个体化护理对乳腺癌皮肤溃烂患者负面情绪、生活质量的影响
2018-04-26彭丽娟范志刚
彭丽娟 范志刚
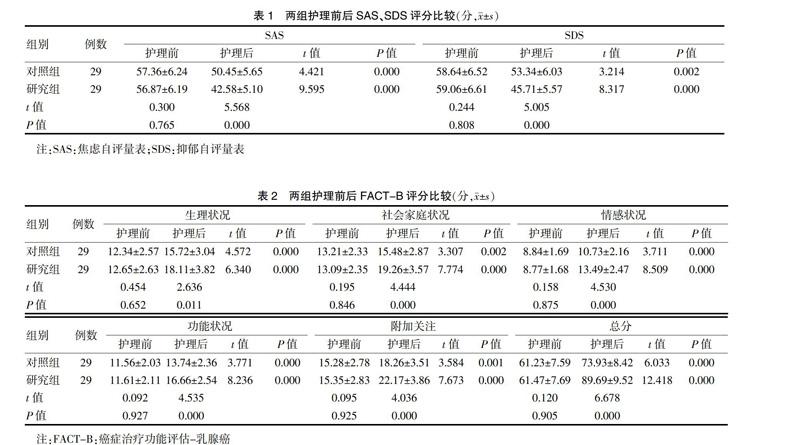
[摘要] 目的 探討个体化护理对乳腺癌皮肤溃烂患者负面情绪、生活质量的影响。 方法 选择2015年12月~2017年5月在西安交通大学医学院附属3201医院收治的乳腺癌皮肤溃烂患者58例作为研究对象,按照随机数字表法分为对照组与研究组,每组各29例。对照组给予常规护理,研究组在对照组基础上给予个体化护理。两组均持续护理4周。比较两组护理前后焦虑自评量表(SAS)评分、抑郁自评量表(SDS)评分及癌症治疗功能评估-乳腺癌(FACT-B)评分。 结果 护理后两组SAS、SDS评分均低于护理前,研究组显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。护理后两组生理状况、社会家庭状况、情感状况、功能状况、附加关注等FACT-B各维度评分及总分均高于护理前,且研究组显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 个体化护理可有效缓解乳腺癌皮肤溃烂患者的负面情绪,提高其生活质量,值得临床推广应用。
[关键词] 个体化护理;乳腺癌;皮肤溃烂;负面情绪;生活质量
[中图分类号] R473.73 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2018)02(a)-0173-04
Influence of individualized nursing on negative emotions and quality of life in skin ulceration patients with breast cancer
PENG Lijuan FAN Zhigang
The Third Department of Medical Oncology, 3201 Affiliated Hospital of Xi′an Jiaotong University Medical College, Shaanxi, Province, Xi′an 723000, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the influence of individualized nursing on negative emotions and quality of life in skin ulceration patients with breast cancer. Methods From December 2015 to May 2017, 58 cases of skin ulceration patients with breast cancer treated in 3201 Affiliated Hospital of Xi′an Jiaotong University Medical College were selected as the research objects and divided into the control group and the study group according to the random number table, with 29 cases in each group. The control group was given routine nursing and the study group was given individualized nursing on the basis of control group. The two groups were all intervened for 4 weeks. The scores of self-rating anxiety scale (SAS), self-rating depression scale (SDS) and functional assessment of cancer therapy-breast (FACT-B) were compared in the two groups. Results After nursing, the scores of SAS and SDS in the two groups were significantly lower than those before nursing, and those in the study group were significantly lower than those of control group, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). After nursing, the physiological status, social and family status, emotional status, functional status, and additional concerns in each dimension of FACT-B and the total score in the two groups were significantly higher than those before nursing (P < 0.05), and those in the study group were significantly higher than those of control group, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). Conclusion Individualized nursing can effectively alleviate negative emotions of skin ulceration patients with breast cancer and improve quality of life. It is worthy of promotion and application.
