网格圈负压式集聚纺集聚须条张力模型
2017-08-01陈南梁
傅 婷, 陈南梁
(东华大学 纺织学院,上海 201620)
网格圈负压式集聚纺集聚须条张力模型
傅 婷, 陈南梁
(东华大学 纺织学院,上海 201620)
通过对网格圈负压式集聚纺集聚须条进行几何建模、力学分析和运动学分析,建立了集聚须条的张力模型.该模型可以用来研究集聚须条张力分布,以及分析影响因素.通过求解张力模型的解析解,可知须条张力在集聚区内沿前进方向呈线性增长.通过对线密度为15.3 tex的纯棉集聚纱进行模拟计算可知,须条与网格圈的摩擦因数、集聚斜槽倾角、集聚负压、集聚须条半径以及集聚管形状对须条张力的影响较为明显,并且在一定条件下得到的须条张力值在0.03~0.12 cN之间.研究结果为集聚纺集聚须条的张力分析提供了方法和借鉴,并为集聚区须条单纤维的运动轨迹分析提供了理论依据.
集聚纺; 网格圈负压式; 张力模型; 解析解
集聚纺作为近20年来最具进步性的纺纱技术之一,已成为近年纺纱领域中研究和应用的热点.集聚纺包含多种形式,其中以绪森公司为代表的网格圈负压式集聚纺纱是集聚纺中应用最为广泛的一种形式,并且具有结构简单、改造方便等特点,但同时也存在器材维护复杂等问题.对于这类集聚纺的研究主要集中在集聚机理[1-2]、纱线结构与性能[3-6]、网格圈材质与制作[7]、气流场分析和集聚槽形式[8-10]等方面.在集聚纱的结构与性能方面,已有许多详尽的研究文献,特别是其与环锭纱的比较,充分展示了集聚纱强力高、毛羽少等优点.集聚区须条的力学分析和运动学也有一些研究报道,主要集中在附加捻度和力矩分析方面[11-17],而很少有关于集聚区须条张力问题的文献报道.集聚区须条的张力问题对纤维的运动、形成附加捻度等均有重要影响.本文将以直槽型网格圈负压式集聚纺为研究对象,通过对须条进行力学分析,建立集聚区须条张力的数学模型,并探讨影响集聚区须条张力的因素,为须条集聚机理分析提供依据.
1 集聚区须条几何模型建立
集聚纺集聚区为一曲面Σ,集聚区开有直线集聚槽,集聚槽上面有网格圈,须条与网格圈接触.在直线形集聚槽上任一点O处,取集聚须条微元段ds,如图1所示.
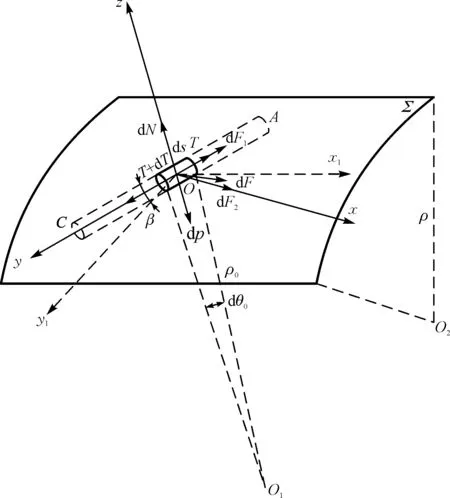
图1 须条微元段ds在直线型槽上的受力图Fig.1 Force diagram of infinitesimal ds of fiber strand in line-shape suction slot
xOy是曲面Σ在O点的切平面,其中y轴为O点的切线方向,即纱线前进运动方向,x轴垂直y轴,z为曲面Σ的法向,建立Oxyz坐标系.x1轴为切平面内与集聚管的轴向平行,y1与x1轴垂直,建立Oxy1z1坐标系,因而yOz和y1Oz是两个法截面.
ρ为曲面Σ的最小曲率半径(m),即为集聚管的曲率半径,其圆心为O2;ρ0为法截面yOz内微元段ds的曲率半径(m),其圆心为O1,且ρ0≈ρ/cosβ; dθ0为集聚须条微元段ds在法截面yOz内所对应的圆心角,(°);β为切平面内y轴与y1轴的夹角,即斜槽与法截面y1Oz的夹角,(°);r为集聚须条半径(m).
根据几何关系,可知在法截面yOz内,有
ds=ρ0dθ0
(1)

图2 微元段ds在平面y1Oz的投影Fig.2 Projection of infinitesimal ds in the plane y1Oz
可得几何关系
dscosβ=ρdθ
(2)
2 集聚区须条力学模型建立
微元段ds在集聚区受到张力、摩擦力、负压吸附力和支持力等作用,重力和因集聚管异形曲面而产生的向心力忽略不计.
T为集聚须条微元段ds两端所受的张力(N);dT为集聚须条微元段ds受到的张力增量(N);dF为集聚须条微元段ds受到的总摩擦力(N);dP为集聚须条受到集聚负压的作用力(N);dN为网格圈对ds的法向支持力(N);μ为集聚须条与网格圈的摩擦因数;p为集聚须条受到负压(Pa);dF1为集聚须条微元段ds在弧线形集聚槽前进方向受到的摩擦力(N);dF2为集聚须条微元段ds在轴向方向受到的摩擦力(N).
根据图1,对集聚须条微元段ds在y轴方向取力的平衡方程式,有
(3)
在z轴方向取力的平衡方程式,有
(4)
其中:dP=2rpds.
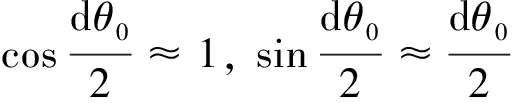
将式(1)代入式(3)、(4),并略去高次项,整理得
阿东心里一直都悲伤着。听罗爹爹跟母亲唠叨,像他们活着时那样说话,便心生感动。再听到后面两句,他险些想笑了。
(5)
将集聚区须条微元段ds受到来自网格圈的摩擦阻力dF沿dF1和dF2方向分解的示意图如图3所示.
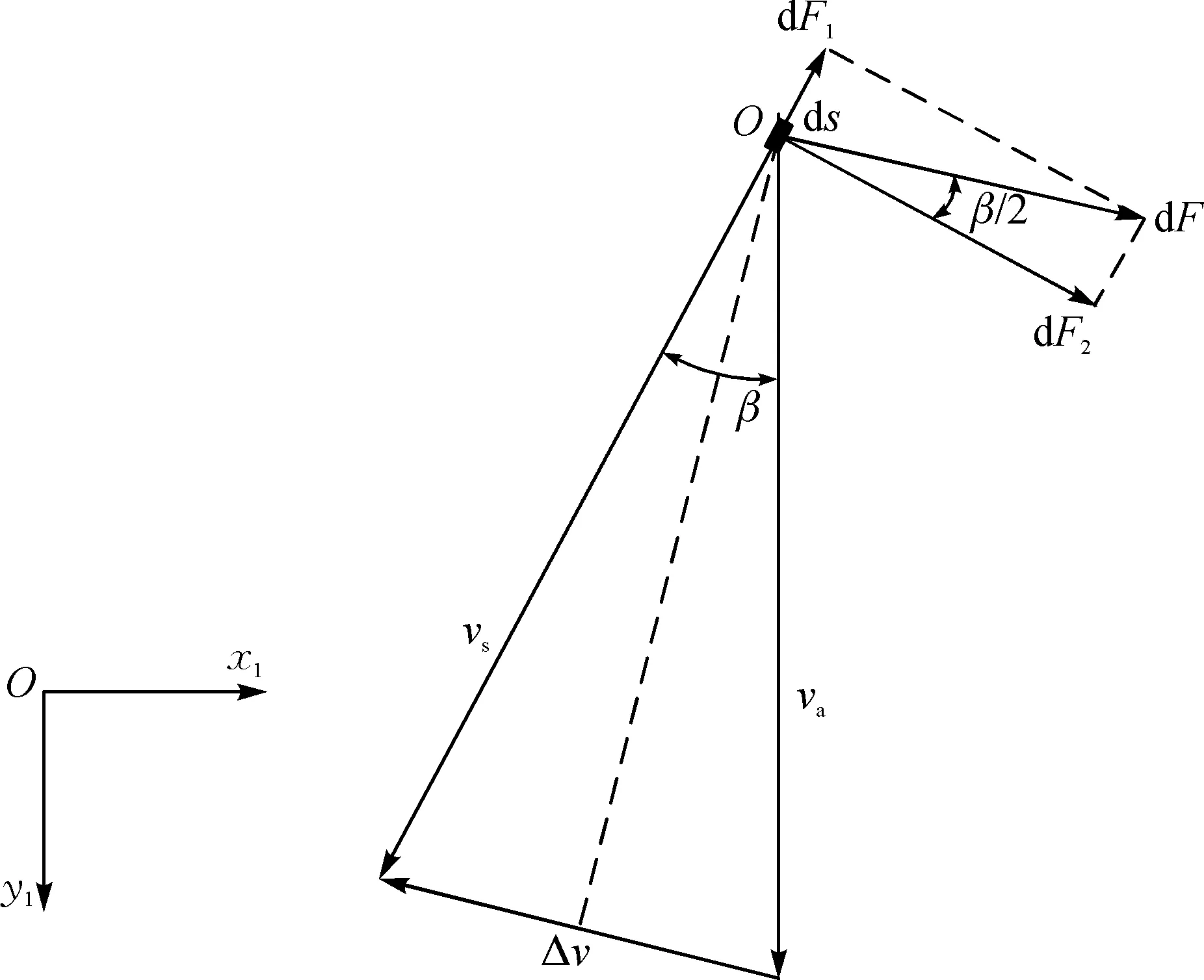
图3 微元段ds受到的摩擦力分解示意图Fig.3 Schematic diagram of factorization of frictional force on infinitesimal ds
va和vs分别为网格圈和纱线的速度,可得
(6)
(7)
代入式(5)得到:
(8)
又根据dF=μdN,代入式(8),整理得
(9)
将式(3)和ρ0≈ρ/cosβ代入式(9),整理得
(10)
对式(10)进行解析求解,变换可得
(11)
两边积分
(12)
由图1可知,起始点为A,终止点为B.A点处,可知θ=0,张力T=0.
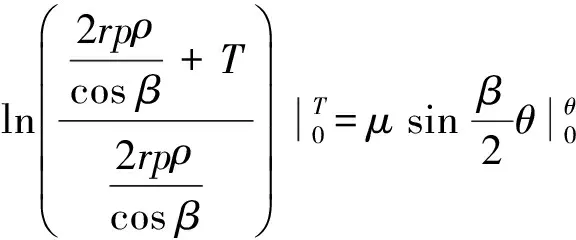
(13)
(14)
由式(14)可知,张力T与斜槽倾斜角度β、集聚负压p、集聚管曲率半径ρ、须条半径r、须条与网格圈的摩擦因数μ和斜槽长度对应的圆心角θ有关.
3 模型分析与讨论
根据式(14)进行模拟计算可知集聚区须条张力的影响因素及其程度,以纺制15.3 tex纯棉集聚纱为例,讨论主要因素对集聚须条张力的影响.试验中各参数设置:棉纤维线密度为0.18 tex;须条半径为0.30~0.40 mm,作为固定参数时设定为 0.35 mm(实际采用图像方法测试获得);集聚负压为1~3 kPa,作为固定参数时,设定为1.96 kPa;集聚管集聚区曲率半径为30~50 mm,作为固定参数时设定为38 mm;摩擦因数为0.25~0.45,作为固定参数时设定为0.35;集聚槽倾斜为0°~20°,作为固定参数时设定为5°.θ是集聚管的结构参数,根据实际情况取为30°.可采用MATLAB编程计算并绘制成图.
取固定参数时的张力T与斜槽长度对应的圆心角θ的关系图如图4所示.由图4可知,随着θ的增大,张力呈线性增长,至30°时,其须条张力为0.042 7 cN.
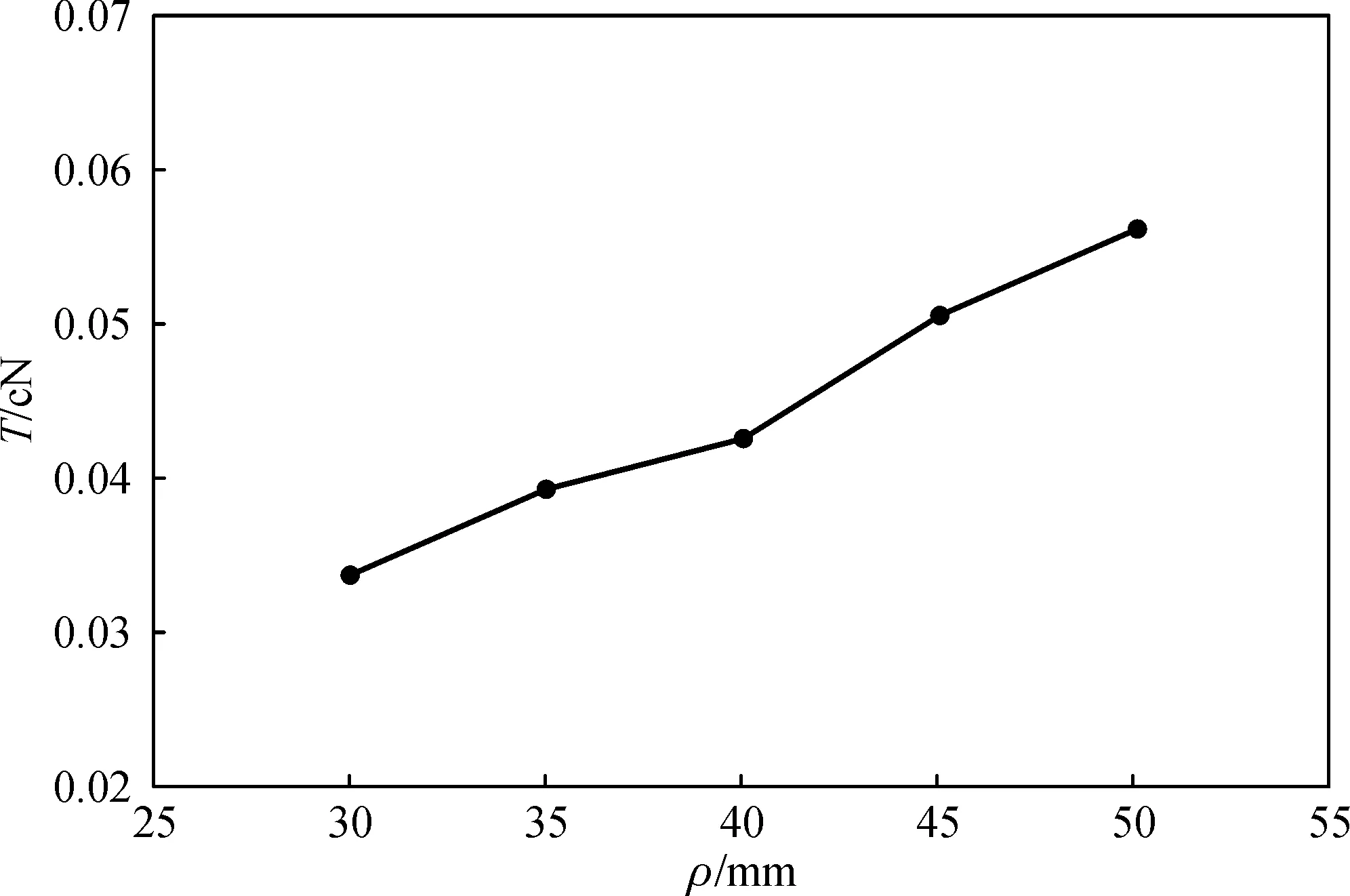
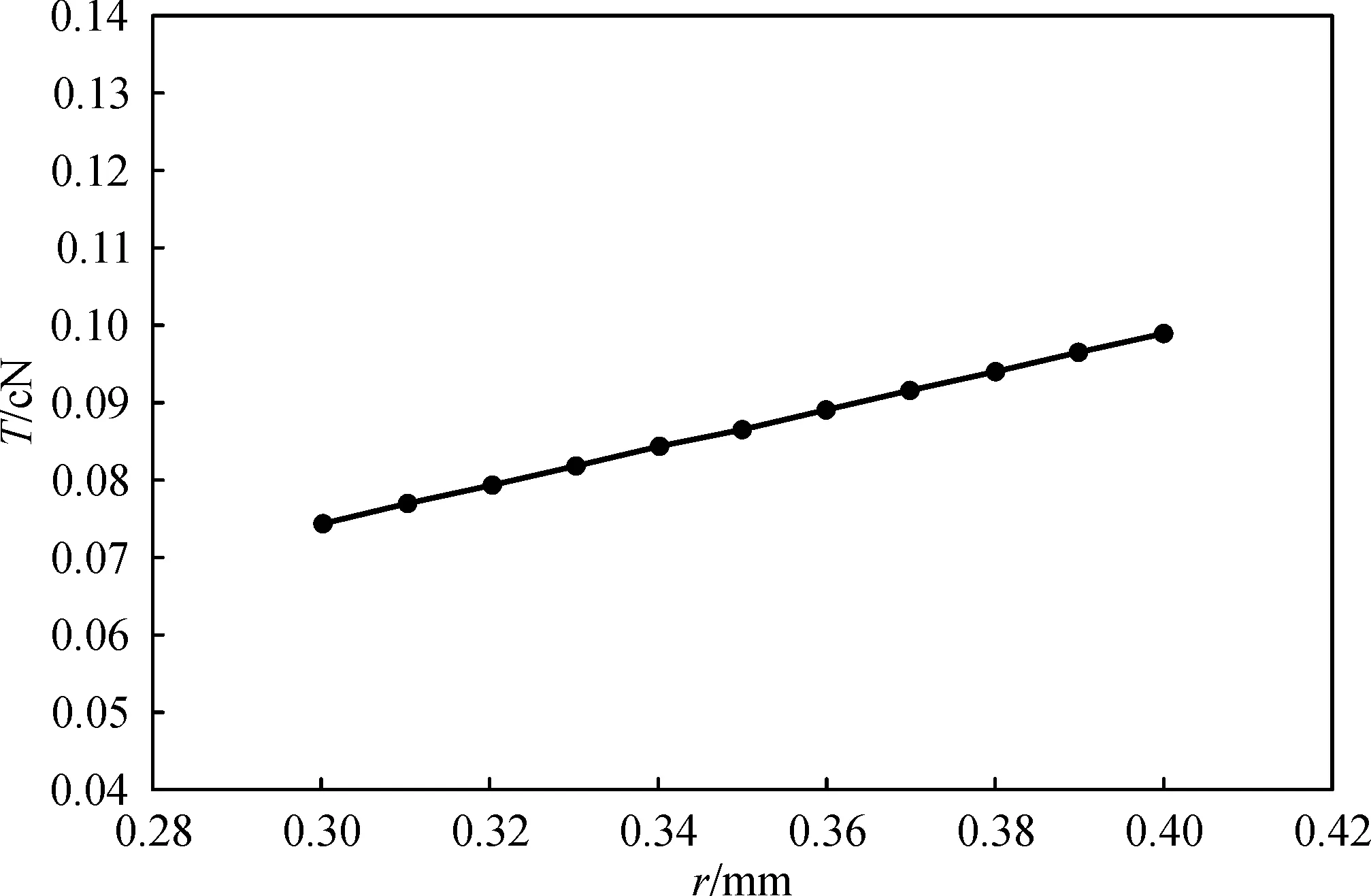
将须条与网格圈的摩擦因数、集聚负压、曲率半径及须条半径等因素进行单因素分析,并约定当某个参数变化时,其余参数取固定参数,变化范围及固定参数详见上文.分别将须条在θ=30°时的张力值与变化参数绘制成图5~8.
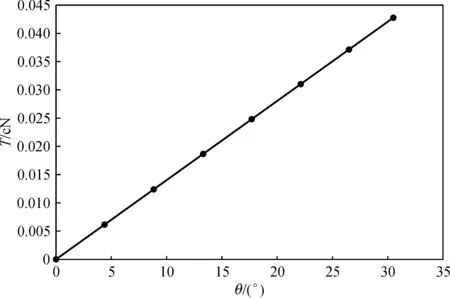
图4 须条张力与θ的关系Fig.4 Relationship between the strand tension and θ
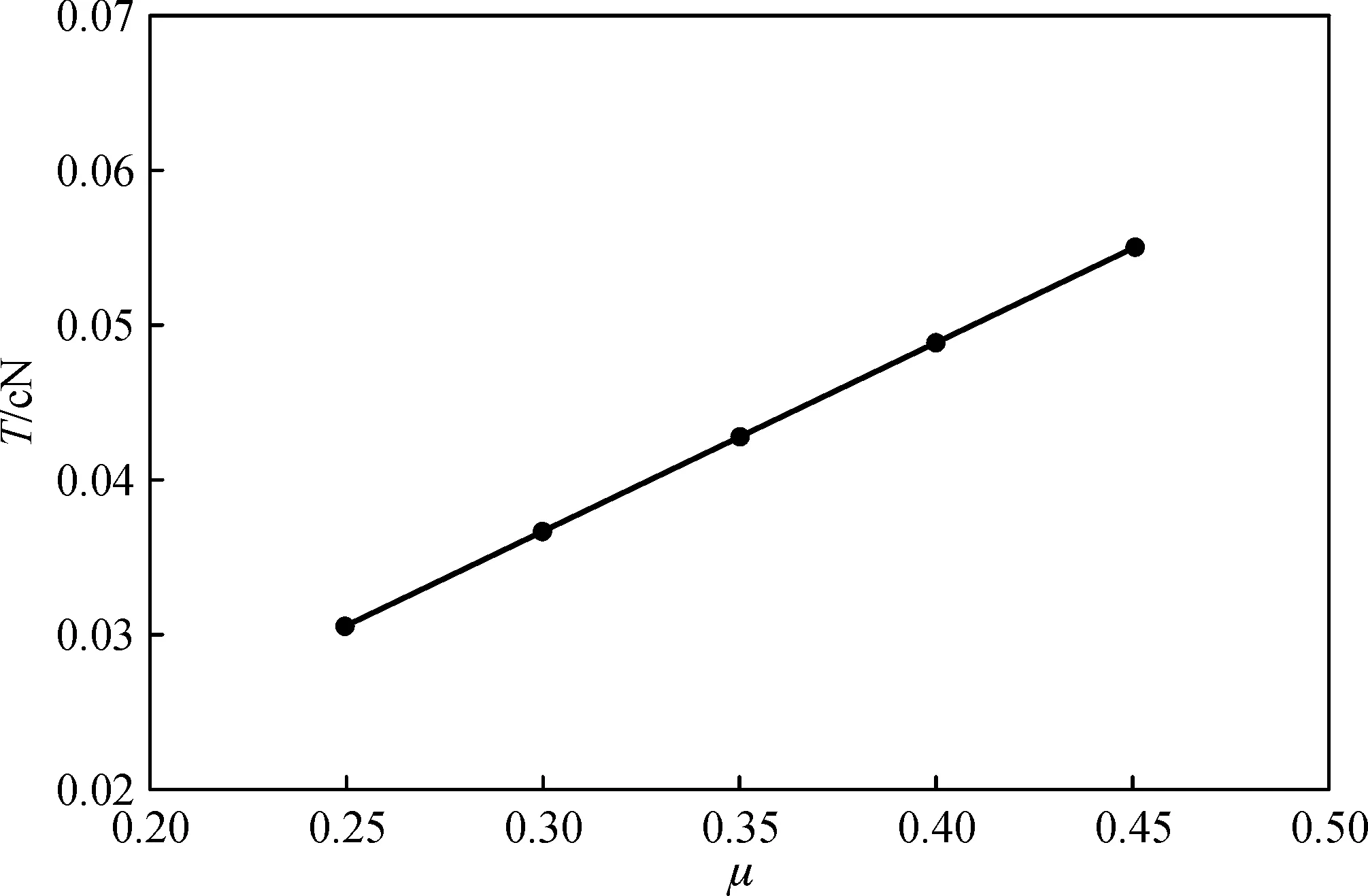
(a) β =5°
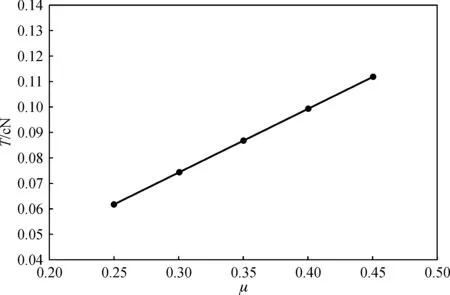
(b) β =10°
(a) β =5°
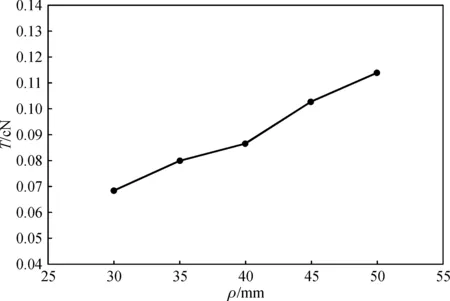
(b) β =10°
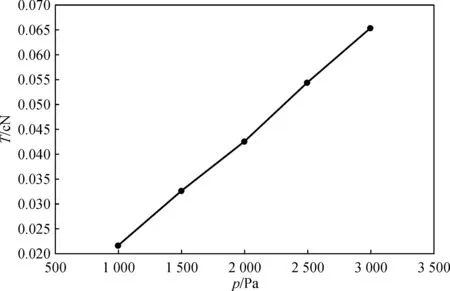
(a) β =5°
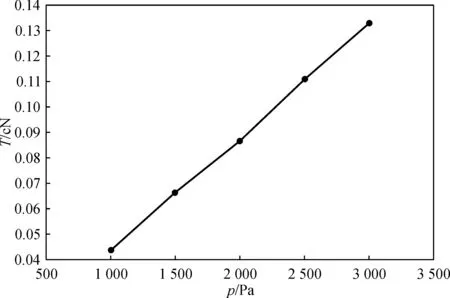
(b) β =10°
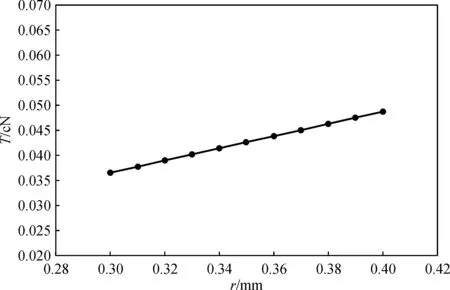
(a) β =5°
(b) β =10°
从图5~8可知,集聚槽倾斜角度对张力影响较大,5°与10°的相比,后者张力值是前者的两倍左右.集聚负压、集聚管曲率半径、须条半径对张力的影响也是比较明显的,呈线性变化.摩擦因数μ和θ角与张力T的关系式是指数方程,但是由于μ和θ的值在0.6以下,故张力值变化趋势也类似于线性变化.β=5°时,须条张力在0.022~0.065 cN之间;β=10°时,须条张力在0.044~0.133 cN之间.
4 结 论
(1) 通过对直线型斜槽网格圈负压式集聚纺集聚区须条进行几何建模、力学分析和运动学分析,建立须条的张力模型,并得到解析解为
(2) 通过模拟计算,分析了张力T与斜槽长度对应的圆心角θ的关系,在其他参数确定的条件下,张力随着θ的增大而几乎呈线性增大.
(3) 通过模拟计算,讨论了斜槽倾斜角度β、集聚负压p、集聚管曲率半径ρ、须条半径r、须条与网格圈的摩擦因数μ与集聚区须条张力之间的关系,结果表明,以上这些因素对张力均有明显影响.
[1] 高金霞,邹专勇,华志宏,等. 网眼罗拉型集聚纺集聚区须条集聚机理分析[J]. 东华大学学报(自然科学版),2009, 35(5): 515-519.
[2] ZOU Z Y, ZHU Y D, HUA Z H, et al. Studies of flexible fiber trajectory and its pneumatic condensing mechanism in compact spinning with lattice apron[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2010, 80(80): 712-719.
[3] KRIFA M, ETHRIDGE M D. Compact spinning effect on cotton yarn quality: Interactions with fiber characteristics[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2006, 76(5): 388-399.
[4] BASAL G, OXENHAM W. Comparison of properties and structures of compact and conventional spun yarns[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2006, 76(7): 567-575.
[5] ALMETWALLY A A, MOURAD M M, HEBEISH A A, et al. Comparison between physical properties of ring-spun yarn and compact yarns spun from different pneumatic compacting systems[J]. Indian Journal of Fiber & Textile Research, 2015, 40(1): 43-50.
[6] YILMAZ D, GOKTEPE F, GOKTEPE O, et al. Packing density of compact yarns[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2007, 77(9): 661-667.
[7] LIU X, SU X, ZHANG H. Effects of lattice apron density on yarn qualities in four-line compact spinning system[J]. Journal of the Textile Institute, 2016, 108(4): 1-12.
[8] HAN C, WEI M, XUE W, et al. Numerical simulation and analysis of airflow in the condensing zone of compact-siro spinning[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2015, 85(14): 1506-1519.
[9] XUE W, WEI M, ZHANG N, et al. Numerical simulation on the condensing effect of suction slot in compact spinning with lattice apron[J]. Journal of the Textile Institute, 2012, 103(10): 1116-1126.
[10] LIU X Y, LIU X J. Numerical simulation of the three-dimensional flow field in four pneumatic compact spinning using the Finite Element Method[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2015, 85(16): 1712-1719.
[11] 周水平,汪军,杨建平.集聚纺集聚区须条变截面部分的力学分析[J].东华大学学报(自然科学版),2005,31(2):20-23,32.
[12] 周水平,汪军,杨建平.集聚纺集聚区须条等截面部分的力学分析[J].东华大学学报(自然科学版),2005,31(3):10-14.
[13] 陆世麟,马洪才,华志宏,等.气流槽聚型紧密集聚纺力矩传递分析[J].东华大学学报(自然科学版),2012,38(3):287-291.
[14] 杨建平,傅婷,汪军.网格圈负压式集聚纺集聚须条附加捻度传递长度研究[J].东华大学学报(自然科学版),2011,37(5):573-578.
[15] WANG Y, HUA Z H, CHENG L H, et al. Simulation and analysis of fiber motion in condensing zone of compact spinning with lattice apron[J]. Journal of Donghua University(English Edition), 2010, 27(5): 600-605.
[16] YANG X, WANG J, YANG J P. Motion analysis of fiber band in compact field of compact spinning[J]. Journal of Donghua University (English Edition), 2006, 23(1): 144-147.
[17] WANG J, LIU H G, YANG J P, et al. Analysis of the additional twists on the fiber band in compact field of compact spinning[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 175-176: 380-384.
(责任编辑:杜 佳)
Tension Model of the Fiber Bundle in Pneumatic Compact Spinning with Lattice Apron
FUTing,CHENNanliang
(College of Textiles, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China)
The tension model of fiber bundle in the condensing zone is established by geometric modeling, mechanical analysis and kinematics analysis of the pneumatic compact spinning with lattice apron, which could be used to study the distribution of tension and analyze influence factors. It was shown that along the direction of forward motion, the tension of fiber bundle in the condensing zone demonstrated a linear increasing tendency based on the analytical solution of this tension model. Through the simulation of pure cotton compact yarn of 15.3 tex, it was found that there was a significant influence of friction factor between compact fiber bundle and the lattice apron, suction slot inclined angle, the negative pressure, the compact fiber bundle radius and the shape of suction tube on the fiber bundle tension. The obtained tension was 0.03 to 0.12 cN. The results provide an approach and instances for the analysis of compact yarn tension in the condensing zone of compact spinning, and the theoretical foundation for the analysis of motion track of single fiber in the condensing zone.
compact spinning; lattice apron with negative pressure; tension model; analytical solution
1671-0444 (2017)03-0346-06
2017-05-21
傅 婷(1980—),女,上海人,助理研究员,博士研究生,研究方向为新型纺纱技术.E-mail:ft@dhu.edu.cn 陈南梁(联系人),男,教授,E-mail:nlch@dhu.edu.cn
TS 104.77
A
