Information Leakage in Quantum Dialogue by Using Non-Symmetric Quantum Channel∗
2018-01-24GanGao高干WeiYanLi李伟艳andYueWang王悦DepartmentofElectricalEngineeringTonglingUniversityTongling244000China
Gan Gao(高干), Wei-Yan Li(李伟艳), and Yue Wang(王悦)Department of Electrical Engineering,Tongling University,Tongling 244000,China
2Engineering Technology Research Center of Optoelectronic Technology Appliance,Tongling University,Tongling 244000,China
The purpose of quantum key distribution(QKD)is to establish an unconditionally secure secret key between two remote authorized parties through the transmission of quantum signals.In 1984,Bennett and Brassard[1]proposed the first QKD protocol by using single randomly polarized photon states.Since then,much attention has been focused on QKD,and some exciting progresses in theoretical and experimental aspects have appeared.As we all know,in the QKD protocol,the two authorized parties just produce a shared key,and then use the key to encrypt and decrypt the secret message.At this moment,we can not help thinking whether there exists the quantum communication protocol that can directly transmit secret messages?In 2001,Long et al.[2]proposed the first quantum secure direct communication(QSDC)protocol,which can realize direct transmission of secret messages.Here,let us introduce what the advantage of QSDC is.QSDC can transmit the secret message directly without first creating a private key to encrypt them.Moreover,QSDC is also the first secure communication protocol that does not use a private key,both in classical cryptography and quantum cryptography.Since the process to create a private key does not exist,QSDC spares the diffculty of key management.And since directly transmitting the secret message,QSDC is instantaneous and more effcient than QKD.In addition,on the site of any authorized party,QSDC need not to change from the quantum channel to the classical channel,ensuring the security of any authorized party’s site.In contrast,the security of sites is assumed in other communication protocols.After the first QSDC protocol[2]was proposed,plenty of interesting researches on QSDC[3−43]are pursued actively.In the QSDC protocol,we see that the secret messages are transmitted by the single-direction way.Similarly,we can not help thinking whether a bidirectional quantum secure communication protocol exists?In 2004,Nguyen put forward the first bidirectional quantum secure communication(BQSDC)protocol,[44]in which the secret messages of two communication parties can be transmitted simultaneously.By the way,BQSDC is also called quantum dialogue(QD).[44−67]However,it is a pity that Man,Zhang,and Li[45]pointed out Nguyen’s QD protocol[44]cannot resist the intercept-and-resend attack,and gave an improved version of the QD protocol.In 2008,Gao et al.[51]again pointed out there exists the drawback of information leakage in Nguyen’s QD protocol[44]from the perspective of information theory and cryptography.After Gao et al.’s work,[51]one tries one’s best to avoid the information leakage when designing QD protocols.
In 2010,Zhan et al.[52]used the non-symmetric quantum channel to propose a QD protocol.In the proposed protocol,the feature of the used quantum channel is interesting.This is because the used quantum channels are symmetric in all previous QD protocols.However,it is somewhat a pity that the Zhan et al.’s protocol[52]has still the drawback of information leakage,that is,an eavesdropper can obtain part secret messages without any active attack.
In the following,we will prove the existence of information leakage in the Zhan et al.’s protocol.[52]Firstly,let us review the Zhan et al.’s protocol in brief.(i)Bob preparesNthree-dimensional Bell states which each is|Ψ〉AB=(|00〉+|11〉+|22〉)AB/andNtwo-dimensional ones which each is|Φ00〉A′B′=(|00〉+|11〉)A′B′/Next,he takes particleAfrom|Ψ〉ABand particleA′from|Φ00〉A′B′to form theSAsequence,and the other particles to form theSBsequence.(ii)Bob selects some Bell states fromSAandSBto check eavesdropping,and these states are denoted withCAandCBsets.The remaining Bell states inSAandSBsequences are denoted withMAandMBsets.(iii)Bob performsUkoperations on particlesAjandA′jinCAset for checking eavesdropping,and also performsUkoperations on particlesAiandA′iinMAset for encoding messages.Then,Bob sends theSAsequence to Alice.(iv)After Alice receives the sequence,Bob announces theCAset.Next,Alice also performsUkoperations on particlesAjandinCAset,and then usesthe basiswhichis composed ofto measure particlesAjand Then,she announces her performing unitary operations,her measurement outcomes and the position for each checking group inCAset.(v)Bob also uses the basis{|Φmn〉}to measure particlesBjandinCBset.According to his measurement outcomes and Alice’s announcement,Bob can judge whether the quantum channel is secure.(vi)Alice performsUkoperations on particlesAiandinMAset to encode her messages.Then,Alice and Bob use the basis{|Φmn〉}to measure particlesAiandinMAset and particlesBiandinMBset,respectively.Moreover,they announce their measurement outcomes.(vii)Alice and Bob decode the secret messages of the other side.
The aboveUk(the subscriptk=1,2,...,6)are defined as follows:
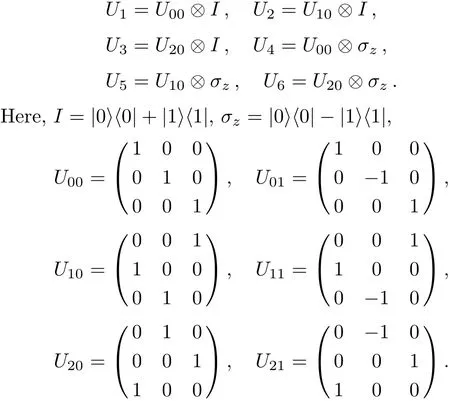
We see there are two communication parties,Alice and Bob in the QD protocol which Zhan et al.[52]employed the non-symmetric quantum channel to design.By using the entanglement swapping of the two EPR pairs(|Ψ〉AiBiandAlice transmits log26 bits of secret messages to Bob,meantime,Bob also transmits log26 bits to Alice.Obviously,2log26 bits of secret messages are transmitted between them.Can all 2log26 bits be transmitted in a secure manner?The answer is no.This is because part of 2log26 bits will be leaked out to the eavesdropper,in other words,the eavesdropper can obtain part from Alice’s and Bob’s announcements without initiatively attacking on the quantum channel.In the following,let us explain this by giving an example.Suppose that Bob’s and Alice’s unitary operations on particleAiandinMAset areU4andU3,respectively.The whole system state evolves as follows:
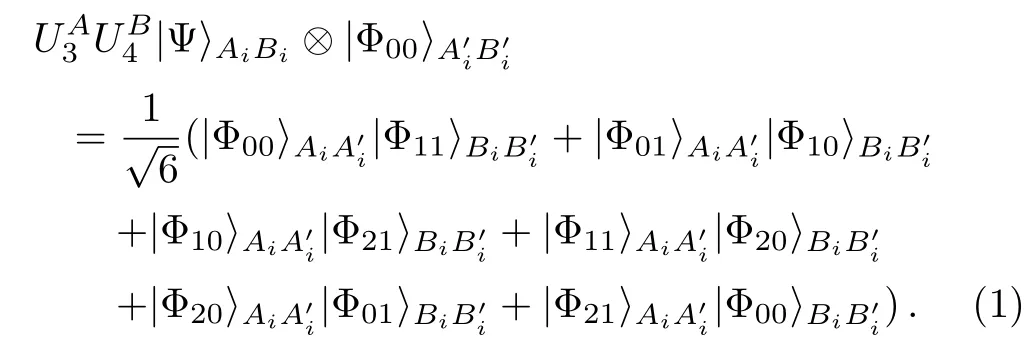
According to Eq.(1),we see there are six possible entanglement swapping outcomes and each happens with the equal probability of 1/6.When Alice and Bob announce their measurement outcomes,that is,their obtaining entanglement swapping outcomes,an eavesdropper can infer that their previously performing unitary operation group must be one of the six groups:Provided that the six groups have an equal probability,the channel should contain only(1/6)log2(1/6)=log26 bits of secret messages for the eavesdropper.Notice that,we just pointed out that the quantity of the transmitted messages between Alice and Bob in Zhan et al.’s protocol[52]is 2log26 bits.As a result,2log26−log26=log26 bits of secret messages will be unknowingly leaked out to the eavesdropper,that is to say,the log26 bits can not be transmitted in a secure manner.By the way,in the quantum communication,all bits of secret messages must be transmitted in a secure manner.Here,we list the example that Bob’s and Alice’s unitary operations areU4andU3,respectively.If their unitary operations are others,the analyzing processes are similar.All cases are summarized in Table 1.Next,we need to make an explanation for the Table.It is seen that there are six rows in Table 1,and there are sixϕmnψmnin the left side of every row and there are sixin the right side.If only the measurement outcome that Alice and Bob announce is any of six leftϕmnψmn,the eavesdropper can conclude the unitary operation that they previously performed to encode secret messages must be limited in six right
Table 1 “ϕmn” denotes the measurement outcome|Φmn〉AiA′ithat Alice makes on particles Aiandin MAset or announces,and“ψmn”denotes the measurement outcome|Φmn〉BiB′ithat Bob makes on particles Biand in MBset or announces.“ϕmnψmn”denotes one possible announcement.
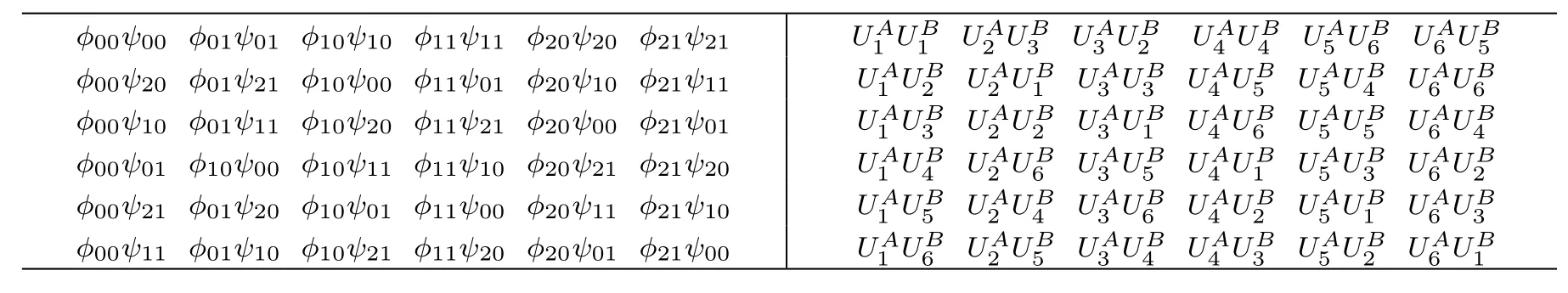
Table 1 “ϕmn” denotes the measurement outcome|Φmn〉AiA′ithat Alice makes on particles Aiandin MAset or announces,and“ψmn”denotes the measurement outcome|Φmn〉BiB′ithat Bob makes on particles Biand in MBset or announces.“ϕmnψmn”denotes one possible announcement.
ϕ00ψ00 ϕ01ψ01 ϕ10ψ10 ϕ11ψ11 ϕ20ψ20 ϕ21ψ21 UA1UB1UA2UB3UA3UB2 UA4UB4UA5UB6UA6UB5 ϕ00ψ20 ϕ01ψ21 ϕ10ψ00 ϕ11ψ01 ϕ20ψ10 ϕ21ψ11UA3UB3UA4UB5UA5UB4UA6UB6 ϕ00ψ10 ϕ01ψ11 ϕ10ψ20 ϕ11ψ21 ϕ20ψ00 ϕ21ψ01UA3UB1UA4UB6UA5UB5UA6UB4 ϕ00ψ01 ϕ10ψ00 ϕ10ψ11 ϕ11ψ10 ϕ20ψ21 ϕ21ψ20 UA1 UB2 UA2 UB1 UA3UB5UA4UB1UA5UB3UA6UB2 ϕ00ψ21 ϕ01ψ20 ϕ10ψ01 ϕ11ψ00 ϕ20ψ11 ϕ21ψ10 UA1 UB3 UA2 UB2 UA3UB6UA4UB2UA5UB1UA6UB3 ϕ00ψ11 ϕ01ψ10 ϕ10ψ21 ϕ11ψ20 ϕ20ψ01 ϕ21ψ00 UA1 UB4 UA2 UB6 UA1 UB5 UA2 UB4 UA1 UB6 UA2 UB5 UA3UB4UA4UB3UA5UB2UA6UB1
Next,we will modify Zhan et al.’s protocol so that it can overcome the information leakage.The modified Zhan et al.’s protocol is described as follows.
(i) Bob preparesNthree-dimensional Bell states whicheachis|Ψ〉ABandNtwo-dimensionalones which each is|Φ00〉A′B′. Next,he takes particleAfrom |Ψ〉ABand particleA′from |Φ00〉A′B′to form(simply calledSAsequence),andtheremainingparticlesform(simply calledSBsequence).
(ii)Bob encodes his secret messages by performing the unitary operation on particlesAiandThen he inserts some decoy particles,which each is randomly in one of the four states:andinto theSAsequence,and sends theSAsequence to Alice.
(iii)After con firming that Alice has received theSAsequence,Bob publishes the positions of decoy particles in the sequence and the states of decoy particles.Next,Alice correctly uses one of the two sets of measuring basis:{|0〉,|1〉}and{|+〉,|−〉},to measure each decoy particle.By comparing the measurements with Bob’s publishing states of decoy particles,she can judge whether the quantum channel is secure.
(iv)Alice encodes his secret messages also by performing the unitary operation on particlesAiandin theSAsequence.Then Alice and Bob use the basisto measure particlesAiandin theSAsequence and particlesBiandin theSBsequence,respectively.Moreover,Alice publishes her measurement outcomes and Bob does not.
(v)Bob inserts some decoy particles into theSBsequence,and also sends the sequence to Alice.After receiving theSBsequence,Alice uses the basisto measure particlesBiand
(vi)Alice can decode Bob’s secret messages,and Bob can also decode Alice’s.
In conclusion,from the perspective of information theory and cryptography,we have successfully proved that the information leakage exists in Zhan et al.’s protocol.According to the above analyzing,the reason that the information leakage exists is that the quantity of transmitted secret messages exceeds the capability of the quantum channel between Bob and Alice.In addition,the existence of information leakage means that one part of secret messages can be transmitted in a secure manner,the other part can not in Zhan et al.’s protocol,which is entirely forbidden in the quantum communication.In order to overcome the drawback of information leakage,we modify Zhan et al.’s protocol by adding the process that theSBsequence is also sent to Alice by Bob.In the modified protocol,it is easily calculated that the quantity of transmitted secret messages and the capability of the quantum channel are equal,and both equal to 2log26 bits.In the end,it is worth reminding that not only common attack strategies,but also the information leakage needs to be considered when we analyze the security of the designing quantum communication protocol.
We thank the anonymous referee for his/her important and helpful suggestions.
[1]C.H.Bennett and G.Brassard,in aProceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers,Systems and Signal Processings,Bangalore,India,IEEE,New York(1984)p.175.
[2]G.L.Long and X.S.Liu,Phys.Rev.A 65(2002)032302.
[3]F.G.Deng,G.L.Long,and X.S.Liu,Phys.Rev.A 68(2003)042317.
[4]F.G.Deng and G.L.Long,Phys.Rev.A 69(2004)052319.
[5]Q.Y.Cai and B.W.Li,Phys.Rev.A 69(2004)054301.
[6]C.Wang,F.G.Deng,and G.L.Long,Opt.Commun.253(2005)15.
[7]C.Wang,F.G.Deng,Y.S.Li,X.S.Liu,and G.L.Long,Phys.Rev.A 71(2005)044305.
[8]Y.Q.Zhang,X.R.Jin,and S.Zhang,Phys.Lett.A 341(2005)380.
[9]Z.X.Man,Z.J.Zhang,and Y.Li,Chin.Phys.Lett.22(2005)18.
[10]M.Lucamarini and S.Mancini,Phys.Rev.Lett.94(2005)140501.
[11]X.H.Li,F.G.Deng,et al.,J.Korean Phys.Soc.49(2006)1354.
[12]X.H.Li,F.G.Deng,and H.Y.Zhou,Phys.Rev.A 74(2006)054302.
[13]H.F.Wang,S.Zhang,K.H.Yeon,and C.I.Um,J.Korean.Phys.Soc.49(2006)459.
[14]J.Wang,Q.Zhang,and C.J.Tang,Phys.Lett.A 358(2006)256.
[15]G.He,J.Zhu,and G.Zeng,Phys.Rev.A 73(2006)012314.
[16]X.H.Li,C.Y.Li,F.G.Deng,P.Zhou,Y.J.Liang,and H.Y.Zhou,Chin.Phys.16(2007)2149.
[17]Y.Xia and H.S.Song,Phys.Lett.A 364(2007)117.
[18]M.Y.Wang and F.L.Yan,Chin.Phys.Lett.24(2007)2486.
[19]S.Lin,Q.Y.Wen,F.Gao,and F.C.Zhu,Phys.Rev.A 78(2008)064304.
[20]X.Yi,Y.Y.Nie,N.Zhou,Y.Huang,Z.Hong,and S.Li,Commun.Theor.Phys.50(2008)81.
[21]X.Yi,Y.Y.Nie,N.Zhou,Y.Huang,and Z.Hong,Int.J.Theor.Phys.47(2008)3401.
[22]G.Gao,Commun.Theor.Phys.50(2008)368.
[23]G.Gao,Commun.Theor.Phys.52(2009)845.
[24]W.F.Cao,Y.G.Yang,and Q.Y.Wen,Sci.Chin.Ser.G.Phys.Mech.Astron.53(2010)1271.
[25]T.J.Wang,T.Li,F.F.Du,and F.G.Deng,Chin.Phys.Lett.28(2011)040305.
[26]B.Gu,C.Y.Zhang,G.S.Cheng,and Y.G.Huang,Sci.China:Phys.Mech.Astron.54(2011)942.
[27]B.Gu,Y.C.Huang,X.Fang,and C.Y.Zhang,Chin.Phys.B 20(2011)100309.
[28]C.W.Tsai,C.R.Hsieh,and T.Hwang,Eur.Phys.J.D 61(2011)779
[29]L.Dong,X.M.Xiu,Y.J.Gao,Y.P.Ren,and H.W.Liu,Opt.Commun.284(2011)905.
[30]G.Gao,M.Fang,and R.M.Yang,Int.J.Theor.Phys.50(2011)882.
[31]Z.W.Sun,R.G.Du,and D.Y.Long,Int.J.Theor.Phys.51(2012)1946.
[32]W.Huang,Q.Y.Wen,H.Y.Jia,S.J.Qin,and F.Gao,Chin.Phys.B 21(2012)100308.
[33]G.Gao,J.Korean,Phys.Soc.62(2013)1093.
[34]B.C.Ren,H.R.Wei,M.Hua,T.Li,and F.G.Deng,Eur.Phys.J.D 67(2013)30.
[35]S.H.Kao and T.Hwang,Quantum Inf.Process.12(2013)3791.
[36]S.J.Xu,X.B.Chen,X.X.Niu,and Y.X.Yang,Commun.Theor.Phys.59(2013)547.
[37]X.F.Zou and D.W.Qiu,Sci.China:Phys.Mech.Astron.57(2014)1696.
[38]H.Lai,et al.,Commun.Theor.Phys.63(2015)459.
[39]Y.Chang,et al.,Commun.Theor.Phys.63(2015)285.
[40]J.Y.Hu,B.Yu,M.Y.Jing,et al.,Light:Science&Applications 5(2016)e16144.
[41]W.Zhang,D.S.Ding,Y.B.Sheng,et al.,arXiv:quanph/1609.09184(2016).
[42]F.Gao,B.Liu,and Q.Y.Wen,Sci.China:Phys.Mech.Astron.59(2016)110311.
[43]F.G.Deng,et al.,Sci.Bulletin 62(2017)46.
[44]B.A.Nguyen,Phys.Lett.A 328(2004)6.
[45]Z.X.Man,Z.J.Zhang,and Y.Li,Chin.Phys.Lett.22(2005)22.
[46]X.Ji and S.Zhang,Chin.Phys.15(2006)1418.
[47]Z.X.Man,Y.J.Xia,and B.A.Nguyen,J.Phys.B:At.Mol.Opt.Phys.39(2006)3855.
[48]Y.Xia,C.B.Fu,F.Y.Li,S.Zhang,and K.H.Yeon,J.Korean,Phys.Soc.48(2006)24
[49]A.D.Zhu,Y.Xia,Q.B.Fan,and S.Zhang,Phys.Rev.A 73(2006)022338.
[50]Z.X.Man and Y.J.Xia,Chin.Phys.Lett.23(2006)1680.
[51]F.Gao,F.C.Guo,Q.Y.Wen,and F.C.Zhu,Sci.Chin.Ser.G-Phys.Mech.Astron.51(2008)559.
[52]Y.B.Zhan,L.L.Zhang,and Y.W.Wang,Commun.Theor.Phys.53(2010)648.
[53]L.Dong,X.M.Xiu,Y.J.Gao,and F.Chi,Opt.Commun.281(2008)6135.
[54]L.Dong,X.M.Xiu,Y.J.Gao,and F.Chi,Commun.Theor.Phys.52(2009)853.
[55]G.F.Shi,X.Q.Xi,X.L.Tian,and R.H.Yue,Opt.Commun.282(2009)2460.
[56]G.F.Shi,Opt.Commun.283(2010)5275.
[57]G.Gao and L.P.Wang,Commun.Theor.Phys.54(2010)447.
[58]G.Gao,Opt.Commun.283(2010)2288.
[59]C.W.Yang and T.Hwang,Quantum Inf.Process.12(2013)2131.
[60]X.R.Yin,W.P.Ma,W.Y.Liu,and D.S.Shen,Quantum Inf.Process.12(2013)3093.
[61]G.Gao,Int.J.Theor.Phys.53(2014)2282.
[62]G.Gao,Mod.Phys.Lett.B 28(2014)1450094.
[63]C.Zheng and G.F.Long,Sci.China:Phys.Mech.Astron.57(2014)1238.
[64]T.Y.Ye and L.Z.Jiang,Phys.Scr.89(2014)015103.
[65]N.R.Zhou,et al.,Int.J.Theor.Phys.53(2014)3829.
[66]T.Y.Ye,Commun.Theor.Phys.63(2015)431.
[67]N.R.Zhou,et al.,Quantum Inf.Process.16(2017)4.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Communications in Theoretical Physics的其它文章
- Elastic Deformation Analysis on MHD Viscous Dissipative Flow of Viscoelastic Fluid:An Exact Approach
- Magnetic Effect Versus Thermal Effect on Quark Matter with a Running Coupling at Finite Densities∗
- Borromean Windows for Three-Particle Systems under Screened Coulomb Interactions∗
- Isotopic Effects on Stereodynamics of the C++H2→ CH++H Reaction∗
- Entropy Generation Analysis in Convective Ferromagnetic Nano Blood Flow Through a Composite Stenosed Arteries with Permeable Wall
- Effects of Interfaces on Dynamics in Micro-Fluidic Devices:Slip-Boundaries’Impact on Rotation Characteristics of Polar Liquid Film Motors∗
