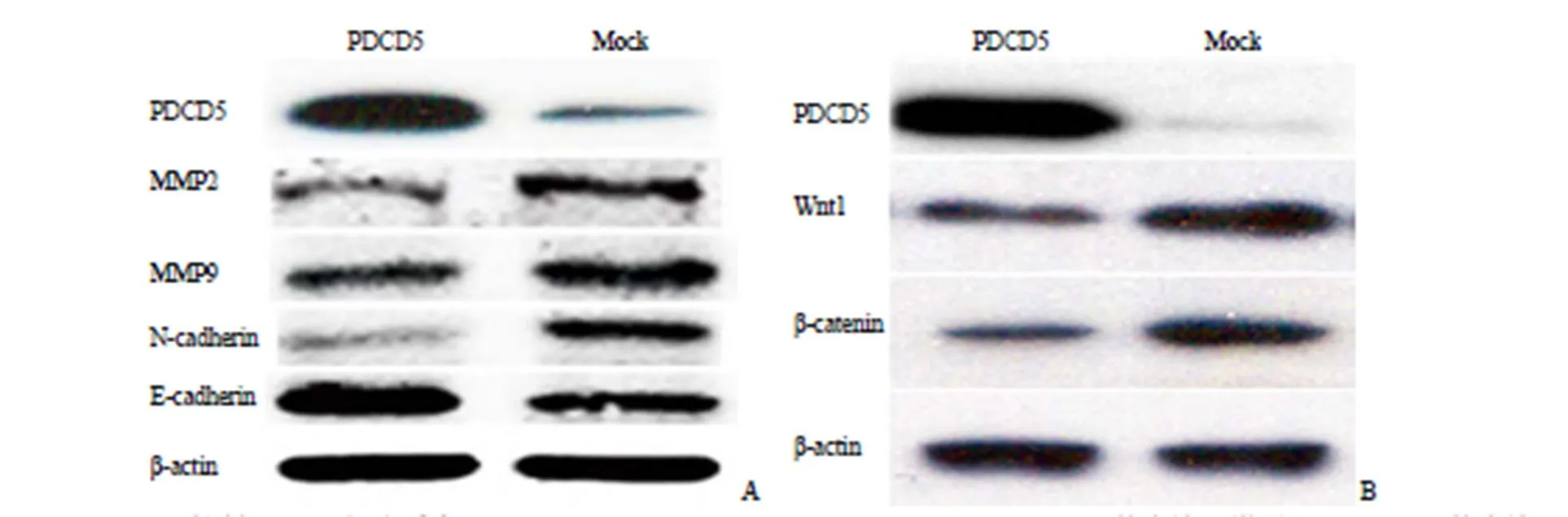
图 3 PDCD5 抑制A498 细胞系中MMP2、MMP9、N-cadherin、Wnt1 及β-catenin 的表达,增强E-cadherin 的表达
(A:蛋白印迹实验提示肾细胞癌细胞系 A498 转染 PDCD5 后MMP2、MMP9、N-cadherin 表达量明显低于对照组,E-cadherin 表达量则高于对照;B:蛋白印迹实验提示肾细胞癌细胞系 A498 转染 PDCD5 后 Wnt1 及β-catenin 表达量明显低于对照组)
Figure 3 PDCD5 inhibited the expression of MMP2, MMP9, N-cadherin, Wnt1, β-catenin and enhanced the expression of E-cadherin in A498 cells line (A: Western blot showed that the expression of MMP2, MMP9 and N-cadherin in A498 cells transfected with PDCD5 was significantly lower than that of the control group, while the expression of E-cadherin was higher than that of the control group; B: Western blot indicated that the Wnt1 and β-catenin expression in A498 cells transfected with PDCD5 was significantly lower than that of the control group)
国内研究发现 PDCD5 在 RCC 中的表达与肾细胞癌的临床分期及 TNM 分期呈正相关,提示 PDCD5 可能在 RCC 的浸润与转移中发挥关键作用[6]。基于以上理论,我们首先检测了 RCC 标本中 PDCD5 表达量,发现肿瘤组织较癌旁对照组明显下调;同时发现 I、II 期患者 PDCD5 表达量明显高于 III、IV 期患者,该结果更进一步提示 PDCD5 可能参与了 RCC 的转移与侵袭过程。为深入探讨 PDCD5 在 RCC 中的意义,我们跟踪收集了35 例 RCC 患者 3 年总体生存率数据,结果表明 PDCD5 表达与生存率也存在正相关性,肿瘤的复发和转移是影响 RCC 患者生存的最重要因素之一[13],该结果表明 PDCD5 参与了 RCC 的转移过程。细胞实验证实过表达 PDCD5 可显著降低 RCC 细胞系的侵袭转移能力,表明 PDCD5 对 RCC 细胞侵袭转移具有明显抑制作用。为进一步在机制上阐述 PDCD5 影响 RCC 侵袭转移能力,我们通过 Western blot 实验发现转染 PDCD5 组 A498 细胞中 MMP2、MMP9 及 N-cadherin 表达量明显下调,而 E-cadherin 则上调。该结果提示 PDCD5 可通过降低 MMP2、MMP9、N-cadherin 表达及上调 E-cadherin,抑制上皮-间质转化,从而使肿瘤细胞转移与侵袭能力下降。在上皮-间质转化过程中,肿瘤细胞侵袭转移能力增强,伴随上皮标志物 E-cadherin 下调,间质标记物 N-cadherin 和波形蛋白上调[14]。本研究中 PDCD5 下调 N-cadherin 及上调 E-cadherin,表明 PDCD5 可以调控 RCC 细胞的 EMT 水平,但具体的调控机制尚待阐明。基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)在癌细胞的侵袭和转移中也发挥重要作用[15],我们发现过表达 PDCD5 可以下调 MMP-2 和MMP-9,后者是 Wnt/β-catenin 信号的下游因素[16],同时蛋白印迹结果也证实转染 PDCD5 后 Wnt1 及 β-catenin 下调,该结果也提示 PDCD5 可能抑制 β-catenin 信号通路,下调 MMP-2 和 MMP-9,进而影响 RCC 的转移与侵袭过程。
通过检测 RCC 病人肿瘤组织中PDCD5 的表达水平,不仅可以更进一步阐释PDCD5 参与 RCC 转移与侵袭的机制,更可能为 RCC 转移的临床诊断指标找到可能的新型标志分子,在 RCC 的预后判断中发挥重要作用。同时,通过细胞实验与初期的机制研究,我们初步探讨了PDCD5 参与 RCC 转移与侵袭的过程,为 RCC 的临床靶向治疗提供了理论与实践可能。
[1] Wang W, Song XW, Zhao CH. Roles of programmed cell death protein 5 in inflammation and cancer (Review). Int J Oncol, 2016, 49(5):1801-1806.
[2] Chinnaiyan AM, Rubin MA. Gene-expression profiles in hereditary breast cancer. Adv Anat Pathol, 2002, 9(1):1-6.
[3] Yang YH, Zhao M, Li WM, et al. Expression of programmed cell death 5 gene involves in regulation of apoptosis in gastric tumor cells. Apoptosis, 2006, 11(6):993-1001.
[4] Fu DZ, Cheng Y, He H, et al. PDCD5 expression predicts a favorable outcome in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol, 2013, 43(3):821-830.
[5] Essers PB, Klasson TD, Pereboom TC, et al. The von hippel-lindau tumor suppressor regulates programmed cell death 5-mediated degradation of Mdm2. Oncogene, 2015, 34(6):771-779.
[6] Tan WL, Xiong L, Zheng SB, et al. Relationship between programmed cell death 5 protein expression and prognosis of renal clear cell carcinoma. J South Med Univ, 2006, 26(9):1316-1318. (in Chinese)谭万龙, 熊林, 郑少斌, 等. 肾透明细胞癌PDCD5表达及与预后的关系. 南方医科大学学报, 2006, 26(9):1316-1318.
[7] Mendiratta P, Rini BI, Ornstein MC. Emerging immunotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol, 2017, 35(12):687-693.
[8] Sánchez-Gastaldo A, Kempf E, González Del Alba A, et al. Systemic treatment of renal cell cancer: a comprehensive review. Cancer Treat Rev, 2017, 60:77-89.
[9] Duran I, Lambea J, Maroto P, et al. Resistance to targeted therapies in renal cancer: The importance of changing the mechanism of action. Target Oncol, 2017, 12(1):19-35.
[10] Buonerba C, Di Lorenzo G, Sonpavde G. Combination therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann Transl Med, 2016, 4(5):100.
[11] Grünert S, Jechlinger M, Beug H. Diverse cellular and molecular mechanisms contribute to epithelial plasticity and metastasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2003, 4(8):657-665.
[12] Mikami S, Oya M, Mizuno R, et al. Recent advances in renal cell carcinoma from a pathological point of view. Pathol Int, 2016, 66(9): 481-490.
[13] Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med, 2017, 376(4):354-366.
[14] Nürnberger J, Bacallao RL, Phillips CL. Inversin forms a complex with catenins and N-cadherin in polarized epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell, 2002, 13(9):3096-3106.
[15] Brown GT, Murray GI. Current mechanistic insights into the roles of matrix metalloproteinases in tumour invasion and metastasis. J Pathol, 2015, 237(3):273-281.
[16] Neth P, Ries C, Karow M, et al. The Wnt signal transduction pathway in stem cells and cancer cells: influence on cellular invasion. Stem Cell Rev, 2007, 3(1):18-29.
Inhibitory effect of PDCD5 on invasion and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma through Wnt/β-catenin pathway and its underlying mechanisms
LIU Hong-feng, ZHANG Cai-hong, ZHANG Xiu-fang, ZHAO Pei-qing
Author Affiliation:Department of Clinical Laboratory, Zibo Central Hospital, Shandong 255036, China
To investigate the expression of PDCD5 levels in patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and its possible mechanisms of invasion and metastasis.
The expression levels of PDCD5 in RCC patient and adjacent tissues were detected by immunohistochemistry. The relationship between PDCD5 and disease stage or prognosis was analyzed, respectively. The transwell and scratch experiments were used to detect the effect of PDCD5 on invasion and metastasis of renal cancer cell line A498. The levels of MMP2, MMP9, E-cadherin, N-cadherin and Wnt/β-catenin pathway in A498 cell transfected with PDCD5 were detected by Western blot.
① Compared to the adjacent tissues, PDCD5 expression in RCC was significantly down-regulated (< 0.001), and was positively correlated with disease stage and prognosis. ②PDCD5 significantly inhibited the metastasis and invasion in renal cancer cell line A498 (< 0.01). ③PDCD5 regulated the expression of MMP-2, MMP9, N-cadherin and the key protein in Wnt/β-catenin pathway in A498 cell line and enhanced the expression of E-cadherin.
PDCD5 regulates the invasion and metastasis by regulating the EMT through Wnt/β-catenin pathway in renal cell carcinoma.
Carcinoma, renal cell; Neoplasm invasiveness; Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Programmed cell death 5; Wnt/β-catenin pathway
ZHAO Pei-qing, Email: bzjzzpq@163.com
山东省自然科学基金面上项目(ZR2015HM031、ZR2014HM042);山东省医药卫生科技发展计划(2016WSA03022)
赵培庆,Email:bzjzzpq@163.com
2018-01-10
10.3969/j.issn.1673-713X.2018.03.007
