辅助函数法求解非线性偏微分方程精确解
2017-11-20赖晓霞
杨 健,赖晓霞
(陕西师范大学 计算机科学学院,陕西 西安 710119)
辅助函数法求解非线性偏微分方程精确解
杨 健,赖晓霞
(陕西师范大学 计算机科学学院,陕西 西安 710119)
在数学和物理学领域,将含有非线性项的偏微分方程称为非线性偏微分方程。非线性偏微分方程用于描述物理学中许多不同的物理模型,范围涉及从引力到流体动力学的众多领域,还在数学中用于验证庞加莱猜想和卡拉比猜想。在求解非线性偏微分方程的过程中,几乎没有通用的求解方法能够应用于所有的方程。通常,可依据模型方程的数学物理背景来先验地假设非线性偏微分方程解的形式,并根据解的特点给出辅助方程。非线性偏微分方程可通过行波变换转化为常微分方程,再借助辅助方程来求解常微分方程。为此,借助行波变换及辅助方程的求解思路对BBM方程和Burgers方程进行了研究,并获得了其双曲正切函数及三角函数形式的精确解。研究结果表明,所采用的方法可广泛应用于若干在数学物理中有典型应用背景的非线性偏微分方程的精确解求解中。
非线性偏微分方程;辅助函数法;BBM方程;Burgers方程;精确解
0 引 言
非线性方程广泛应用于物理学和应用数学的许多分支,尤其在流体力学、固态物理学、等离子物理和非线性光学等。非线性方程的解能够揭示物理模型的许多性质。
为了求解非线性方程,提出了很多方法,如反散射变换法[1]、Hirota方法[2]、Bäcklund变换法[3]、Darboux变换法[4]、对称约化方法[5]、混合指数法[6]、齐次平衡法[7]、推广的tanh法[8]、Exp-函数法[9-10]、椭圆函数法[11]、辅助函数法[12]等。
利用现代计算机符号计算系统来寻找非线性偏微分方程的孤立波解,这是当前一个十分活跃的研究领域。为此,将使用辅助函数法并且借助符号计算系统Maple,在研究两个非线性演化方程BBM[13-14]和Burgers[15-17]的基础上,获得了精确解,并且给出了具体实现步骤。
1 辅助函数法
步骤1:将偏微分方程转化为常微分方程。给定的偏微分方程为:
P(u,ut,ux,uxt,uxx,utt…)=0
(1)
函数u=u(x,t)包含两个自变量x,t,引入波变换:
u(x,t)=φ(ξ),ξ=kx-ct
(2)
可将方程(1)转化为常微分方程:
P(φ,φ',φ'',φ''',…)=0
(3)
步骤2:假设方程(3)的精确解具有如下形式:
(4)
其中,ai为待定系数;而幂级数的最高次幂m可通过平衡常微分方程的最高阶导数项和非线性项来确定;f(ξ)满足如下辅助方程:
f(ξ)'=f(ξ)2+λf(ξ)+μ
(5)
则对应辅助方程的解有:
解1:
当λ=0,μ=0时,有:

(6)
解2:
当λ=0,μ>0时,有:

(7)

(8)
解3:
当λ=0,μ<0时,有:

(9)

(10)
解4:
当λ≠0,μ=0时,有:

(11)
解5:
当λ≠0,μ≠0,λ2-4μ>0时,有:
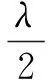

(12)
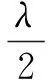

(13)
解6:
当λ≠0,μ≠0,λ2-4μ=0时,有:

(14)
解7:
当λ≠0,μ≠0,λ2-4μ<0时,有:
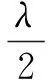

(15)
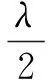

(16)
其中,C0为积分常数。
步骤3:通过常微分方程获得非线性代数方程组。把假设的具有式(4)形式的解和辅助函数(5)带入方程(3)中,合并f(ξ)的同次幂项,并令其各项系数和等于零,由此得到关于形式解(4)中各项的系数ai和c,k的一个非线性代数方程组。
步骤4:利用吴消元法求解代数方程组,确定待定量ai,c,k。
步骤5:将上面求得的ai带入解(4)中,即可得到方程的形式解。
步骤6:将c,k分别带入式(6)~(16),得出的精确形式再带入式(4)的形式解中,可最终获得方程解的精确解。
从上可以看出,非线性代数方程组,不仅计算量大,而且可能无法直接求解,而吴消元法为其求解建立了完备的理论。利用吴消元法,并借助符号计算系统Maple使求解成为可能。
2 方法应用
2.1Benjamin-Bona-Mahonye方程
考虑如下形式BBM方程:
ut+αux+βuux-γuxxt=0
(17)
将式(2)带入式(17),将其转化为常微分方程:
(α-ck)φ'+βφφ'+cγk2φ'''=0
(18)
其中,φ'=dφ/dξ。
平衡式(18)中的φφ'和φ'''两项,得到等式m+3=2m+1,解得m=2。
于是,可设方程解的形式如下:
φ(ξ)=a0+a1f(ξ)+a2f(ξ)2
(19)
将式(19)和式(5)带入式(18),然后合并f(ξ)的同次幂项系数,得到非线性代数方程组:
(20)
求解式(20)可得:
(21)
其中,k,a2为任意常数。
将所求得的式(21)带入式(19)中得到BBM方程的形式解:


(22)
再将式(6)~(16)的结果分别带入式(22),可获得如下七组解:
解1:
当λ=0,μ=0时

(23)

解2:
当λ=0,μ>0时

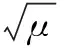
(24)

a2μcot[(ξ+C0)]2
(25)

解3:
当λ=0,μ<0时

a2μtanh[(ξ+C0)]2
(26)

a2μcoth[(ξ+C0)]2
(27)

BBM方程是刻画波随时间演化的模型方程,该精确解析解不但给出了波的形状,也精确刻画了解随时间的演化图。
当α=1,β=1,γ=5,μ=-1,a2=0.002,k=0.8,C0=0时,式(26)精确解析解如图1所示。
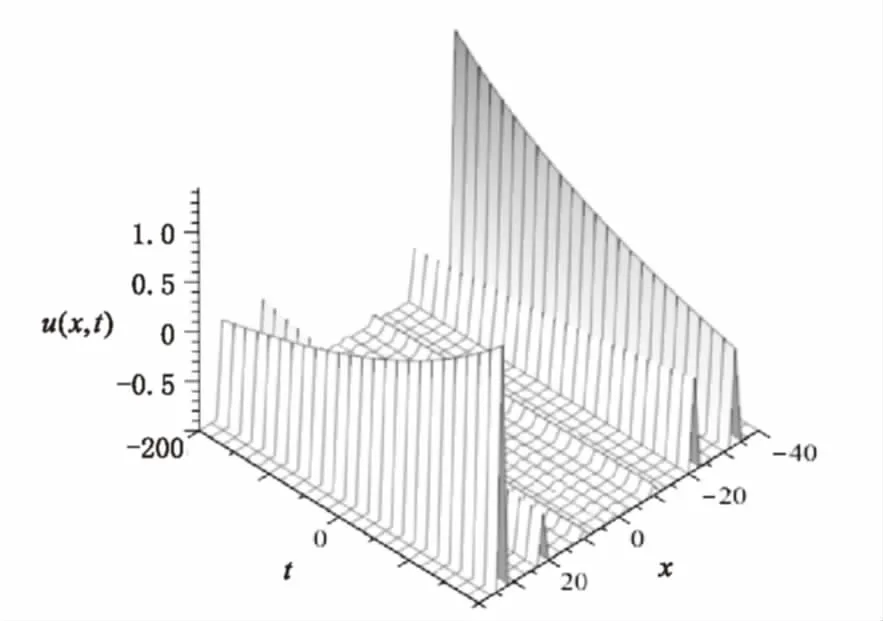
图1 式(26)精确解析解
α=1,β=2,γ=1,μ=-1,a2=2,k=1,C0=0时,式(27)精确解解析如图2所示。

图2 式(27)精确解析解
解4:
当λ≠0,μ=0时

a2λf(ξ)+a2f(ξ)2
(28)

解5:
当λ≠0,μ≠0,λ2-4μ>0时


(29)



(30)
解6:
当λ≠0,μ≠0,λ2-4μ=0时

a2λf(ξ)+a2f(ξ)2
(31)

解7:
当λ≠0,μ≠0,λ2-4μ<0时


(32)

2.2Burgers方程
考虑如下形式的Burgers方程:
ut+uux+puxx=0
(33)
将式(2)带入式(32),将其转化为常微分方程:
-cφ'+kφφ'+k2pφ''=0
(34)
其中φ'=dφ/dξ。
平衡(33)式中的φφ'和φ''两项,得到等式m+2=2m+1,解得m=1。于是设方程解的形式为:
φ(ξ)=a0+a1f(ξ)
(35)
将式(34)和式(5)带入式(33),然后合并f(ξ)的同次幂项系数,同样可得如下非线性代数方程组:
(36)
求解非线性代数方程组(35)可得:
(37)
其中,a0,k为任意常数。
将所求得的式(36)带入式(34)中可得Burgers方程的形式解:
u(x,t)=a0-2pkf(ξ)
(38)
再将式(6)~(16)的结果分别带入式(37),可获得Burgers方程如下七组解:
解1:
当λ=0,μ=0时

(39)
其中,ξ=kx-ka0t,k,a0为任意常数。
解2:
当λ=0,μ>0时

(40)

(41)
其中,ξ=kx-ka0t,k,a0为任意常数。
解3:
当λ=0,μ<0时

(42)

(43)
其中,ξ=kx-ka0t,k,a0为任意常数。
这两个解也给出了波的形状,精确刻画了解随时间的演化图。
a0=0.05,p=1,k=2,μ=-1,C0=0时,式(42)精确解析解如图3所示。

图3 式(42)精确解析解
a0=2,p=1,k=2,μ=-1,C0=0时,式(43)精确解析解如图4所示。

图4 式(44)精确解析解
解4:
当λ≠0,μ=0时
u(x,t)=a0-2pkf(ξ)
(44)
其中,ξ=kx-(pk2λ+ka0)t,k,a0为任意常数,f(ξ)为式(11)。
解5:
当λ≠0,μ≠0,λ2-4μ>0时
u(x,t)=a0-2pkf(ξ)
(45)
其中,ξ=kx-(pk2λ+ka0)t,k,a0为任意常数,f(ξ)为分别为式(12)、(13)。
解6:
当λ≠0,μ≠0,λ2-4μ=0时
u(x,t)=a0-2pkf(ξ)
(46)
其中,ξ=kx-(pk2λ+ka0)t,k,a0为任意常数,f(ξ)为式(14)。
解7:
当λ≠0,μ≠0,λ2-4μ<0时
u(x,t)=a0-2pkf(ξ)
(47)
其中,ξ=kx-(pk2λ+ka0)t,k,a0为任意常数,f(ξ)分别为式(15)、(16)。
3 结束语
为了求解非线性偏微分方程的精确解,基于方程形式解假设,通过行波变换并引入辅助方程得到了一个代数方程组,可获得相关的精确解。所提出的辅助方程在系数λ,μ取值不同时,所获得的解的形式也不相同,其中包括了可较好刻画波的演化性质的孤立波解。研究结果表明,所提出的辅助函数方法已可适用于一部分非线性偏微分方程和方程组的构造和分析中。
[1] Ablowitz M J,Kaup D J,Newell A C.The inverse scattering transform-Fourier analysis for nonlinear problems[J].Studies in Applied Mathematics,1974,53(4):249-315.
[2] Hirota R.Exact solution of the Korteweg-de Vries equation for multiple collisions of solitons[J].Physical Review Letters,1971,27(18):1192-1194.
[3] Wahlquist H D, Estabrook F B. Bäcklund transformation for solutions of the Korteweg-de Vries equation[J].Physical Review Letters,1973,31(23):1386.
[4] Matveev V B,Salle M A.Darboux transformation and solitons[J].Journal of Neurochemistry,1991,42(6):1667-1676.
[5] Olver P J.Applications of lie groups to differential equations[M].[s.l.]:Springer Science & Business Media,2000.
[6] Hereman W,Takaoka M.Solitary wave solutions of nonlinear evolution and wave equations using a direct method and MACSYMA[J].Journal of Physics A Mathematical & General,1990,23(21):4805-4822.
[7] Wang M,Zhou Y,Li Z.Application of a homogeneous balance method to exact solutions of nonlinear equations in mathematical physics[J].Physics Letters A,1996,216(1):67-75.
[8] Fan E.Extended tanh-function method and its applications to nonlinear equations[J].Physics Letters A,2000,277(4):212-218.
[9] He J H,Wu X H.Exp-function method for nonlinear wave equations[J].Chaos Solitons & Fractals,2006,30(3):700-708.
[10] Naher H,Abdullah F A,Akbar M A.New traveling wave solutions of the higher dimensional nonlinear partial differential equation by the exp-function method[J].Journal of Applied Mathematics,2012(2):1-7.
[11] Liu S,Fu Z,Liu S,et al.Jacobi elliptic function expansion method and periodic wave solutions of nonlinear wave equations[J].Physics Letters A,2001,289(1):69-74.
[12] Jiong S.Auxiliary equation method for solving nonlinear partial differential equations[J].Physics Letters A,2003,309(5):387-396.
[13] 叶彩儿,张卫国.求BBM方程精确行波解的新方法[J].上海理工大学学报,2010,32(4):307-310.
[14] Singh K,Gupta R K,Kumar S.Benjamin-Bona-Mahony (BBM) equation with variable coefficients:similarity reductions and Painlevé analysis[J].Applied Mathematics & Computation,2011,217(16):7021-7027.
[15] 田 强,赵国忠.Burgers方程的指数型差分格式[J].内蒙古大学学报:自然科学版,2009,40(1):37-41.
[16] 孔翠翠,孔姗姗.精确求解Burgers方程[J].南阳师范学院学报,2010,9(9):4-11.
[17] 陈 宁,顾海明.Burgers方程的交替分组迭代法[J].理论数学,2014,4(4):122-129.
AuxiliaryFunctionMethodforExactSolutionofNonlinearPartialDifferentialEquation
YANG Jian,LAI Xiao-xia
(School of Computer Science,Shaanxi Normal University,Xi’an 710119,China)
In mathematics and physics,a nonlinear partial differential equation is a partial differential equation with nonlinear terms,which can describe many different physical models ranging from gravitation to fluid dynamics,and have been adopted in mathematics to solve problems such as the Poincaré conjecture and the Calabi conjecture.There are almost no general solutions that can be applied for all equations.Nonlinear partial differential equation usually originates from mathematical and physical fields,such that the ansatz of the solutions has been given and an auxiliary function has been provided according to its mathematical and physical features.They can be transmitted to an ordinary differential equations via a traveling wave transformation.Through introduction of the auxiliary function into the ordinary differential equation a set of nonlinear algebra equations is acquired,which can supply solutions original partial differential equation in solving process.Therefore,BBM equation and Burgers equation can be solved with the auxiliary function.The exact solutions include tangent function and trigonometric functions.The research shows that the proposed auxiliary function method can be applied to solve some other nonlinear partial differential equations with mathematical and physical background.
nonlinear partial differential equation;auxiliary function method;BBM equation;Burgers equation;exact solution
2016-10-18
2017-02-13 < class="emphasis_bold">网络出版时间
时间:2017-07-19
国家自然科学基金资助项目(11471004)
杨 健(1991-),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为非线性计算和符号推导。
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1450.TP.20170719.1108.022.html
TP39
A
1673-629X(2017)11-0196-05
10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2017.11.042
