非磁化冷等离子体柱中的模式辐射特性分析∗
2017-08-01李文秋王刚苏小保
李文秋王刚苏小保
1)(中国科学院电子学研究所,北京 100190)
2)(中国科学院大学,北京 100049)
非磁化冷等离子体柱中的模式辐射特性分析∗
李文秋1)2)†王刚1)2)苏小保1)2)
1)(中国科学院电子学研究所,北京 100190)
2)(中国科学院大学,北京 100049)
(2016年10月8日收到;2016年12月6日收到修改稿)
利用亥姆霍兹方程和场匹配法,推导出了被圆柱介质管包裹的均匀非磁化冷等离子体柱中各角向模的色散关系.数值计算并分析了角向对称模(m=0模)、非角向对称模(=0模)的色散特性以及在不同波频率下各模式的辐射特性.研究发现,在波频率ω小于等离子体频率ωpe条件下,当ω一定时,各模式的传播速度随着ωpe的增大逐渐接近光速;m=1角向模式属于端向辐射,其主瓣辐射方向在轴向,而且随着ω的增大,其主瓣宽度逐渐变小,且出现幅值极小的副瓣;对于=1模式,其主瓣辐射方向均与轴向存在一定夹角,既不属于端向辐射也不属于法向辐射,且随着ω的增大,其主瓣宽度逐渐变小;各个模式的传播功率随着ω的增大逐渐增大.
等离子体,角向模式,辐射方向图,色散关系
1 引 言
近年来,关于等离子体技术在飞行器表面隐身、电离层通信方面的应用正受到越来越多的关注.Trivelpiece和Gould[1]对等离子体柱中的等离子体模式的传播、衰减特性做了详尽的理论研究.美国海军实验室Alexe ff[2]首次提出等离子体隐身天线的构想.Kirichenko等[3−5]和Ye等[6]理论分析了等离子体柱中角向对称、非角向对称波的辐射特性.基于等离子体介质层中对于电磁模式耦合转换特性的大量研究[7−9],美国诺斯罗普格鲁门公司首次将等离子体隐身技术应用到B-2隐身轰炸机上,使其雷达散射截面急剧减小[10].国内林敏等[11]对垂直入射到具有金属衬底的非磁化等离子体中的电磁波的衰减特性进行了理论与实验研究.
由于等离子体柱表面电磁波的辐射特性对于电磁波频率、等离子体密度独特的依赖性,使得对其各种角向模式的分析变得异常复杂.国外对于电磁波频率小于等离子体频率条件下等离子体柱中角向对称模(m=0模)的辐射特性已有初步研究,但对于非角向对称模(=0模)的色散特性及其辐射特性的研究尚未开始.本文利用Krook形式Boltzmann-Vlasov方程得到复数形式的等离子体电导率表达式、亥姆霍兹方程和场匹配法得到各模式的一般色散方程,然后结合远区天线辐射场方程,得到角向对称模与非角向对称模的辐射特性,并比较了两者辐射特性的区别.
2 理论模型
考虑一个半径为a的非磁化冷等离子体柱被内半径为a、外半径为b的玻璃管包裹,整个模型如图1所示.等离子体柱中等离子体密度均匀分布.电磁波的传播因子为ej(mφ+kzz−ωt).从Maxwell方程得到纵向场分量Ez和Bz满足的波动方程:


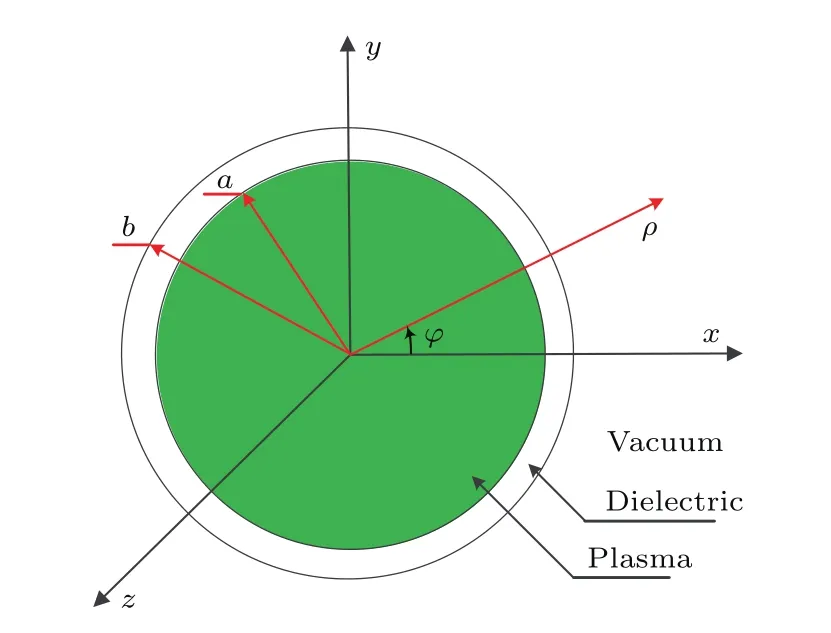
图1 被玻璃管包裹的等离子体柱横向截面示意图Fig.1.Cross section of plasma column surround by glass.
2.1 色散方程
2.1.1 各区域场量表达式
如图1所示,系统沿径向分为等离子体区(I区),玻璃管介质区(II区),真空区(III区).
I区:等离子体
利用(1)式求解纵向场分量,利用场的横向分量与纵向分量之间的关系,可得到I区中角向模数为m的电磁波的场分量为:


其中,Am,Bm为幅值系数;为等离子体中的横向波数;Im(·)为m阶第一类修正贝塞尔函数,为m阶第一类修正贝塞尔函数的导数.
II区:玻璃管介质区
利用(2)式求解纵向场分量,利用场的横向分量与纵向分量之间的关系,可得到I区中角向模数为m的电磁波的场分量为:

III区:真空区
利用(3)式求解纵向场分量,利用场的横向分量与纵向分量之间的关系,可得到I区中角向模数为m的电磁波的场分量为:
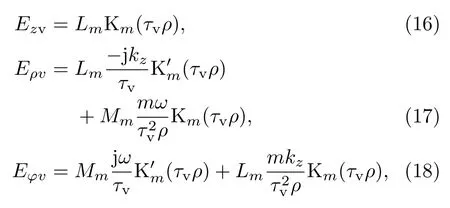

其中,Lm,Mm为幅值系数;为真空中的横向波数.
2.1.2 边界条件
利用模式在ρ=a,ρ=b处电场、磁场切向分量连续的边界条件,借助场匹配法,得到各个区域场量幅值系数之间的矩阵形式关系:
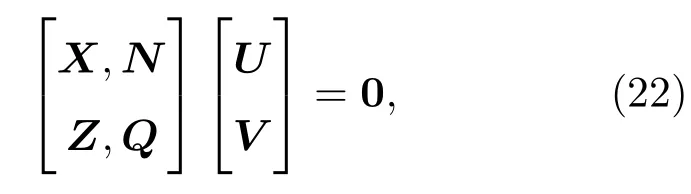
其中,U=(Am,Bm,Cm,Dm)T,V=(Em,Fm,Lm,Mm)T;X,N,Z,Q(分别为4×4矩阵)组成系数矩阵.
2.1.3 色散方程的导出
由(22)式可知,(U,V)T存在非零解的必要条件是系数矩阵行列式的值为零,即
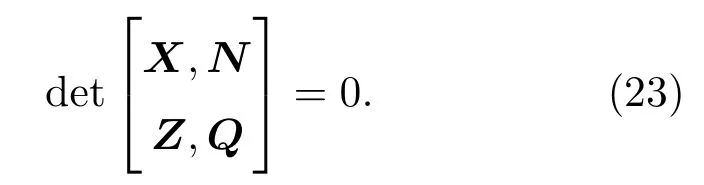
由于X,N,Z,Q各个系数矩阵中存在诸多零元素,故可对(23)式进行变换和降阶,得到

(24)式即为所求的色散方程.其中元素aij,bij由下列式子给出:
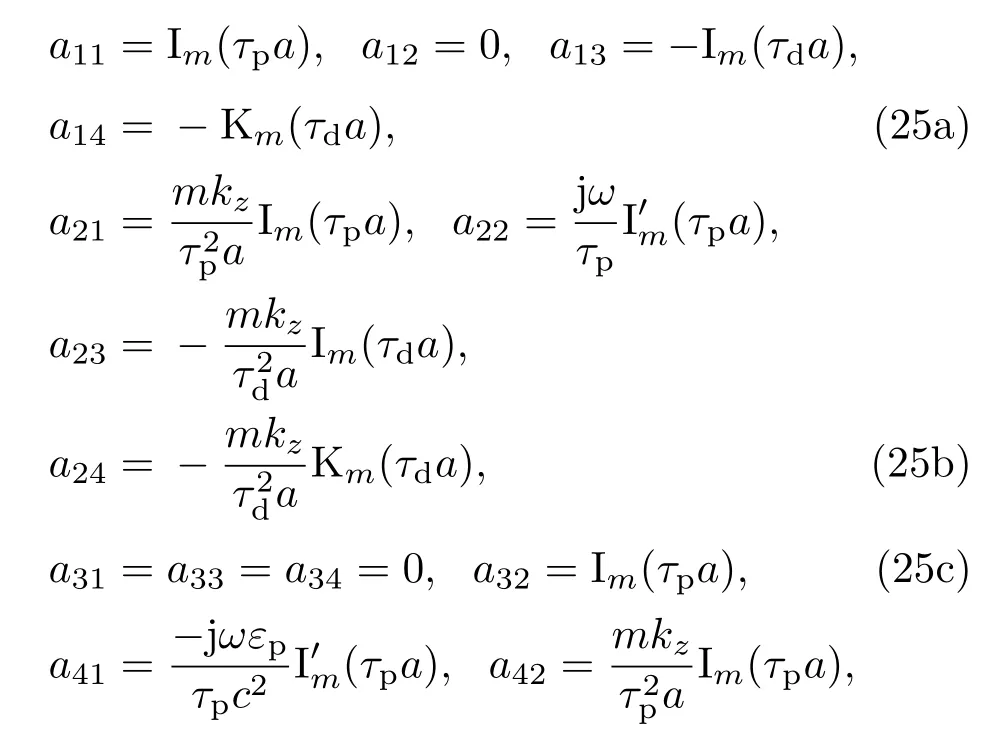

2.2 模式辐射特性
远场辐射可由矢势求得,矢势由下式给出:
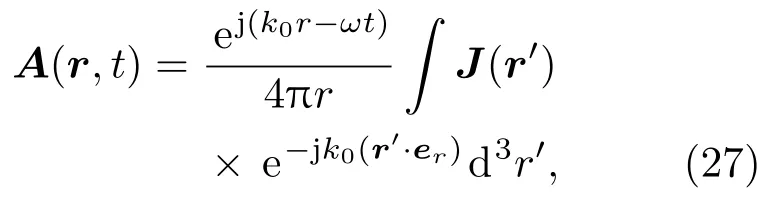
其中J(r′)=σpEp(r′)是等离子体柱中r′(ρ,φ,z)点产生的感应电流,r′(r,θ,φ)是球坐标系下场点矢量,σp为等离子体电导率.
利用Krook形式Boltzmann-Vlasov方程,得到复数形式的等离子体电导率[12]:


将(29)式代入(28)式,最终得到冷等离子体情况下的等离子体电导率:

求得矢势A后,再根据麦克斯韦方程,得到远区电场和磁场:

联合(4)式—(6)式、(27)式、(31)式、(32)式,由坡印廷矢量S=E×H得到辐射功率分布[5]:
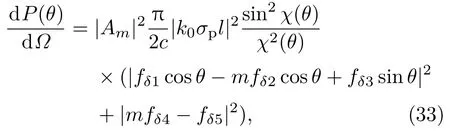
其中l为等离子体柱长度,m为角向模数,χ(θ)=(k0l/2)·(kz/k0−cosθ),fδi(θ)(i=1,2,3,4,5)为:
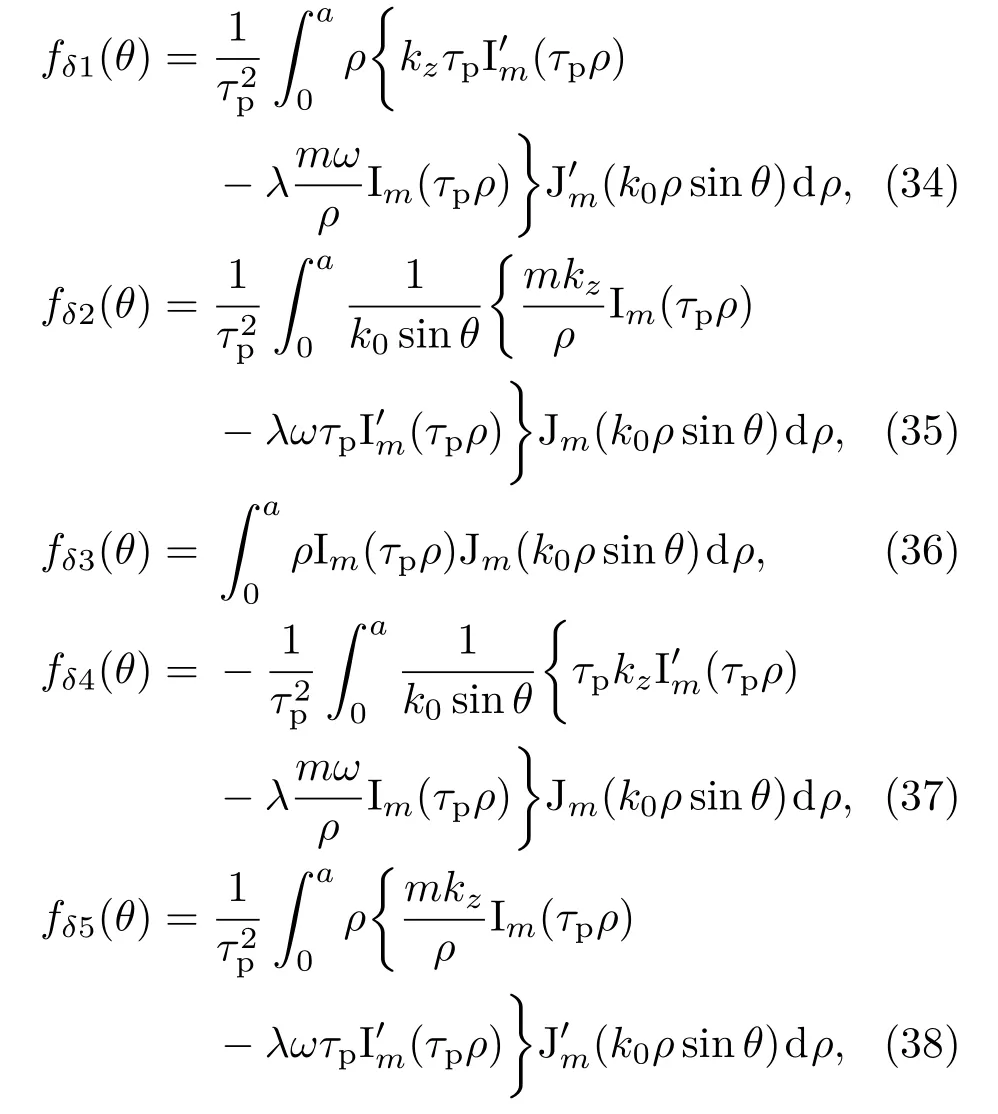
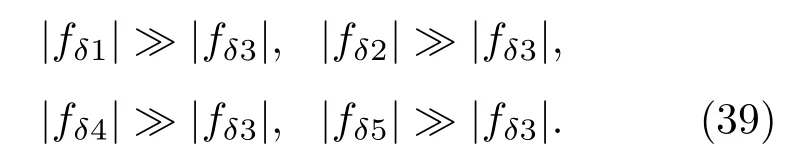
作为等离子体天线的重要特性,其角向模数为m的电磁波的传输功率PTm可由下式给出:

3 数值计算与结果分析
对于a=2 cm,b=2.2 cm的情形,利用(24)式,分别数值计算所得到不同ωpea/c值条件下m=0模、m=1模的色散曲线如图2、图3所示.参数ωpea/c是等离子体柱半径与表面波渗透到无损耗冷等离子体中的无功趋肤深度(δ=c/ωpe)之比.由图3可知,当ωpea/c由1→∞增大时,m=0模、m=1模的场逐步集中在等离子体柱表面,传播相速度逐渐接近光速.
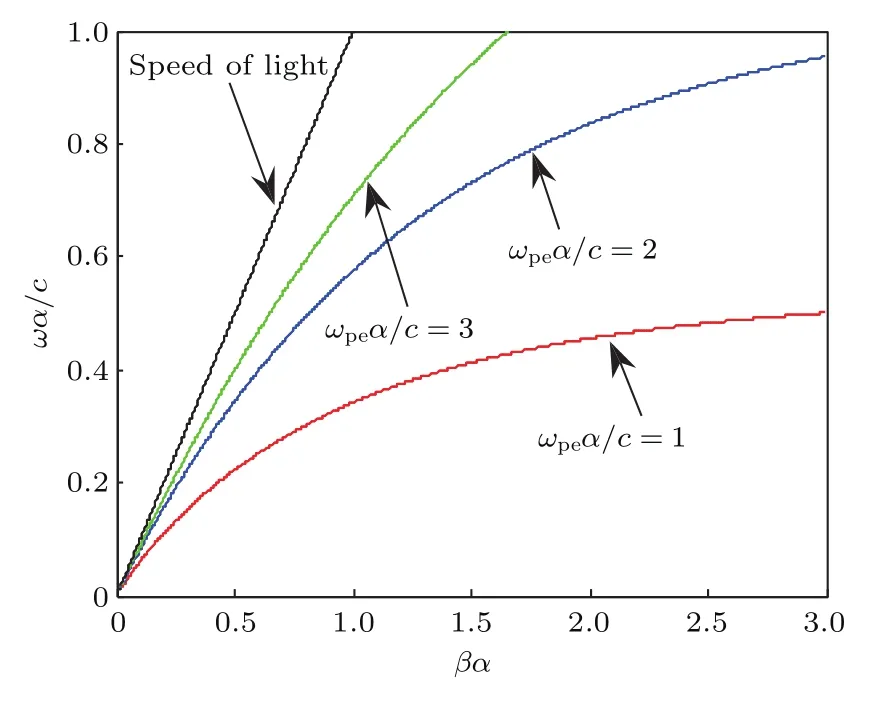
图2 m=0模色散曲线Fig.2.Dispersion curves of m=0 mode.

图3 m=1模色散曲线Fig.3.Dispersion curves of the m=1 mode.
图4描述了a=2 cm,b=2.2 cm,ωpea/c=2,l=0.5 m,f=250 MHz参数条件下m=0,m=1,m=2模的归一化辐射方向图曲线.由图可知,m=1模属于轴向辐射模,m=0模属于非标准法向辐射模且其主瓣辐射方向与等离子体柱轴向存在一定夹角,这一理论结果与Kirichenko等[5]的计算结果非常符合;赵国伟等[13,14]对m=0模辐射特性所得理论与实验性结果也与图4中m=0模所示计算结果符合良好.m=1模与m=0,m=2模辐射特性存在显著差异,原因如下.由(39)式可知,等离子体柱中轴向、角向电场分量对于辐射能量的贡献极小;且从(33)式可以看出,当m=1时,辐射在θ=0时达到最大值;而对于=1模,其主瓣辐射方向均与等离子体柱轴向存在一定夹角.

图4 m=0,m=1,m=2模归一化辐射方向图Fig.4.Normalized patterns for the m=0 mode,m=1 mode,and m=2 mode.
图5描述了a=2 cm,b=2.2 cm,ωpea/c=2,l=0.5 m参数条件下m=0模,m=1模,m=2模的归一化辐射方向图随频率的变化曲线.由图可知,随着工作频率的增加,对于m=0模和m=2模,其主瓣辐射方向与轴向的夹角逐渐变小,且出现较大幅值的旁瓣,主瓣宽度亦逐渐减小;而对于m=1模,随着工作频率的增加,其主瓣宽度逐渐变小,但其旁瓣幅值相对主瓣幅值虽略有增加,但依然可忽略.这种不同模式辐射方向特性随工作频率的变化特点暗示,随着工作频率接近甚至大于等离子体频率,各种模式开始渗入等离子体柱内部并在等离子体柱内部进行复杂的散射过程,导致模式以不同的出射夹角向外辐射.正是这种电磁模式与等离子体独特的互作用机制,导致与传统金属天线辐射特性相比,等离子体柱天线呈现出其辐射特性对于参量(工作频率,等离子体密度等)的高度依赖性.
图6描述了a=2 cm,b=2.2 cm,ωpe=100 GHz,l=0.5 m参数条件下m=0模,m=1模,m=2模的归一化(基于PT0进行归一化)传输功率随信号频率的变化关系曲线.由图6可知,随着工作频率的增加,m=0模,m=1模,m=2模的传输功率逐渐增大,且传输功率幅值与角向模数成反比.这暗示在等离子体柱中m=0模占据能量主要比例.这是由于随着信号频率的增大,波在等离子体柱表面的散射逐渐减小,并开始进入等离子体柱内部传播,导致整个馈入天线系统中的辐射能量比例减小,即沿着等离子体柱内部传播的能量比例增大.

图5 m=0,m=1模归一化辐射方向图随信号频率的变化关系 (a)f=0.25 GHz;(b)f=0.5 GHz;(c)f=1 GHzFig.5.Frequency dependence of normalized patterns of the m=0 mode and m=1 mode on signal frequency:(a)f=0.25 GHz;(b)f=0.5 GHz;(c)f=1 GHz.
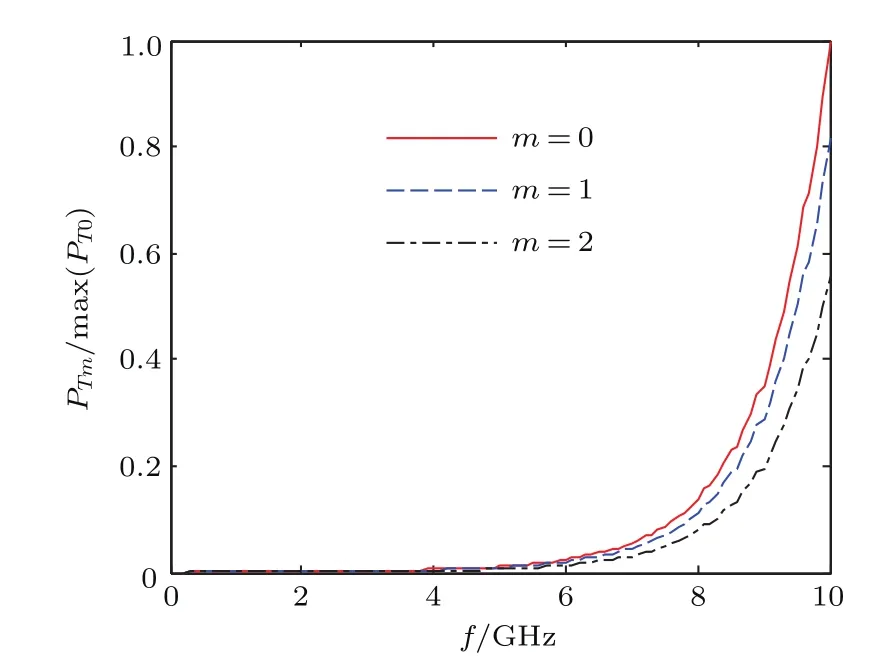
图6 m=0,m=1,m=2模归一化传输功率随信号频率的变化关系Fig.6.Frequency dependence of normalized transmission power of the m=0 mode,m=1 mode,and m=2 mode on signal frequency.
4 结 论
从建立均匀非磁化冷等离子体填充圆柱介质管系统的物理模型出发,通过数值计算分析了各模式的色散特性及它们各自的辐射特性,在ω<ωpe条件下得到了以下结论:1)当ω一定时,随着ωpe的增大,各角向模式的传播速度逐渐接近光速;2)对于m=1角向非对称模式,其主瓣辐射方向在轴向,属于端向辐射;而且随着ω的增大,其主瓣宽度变窄,且出现幅值极小的副瓣;3)对于=1的其他角向模式,其主瓣辐射方向均与轴向存在一定夹角,既不属于端向辐射也不属于法向辐射;而且随着ω的增大,其主瓣辐射方向与轴向夹角逐渐变小,主瓣宽度逐渐变窄,且出现幅值较大的副瓣.综上分析,m=1模等离子体柱可用作轴向辐射模天线,其可应用于空间高分辨率卫星,类似于轴向模螺旋天线,通过改变工作频率,可调节其主波束宽度和辐射强度,从而达到特定分辨率要求;而鉴于m=0模在辐射能量中所占的统治地位,在低频时其可用作法向模辐射天线,在高频时其可用作多波束辐射天线,即可通过改变信号工作频率来实现等离子体柱的辐射方向图重构.
[1]Trivelpiece A W,Gould R W 1959J.Appl.Phys.30 1784
[2]Alexe ffI 1968Phys.Fluids11 1591
[3]Kirichenko Y V,Lonin Y F,Onishchenko I N 2011Radioelectron.Commun.Syst.54 613
[4]Kirichenko Y V,Lonin Y F,Onishchenko I N 2014Radioelectron.Commun.Syst.57 474
[5]Kirichenko Y V,Lonin Y F,Onishchenko I N 2014J.Commun.Technol.Electron.59 269
[6]Ye H Q,Gao M,Tang C J 2011IEEE Trans.Antennas Propag.59 1497
[7]Wu K B,Hsu J Y 2012Phys.Plasmas19 022111
[8]Jia G,Xiang N,Wang X,Huang Y,Lin Y 2016Phys.Plasmas23 012504
[9]Kalaee M J,Katoh Y 2016Phys.Plasmas23 072119
[10]Chen S Q 2001International Aviation2001 10
[11]Lin M,Xu H J,Wei X L,Liang H,Zhang Y H 2015Acta Phys.Sin.64 055201(in Chinese)[林敏,徐浩军,魏小龙,梁华,张艳华2015物理学报64 055201]
[12]Chen F F 1991Plasma Phys.Controlled Fusion33 339
[13]Zhao G W,Xu Y M,Chen C 2006Acta Phys.Sin.55 3458(in Chinese)[赵国伟,徐跃民,陈诚 2006物理学报55 3458]
[14]Zhao G W,Wang Z J,Xu Y M,Liang Z W,Xu J 2007Acta Phys.Sin.56 5304(in Chinese)[赵国伟,王之江,徐跃民,梁志伟,徐杰2007物理学报56 5304]
PACS:52.40.Fd,43.25.Fe,52.40.Db,11.55.Fv DOI:10.7498/aps.66.055201
Analysis of mode radiation characteristics in a non-magnetized cold plasma column∗
Li Wen-Qiu1)2)†Wang Gang1)2)Su Xiao-Bao1)2)
1)(Institute of Electronics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100190,China)
2)(University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China)
8 October 2016;revised manuscript
6 December 2016)
The electromagnetic surface waves which propagate along a non-magnetized cold plasma column have a great value in the application of plasma antenna.In this paper,the dispersion properties,the transmission power distributions,and the radiation patterns for these electromagnetic surface waves which have lower frequencies than the electron plasma frequency are analyzed numerically.Based on Helmholtz equation,the specific expression of dispersion equation is derivedby the field matching method,then the exact values of complex axial wave vectorkzunder different wave frequencies are obtained by solving the transcendental dispersion relation.Using the specific value ofkzobtained above,the exact expressions of transmission power profile in the plasma column and field profiles in the three regions,i.e.,plasma,dielectric,and free space are derived,respectively.Finally,based on the complex form of electric conductivity that is derived from the Boltzmann-Vlasov equation with Krook term and the complex axial wave vectorkzobtained above,the influence of the parameterωpea/con phase property,and the dependence of radiation pattern and transmission power profile on wave frequency of the non-magnetized cold plasma column in a cylindrical dielectric tube system are analyzed.The results show that the electron plasma frequency has a significant influence on the phase property,which is evidently confirmed by the fact that the propagation velocities of the three modesm=0,m=1 andm=2 are all near to the light speed when the value of parameterωpea/cgradually increases.Meanwhile,through the investigation of the radiation patterns for the three modes,an important conclusion is that the radiation pattern has evident dependence on wave frequency.While the radiation direction of the main lobe is in the axial direction for them=1 mode,the=1modes each have an angle between the radiation direction of the main lobe and the axial direction,this crucial conclusion is in good agreement with the theoretical calculation results obtained from other researcher.Further,we find that with the increase of wave frequency,the angle between the main lobe radiation direction and the axial direction turns smaller for each ofm=0 andm=2 modes,and the width of main lobe gradually narrows for each of all modes,and the amplitude of the first side lobe becomes notable for each ofm=0 andm=2 modes and ignorable for them=1 mode.Also,the transmission power increases as the wave frequency increases for each of all modes.These theoretical calculation results provide a detailed theoretical reference for the designing of plasma stealth and high-precision requirements of plasma antenna design,and giving a comprehensive optimization guidance for the modulation of plasma antenna.
plasma,azimuthal mode,radiation pattern,dispersion relation
PACS:52.40.Fd,43.25.Fe,52.40.Db,11.55.Fv
10.7498/aps.66.055201
∗国家高技术研究发展计划(批准号:2013AA8035040C)资助的课题.
†通信作者.E-mail:beiste@163.com
*Project supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China(Grant No.2013AA8035040C).
†Corresponding author.E-mail:beiste@163.com
