肾癌术后患者5-氟尿嘧啶血药浓度与肾功能及毒副作用的相关性研究
2017-08-07蔡维敏陈婷婷符克英
蔡维敏,陈婷婷,魏 英,符克英
·论著·
肾癌术后患者5-氟尿嘧啶血药浓度与肾功能及毒副作用的相关性研究
蔡维敏1*,陈婷婷1,魏 英1,符克英2
目的 探讨肾癌术后患者5-氟尿嘧啶(5-FU)血药浓度与肾功能、毒副作用的关系,为实施个体化治疗提供依据。方法 选取2013年8月—2016年2月在海南省人民医院泌尿外科行肾癌根治性切除术患者92例为研究对象,均给予基于5-FU的综合化疗,共4个疗程。检测化疗后5-FU血药浓度与肾功能指标尿素氮(BUN)、肌酐(Cr)水平,采用WHO毒性分级标准评价骨髓抑制、胃肠道反应、手足综合征、口腔黏膜炎等毒副作用的严重程度。根据5-FU血药浓度,将患者分为<300.0 μg/L组(42例)和≥300.0 μg/L组(50例)。结果 92例患者5-FU血药浓度为179.2~1 589.6 μg/L,平均(569.5±29.5)μg/L。≥300.0 μg/L组血清BUN、Cr水平均高于<300.0 μg/L组,骨髓抑制、胃肠道反应、手足综合征、口腔黏膜炎等毒副作用严重程度均高于<300.0 μg/L组(P<0.05)。5-FU血药浓度与BUN、Cr水平呈正相关(r=0.413,P=0.008;r=0.398,P=0.010)。结论 肾癌术后患者5-FU血药浓度变异性较大,5-FU血药浓度过高可导致肾功能异常,加重毒副作用,临床可通过监测5-FU血药浓度为实施个体化治疗提供依据。
肾肿瘤;氟尿嘧啶;血药浓度;肾功能;药物毒性
蔡维敏,陈婷婷,魏英,等.肾癌术后患者5-氟尿嘧啶血药浓度与肾功能及毒副作用的相关性研究[J].中国全科医学,2017,20(23):2858-2861.[www.chinagp.net]
CAI W M,CHEN T T,WEI Y,et al.Correlation of plasma concentration of 5-fluorouracil with renal function and adverse effects of 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in patients with radical surgery for renal cell carcinoma[J].Chinese General Practice,2017,20(23):2858-2861.
肾癌是泌尿系统常见的恶性肿瘤之一,约占成年人恶性肿瘤的3.0%。手术结合术后化疗为肾癌的主要治疗方法,但由于肾癌的恶性程度较高,部分患者对化疗不太敏感[1-2]。5-氟尿嘧啶(5-fluorouracil,5-FU)持续静脉滴注是肾癌的常用化疗方法,进入人体内的5-FU主要由肝脏代谢,其中80%~85%由肝脏二氢嘧啶脱氢酶(DPD)将5-FU降解为二氢氟尿嘧啶[3-4]。DPD是5-FU代谢的关键性限速酶,与5-FU化疗时的毒副作用有密切关系,对预后与肾功能也有明显影响[5-6]。相关研究表明,5-FU的治疗窗窄,血药浓度偏高易引起各种毒副作用,血药浓度偏低则不会产生相应的化疗效果[7-8]。并且,由于存在个体差异,同样的剂量可能产生不同的治疗效果和毒副作用[9]。本研究通过对5-FU血药浓度的检测,结合肾功能、化疗疗效及毒副作用的分析,探讨肾癌术后患者化疗血药浓度与肾功能的相关性,为临床合理用药提供依据。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象 选取2013年8月—2016年2月在海南省人民医院泌尿外科行肾癌根治性切除术患者92例为研究对象,其中男52例,女40例;年龄21~78岁,平均年龄(65.2±3.2)岁;体质指数(22.1±2.2)kg/m2;肿瘤直径(3.4±0.4)cm;肿瘤类型为透明细胞癌62例,颗粒细胞癌17例,混合细胞癌13例;临床分期为Ⅰ期40例,Ⅱ期30例,Ⅲ期22例。纳入标准:经组织病理学或细胞学检查确诊为肾癌;化疗前血常规无异常;年龄18~80岁;预计生存期≥3个月;既往4周内未接受化疗、放疗或其他手术;无其他不能耐受本研究的躯体或心理疾病;CT扫描无脑转移;对本研究知情同意。本研究得到海南省人民医院医学伦理委员会批准。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 化疗 患者均给予基于5-FU的综合化疗,紫杉醇(江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司)75 mg/m2静脉滴注3 h;亚叶酸(江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司)200 mg/m2静脉滴注2 h;5-FU(上海旭东海普药业有限公司)375 mg/m2静脉注射;5-FU 2.5 g/m2静脉滴注46 h。每2周重复1次,2次/疗程,治疗观察4个疗程。
1.2.2 实验室测定 在治疗后当日进行5-FU血药浓度的测定,抽取患者空腹静脉血,4 ℃条件下以3 000 r/min离心10 min,分离取上层血浆放置于-80 ℃冰箱待测。在色谱分析中,流动相用0.01 mol/L缓冲液KH2PO2H3PO(pH为3.0),流速1 ml/min,温度37 ℃,对照物为标准5-FU,采用Agilent色谱仪(美国ABBOTT公司),在波长为270 nm处测定5-FU浓度[4]。采用AU2700型全自动生化分析仪(日本奥林巴斯公司)检测尿素氮(BUN)、肌酐(Cr)水平。
1.2.3 毒副作用评价 化疗结束后,采用WHO毒性分级标准评价毒副作用,主要包括骨髓抑制、胃肠道反应、手足综合征、口腔黏膜炎等,根据严重程度分为Ⅰ~Ⅳ级[6]。
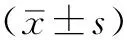
2 结果
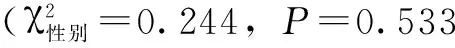
2.2 肾功能指标比较 ≥300.0 μg/L组血清BUN、Cr水平均高于<300.0 μg/L组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表1)。
2.3 毒副作用 ≥300.0 μg/L组骨髓抑制、胃肠道反应、手足综合征、口腔黏膜炎等毒副作用严重程度均高于<300.0 μg/L组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表2)。
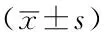
Table 1 Comparison of levels of renal function markers between the two groups
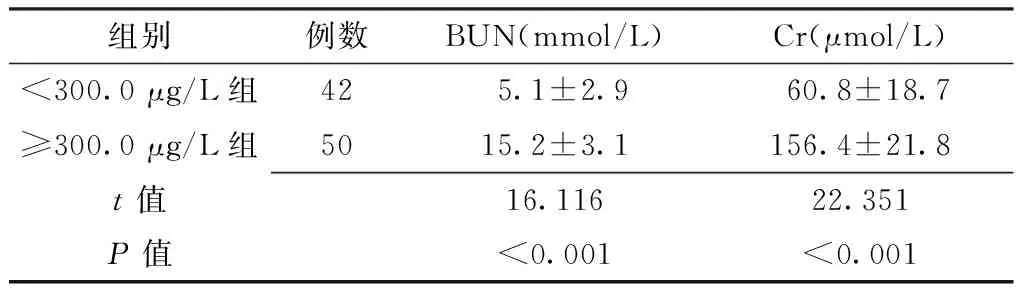
组别例数BUN(mmol/L)Cr(μmol/L)<300.0μg/L组42 5.1±2.9 60.8±18.7 ≥300.0μg/L组5015.2±3.1156.4±21.8t值16.11622.351P值<0.001<0.001
注:BUN=尿素氮,Cr=肌酐
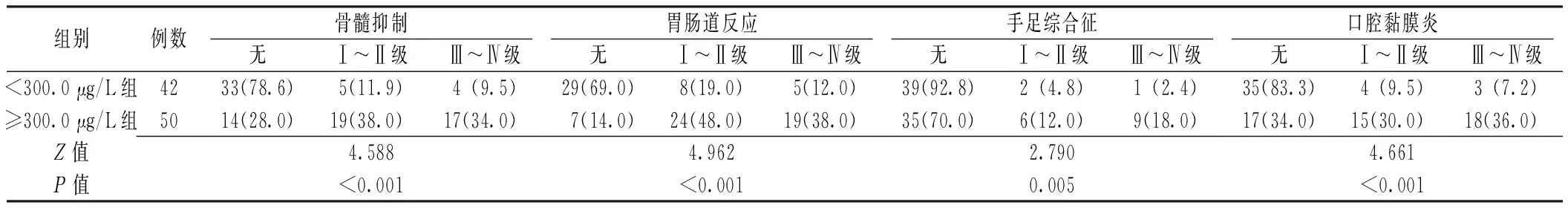
表2 两组毒副作用严重程度比较〔n(%)〕
2.4 相关性分析 Pearson相关分析显示,5-FU血药浓度与BUN、Cr水平呈正相关(r=0.413,P=0.008;r=0.398,P=0.010)。
3 讨论
肾癌是泌尿系统常见的恶性肿瘤之一,全世界每年死于肾癌近10万例,而我国肾癌发病率仅次于膀胱癌,居泌尿系肿瘤第二位[10]。手术为肾癌的主要治疗方法,但需要在术后配合合理的化疗。5-FU是肾癌化疗的常用药,化疗后的毒副作用和疗效个体差异较大,有时会出现致命的毒性,为此需进行化疗药物血药分析,寻找到最佳剂量以达到最好的效果[11]。
5-FU在体内的代谢过程受多种因素影响,其中最重要的影响因素为DPD,DPD可将80%的5-FU转化为二氢氟尿嘧啶排出体外,减少5-FU在体内的蓄积,而5-FU的转化与患者性别、年龄、肿瘤分期、病理类型、肿瘤部位有一定的相关性,具有生理节律性[12-13]。本研究显示,92例肾癌患者5-FU血药浓度变异较大(179.2~1 589.6 μg/L),平均(569.5±29.5)μg/L。根据患者5-FU血药浓度变化规律可及时调整5-FU的用药剂量及给药间隔,对减轻5-FU的毒副作用,提高患者的生存质量有重要意义。
肾癌的发病机制涉及神经内分泌的激活、氧化应激、炎性因子异常表达、血流动力学异常等,最终可导致肾功能不全,影响肾功能[14]。并且,肾癌也可致肾组织结构损坏,肾单位减少,导致肾功能下降[15]。而5-FU静脉给药后其血浆清除t1/2为6~20 min,5-FU持续静脉滴注可使药物更长时间地作用于S期细胞,也能增加药物的剂量强度[16-17]。本研究显示,5-FU血药浓度≥300.0 μg/L组血清BUN、Cr水平均高于<300.0 μg/L组;Pearson相关分析显示,5-FU血药浓度与BUN、Cr水平呈正相关。表明5-FU血药浓度过高可导致有效肾单位的减少及肾功能的减退,应根据患者肾功能指标的变化及时调整5-FU剂量。
5-FU是当前常用的化疗药物之一,其用法有多种,毒副作用也各不相同[18]。相关研究表明,肾癌患者对以5-FU持续静脉滴注的化疗方案毒副作用有明显的个体差异;即使是同一患者在不同疗程毒副作用的严重程度也不尽相同[19]。目前临床多是通过检测5-FU血药浓度来控制毒副作用的发生[20-21]。本研究显示,5-FU血药浓度≥300.0 μg/L组骨髓抑制、胃肠道反应、手足综合征、口腔黏膜炎等毒副作用严重程度均高于<300.0 μg/L组。表明肾癌患者可通过检测5-FU血药浓度,使5-FU稳态血药浓度维持在一定的水平以预防毒副作用。
综上所述,肾癌术后患者5-FU血药浓度变异性较大,5-FU血药浓度过高可导致肾功能异常,加重毒副作用,临床可通过监测5-FU血药浓度为实施个体化治疗提供依据。本研究尚存在一定的局限性,如样本量相对较小,未动态监测5-FU血药浓度,未来需更加完善相关数据收集过程,进一步分析5-FU血药浓度与肾癌术后患者肾功能及毒副作用的关系。
作者贡献:蔡维敏进行文章的构思与设计、研究的实施与可行性分析、统计学处理、结果的分析与解释、撰写论文,对文章整体负责,并监督管理;陈婷婷、魏英进行数据收集、整理;符克英进行论文的修订,负责文章的质量控制及审校。
本文无利益冲突。
[1]FUKUDO M,ITO T,MIZUNO T,et al.Exposure-toxicity relationship of sorafenib in Japanese patients with renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Clin Pharmacokinet,2014,53(2):185-196.DOI:10.1007/s40262-013-0108-z.
[2]黄焱,穆中一,林洪丽,等.肾癌患者术后化疗联合DC-CIK免疫治疗临床疗效研究[J].临床军医杂志,2016,44(1):7-10.DOI:10.16680/j.1671-3826.2016.01.03. HUANG Y,MU Z Y,LIN H L,et al.The clinical effects of chemotherapy combined with DC-CIK cells treatment after curative resection for renal cell carcinoma[J].Clinical Journal of Medical Officer,2016,44(1):7-10.DOI:10.16680/j.1671-3826.2016.01.03.
[3]解吉来.白细胞介素-11及其受体在泌尿生殖系肿瘤的研究进展[J].检验医学与临床,2016,13(4):554-556.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2016.04.052. XIE J L.Research progress of interleukin-11 and its receptor in genitourinary tumors[J].Laboratory Medicine and Clinic,2016,13(4):554-556.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2016.04.052.
[4]鞠颖慧,周琰,彭颖斐,等.液相色谱串联质谱检测血浆5-氟尿嘧啶方法的建立及其临床应用[J].中华医学杂志,2016,96(10):817-821.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.10.014. JU Y H,ZHOU Y,PENG Y F,et al.Establishment and clinical application of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method for simultaneous determination of plasma 5-fluorouracil[J].National Medical Journal of China,2016,96(10):817-821.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.10.014.
[5]THIERY-VUILLEMIN A,MOUILLET G,NGUYEN TAN HON T,et al.Impact of everolimus blood concentration on its anti-cancer activity in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma[J].Cancer Chemother Pharmacol,2014,73(5):999-1007.DOI:10.1007/s00280-014-2435-7.
[6]汪群锋.转移性肾癌的治疗新进展[J].国际泌尿系统杂志,2016,36(1):133-138.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4416.2016.01.040. WANG Q F.New progress in the treatment of metastatic renal[J].International Journal of Urology and Nephrology,2016,36(1):133-138.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4416.2016.01.040.
[7]王永强,张永富,高振利,等.肾脏伴其他脏器的多原发恶性肿瘤111例临床分析[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2015,21(10):736-741.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2015.10.004. WANG Y Q,ZHANG Y F,GAO Z L,et al.Clinical analysis and prognostic study of multiple primary malignancies associated with kidney malignant tumor:report of 111 cases[J].Chinese Journal of Urology,2015,21(10):736-741.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6702.2015.10.004.
[8]SUTTLE A B,BALL H A,MOLIMARD M,et al.Relationships between pazopanib exposure and clinical safety and efficacy in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma[J].Br J Cancer,2014,111(10):1909-1916.DOI:10.1038/bjc.2014.503.
[9]姜福全,杨建武,杨鹤鸣,等.微波消融联合5氟尿嘧啶瘤内注射治疗结肠癌荷瘤鼠的疗效评价[J].海南医学院学报,2015,21(10):1309-1312.DOI:10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20150626.016. JIANG F Q,YANG J W,YANG H M,et al.Curative effect evaluation of microwave ablation combined with 5-fluorouracil intratumoral injection in treating colon cancer tumor-bearing mice[J].Journal of Hainan Medical University,2015,21(10):1309-1312.DOI:10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20150626.016.
[10]MINGUET J,SMITH K H,BRAMLAGE C P,et al.Targeted therapies for treatment of renal cell carcinoma:recent advances and future perspectives[J].Cancer Chemother Pharmacol,2015,76(2):219-233.DOI:10.1007/s00280-015-2770-3.
[11]冯莉,韩晶,左静,等.结直肠癌胸苷酸合成酶表达与氟尿嘧啶敏感性和临床病理特征及预后的相关性研究[J].中国全科医学,2014,17(6):666-670.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2014.06.017. FENG L,HAN J,ZUO J,et al.Correlation between thymidylate synthase expression and fluorouracil sensitivity,clinicopathological features and prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer[J].Chinese General Practice,2014,17(6):666-670.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2014.06.017.
[12]AKITA H,ISHIBA R,TOGASHI R,et al.A neutral lipid envelope-type nanoparticle composed of a pH-activated and vitamin E-scaffold lipid-like material as a platform for a gene carrier targeting renal cell carcinoma[J].J Control Release,2015,200:97-105.DOI:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.12.029.
[13]KEIL C,GÖTZE L,OLBERT P,et al.Metastasized renal cell carcinoma.Measurement of plasma levels of the tyrosine kinase inhibitors sunitinib,sorafenib and pazopanib[J].Urologe A,2015,54(6):811-818.DOI:10.1007/s00120-014-3711-1.
[14]CHEN Y,RINI B I,BAIR A H,et al.Population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling of 24-h diastolic ambulatory blood pressure changes mediated by axitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma[J].Clin Pharmacokinet,2015,54(4):397-407.DOI:10.1007/s40262-014-0207-5.
[15]朱鸿飞,顾云斌,张栋.肾动脉化疗栓塞治疗老年患者肾癌的临床价值[J].中国血液流变学杂志,2015,14(1):112-114.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-881X.2015.01.038. ZHU H F,GU Y B,ZHANG D.Clinical value of transcatheter renal arterial chemoembolization for treating elderly patients with advanced renal cancer[J].Chinese Journal of Hemorheology,2015,14(1):112-114.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-881X.2015.01.038.
[16]RINI B I,MELICHAR B,FISHMAN M N,et al.Axitinib dose titration:analyses of exposure,blood pressure and clinical response from a randomized phaseⅡstudy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma[J].Ann Oncol,2015,26(7):1372-1377.DOI:10.1093/annonc/mdv103.
[17]李俊,樊娜,沈丽达.血清胱抑素C监测化疗致肾功能损伤的研究进展[J].中国医药,2016,11(3):453-456.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4777.2016.03.036. LI J,FAN N,SHEN L D.Progresses of cystatin C in monitoring chemotherapy-induced renal disfunction[J].China Medicine,2016,11(3):453-456.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4777.2016.03.036.
[18]SARDI I,FANTAPPIO,LA MARCA G,et al.Delivery of doxorubicin across the blood-brain barrier by ondansetron pretreatment:a study in vitro and in vivo[J].Cancer Lett,2014,353(2):242-247.DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.07.018.
[19]LU C,LI J,XU K,et al.Fabrication of mAb G250-SPIO molecular magnetic resonance imaging nanoprobe for the specific detection of renal cell carcinoma in vitro[J].PLoS One,2014,9(7):1898-1912.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0101898.
[20]马红莲,惠周光,赵路军,等.不可切除Ⅲ期NSCLC持续静脉泵注恩度联合同期放化疗前瞻性多中心Ⅱ期临床试验初步结果[J].中华放射肿瘤学杂志,2016,25(2):114-119.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4221.2016.02.006. MA H L,HUI Z G,ZHAO L J,et al.Continuous intravenous pumping (CIP) of recombinant human endostatin (Endostar) combined with concurrent radiochemotherapy in patients with unresectable stage Ⅲ non-small-cell lung cancer:preliminary data of a prospective multicenter phase Ⅱ clinica[J].Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology,2016,25(2):114-119.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4221.2016.02.006.
[21]MIZUNO T,FUKUDO M,FUKUDA T,et al.The effect of ABCG2 genotype on the population pharmacokinetics of sunitinib in patients with renal cell carcinoma[J].Ther Drug Monit,2014,36(3):310-316.DOI:10.1097/FTD.0000000000000025.
(本文编辑:吴立波)
Correlation of Plasma Concentration of 5-fluorouracil with Renal Function and Adverse Effects of 5-fluorouracil-based Chemotherapy in Patients with Radical Surgery for Renal Cell Carcinoma
CAIWei-min1*,CHENTing-ting1,WEIYing1,FUKe-ying2
1.UrologicSurgery,HainanGeneralHospital,Haikou570311,China2.CentralLaboratory,HainanGeneralHospital,Haikou570311,China
*Correspondingauthor:CAIWei-min,Nurse-in-charge;E-mail:caiweimin38@163.com
Objective To investigate the correlation of plasma concentration of 5-fluorouracil(5-FU) with renal function and adverse effects of 5-FU-based chemotherapy in patients with radical surgery for renal cell carcinoma,so as to provide a reference for developing individualized treatment for these patients.Methods We enrolled 92 consecutive cases of renal cell carcinoma who
radical surgery and four cycles of 5-FU-based comprehensive chemotherapy from August 2013 to February 2016.The measurement of plasma concentration of 5-FU and levels of renal function markers,such as BUN and Cr was performed after the chemotherapy.Patients who had plasma concentration of 5-FU <300.0 μg/L and ≥300.0 μg/L were assigned to <300.0 μg/L group(n=42) and ≥300.0 μg/L(n=50) group,respectively.The WHO Toxicity Grading Scale for Determining the Severity of Adverse Events was used to assess the severity of adverse effects of the chemotherapy,such as myelosuppression,gastrointestinal reactions,hand-foot syndrome,and oral mucositis.Results The plasma concentration of 5-FU in all the participants ranged from 179.2 μg/L to 1 589.6 μg/L,averaged (569.5±29.5)μg/L.Compared with those in the <300.0 μg/L group,patients in the ≥300.0 μg/L group had much higher levels of serum BUN and Cr,and they were more serious on myelosuppression,gastrointestinal reactions,hand-foot syndrome,and oral mucositis(P<0.05).Pearson correlation analysis showed that the BUN and Cr levels increased with the plasma concentration of 5-FU(r=0.413,P=0.008;r=0.398,P=0.010).Conclusion The plasma concentration of 5-FU varies greatly in patients with radical surgery for renal cell carcinoma receiving 5-FU-based chemotherapy.Excessive high plasma concentration of 5-FU can lead to abnormal renal function and aggravate the adverse effects of the chemotherapy.Therefore,the plasma concentration of 5-FU can be used as a reference for developing individualized treatment for such patients.
Kidney neoplasms;Fluorouracil;Plasma concentration;Kidney function;Drug toxicity
2012年度海南省卫生厅医学科研项目(琼卫2012PT-16)
R 737.11
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2017.23.011
2016-12-14;
2017-06-09)
1.570311海南省海口市,海南省人民医院泌尿外科 2.570311海南省海口市,海南省人民医院中心实验室
*通信作者:蔡维敏,主管护师;E-mail:caiweimin38@163.com
