苏打盐碱地围堤养鱼改良土壤的生物性状
2018-02-28张庆国马玉露侯迷红萨如拉马金慧吕秀艳
范 富,张庆国,马玉露,侯迷红,萨如拉,马金慧,吕秀艳
苏打盐碱地围堤养鱼改良土壤的生物性状
范 富1,2,张庆国1,马玉露1,侯迷红1,萨如拉1,马金慧1,吕秀艳1
(1. 内蒙古民族大学农学院,通辽 028043; 2. 内蒙古自治区饲用作物工程技术研究中心,通辽 028000)
为探讨盐碱地围堤养鱼对盐碱地改良效果,2016年对盐碱裸地土、围堤养鱼3,5,8 a的鱼塘淤泥及围堤养鱼5 a后种稻土壤进行分析,测定了各处理土壤样品生物性状及土壤呼吸作用。结果表明,围堤养鱼5a后种稻对微生物的改良效果最明显,与盐碱裸地土相比,细菌、纤维素分解菌、亚硝酸细菌、磷细菌的数量分别增加了2.60×106,0.66×104,7.84×105,0.55×105cfu/g。除多酚氧化酶在盐碱裸地中的活性最大之外,其他酶活性在围堤养鱼5 a的土壤中改良效果最明显,脲酶、磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶、纤维素酶的活性分别提高了0.008 mg/(g·24 h),0.153 mg/(g·24 h),2.035 mg/(g·20 min),0.399 mg/(g·72 h)。CO2释放量在围堤养鱼8 a土壤里最大,比原碱土增加了7.41 mg/g。只有细菌与土壤呼吸呈显著正相关(<0.05),土壤生物性状与土壤呼吸作用没有相关性。
土壤;微生物;酶;苏打盐碱地;围堤养鱼;生物性状
0 引 言
苏打盐碱地是中国盐碱化国土资源的主要类型之一[1]。内蒙古通辽市由于受半干旱季风气候,地下水状况以及元素迁移的地球化学过程等因素的影响,导致其境内形成了大面积的盐碱土[2-11]。通辽市有碱化盐土1.7万hm2、草甸碱土13.9万hm2和苏打盐碱化土壤52.6万hm2,土壤生产力极低,大部分荒芜的裸碱土。所以,改良并合理利用盐碱地已经成为当今人们关注的一项重要问题。
盐碱地围堤养鱼后种稻是改良盐碱地行之有效的途径。西辽河流域低洼盐碱地属于苏打碱化土壤,碱化度高,围堤积水后水质不易调控,干旱水体浓缩更易导致碱化度增高,危及鱼类的正常生命活动。通过引注深层地下水及合理施肥,稀释、酸化中和、离子代换以减少水体的盐碱成分,养鱼5 a后既培肥水体,又改善水体生态。养鱼5 a后种稻更加速盐碱地的修复,原因是水稻在生命活动过程中借助发达的根系,释放出大量的二氧化碳溶于水而形成碳酸;碳酸一方面可中和碳酸钠和重碳酸钠,降低土壤的pH值,另一方面促进土壤中含有的难溶性碳酸钙的溶解;溶液中钙离子与土壤胶体吸附的钠离子发生交换,交换出来的钠离子随灌溉水被淋洗。
近年来,很多研究者探究挖坑养鱼对盐碱地的改良效果。杨富亿[12]利用盐碱地稻田养鱼的方式改良盐碱地,研究表明,稻田养鱼对盐碱地的改良效果十分显著。龙藏瑞[13]利用低洼盐碱地藕塘养鱼技术来改良盐碱地,也取得了显著的成效。缴建华等[14]研究了盐碱地封闭循环水养鱼对盐碱地水质的变化。
本次试验是在通辽市科尔沁左翼中旗代力吉镇进行的,分析围堤养鱼不同年限鱼塘内淤泥的生物性状及呼吸作用。土壤酶活性、土壤微生物数量是表示土壤肥力水平的重要指标。此种改良方式,在本区域后续的盐碱地利用上,有一定的参考价值。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验区土壤性质
试验在通辽市科尔沁左翼中旗代力吉镇进行,未改良过的土壤pH值为9.52;原始土壤呼吸值为1.10 mg/g;细菌、磷细菌、纤维素分解菌、亚硝酸细菌的原始数量分别为1.15×106,0.17×105,1.89×104,0.24×105cfu/g;多酚氧化酶、脲酶、磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶、纤维素酶在原碱裸地中的活性分别为0.408 mg/(g·24 h)、0.079 mg/(g·24 h)、0.032 mg/(g·24 h)、0.435 mg/(g·20 min)、1.918 mg/(g·72 h)。
1.2 试验过程
于2016年10月12日在通辽市代力吉镇采样,在围堤养鱼池塘旁将未处理过的盐碱裸地土作为对照,在围堤养鱼3 a、养鱼5 a、养鱼8 a池塘内部采用对角线的方式分别采取5点0~20 cm的淤泥,在围堤养鱼5 a后种稻的大田里以同样的方式取5点0~20 cm土样。将土样混合均匀,装入无菌袋,放入冰箱中在4 ℃下低温保存。
1.3 试验设计方案
在盐碱地围堤养鱼区设4个处理,将围堤养鱼3、5、8 a及围堤养鱼5 a后种稻的土样分别标记为Y1、Y2、Y3、S,将盐碱裸地土作为对照,在试验记录中标记为CK。
1.4 测试项目及方法
采用稀释法测定亚硝酸细菌、纤维素分解菌、磷细菌,采用稀释平板涂布法测定细菌[15],采用比色法测定磷酸酶、脲酶、纤维素酶、多酚氧化酶,采用滴定法测定H2O2酶,采用碱吸收滴定法测定土壤的呼吸作用[16]。
1.5 数据处理与分析
利用Wps软件与DPS (Data Processing System)3.01软件对数据进行处理与分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 盐碱地围堤养鱼土壤内微生物数量的变化
由表1可知,相同处理下,土壤中细菌数量最多。在不同处理下,Y3的细菌数量最多,比CK增加了2.60×106cfu/g;Y3与其他处理之间有差异,与Y2有显著差异。纤维素分解菌在Y1中的数量最多,比CK增加了5.21×104cfu/g,而在Y2和Y3中,纤维素分解菌的数量分别减少了0.56×104和1.22×104cfu/g,Y1与其他处理之间有显著差异,其他处理之间无差异。亚硝酸细菌在S中数量最高,比CK增加了7.84×105cfu/g,而在Y1的土壤中,亚硝酸细菌的数量下降了0.09×105cfu/g,各处理之间无差异。磷细菌在Y2数量最高,比CK增加了0.87×105cfu/g,Y2与Y1有显著差异。在S下纤维素分解菌、亚硝酸细菌、磷细菌的数量比Y3的多,可能是因为在Y3下,养鱼时间较长,氧分消耗量大,微生物活动性较小,而在S下,微生物活动性较大。

表1 盐碱地围堤养鱼土壤内微生物数量的变化
注:CK,Y1,Y2,Y3和S分别表示盐碱裸地土、围堤养鱼3, 5, 8 a及围堤养鱼5 a后种稻。大小写字母分别表示同列数据在<0.01和<0.05水平下差异显著。下同。
Note: CK, Y1, Y2 Y3, S were the samples of saline alkalin soil, diking for fish 3, 5, 8 a, and dike fishing 5 a +rice planting. Different capital and lower letters with in same line indicate significant difference at<0.01 and<0.05. The same as below.
2.2 盐碱地围堤养鱼土壤内酶活性的变化
由表2可知,相同处理下,土壤脲酶活性最小,土壤纤维素酶活性最大。在不同处理下,多酚氧化酶活性在CK中最大。脲酶活性在Y2中最大,比CK增加了0.008 mg/(g·24 h),在Y3中活性最小,比CK下降了0.034 mg/(g·24 h),各处理间无差异。磷酸酶在Y2中活性最大,比CK增加了0.153 mg/(g·24 h),Y1、Y3、S间无显著差异,CK、Y1、Y2处理之间有显著差异(0.01)。过氧化氢酶在Y3中的活性最大,比CK增加了2.035 mg/(g·20 min),各处理间差异显著。纤维素酶在S中活性最大,比CK增加了1.611 mg/(g·72 h),Y3比CK增加0.399 mg/(g·72 h)各处理间无差异。在S处理下的脲酶、磷酸酶的活性比Y2的大,说明土壤中N、P含量有所下降,可能是因为S是在养鱼5 a后的第一年,并没有对水稻进行施肥,所以酶活性下降。

表2 盐碱地围堤养鱼土壤内酶活性的变化
2.3 盐碱地围堤养鱼土壤呼吸变化
由表2可知,各处理土壤呼吸状况,CK的CO2排放量最小,Y3的CO2排放量最大,Y3比CK增长了7.41 mg/g,CK与Y1、Y2与S间无显著差异。
2.4 盐碱地围堤养鱼土壤呼吸与酶活性和微生物数量的相关分析
由表3可知,土壤呼吸作用与多酚氧化酶和脲酶的活性呈负相关,与磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶和纤维素酶的活性呈正相关,但均不显著。由此表明,土壤呼吸作用与各种酶活性之间没有显著性的关系。土壤的呼吸作用只与纤维素分解菌呈负相关,与细菌、亚硝酸细菌、磷细菌都为正相关;其中,只与细菌成显著相关。由此分析,土壤呼吸作用与土壤微生物数量没有较大的关联性。
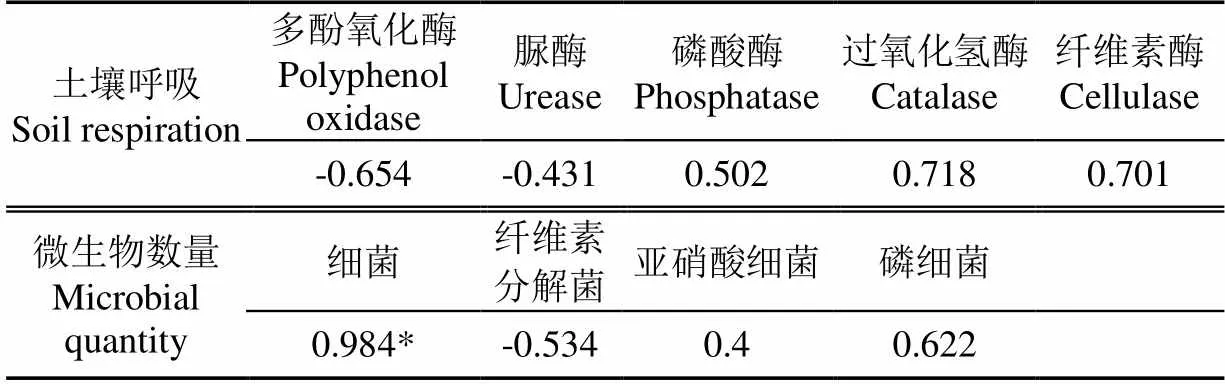
表3 盐碱地围堤养鱼土壤呼吸与酶活性和微生物数量的相关分析
注:=5,=5;*表示显著相关(<0.05);**表示极显著相关(<0.01)。
Note:=5,=5, * indicates significant correlation (<0.05); ** indicates very significant correlation (<0.01).
3 讨 论
前人开发盐碱地稻田养鱼试验[17],开发改造天然盐碱泡沼用以养鱼[18],开发改造盐碱闭流区苇塘;以地下水和稻田排水为水源,采取注水与施肥相结合的盐碱水质淡化措施[19];已取得初步结果[20];王建玉等[21]利用盐碱滩地开挖池塘、抬田,抬田种植农作物、水果,实现了鱼-农-果立体综合开发综合治理的良好经济效益和生态效益;种稻和养鱼都能促进土壤脱盐脱碱[22];养鱼活动势必对水体中其他生物群落以及整个系统的结构和功能产生一定的下行影响[23-24]。投饵和投饵养鱼围隔水体中总氮、溶解性氮以及硝态氮浓度下降,氨氮和颗粒态氮浓度增加[25]。投饵养鱼极大降低了水体中氮磷质量浓度比[26]。不同的围堤养鱼年份对盐碱地的生物性状改良效果不同。由表1和表2可知,多酚氧化酶活性随pH值的增加而增大,这与郝建朝[27]的研究结果一致,所以多酚氧化酶在原碱裸地土中的活性最大。杨富亿等[28]提出,池塘淤泥中存在大量细菌,好气性细菌一般是在淤泥表层占优势,在淤泥中由于缺乏氧气,嫌气性细菌占优势。所以,随着养鱼年份的增长,细菌数量呈上升趋势。但是,并不是养鱼时间越长改良效果越好,部分特性在5 a后水稻土中的效果比养鱼8 a的好,盐碱地围堤养鱼种稻,成为了水稻-水-土壤界面,提高了光、热、气的交换性能,土温、水温升高,促进土壤养分快速分解,从而使土壤微生物活性、酶活性进一步加强;这与张金宗[29]研究结果一致。霍洪明等[30]认为,土壤呼吸与土壤生物特性存在着一定的关系,随着土壤呼吸值的增加,细菌数量会增加,酶活性也会增大,但本试验中,土壤呼吸值与生物特性并没有多大的关系,可能与采样时间和试验过程中的误差所导致,采样时间在夏季,鱼的活动量较小,水中含氧量较少,影响着土壤的生物特性。
4 结 论
不同的围堤养鱼年份对盐碱地的改良效果不同,围堤养鱼5a后种稻对微生物的改良效果最明显,细菌、纤维素分解菌、亚硝酸细菌、磷细菌的数量都呈上升趋势,与盐碱裸地土相比,分别增加了2.60×106,0.66×104,7.84×105,0.55×105cfu/g。
除多酚氧化酶在盐碱裸地土中的活性最大之外,其他酶的活性在围堤养鱼5 a的土壤中最理想,脲酶、磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶、纤维素酶的活性分别提高了0.008 mg/(g·24 h),0.153 mg/(g·24 h),2.035 mg/(g·20 min),0.399 mg/(g·72 h)。CO2的释放量在围堤养鱼8a的土壤里最大,比原碱土增加了7.41 mg/g。
土壤的生物性状与土壤的呼吸作用相关性不显著;养鱼8 a土样细菌的数量与其他处理有极显著差异。总体来说,在本次试验中,围堤养鱼5 a后种稻是改良盐碱地最有效的方式。
[1] 杨富亿. 吉林省西部盐碱地稻田养鱼研究[J]. 吉林农业大学学报,1994,23(6):1091-1096.
Yang Fuyi. The research on fish farming in saline land of western Jilin province[J]. Jilin Agricultural University Journal, 1994, 23(6): 1091-1096. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 姜隽. 疏水性有机物在生物富集中对有机物的吸附[J]. 山
西科技,2016,31(6):62-65.
Jiang Juan. Adsorption of hydrophobic organic compounds on organic compounds in the BCF[J]. Shanxi Science and Technology, 2016, 31(6): 62-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 范富,张庆国,邰继承,等. 通辽市盐碱地形成及类型划分[J]. 内蒙古民族大学学报,2009,24(4):409-413.
Fan Fu, Zhang Qingguo, Tai Jicheng, et al. The formation and classification of saline-alkali soil in Tongliao City[J]. Inner Mongolia University Journal, 2009, 24(4): 409-413. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 王佳丽,黄贤金,钟太洋,等. 盐碱地可持续利用研究综述[J]. 地理学报,2011,66(5):673-682.
Wang Jiali, Huang Xianjin, Zhong Taiyang, et al. Review on sustainable utilization of salt-affected land[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2011, 66(5): 673-682. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 范富,张庆国,侯迷红,等. 玉米秸秆隔离层对西辽河流域盐碱土碱化特征及养分状况的影响[J]. 水土保持学报,2013,27(3):131-137.
Fan Fu, Zhang Qingguo, Hou Mihong, et al. Effect of maize straw solation layer on alkalization characteristics and nutrient status of saline-alkali soil in West Liaohe Region[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(3): 131-137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 潘延鑫,罗纨,贾忠华,等. 盐碱地排水沟蓄水后底泥与水体盐分交换试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(2):81-87.
Pan Yanxin, Luo Wan, Jia Zhonghua, et al. Experiment on salt exchange between sediments and ponding water in drainage ditches of saline farmland[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(2): 81-87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 窦超银,康跃虎,万书勤,等. 覆膜滴灌对地下水浅埋区重度盐碱地土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(3):44-51.
Dou Chaoyin, Kang Yuehu, Wan Shuqing, et al. Effect of mulch-drip irrigation on soil enzyme activities of saline-sodic soil with shallow water table[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(3): 44-51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 赵辉,杨涓,腾迎凤,等. 脱硫渣废弃物对盐碱地油葵根际微生物数量及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报,2010,19(11):2718-2721.
Zhao Hui, Yang Juan, Teng Yingfeng, et al. Effects of gypsum application rate on the quantity of microorganisms and activity of enzymes inrhizospheric[J]. Ecology and Enviromental Sciences, 2010, 19(11): 2718-2721. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 范富,徐寿军,宋桂云,等. 玉米秸秆造夹层处理对西辽河地区盐碱地改良效应研究[J]. 土壤通报,2012,43(3):696-701.
Fan Fu, Xu Shoujun, Song Guiyun, et al. Research on the improvement of saline-alkali soil by maize straw interlayer measures in West Liaohe Region[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2012, 43(3): 696-701. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李凤霞,王学琴,郭永忠,等. 不同改良措施对银川平原盐碱地土壤性质及酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持研究,2012,19(6):13-18.
Li Fengxia, Wang Xueqin, Guo Yongzhong, et al. Effect of soil properties and soil enzyme measures activity in different improvement of saline-alkali soil in Yinchuan Plain[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conscrvation, 2012, 19(6): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 王金满,杨培岭,张建国,等. 脱硫石膏改良碱化土壤过程中的向日葵苗期盐响应研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2005,21(9):33-37.
Wang Jinman, Yang Peiling, Zhang Jianguo, et al. Salinity effect on sunflower at seedling stage during improving sodic soils reclaimed with by-product from flue gas desulphurization (BFGD)[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2005, 21(9): 33-37. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 杨富亿. 苏打盐碱地稻田养鱼[J]. 资源开发与市场,2000,16(2):67-69.
Yang Fuyi. Rice field fish culture in soda saline-alkali land[J]. Resource Development & Market, 2000, 16(2): 67-69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 龙藏瑞. 低洼盐碱地藕塘养鱼技术[J]. 实用生产技术推广,2014,34(13):24-38.
Long Cangrui. The low-lying saline lotus root fish technology[J]. Practical Production Technology Extension, 2014, 34(13): 24-38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 缴建华,吴会民. 滨海型盐碱地封闭循环水养鱼池塘水质变化的研究[J]. 淡水渔业,2008,38(3):63-64.
Jiao Jianua, Wu Huimin. The water quality variation of closed recycled aquiculture system in pond of coastal saline-alkaline land[J]. Fresh Water Fisheries, 2008, 38(3): 63-64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 许光辉. 土壤微生物分析方法手册[M]. 北京:北京农业出版社,1983:103-131.
[16] 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京:北京农业出版社,1983:274-339.
[17] 杨富亿. 松嫩平原盐碱地稻田养鱼技术[J]. 水产科学,1993,12(7):18-21.
Yang Fuyi. The technology of raising fish in the saline alkali paddy field of Songnen Plain[J]. Fishery Sciences, 1993, 12(7): 18-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 杨富亿,李秀军,裘善文.盐碱泡沼养鱼试验[J]. 水产科学,1993,12(8):9-12.
Yang Fuyi, Li Xiujun, Qiu Shanwen. Salt alkali soaking fish culture[J]. Fishery Sciences,1993, 12(8): 9-12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 杨富亿. 盐碱闭流洼地苇塘养鱼试验报告[J]. 水产科学,
1995,14(5):10-14,7. Yang Fuyi. Salt closed flow test report Weitang fish[J]. Fishery Sciences, 1995, 14(5): 10-14, 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 蒋高中,惠富平. 我国综合养鱼生态模式及其发展思路[J]. 家畜生态学报,2007,28(1):102-104.
Jiang Gaozhong, Hui Fuping. Ecological models and development approach of integrated fish farming in China[J]. Acta Ecologiae Animalis Domastici, 2007, 28(1): 102-104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 王建玉,王显智. 利用盐碱滩地综合开发鱼农果[J]. 山西水利科技,1995(2):86-88.
[22] 潘宏,严少华,葛兆健,等.千秋滩涂种稻和养鱼初期土壤化学环境的变化及对策[J]. 垦殖与稻作,1996(1):31-32.
Pan Hong, Yan Shaohua, Ge Zhaojian, et al. A rice and fish beach early changes of soil chemical environment and Countermeasures[J]. Reclaiming and Rice Cultivation, 1996(1): 31-32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 钟金香,林小涛,许忠能,等. 放养鱼类对淡水生态环境的下行影响[J]. 暨南大学学报:自然科学版,2001,22(5):131-136.
Zhong Jinxiang, Lin Xiaotao, Xu Zhongneng, et al. The top-down effect of fish stocking on the freshwater environment[J]. Journal of Jinan University: Natural Science, 2001, 22(5): 131-136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 吴敏,黄岁樑,杜胜蓝,等.投饵养鱼对潘家口水库藻类生长影响的围隔试验研究[J]. 生态环境学报,2010,19(8):1906-1911.
Wu Min, Huang Suiliang, Du Shenglan, et al. Experimental research on algae with fish culturing in the Panjiakou reservoir by the use of enclosures[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2010, 19(8): 1906-1911. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 吴敏,黄岁樑,杜胜蓝,等. 投饵养鱼对潘家口水库水质影响围隔试验:氮素[J]. 水利学报,2013,44(9):1030-1036.
Wu Min, Huang Suiliang, Du Shenglan, et al. Enclosure experimental research with fish culturing in the Panjiakou ReservoirⅠ.Effects of fish food and fish species on nitrogen flux[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2013, 44(9): 1030-1036. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 吴敏,黄岁樑,臧常娟,等. 投饵养鱼对潘家口水库水质影响围隔试验Ⅱ:磷素[J]. 生态环境学报,2013,44(10):1204-1209.
Wu Min, Huang Suiliang, Zang Changjuan, et al. Enclosure experimental research with fish culturing in the Panjiakou ReservoirⅡ. Effects of fish food and fish species on phosphorus flux[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2013, 44(10): 1204-1209. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 郝建朝. 土壤多酚氧化酶性质研究及意义[J]. 土壤学报,2006,37(3):470-474. Hao Jianchao. Properties of polyphenol oxidase in soil and its significance[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2006, 37(3): 470-474. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 杨富亿,李秀军,王志春,等.吉林省西部苏打盐碱地养鱼稻田微生物研究[J]. 吉林农业大学学报,2003,25(6):606-610.
Yang Fuyi, Li Xiujun, Wang Zhichun, et al. Mieroorganisms of fish-rice ecosystem in soda saline-aikaline land[J]. Jilin Agricultural University Journal, 2003, 25(6): 606-610. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 张金宗. 养鱼池塘淤泥的性质、作用和改良办法[J]. 现代渔业信息,2004,19(3):25-26.
Zhang Jinzong. Character, function and provement of silt in the fish pond[J]. Modern Fisheries in Formation, 2004, 19(5): 25-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 霍洪明,艾娟,于喜丰,等. 盐碱地池塘高效益的探讨[J]. 黑龙江水产,1998(1):39-40.
Huo Hongming, Ai Juan, Yu Xifeng, et al. Discussion on high benefit of pond in saline alkali soil[J]. Heilongjiang Fisheries, 1998(1): 39-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Improving biological traits by soda alkali-saline land diking for fish
Fan Fu1,2, Zhang Qinguo1, Ma Yulu1, Hou Mihong1, Sa Rula1, Ma Jinhui1, Lü Xiuyan1
(1.028043,; 2.,028000,)
Soda saline-alkali land is one of the main types of salinized land resources in China. Due to the influence of semi-arid monsoon climate, groundwater condition and geochemical process of element migration in Tongliao City of Inner Mongolia, a large area of saline-alkali soil has been formed. The low-lying saline-alkali land in the West Liaohe River Basin belongs to the soda alkaline soil with high alkalinity. And for most of the barren bare alkaline soil, soil productivity was very low. Planting rice after embankment and fish culture in saline-alkali soil was one of the effective ways of improving saline-alkali soil. In order to investigate the improvement effect of embankment and fish culture on saline-alkali soil, the biological traits and respiration of various soil samples were tested in 2016.The pH value of soil samples was 9.52,and soil respiration was 1.10 mg/g.The activity of soil enzyme and the amount of soil microorganism were the important indices to indicate the soil fertility level. The biological traits included the numbers of microorganisms (nitrite bacteria, cellulose decomposing bacteria, phosphorus bacteria), which were counted with dilution flat plate coating method,and the soil enzyme activity included phosphatase, urease, cellulase, polyphenol oxidase, and catalase, which were determined by colorimetric method and titration method.Additionally, the soil respiration was measured by alkali absorption titration method. The soil samples were taken from the ponds in Horqin Left Middle Banner, Tongliao City, where fish culture lasted for 3, 5 and 8 years, respectively, and rice was planted after 5-year fish culture and bare alkaline soil was taken as the control. The results showed that among the fish culture of different years, planting rice after 5-year fish culture had the most obvious improvement effect on the microorganism. Compared with the bare saline soil, the numbers of soil bacteria, cellulose decomposing bacteria, rice nitrite bacteria, and phosphorus bacteria were increased respectively by 2.60×106, 0.66×104, 7.84×105, and 0.55×105cfu/g. It was not that the longer the fish culture time, the better the improvement effect on the soda saline-alkali land. Except the activity of polyphenol oxidase that was the highest in the bare alkaline soil, all the other enzyme activities had the most obvious improvement in the soil of fish culture for 5 years. The activities of urease, phosphatase, catalase and cellulase were increased respectively by 0.008 mg/g every 24 h, 0.153 mg/g every 24 h, 2.035 mg/g every 20 min and 0.399 mg/g every 72 h. The release amount of CO2was the highest in the soil of fish culture for 8 years, 7.41 mg/g higher than that in the bare alkaline soil. Only bacteria number was positively correlated with soil respiration (<0.05). There was no correlation between soil biological properties and soil respiration. The research has a certain reference value to the regional follow-up use of the saline-alkali land. In the early stage of utilization, we should pay attention to the improvement of fertilizer, increase the application of organic manure, rationally arrange irrigation, and make the utilization of soda salinized soil develop in a benign direction. We will study the effect of different ages on the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium of the soda saline-alkali soil after embankment and fish culture. It will provide a reliable basis for the protection and utilization of soda saline-alkali land resources.
soils; microorganism; enzymes; soda alkali-saline land; diking fish; biological traits
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.019
S156.4
A
1002-6819(2018)-02-0142-05
2017-08-02
2017-12-03
国家自然基金项目(31760372);内蒙古自然科学基金项目(2013MS0605);内蒙古自治区科技创新引导项目(KJCX1602);内蒙古自治区饲用作物工程技术研究中心开放课题(MDK2017002)
范 富,男,内蒙古化德人,教授,主要从事植物营养调控和土壤改良方面的研究。Email:fanfu63@163.com
范 富,张庆国,马玉露,侯迷红,萨如拉,马金慧,吕秀艳. 苏打盐碱地围堤养鱼改良土壤的生物性状[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(2):142-146. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.019 http://www.tcsae.org
Fan Fu, Zhang Qinguo, Ma Yulu, Hou Mihong, Sa Rula, Ma Jinhui, Lü Xiuyan. Improving biological traits by soda alkali-saline land diking for fish[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(2): 142-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.02.019 http://www.tcsae.org
