两类Lorenz型混沌模型的动力学行为研究*
2018-03-19张付臣陈修素李如意何毅章
张付臣, 陈 睿, 陈修素,李如意, 曾 偲, 何毅章
(1. 重庆工商大学 数学与统计学院, 重庆 400067;2.重庆工商大学 信息化办公室, 重庆 400067;3. 成都市第七中学, 成都 610041)
1 研究背景
1963年,美国气象学家Lorenz[1]在研究大气运动时发现了第一个具有“蝴蝶效应”的Lorenz混沌系统,大量专著和论文研究了Lorenz混沌系统的定性与定量动力学行为,包括奇点及其稳定性、奇点的局部拓扑结构和平衡点的局部分岔、同宿轨线和异宿轨线的扰动与保持性、周期解的存在性及其稳定性、混沌同步与控制等[2-12]。Lorenz混沌系统、Chua’s电路系统、Rössler系统、Chen系统、Lu系统等混沌系统在自然科学和工程领域都有着广泛的应用[13-15]。
2 主要数学结果
一类用于描述Couette-taylor流复杂动力学行为的三维Lorenz型混沌系统[16]
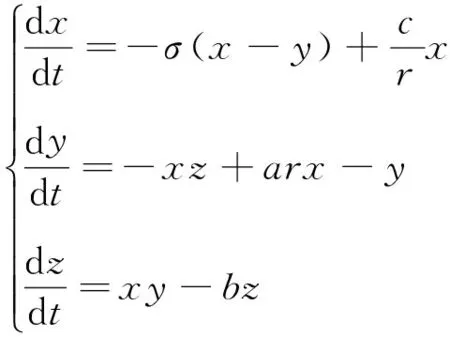
(1)
其中a,b,c,r,σ为混沌系统(1)的正参数。且有r为系统式(1)的雷诺参数,σr-c>0。
一类用于描述不可压缩磁流体动力学行为的方程为[17]
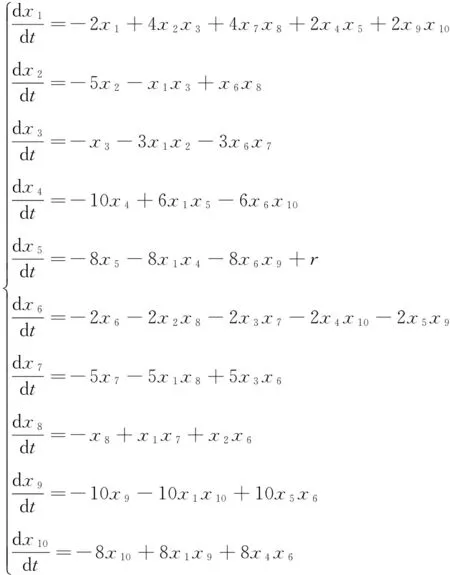
(2)
其中r>0为混沌系统式(2)的雷诺参数,决定着系统式(2)的分岔和混沌行为。
混沌系统式(1)和式(2)奇点的局部分岔、李雅普诺夫指数、庞加莱截面、功率谱及其返回映射等在文献[16-17]中已经研究过。下面将研究系统式(1)和式(2)的最终界和全局吸引域。
定理1 对任意的a>0,b>0,r>0,σ>0,σr>c>0,则
R2,∀m>0,∀λ≠0}
(3)
是系统式(1)的一个最终界与正向不变集。这里
证明定义广义李雅普诺夫函数

(4)
沿着系统式(1)正半轨线求导数
-2dmx2-2λ2y2-2bλ2z2+2b(σm+arλ2)z,
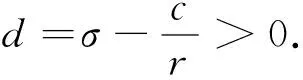

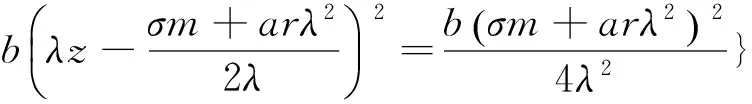
(5)

上述问题等价于:
引入新的变量,令
则上述问题转化为
通过计算可以得到:
容易证明式(3) 为混沌系统式(1)正半轨线的一个最终有界集和正向不变集。
定理2 令X(t)=(x(t),y(t),z(t))为系统式(1)的任意一个解。则对于任意a>0,b>0,r>0,σ>0,σr>c>0, 令
V(X)=V(x,y,z)=mx2+λ2y2+

θ=min(b,d,1)>0,d=
则当V(X(t))>Lλ,m,V(X(t0))>Lλ,m时,对于系统式(1)的轨线有如下估计式
V(X(t))-Lλ,m≤〈V(X(t0))-Lλ,m〉e-θ(t-t0)
从而
Ψ={(x,y,z)|mx2+λ2y2+
(6)
为系统式(1)的一个全局指数吸引集。
证明定义广义李雅普诺夫函数
V(X)=V(x,y,z)=mx2+λ2y2+

对上述广义李雅普诺夫函数求导数
-2dmx2-2λ2y2-2bλ2z2+2b(σm+arλ2)z≤
-dmx2-λ2y2-bλ2z2+2b(σm+arλ2)z=
当V(X(t))>Lλ,m,V(X(t0))>Lλ,m,则有
V(X(t))≤V(X0)e-θ(t-t0)+Lλ,m(1-e-θ(t-t0))
整理得
V(X(t))-Lλ,m≤〈V(X0)-Lλ,m〉e-θ(t-t0)
让t→+∞, 且对上面不等式两边取上极限有
从而有
Ψ={(x,y,z)|mx2+λ2y2+
为系统式(1)的一个全局指数吸引集。
定理3 令X(t)=(x1(t),x2(t),x3(t),x4(t),x5(t),x6(t),x7(t),x8(t),x9(t),x10(t))为系统式(2)的任意一个解。则对于任意r>0, 令
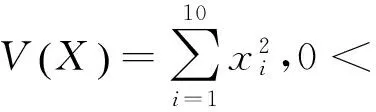
则当V(X(t))>M,V(X(t0))>M时,对于系统式(2)的正半轨线有如下的估计式
V(X(t))-M≤〈V(X(t0))-M〉e-θ(t-t0).
从而

(7)
为系统式(2)的一个全局指数吸引集。

当V(X(t))>M,V(X(t0))>M,则有
V(X(t))≤V(X0)e-θ(t-t0)+M(1-e-θ(t-t0))
整理得
V(X(t))-M≤[V(X0)-M]e-θ(t-t0)
让t→+∞, 且对上面不等式两边取上极限有

从而Ψ1={(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5,x6,x7,x8,x9,x10)|


3 结 论
研究了两类混沌模型的全局吸引性和最终界,研究方法适用于其他混沌系统的研究,研究结果对混沌系统的混沌控制的应用将起到一定的参考价值。
[1] LORENZ E N. Deterministic Non-periods Flows[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1963, 20:130-141
[2] BALLESTEROS A, BLASCO A, MUSSO F. Integrable Deformations of Rössler and Lorenz Systems from Poisson-Lie Groups[J]. Journal of Differential Equations, 2016, 260(11): 8207-8228
[3] COOMES B A. The Lorenz System does not Have a Poly-nomial Flow[J]. Journal of Differential Equations, 1989, 82(2): 386-407
[4] LEONOV G A. On Estimates of the Bifurcation Values of the Parameters of a Lorenz System[J]. Russian Mathematical Surveys, 1988, 43(3): 216-217
[5] WU K S, ZHANG X. Darboux Polynomials and Rational First Integrals of the Generalized Lorenz Systems[J]. Bulletin Des Sciences Mathématiques, 2012, 136(3): 291-308
[6] DOEDEL E J, KRAUSKOPF B, OSINGA H M. Global Organization of Phase Space in the Transition to Chaos in the Lorenz System[J]. Nonlinearity, 2015, 28(11): 113-139
[7] YANG Q G, ZHANG K M, Chen G R. Hyperchaotic Attractors from a Linearly Controlled Lorenz System[J]. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2009, 10(3): 1601-1617
[8] ZHANG F C, ZHANG G Y. Further Results on Ultimate Bound on the Trajectories of the Lorenz System[J]. Qualitative Theory of Dynamical Systems, 2016, 15(1): 221-235
[9] ZHANG F C, MU C L, ZHOU S M,et al. New Results of the Ultimate Bound on the Trajectories of the Family of the Lorenz systems[J]. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems-series B, 2015, 20(4): 1261-1276
[10] ZHANG F C, LIAO X F, MU C L. On Global Boundedness of the Chen System[J]. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems-Series B, 2017, 22(4): 1673-1681
[11] ZHANG F C, LIAO X F, ZHANG G Y,et al. Dynamical Analysis of the Generalized Lorenz Systems[J]. Journal of Dynamical and Control Systems, 2017, 23(2): 349-362
[12] ZHANG F C, LIAO X F, ZHANG G Y,et al. Dynamical Behaviors of a Generalized Lorenz Family[J]. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems-Series B, 2017, 22(10): 3707-3720
[13] SPARROW C. The Lorenz Equations:Bifurcations Chaos and Strange Attractors[M].New York:Springer Science & Business Media, 2012
[14] BRAGIN V, VAGAITSEV V.Algorithms for Finding Hidden Oscillations in Nonlinear Systems[J]. Journal of Computer and Systems Sciences International, 2011, 50: 511-543
[15] LIU X W, CHEN T P. Boundedness and Synchronization of Y-coupled Lorenz Systems with or Without Controllers[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 2008, 237(5): 630-639
[16] WANG H Y. The Dynamical Behavior and Numerical Simulation of Lorenz Equations of Spiral-flow Type Systems[J]. Numerical Mathematics A Journal of Chinese Universities, 2016, 38(3): 201-212
[17] WANG H Y. The Dynamical Behaviors and Numerical Simulation of a Five-mode Lorenz-like System of the MHD Equations for a Two-dimensional Incompressible Fluid on Attorus[J]. Acta Mathematica Scientia, 2017, 37(1): 199-216
