偏头痛风火候患者静息状态下脑功能连接的初步探讨
2017-10-10吴宏赟梁延琛侯金萍李春林
吴宏赟,梁延琛,侯金萍,李春林
(1.山东中医药大学附属医院脑病科,小儿骨科,山东 济南 250014;2.山东省莱芜市中医医院脑病科,山东 莱芜 271199)
论 著
偏头痛风火候患者静息状态下脑功能连接的初步探讨
吴宏赟1a,梁延琛1b,侯金萍2,李春林1a
目的:采用静息态fMRI探讨偏头痛风火候患者的自发神经元活动特征。方法:纳入符合标准的30例偏头痛风火候患者和30例健康对照者,对其行静息态fMRI扫描。数据处理方法:①局部一致性(ReHo)分析寻找差异脑区;②功能连接分析,选择ReHo分析所得的差异脑区为种子点,进行种子点与全脑的功能连接分析。结果:①偏头痛组和对照组ReHo值差异脑区为左侧小脑、左侧额叶直回、右侧上外额叶、右侧背外侧额上回、左侧边缘叶。②与对照组相比,各ROI与全脑功能连接情况为偏头痛风火候患者左侧小脑与左侧颞上回、左侧顶下小叶、右侧岛叶功能连接减弱(均P<0.05);左侧眶叶直回与右侧梭状回功能连接减弱(均P<0.05);右侧上外额叶与右侧小脑山坡、左侧额上回功能连接减弱,与左侧额眶皮质、右侧运动前区功能连接增强(均P<0.05);右侧背外侧额上回与左侧中央前回功能连接减弱,与右侧颞下回、右侧下脚后区功能连接增强(均P<0.05)。左侧边缘叶与全脑功能连接无差异。结论:偏头痛风火候患者头痛发作间期脑功能异常有助于理解风火候偏头痛的发病机制。
偏头痛;风火候;静息态功能磁共振;功能连接
偏头痛作为一种慢性神经系统疾病,严重影响患者的工作和生活,但目前其病理生理机制尚不明确[1],且缺乏能诊断的特异影像学指标。偏头痛属“头风”、“头痛”范畴,中医认为风、火是偏头痛的主要病机。头痛分为风痰候、风瘀候、风火候等5个类型,而风火候是其中最常见的证型[2-3]。目前,fMRI是研究脑功能成像的首选方法,研究内容主要集中于神经、精神疾病等方面,对偏头痛的研究很少[4-7]。本研究以功能连接为切入点研究静息状态下偏头痛风火候患者的脑功能异常情况,旨在为偏头痛风火候的发病机制提供新依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
1.1.1 受试者来源 受试者均为山东中医药大学在校硕士研究生,且均为右利手。其中偏头痛风火候患者 30 例,男 11 例,女 19 例,年龄(25.100±0.995)岁;健康对照组30例,男11例,女19例,年龄(25.700±1.725)岁。2组性别、利手和学历分布具有可比性(均P>0.05)。
1.1.2 诊断标准 偏头痛风火候患者需同时满足以下标准:西医诊断符合《国际头痛疾病分类(第2版)》(ICHD-Ⅱ)中无先兆偏头痛的诊断标准[8]。 中医诊断符合《头风诊断与疗效评定标准》中头风病诊断标准[9]。中医证候诊断符合《头风诊断与疗效评定标准》中风火候诊断标准[9]。
1.1.3 纳入标准 ①符合诊断标准;②18岁≤年龄≤30岁;③病程在半年以上且最近1个月有偏头痛发作;④焦虑自评量表(self-rating anxiety scale,SAS)评分≤59分且抑郁自评量表(self-rating depression scale,SDS)评分≤62分;⑤右利手;⑥无 fMRI检查禁忌证;⑦知情同意者。
1.1.4 排除标准 ①年龄不符合纳入标准;②女性处于月经期、妊娠期或哺乳期;③正在使用阿片类、抗精神病药物等;④有严重原发病、精神病患者;⑤有MRI检查禁忌者;⑥SAS评分≥60分或SDS评分≥63分;⑦左利手。
1.1.5 剔除标准 ①发现颅脑结构异常或有器质性疾病者;②未完成扫描者;③错误纳入者。
1.2 仪器与方法
1.2.1 fMRI扫描方法 采用Philips Achieva 3.0 T MRI扫描仪。受试者取仰卧位,保持静息状态[10]。依次扫描定位像、BOLD像、结构像(3D T1WI)。扫描范围自颅顶到颅底。BOLD扫描参数:TR 3 000 ms,TE 35 ms,矩阵 128×128,FOV 230 mm×230 mm,翻转角 90°,层厚 5 mm。 3D T1WI扫描参数:TR 8.0 ms,TE 3.8 ms,矩阵 512×512,FOV 250 mm×250 mm,翻转角12°,层厚1 mm。
1.2.2 静息态fMRI数据处理流程 采用MRIconvert软件将DICOM格式转换NIfTI格式。数据预处理包括:①去除前10个时间点数据;②时间层校正;③头动校正;④空间标准化;⑤空间平滑;⑥去线性漂移;⑦滤波。用ReHo分析寻找差异脑区。功能连接(functional connectivity,FC)具体方法:①选取 ReHo分析获得的差异脑区为种子点;②制作种子点mask:运行Rest1.8中viewer,导入差异脑区T图,进行alphasim校正,设定P<0.001,输入差异脑区峰值点坐标,得到种子点mask作为ROI;③运行Rest1.8中Fun.Connectivity的Voxel wise计算ROI与全脑FC。
2 结果
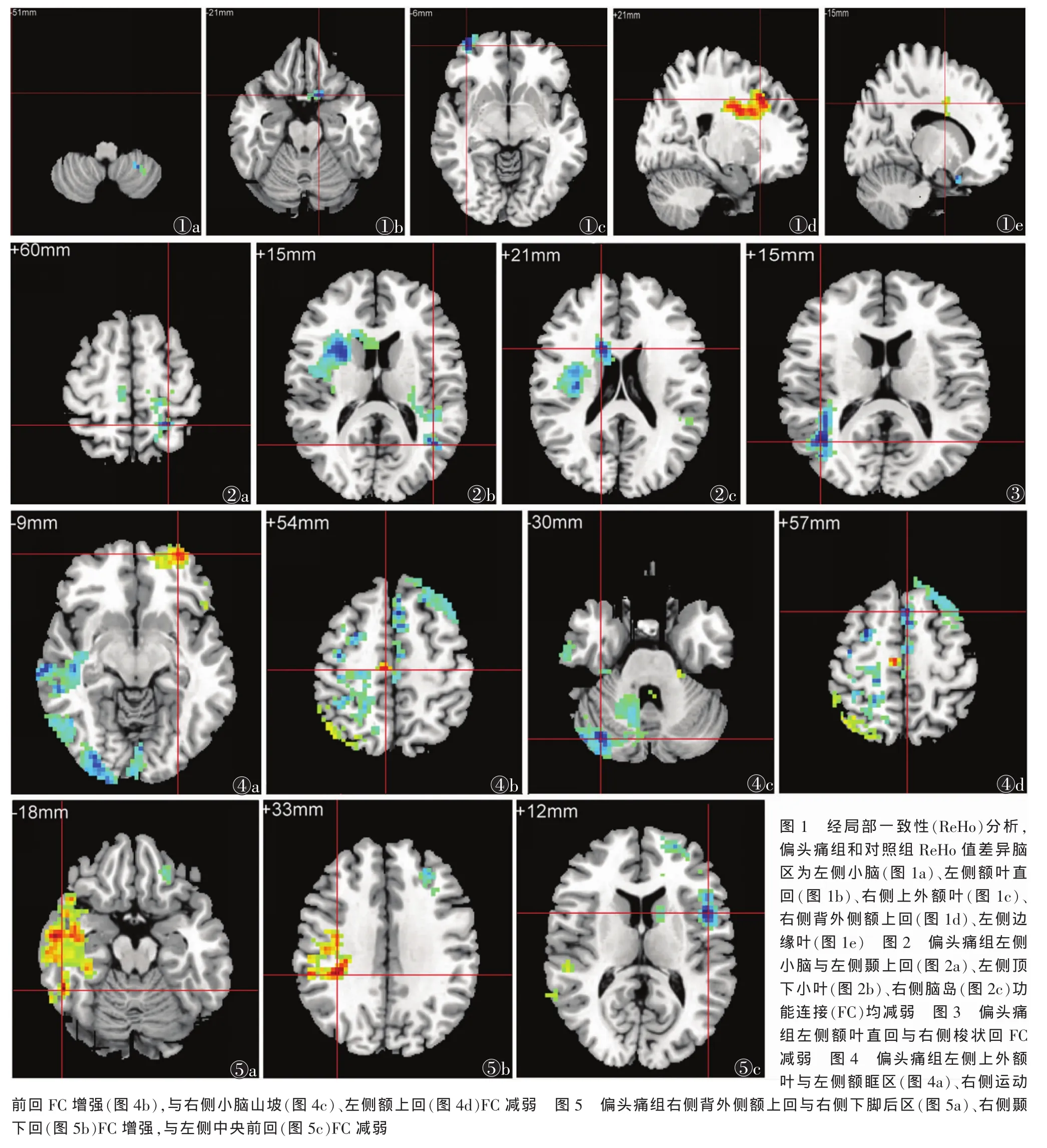
2.1 ReHo分析结果 偏头痛组和对照组ReHo值差异脑区为左侧小脑、左侧额叶直回、右侧上外额叶、右侧背外侧额上回、左侧边缘叶(表1,图1)。
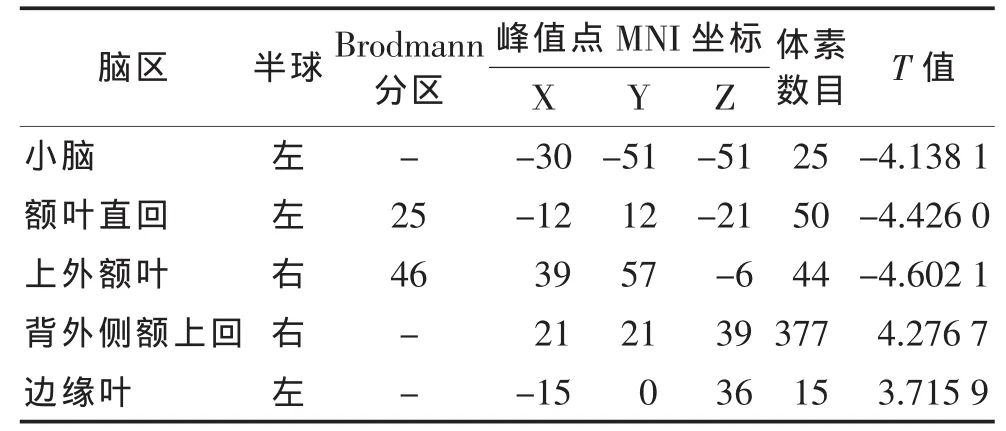
表1 偏头痛组和对照组ReHo值差异脑区
2.2 种子点与全脑FC比较 以左侧小脑、左侧额叶直回、右侧上外额叶、右侧背外侧额上回、左侧边缘叶作为种子点,比较各种子点与全脑区间FC的变化。
2.2.1 左侧小脑与全脑FC情况(表2,图2) 与对照组相比,偏头痛组左侧小脑与左侧颞上回、左侧顶下小叶、右侧岛叶FC均减弱(均P<0.05)。
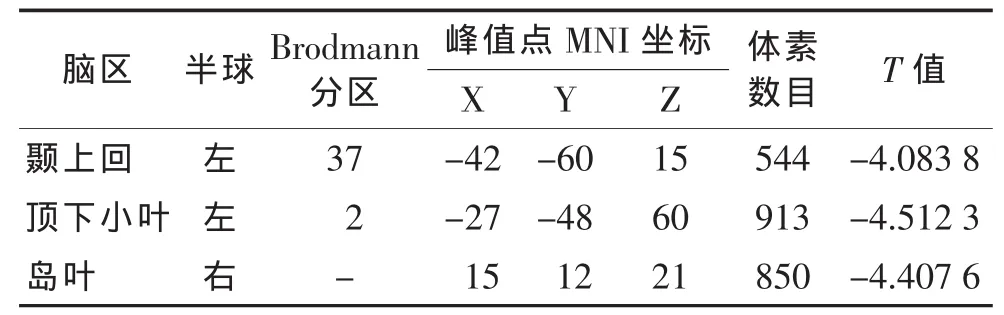
表2 偏头痛组和对照组左侧小脑与全脑FC差异
2.2.2 左侧额叶直回与全脑FC情况(表3,图3) 与对照组相比,偏头痛组左侧额叶直回与右侧梭状回FC 减弱(P<0.05)。
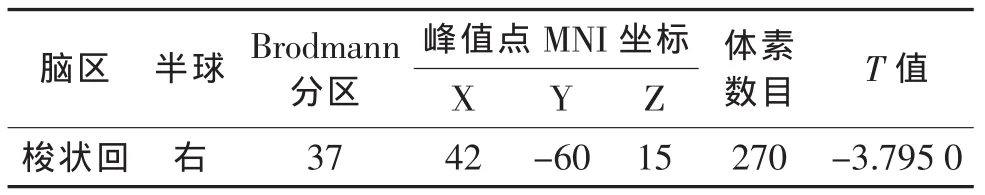
表3 偏头痛组和对照组左侧额叶直回与全脑FC差异
2.2.3 左侧上外额叶与全脑FC情况(表4,图4) 与对照组相比,偏头痛组左侧上外额叶与左侧额眶皮质、右侧运动前回FC增强,与右侧小脑山坡、左侧额上回 FC 减弱(均 P<0.05)。
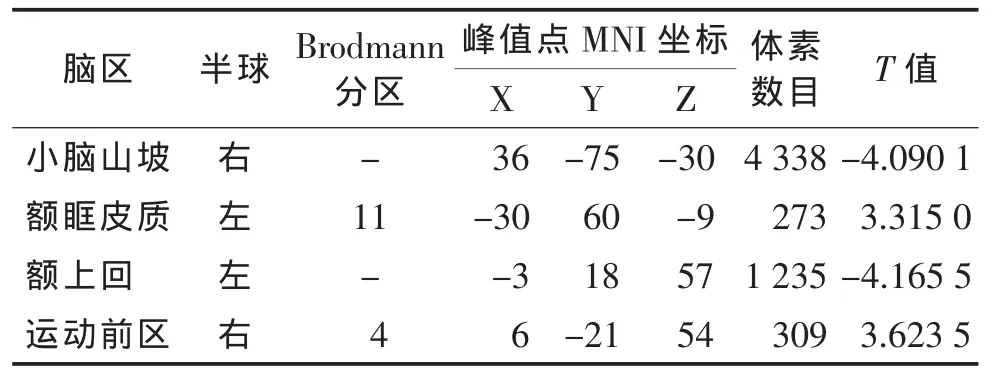
表4 偏头痛组和对照组左侧上外额叶与全脑FC差异
2.2.4 右侧背外侧额上回与全脑FC情况(表5,图5) 与对照组相比,偏头痛组右侧背外侧额上回与右侧下脚后区、右侧颞下回FC增强,与左侧中央前回 FC 减弱(均 P<0.05)。
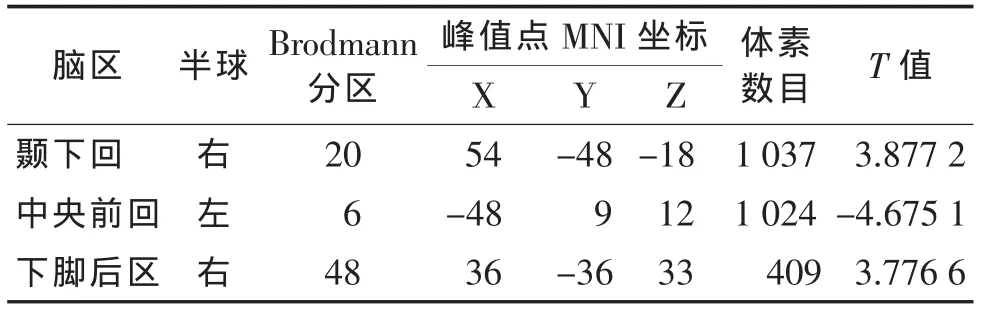
表5 偏头痛组和对照组右侧背外侧额上回与全脑FC差异
2.2.5 左侧边缘叶与全脑FC情况 左侧边缘叶与全脑未发现差异脑区。
3 讨论
运用FC方法可评价远隔脑区之间功能活动方面的同步性。若不同脑区之间BOLD信号的波动在时间上具有高度同步性,则可推测这些脑区形成了一个关系密切的神经网络。疾病可影响脑功能,导致FC发生改变,而临床表现可能与FC改变有关。本研究结果显示,偏头痛风火候共5个ReHo值异常脑区,其中4个与全脑FC发生改变。这些改变与偏头痛风火候临床症状有关联。
3.1 左侧小脑的FC情况 偏头痛风火候发病与肝经密切相关,肝主情志,肝疏泄不及导致肝气郁结,临床可表现为抑郁情绪。抑郁青少年颞上回存在结构改变,体积明显缩小[11]。偏头痛风火候患者左侧颞上回FC减弱,可能与其易出现抑郁情绪有关,持续时间较长者可能出现颞上回体积缩小等结构改变。
顶下小叶受损可导致注意力和应对突发事件能力的下降[12],偏头痛风火候患者出现注意力不集中,可能与顶下小叶FC下降有关。
岛叶是内侧痛觉系统的重要组成部分,在疼痛的感知、认知和痛觉情绪的产生中有重要作用[13-14]。偏头痛风火候头痛的产生机制可能与岛叶的FC下降有关。
本研究中,偏头痛组左侧小脑与左侧颞上回、左侧顶下小叶、右侧岛叶FC均减弱。
3.2 左侧额叶直回的FC情况 梭状回在社会认知及情绪表达中起重要作用。抑郁认知易感者常存在右侧梭状回功能损伤,且右侧梭状回灰质密度的减少与注意偏向负性刺激密切相关[15]。急躁易怒等情绪在偏头痛风火候患者中较其他证候患者常见,可能与右侧梭状回FC减弱有关。本研究中,偏头痛组左侧额叶直回与右侧梭状回FC减弱。
3.3 右侧上外额叶的FC情况 一般认为,小脑的主要功能是协调随意运动和负责平衡。近期研究[16-17]显示,小脑是痛觉形成过程中重要一环,偏头痛患者存在小脑功能和结构改变。且恶心症状的发生与小脑山坡、小脑扁桃体等部位的激活呈负相关[18]。
本研究中,偏头痛组右侧上外额叶与左侧额眶区、右侧运动前回FC增强,与右侧小脑山坡、左侧额上回FC减弱。额叶是大脑发育中最高级的部分,其功能复杂,右侧上外额叶与左侧额眶区、右侧运动前回、左侧额上回之间FC异常,说明额叶内部不同结构间功能联系发生改变。眶额皮质是控制复杂行为和自动情绪反应的主要部位。本研究中偏头痛风火候患者组的左侧眶额皮质FC增强,可能是由于慢性疼痛患者产生负性情绪,导致眶额皮质在结构和功能上出现异常。前额皮质也通过脑干间接参与疼痛的调节,该部位异常可导致疼痛在下行传导时发生改变[19],偏头痛风火候患者左侧额上回出现FC下降,这可能与其调节疼痛的功能异常有关。额叶运动前区是自主神经皮质中枢的一部分,偏头痛平衡功能的失常(如眩晕)及偏头痛发作时出现的心悸、多汗等自主神经症状,可能与此区功能的损伤有关。
3.4 右侧背外侧额上回的FC情况 颞下回是促进认知处理和情绪调节的主要联合区,它与杏仁核联系密切,而杏仁核参与疼痛感知和情绪反应,可推测颞下回也与疼痛、情绪有关[20]。下脚后区位于颞叶内侧,是边缘系统的一部分,与人类的学习、记忆、精神、行为等功能有关。本研究中偏头痛患者组右侧下脚后区、右侧颞下回FC增强,可能与偏头痛患者伴抑郁焦虑情绪有关。
中央前回是管理对侧半身随意运动的中枢,但研究[21]显示抑郁认知易感者左侧中央前回灰质体积减少。本研究也发现,偏头痛风火候患者中央前回功能异常,风火候患者常头痛程度较重,易导致抑郁情绪,推测中央前回可能参与了偏头痛情绪功能异常的发生。
综上所述,静息态fMRI可出现偏头痛风火候患者的脑区功能异常,有助于发现其发病机制。本研究不足之处:①所选患者均为在校学生,范围局限,样本量小,患者病程较短,病情较轻,未根据病情轻重、病程进行分层研究。②局限于无先兆的偏头痛风火候患者,未涉及偏头痛的其他证型及有先兆的偏头痛患者。今后应扩大样本量及偏头痛类型,深入探讨偏头痛患者脑功能随病情进展的变化。
[1]贾建平,霍丽英,王伟.神经病学[M].6版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2008:166.
[2]黄益兴,任占利,王顺道,等.头风病证候诊断标准的研究[J].脑与神经疾病杂志,1997,5(3):144-147.
[3]马壮壮,梁茂新.偏头痛中医辨证存在问题与对策[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(2):412-414.
[4] Gusnard DA,Raichle ME.Searching for a baseline:functional imaging and the resting human brain[J].Nat Rev Neurosci,2001,2:685-694.
[5] Placido B,Rosario G,Antongiulio V,et al.Migraine with and without aura:electrophysiological and functional imaging evidence[J].Funct Neurol,2005,20:29-32.
[6] Stankewitz A,Aderjan D,Eippert F,et al.Trigeminal nociceptive transmission in migraine predicts migraine attacks[J].J Neurosci,2011,31:1937-1943.
[7] Mainero C,Boshyan J,Hadjikhani N.Altered functional magnetic resonanceimagingresting-state connectivityin periaqueductal gray networks in migraine[J].Ann Neurol,2011,70:838-845.
[8] Olesen J,Busser MG,Diener HD,et al.Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society.Classification and diagnostic criteria for headache disorders:2nd edition[J].Cephalalnia,2004,24:S9-S160.
[9]国家中医药管理局全国脑病急症协作组.头风诊断与疗效评定标准[J]. 北京中医学院学报,1993,16(3):69.
[10] Biswal B,Yetkin FZ,Haughton VM,et al.Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI[J].Magn Reson Med,1995,34:537-541.
[11] Pan LA,Ramos L,Segreti A,et al.Right superior temporal gyrus volume in adolescents with a history of suicide attempt[J].Br J Psychiatry,2015,206:339-340.
[12] Singh-Curry V,Husain M.The functional role of the inferior parietal lobe in the dorsal and ventral stream dichotomy[J].Neuropsychologia,2009,47:1434-1448.
[13] Apkarian AV,Bushnell MC,Treede RD,et al.Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease[J].Eur J Pain,2005,9:463-484.
[14] Treede RD,Kenshalo DR,Gracely RH,et al.The cortical representation of pain[J].Pain,1999,79:105-111.
[15] van Reekum CM,Urry HL,Johnstone T,et al.Individual differences in amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex activity are associated with evaluation speed and psychological wellbeing[J].J Cogn Neurosci,2007,19:237-248.
[16] Ostrowsky K,Isnard J,Ryvlin P,et al.Functional mapping of the insularcortex:clinical implication in temporal lobe epilepsy[J].Epilepsia,2000,41:681-686.
[17] Sándor PS,Mascia A,Seidel L,et al.Subclinical cerebellar impairment in the common types of migraine:a three dimensional analysis of reaching movements[J].Ann Neurol,2001,49:668-672.
[18] Farmer AD,Ban VF,Coen SJ,et al.Visually induced nausea causes characteristic changes in cerebral,autonomic and endocrine function in humans[J].J Physiol,2015,593:1183-1196.
[19] Gardner K,Barmada MM,Ptacek LJ,et al.A new locus for hemiplegic migraine maps to chromosome 1q31[J].Neurology,1997,49:1231.
[20] Cheng K,Saleem KS,Tanaka K.Organization of corticostriatal and corticoamygdalar projections arising from the anterior inferotemporal area TE of the macaque monkey:a phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin study[J].J Neurosci,1997,17:7902-7925.
[21]张小崔.抑郁认知易感者脑结构及静息态脑功能磁共振成像研究[D]. 长沙:中南大学,2014.
Rudimen analysis of connectivity changes in migraine’s disease with feng-huo type in resting state
WU Hongyun,LIANG Yanchen,HOU Jinping,LI Chunlin.Department of Encephalopathy,Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jinan,250014,China.
Object:Imageology study has shown that the brain structure and function in patients with migraine of feng-huo type have changed.This study used the characteristic of spontaneous neuronal activity in patients with migraine of feng-huo type to discuss resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging technology.The research also analyzed the change of migraine resting state brain functional connectivity.It can give us a better understanding of the pathogenesis of migraine of feng-huo type.Methods:Incorparate 30 patients with migraine of feng-huo type,and also choose 30 healthy persons.They had the same age,gender,and education level.Compare the differences among them.Let them make resting state fMRI scan.Then use ReHo analysis and functional connectivity analysis to analyze the two kinds of methods of data processing:①ReHo analysis:through analyzing the differences of the two tested groups of ReHo in different brain regions to find out the different brain regions.Then use REST 1.8 single sample and two sample T test to find differences in brain areas. ②FC analysis:select differences in brain regions of local consistency analysis as the seed point,analyze the seed point and the whole brain function connectivity.Results:①The differences between migraine were in brain regions of ReHo for left cerebellum,left frontal straight back,right frontal lobe,right outside the dorsolateral frontal gyrus,the left edge of the leaf. ②Compared with healthy controls,the region of interest and whole brain functional connectivity showed that the functional connectivity of migraine patients with gout condition of heat left cerebellum and left superior temporal gyrus,left inferior parietal lobule,right insula decreased functional connectivity(P<0.05);the functional connectivity of the left orbital lobes straight back and right fusiform gyrus had decreased (P<0.05);the function of the right frontal lobe;outer connected with the right cerebellum,left superior frontal gyrus weaken.The functional connectivity of the frontal orbital region,right premotor area had increased (P<0.05).The functional connectivity of the right dorsolateral frontal gyrus and left precentral gyrus had decreased,connected with the foot back function enhancement of the right inferior temporal gyrus,the lower (P<0.05).The left edge of the leaf and whole brain functional connectivity were without difference.Conclusion:The patients with migraine of feng-huo type headache interval function appear abnormal brain regions.The pathogenesis of these findings contribute to the understanding of migraine of feng-huo type.
migraine;feng-huo type;resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging;functional connectivity
2017-03-04)
10.3969/j.issn.1672-0512.2017.05.002
山东省自然基金项目(ZR2014CL013,ZR2015HL106)。
李春林,E-mail:37673261@qq.com。
