尿微量蛋白、胱抑素C、糖化血红蛋白及晚期糖基化终末产物对糖尿病早期肾损伤的应用评价
2018-01-12朱晓英施笑娅徐象威
朱晓英+施笑娅+徐象威

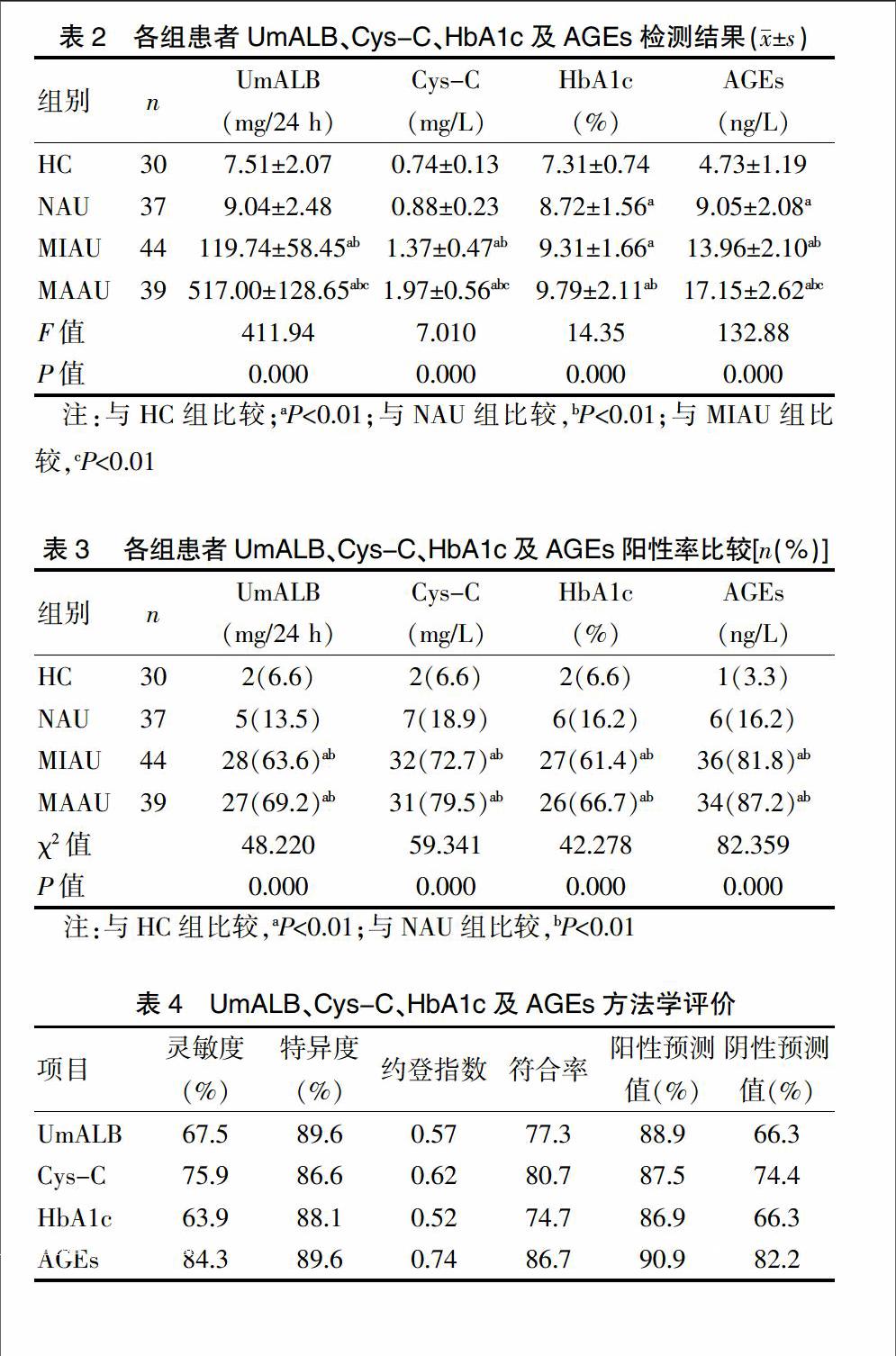
[摘要] 目的 探討尿微量白蛋白(UmALB)、胱抑素C(Cys-C)、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)及晚期糖基化终末产物(AGEs)四项指标对糖尿病早期肾功能损伤的临床价值。 方法 选择2015年12月~2016年12月符合标准的糖尿病患者120例,分为正常白蛋白尿组(NAU)37 例、微量白蛋白尿组(MIAU)44例和大量白蛋白尿组(MAAU)39例。选择同期30例健康体检人群为对照组(HC),比较各组UmALB、Cys-C、HbA1c、AGEs浓度水平及阳性率,并行方法学指标评价。 结果 ①四组患者一般资料无统计学差异(P>0.05)。②四组患者UmALB、Cys-C、HbA1c、AGEs浓度水平均有统计学差异(P<0.01)。其中NAU组HbA1c、AGEs水平明显高于HC组(P<0.01);MIAU组UmALB、Cys-C、AGEs水平明显高于NAU组(P<0.01);MAAU组四项指标均明显高于NAU组(P<0.01),且与MIAU组比较,UmALB、Cys-C、AGEs结果有统计学差异(P<0.01)。③各组检测方法阳性率有统计学差异(P<0.01)。其中MIAU组与MAAU组的阳性率明显高于HC组与NAU组(P<0.01)。方法学评价上AGEs最高,其次为Cys-C、UmALB、HbA1c。 结论 UmALB、Cys-C、HbA1c、AGEs对糖尿病早期肾功能损伤具有重要的诊断价值,其中AGEs、Cys-C检测准确度更为可靠,值得临床进一步推广。
[关键词] 糖尿病肾病;晚期糖基化终末产物;血清胱抑素C;尿微量蛋白;糖化血红蛋白
[中图分类号] R446.12;R587.2;R692.9 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2017)33-0116-05
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the application value of four indices of urinary microalbumin(UmALB), cystatin C(Cys-C), glycosylated hemoglobin(HbA1c) and advanced glycation end products(AGEs) on early diabetic kidney injury. Methods 120 patients with diabetes who were in accordance with the standard from December 2015 to December 2016 were selected. Among them, there were 37 patients in the normal albuminuria group(NAU), 44 patients in the microalbuminuria group(MIAU) and 39 patients in the macroalbuminuria group(MAAU). 30 healthy people were selected as the control group(HC) during the same period of time. The concentration levels of UmALB, Cys-C, HbA1c, AGEs and the positive rate were compared between groups, and evaluation of methodological indicators was carried out. Results ①There was no statistically significant difference in general data between the four groups(P>0.05). ②The concentration levels of UmALB, Cys-C, HbA1c and AGEs in the four groups were statistically different(P<0.01). The levels of HbA1c and AGEs in NAU group were significantly higher than those in HC group(P<0.01); the levels of UmALB, Cys-C and AGEs in MIAU group were significantly higher than those in NAU group(P<0.01); the four indices in the MAAU group were significantly higher than those in the NAU group(P<0.01). Compared with MIAU group, the results of UmALB, Cys-C and AGEs were statistically different(P<0.01). ③The positive rate of test methods in each group was statistically different(P<0.01). The positive rate in MIAU group and MAAU group was significantly higher than that in HC group and NAU group(P<0.01). In methodological evaluation, the highest was AGEs, followed by Cys-C, UmALB, and HbA1c. Conclusion UmALB, Cys-C, HbA1c and AGEs have important diagnostic value in early diabetic kidney injury, in which the test accuracy of AGEs and Cys-C is more reliable, which is worthy of further clinical promotion.endprint
