肩峰撞击征二型肩峰行关节镜下肩峰成形术与关节镜下单纯肩峰下清理术疗效比较
2017-08-01苏雨亮杨梁
苏雨亮 杨梁
·论著·
肩峰撞击征二型肩峰行关节镜下肩峰成形术与关节镜下单纯肩峰下清理术疗效比较
苏雨亮 杨梁
目的分析评价关节镜下肩峰成形术与关节镜下单纯肩峰下清理术在治疗肩峰撞击征二型肩峰患者的疗效比较。方法选取2013年6月至2014年12月大连医科大学附属第二医院收治的57例肩峰撞击征二型肩峰患者,随机分成2组,其中行关节镜下肩峰成形术组32例,男20例,女12例,平均年龄(51.53±8.87)岁(39~68岁);行关节镜下单纯肩峰下清理术组25例,男13例,女12例,平均年龄(53.52±8.53)岁(42~70岁)。术前、术后定期使用美国加州大学洛杉矶分校(University of California at Los Angeles,UCLA)肩关节评分对肩关节功能随访评测。结果所有患者均获得随访,随访平均时间(7.95±3.65)个月(3~18个月)。关节镜下肩峰成形术组术前UCLA评分(9.43±1.34)分,末次随访评分(33.15±3.78)分,优良率88%;关节镜下单纯肩峰下清理术组术前 UCLA评分(6.40±1.15)分,末次随访评分(32.68±3.95)分,优良率84%。两组末次测评的UCLA评分较术前均明显提高,两组术后UCLA评分及优良率比较差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.009,P>0.05)。结论关节镜下肩峰成形术与关节镜下单纯肩峰下清理术都能明显改善肩峰撞击征二型肩峰患者的症状。肩峰撞击征二型肩峰患者更推荐行关节镜下单纯肩峰下清理术。
肩峰撞击征;二型肩峰;肩峰成形术;肩峰下清理术
肩峰撞击征是引起肩部疼痛的主要原因之一。在经历至少3个月的保守治疗,如烤电、热敷、肩峰下间隙麻醉性药物注射,仍达不到满意效果时,手术干预成为其解决症状的可靠手段。目前肩峰撞击征的主要手术治疗方式有肩峰成形术与肩峰下清理术两种方式。本文定位于肩峰形态分型中的二型肩峰,探讨现有主流术式肩峰成形术与肩峰下清理术的疗效比较及哪一种术式对于肩峰撞击征二型肩峰患者更具应用价值。
资料与方法
一、一般资料
2013年6月至2014年12月大连医科大学附属第二医院关节外科诊治的肩峰撞击征二型肩峰患者57例,随机分成2组,其中关节镜下肩峰成形术组患者32例(A组),男20例,女12例,平均年龄(51.53±8.87)岁(39~68岁);关节镜下单纯肩峰下清理术组患者25例(B组),其中男13例,女12例,平均年龄(53.52±8.53)岁(42~70岁)。两组患者一般情况比较见表1。所有患者均存在患肩疼痛,主动活动范围受限。肩峰撞击征专科检查:Neer sign(+),Hawkins sign(+),Job试验(-),疼痛弧为60~120°。冈上肌出口位X线片提示为二型肩峰。经过平均(7.95±3.65)个月(3~18个月)的保守治疗未达到患者满意要求。MRI提示肩袖断裂需缝合肩袖的患者及肩部存在其他结构区紊乱,如盂肱关节不稳、冻结肩、Bankart损伤、肩锁关节炎等排除在本次实验之外。
二、手术方法
采用侧卧位,患者躯干向后倾斜30°,患肩外展4 5°,前倾15°,牵引重量约3kg。采用标准后侧入路进入盂肱关节内,探查盂肱关节内盂唇、肩胛下肌、关节囊韧带及肱二头肌长头肌腱止点复合体情况。探查上方肩袖下表面是否存在肩袖撕裂,肱二头肌长头肌腱鞘膜是否存在炎症磨损表现。
表1 两组患者一般情况比较
1.肩峰下清理术:盂肱关节探查完毕后,经同一后侧入路进入肩峰下间隙,于肩峰外侧缘中线靠前选取前外侧入路,通过前外侧入路彻底切除滑囊组织暴露下方肩袖肌腱,正常肩袖肌腱呈白色,发亮,肌腱纤维整齐平行排列。而病变的肩袖组织呈灰色,发暗,纤维排列紊乱,个别患者肩袖肌腱存在小撕裂,但肌腱厚度仍足以维持肩袖正常功能,不需要通过缝合加强。此种情况下需要通过刨刀沿肩袖纤维走行方向摆动清除变性的肩袖肌腱组织,这种变性组织是引起症状的主要因素之一(图1~3)。
2.肩峰成形术:在单纯清理基础上,镜头以后侧入路为观察入路,外侧入路进入射频部分解离前外侧肩峰端喙肩韧带止点,暴露肩峰下表面骨质,可探查到肩峰前外侧缘稍弯曲,与二型肩峰描述相同,个别患者在弯曲肩峰末端可探查到增生骨刺。进入3.5mm打磨头自肩峰前外侧缘开始逐层打磨肩峰至肩峰弯曲部分变平为止。为保证肩峰下表面的平坦,镜头与打磨头交换入路,以前外侧入路为观察入路,打磨头自后侧入路进入补充打磨肩峰下表面直至视野下平坦(图4~6)。
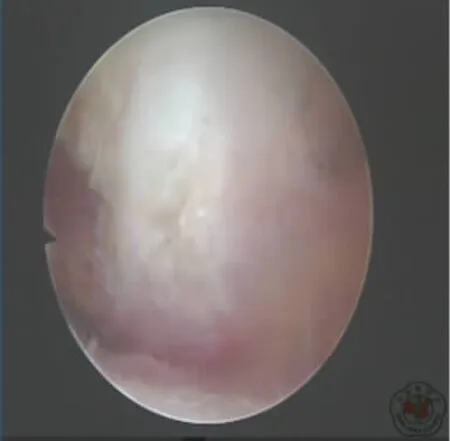
图1 清理前肩峰下间隙
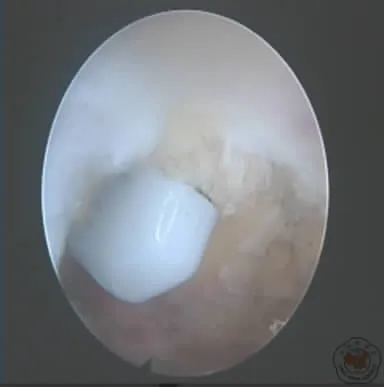
图2 射频止血清理滑膜
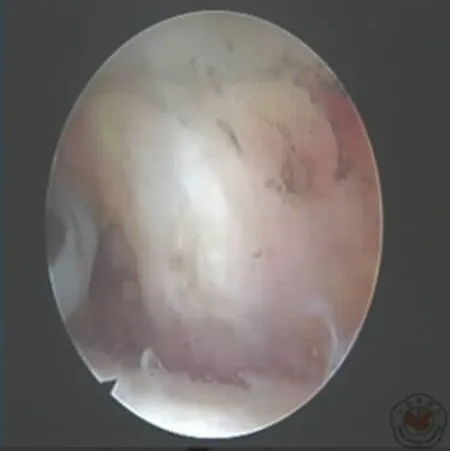
图3 清理后肩峰下间隙
三、术后处理
术后第2天开始康复功能锻炼。1~6周以被动活动范围为主,避免关节囊粘连;7~12周开始主动锻炼恢复肩袖肌群及三角肌肌力;4~6个月可适当参加低对抗性或低频率抬臂过肩运动;6~12个月可尝试性进行高强度对抗性运动或高频率抬臂过肩运动。
四、随访及疗效评价
患者分别于术后1周、6周、12周定期随访。随访内容包括:功能锻炼情况,患肢主动及被动活动度,患肢肌力。两组患者于术前、术后定期采用美国加州大学洛杉矶分校(university of California at Los Angeles,UCLA)肩关节评分对患者肩关节功能进行评价。UCLA评分满分35分,其中疼痛及功能评价分别为10分,活动度、肌力及满意度评价分别有5分,34~35分为优秀;28~33分为良好;21~27分为可;0~20分为差。
图4 肩峰下间隙喙肩韧带情况
图5 喙肩韧带肩峰附着端射频分离,显露肩峰骨质形态
五、统计学分析
使用SPSS 19.0统计软件进行数据分析。对于计数资料使用卡方检验;计量资料用±s表示,并进行正态检验。两组之间比较采用t检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
图6 打磨后二型肩峰变成一型肩峰
结 果
两组患者全部完成随访,未出现因症状恶化需要二次手术情况,未出现因其他影响肩部症状的疾病。其中大部分患者术后症状及功能改善明显,UCLA评分均较术前改善明显。
术前 A 组 UCLA 评分(9.43±1.34)分,B 组UCLA评分(9.64±1.41)分,两组间患者肩关节功能差异无统计学意义(t=0.574,P>0.05)。术后1周 A组 UCLA评分(14.19±1.73)分,B组 UCLA评分(14.60±1.44)分,术后1周两组肩关节功能恢复较术前明显改善,两组间差异无统计学意义(t=0.954,P>0.05)。术后6周 A 组 UCLA 评分(20.56±2.69)分,B 组 UCLA 评分(22.16±2.46)分,两组间肩关节功能恢复差异无统计学意义(t=1.312,P>0.05)。术后12周 A 组 UCLA 评分(26.47±3.26)分,B 组 UCLA 评分(27.00±3.41)分,两组间肩关节功能恢复差异无统计学意义(t=0.597,P>0.05)。末次随访 A 组 UCLA 评分(33.15±3.78)分,B 组 UCLA 评分(32.68±3.95)分,两组间肩关节功能恢复差异无统计学意义(t=0.457,P>0.05,图7)。
A组平均随访时间为(11.34±2.03)个月(8~15个月),UCLA评分自术前(9.43±1.34)分改善到术后末次随访(33.15±3.78)分,其中 UCLA评分分级优有21人(66%),良有7人(22%),一般有3人(9%),差有1 人(3%),优良率为 88%;B 组平均 随访时间为(11.20±1.89)个月(8~15个月),UCLA评分自术前(9.64±1.41)分改善到术后末次随访(32.68±3.95)分,其中按照 UCLA评分分级优13人(52%),良8人(32%),一般3人(12%),差1人(4%),优良率为84%(图8)。
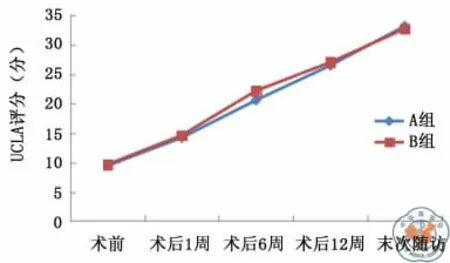
图7 两组患者不同时间段UCLA评分变化趋势图
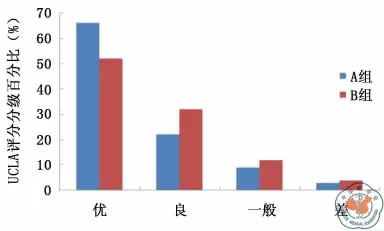
图8 两组患者末次随访中UCLA评分分级情况比较
讨 论
Bigliani于1986年介绍了一种肩峰分类的方法,其中Ⅰ型为平坦型,Ⅱ型为弯曲型,Ⅲ型为钩型。这种肩峰的分类方法简便、易用,通过一张冈上肌出口位X线片即可实现,尽管后续改良肩峰分型[1]及四型肩峰[2]相继提出,临床中肩峰的三度分型接受度最高、应用最广泛。
作者于临床中发现Ⅰ型肩峰前外侧缘较平坦,对肩峰下间隙的影响较小,即使肩袖退变导致其限制肱骨头的作用减弱,在抬臂过肩时肱骨头的上移也很难造成肩峰下间隙的过度狭窄而导致肩袖与肩峰产生撞击。Ⅰ型肩峰的肩峰撞击征患者其症状产生多与肩袖退变引起的撕裂或者肩峰下滑囊炎存在直接关系;而Ⅲ型肩峰由于其末端向下弯曲,肩峰下间隙极度缩窄,并且Ⅲ型肩峰牵拉性骨刺发生率明显高于Ⅰ型与Ⅱ型肩峰[3],牵拉性骨刺产生进一步缩窄了肩峰下间隙,加剧了肩袖与肩峰前外侧撞击的几率[4]。并且术中发现随着年龄的增加Ⅲ型肩峰的出现几率也随之增加,文献中存在报道喙肩韧带的牵拉是导致Ⅲ型肩峰形成的一个重要诱因[5]。
肩峰成形作为Neer[6]的重要成就之一在临床应用十分广泛,其对肩峰前1/3的切除有效的解除了抬臂过肩过程中肩峰与肩袖间产生的高压力。Ellman[7]在肩峰撞击征的治疗中将关节镜的引入改变了传统的切开治疗方式,其较小的侵入性、相对短的住院周期及短时间内即可恢复工作等优势让其逐渐取代了传统的切开手术[8-9]。
肩峰成形是在外因主导的前提下提出的,即肩峰撞击征的病因主要以出口的狭窄为主,人为的增加出口的高度理论上可避免撞击的再次发生。但越来越多的学者[10-11]发现退行性病变因素在肩峰撞击征的发生中占有更重要的地位。退变因素的发生主要与频繁抬臂过肩运动有关,如掷类运动员、游泳运动员、重体力劳动者。频繁负荷造成肩袖肌腱的疲劳性力弱,一方面导致其对抗肱骨头的作用降低,在抬臂过肩时引起继发性撞击发生;另一方面肩袖肌腱过度负荷导致肱骨大结节止点处出现撕裂引起症状(这种撕裂多发生于肩袖关节面[12])。
基于此病因作者认为肩峰成形的实施虽可有效缓解症状,但并不能解决退变问题的发生、发展,并且肩峰前外侧的切除及喙肩韧带的离断是以牺牲肩关节的稳定性为代价。喙肩韧带,肩关节运动的重要静态稳定结构,切除后将进一步加剧肩袖肌腱的负荷承受[13],理论上将加剧肩袖退变的发生[14]。在强调喙肩韧带重要作用的驱动下部分学者开始探索肩峰成形中喙肩韧带的保留可能[15-16]。
2005年Budoff等[17]介绍了通过单纯清理术的方式治疗肩峰撞击征,平均随访了114个月取得了79%的优良率。随后相关关节镜下清理术的报道[18]都取得了不差于肩峰成形术的效果。病变肩袖肌腱及滑囊的彻底清理缓解了患者的症状,而喙肩韧带完整性及肩峰前外部位保留,避免了对肩关节稳定结构的破坏。
在目前体育运动日渐流行的前提下,术后能继续参与高强度体育运动是患者希望通过手术达到的主要目的。作者接触的患者群体中普遍对肩部稳定性的要求较高,而肩部的退行性改变,如牵拉性骨刺或者Ⅲ型肩峰并不常见,因此尽量保留其稳定结构如喙肩韧带等对这一患者群体具有积极意义。
目前的共识是对于大部分Ⅰ型肩峰患者可单纯行关节镜下肩峰下清理术,而对于Ⅲ型肩峰患者,考虑到大多数患者存在肩峰下间隙的过于狭窄,作者认为外因仍占主导地位,行关节镜下肩峰成形术成为了最适合的治疗手段。2004年Gartsman等[19]学者发表了一篇前瞻性随机研究将Ⅱ型肩峰作为样本纳入条件,而对于Ⅱ型肩峰并没有过多讨论。而本研究则是以Ⅱ型肩峰为强调内容进行的手术对比分析。
本研究样本量较小及时间较短,需要临床更大样本量及长期随访的数据支持。本文的目的在于探索个体化治疗在临床中的应用。Ⅱ型肩峰术式研究只是迈出重要的一小步,在这一成熟领域仍然有很多问题亟待各位关节外科或者运动医学方面的学者去解决。谨以此希望为肩峰撞击征的治疗提供微薄之力。
[1]Nasca RJ,Salter EG,Weil CE.Current concepts review.Subacromial impingement syndrome(79-A:1854-1868,Dec.1997)[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1998,80(12):1852-1853.
[2]Gagey N,Ravaud E,Lassau P.Anatomy of the acromial arch:correlation of anatomy and magnetic resonance imaging[J].Surg Radiol Anat,1993,15(1):63-70.
[3]Natsis K,Tsikaras P,Totlis T,et al.Correlation between the four types of acromion and the existence of enthesophytes:a study on 423dried scapulas and review of the literature[J].Clin Anat,2007,20(3):267-272.
[4]Ogawa K,Yoshida A,Inokuchi W,et al.Acromial spur:relationship to aging and morphologic changes in the rotator cuff[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2005,14(6):591-598.
[5]Shah NN,Bayliss NC,Malcolm A.Shape of the acromion:congenital or acquired--a macroscopic,radiographic,and microscopic study of acromion[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2001,10(4):309-316.
[6]Neer CS.Anterior acromioplasty for the chronic impingement syndrome in the shoulder:apreliminary report[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1972,54(1):41-50.
[7]Ellman H.Arthroscopic subacromial decompression:analysis of one-to three-year results[J].Arthroscopy,1987,3(3):173-181.
[8]Biberthaler P,Beirer M,Kirchhoff S,et al.Significant benefit for older patients after arthroscopic subacromial decompression:along-term follow-up study[J].Int Orthop,2013,37(3):457-62.
[9]Yu E,Cil A,Harmsen WS,et al.Arthroscopy and the dramatic increase in frequency of anterior acromioplasty from 1980to 2005:an epidemiologic study [J].Arthroscopy,2010,26(9):S142-S147.
[10]Michener LA,McClure PW,Karduna AR.Anatomical and biomechanical mechanisms of subacromial impingement syndrome[J].Clin Biomech(Bristol,Avon),2003,18(5):369-379.
[11]Mackenzie TA,Herrington L,Horlsey I,et al.An evidencebased review of current perceptions with regard to the subacromial space in shoulder impingement syndromes:Is it important and what influences it?[J].Clin Biomech(Bristol,Avon),2015,30(7):641-648.
[12]Ozaki J,Fujimoto S,Nakagawa Y,et al.Tears of the rotator cuff of the shoulder associated with pathological changes in the acromion.A study in cadavera [J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1988,70(8):1224-1230.
[13]Su WR,Budoff JE,Luo ZP.The effect of coracoacromial ligament excision and acromioplasty on superior and anterosuperior glenohumeral stability [J].Arthroscopy,2009,25(1):13-18.
[14]Hsu HC,Luo ZP,Cofield RH,et al.Influence of rotator cuff tearing on glenohumeral stability [J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,1997,6(5):413-422.
[15]Denard PJ,Bahney TJ,Kirby SB,et al.Contact pressure and glenohumeral translation following subacromial decompression:how much is enough?[J].Orthopedics,2010,33(11):805.
[16]Torrens C,López JM,Verdier E,et al.Open anterior acromioplasty with preservation of the coracoacromial ligament:a modified surgical technique[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2003,12(1):9-14.
[17]Budoff JE,Rodin D,Ochiai D,et al.Arthroscopic rotator cuff debridement without decompression for the treatment of tendinosis[J].Arthroscopy,2005,21(9):1081-1089.
[18]Henkus E,de Witte B,Nelissen G,et al.Bursectomy compared with acromioplasty in the management of subacromial impingement syndrome:aprospective randomisedstudy[J].J Bone Joint Surg Br,2009,91(4):504-510.
[19]Gartsman GM,O′connor DP.Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with and without arthroscopic subacromial decompression:a prospective,randomized study of one-year outcomes[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2004,13(4):424-426.
Clinical outcomes of arthroscopic acromioplasty versus arthroscopic subacromial debridement for curved acromion in subacromial impingement syndrome
Su Yuliang,Yang Liang.Department of Jiont Surgery,the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University,Dalian 116023,China
C
orresponding author:Yang Liang,Email:yangliangyang@126.com
BackgroundSubacromial impingement syndrome is one of the main cause of shoulder pain.When the satisfactory effect is not achieved with at least 3months of conservative treatments including diathermy,hot compress and subacromial injection of the narcotic drugs,surgery becomes a reliable option for relieving the symptoms.Nowadays,arthroscopic acromioplasty and arthroscopic subacromial debridement are the two most commonly used surgical approaches in treating the subacromial impingement syndrome.The purpose of this study is to discuss the efficiency comparison between arthroscopic acromioplasty and arthroscopic subacromial debridement and their applicational values in better treating the type II acromion with subacromial impingement syndrome.Methods(1)General data.From June 2013to December 2014,57patients have been diagnosed with the type II acromion with subacromial impingement syndrome using the radiography in the second hospital of Dalian medical university.Through prospective randomized controlled method,patients were randomly assigned into 2groups:32patients(20male and 12female)in the arthroscopic acromioplasty group with a mean age of(51.53±8.87)years(39to 68years);25patients(13male and 12female)in the arthroscopic subacromial debridement group with a mean age of(53.52±8.53)years(42to 70years).Before the surgery was considered,all patients were suffered from shoulder pain and limited scope of active activities.The following specialized examinations were done:Neer sign(+),Hawkins sign(+),Job test(-),painful arc:60-120°.The X-ray of the exit position of supraspinatus muscle suggested the type II acromion.All patients who followed the protocol of conservative treatment with a mean time of(7.95±3.65)months(3to 18months)did not meet their satisfaction.The patients with rotator cuff fractures suggested by MRI and other structural disorders of the shoulder including glenohumeral instability,frozen shoulder,Bankart damage and acromioclavicular arthritis were excluded from this study.(2)Operation method.The patient was kept with lateral position,and the trunk leaned back to 30degrees with the shoulder abduction of 45 degrees.The forerake was 15degrees,and the traction weight was about 3kg.The glenohumeral joint was accessed from the standard posterior approach to explore glenohumeral labrum,subscapularis muscle,joint capsule ligament and long head of biceps tendon complex.Presences of the fracture on the bottom surface of the upper rotator cuff and the inflammation and wearing at the tendon sheath of the long head of biceps brachii muscle were further examined.①The arthroscopic subacromial debridement.After the glenohumeral joint examination,the subacromial space was accessed from the same posterior approach.The slippery bursa tissue was removed through the anterolateral approach in order to exposed the rotator cuff tendon.The healthy rotator cuff tendon is white,shiny,and the tendon fibers neatly arrange in parallel.However,the rotator cuff that undergoes pathological changes is gray,dark and disordered.While small torn existed in the rotator cuff tendon of individual patients,strengthen by suture was not required as the thickness of the tendon was enough to maintain the normal function of the rotator cuff.It is necessary to use the plane cutter to clean up the denatured shoulder sleeve tendon tissue along the shoulder sleeve fiber because the degenerate tissue is one of the main factors that cause the symptoms.②The arthroscopic acromioplasty.On the basis of simple cleaning,the arthroscopy lens accessed in to observe from the posterior approach.Then,the end of coracoacromial ligament of the anterolateral acromial was dissociated from the lateral approach to exposed the subacromial surface.Similar to the description of the type II acromion,it was found that the anterolateral margin of the acromion was slightly curved.The hyperplasia bone spur was even probed at the end of the curved acromion for some patients.The 3.5mm grinding head was applied to flatten the curved anterolateral margin of the acromion.In order to ensure that the surface of the acromion is flat,the lens and the grinding head exchange approaches by having the anterolateral approach for observation and the posterior approach for supplemental polishing by the;grinding head.(3)Postoperative management.Rehabilitation exercise was performed starting from the second day after operation.From 1week to 6weeks,the passive activity was executed to avoid the joint adhesion.During the same period,the passive range of motion of the shoulder was also under recovery through practices.From 7weeks to 12weeks,the strengths of the rotator cuff muscle and the deltoid muscle were recovered via active exercise.From 4months to 6months,the low antagonistic movement or the low frequency movement of arm lifting over the shoulder was encouraged to participate appropriately.From 6months to 12months,the high-intensity combat sports or the high frequency movement of arm lifting over the shoulder was recommended to be tried.(4)Follow-up and curative effect evaluation.After the operation,the patients were followed up at the time point of 1week,6weeks,12 weeks.The contents of the follow-up included:functional exercises,active and passive activities of the affected limb,and the muscle strength of the affected limb.The University of California at Los Angeles(UCLA)shoulder score was regularly used to evaluate the shoulder joint function of the two groups of patients preoperatively and postoperatively.The pain and the functional evaluation include a score range of 10points:0point for the worst and 10points for the best;The activity,the muscle strength and the satisfactory evaluation include a score range of 5points:0points for the worst and 5 points for the best;The UCLA evaluation has a full score of 35points:34-35for excellence;28-33for good;21-27for acceptable;0-20for poor.ResultsTwo groups of patients with a total number of 57 cases were all followed-up,and the second operation caused by the worsening of the symptoms was never required.Furthermore,other disease that affects the shoulder symptoms did not occur.The symptom,the function and the UCLA evaluation of the majority of patients have obviousimprovements after the surgery.The arthroscopic acromioplasty group gets the preoperative UCLA score of (9.43 ± 1.34)points,and the arthroscopic subacromial debridement group get the preoperative UCLA score of(9.64±1.41)points.There is no significant statistical difference between the joint function of the two groups of patients (P >0.05).After 1week,the arthroscopic acromioplasty group gets the UCLA score of(14.19±1.73)points.During the same period,the arthroscopic subacromial debridement group get the UCLA score of(14.60±1.44)points.There is no significant improvement of the shoulder joint function for both groups 1week after the operation(P>0.05),and there is no significant statistical difference between the two groups(P >0.05).After 6 weeks,the arthroscopic acromioplasty group gets the UCLA score of(20.56±2.69)points.At the same time,the arthroscopic subacromial debridement group get the UCLA score of(22.16±2.46)points.There is significant improvement of the shoulder joint function for both groups 6weeks after the surgery(P >0.05),and there is no significant statistical difference between the two groups(P>0.05).After 12weeks,the arthroscopic acromioplasty group gets the UCLA score of(26.47±3.26)points.At the same time,the arthroscopic subacromial debridement group get the UCLA score of(27.00±3.41)points.There is significant improvement of the shoulder joint function for both groups 12 weeks after the operation(P >0.05),and there is no significant statistical difference between the two groups(P >0.05).During the last follow-up,the arthroscopic acromioplasty group gets the UCLA score of(33.15±3.78)points.Meanwhile,the arthroscopic subacromial debridement group get the UCLA score of(32.68±3.95)points.There is no significant statistical difference between the recovery of the shoulder joint function of the two groups (P >0.05).After (11.34±2.03)months (8-15 months)of follow-up,the UCLA score of the arthroscopic acromioplasty group increases from (9.43±1.34)points to(33.15±3.78)points.After(11.20±1.89)months of follow-up,the UCLA score of the arthroscopic subacromial debridement group increases from (9.64±1.41)points to (32.68±3.95)points.The percentages of good and excellent are found to be 88%for the arthroscopic acromioplasty group and 84%for the arthroscopic subacromial debridement group.Conclusions While both surgical methods can significantly relieve the symptoms of patients with type II acromion,the arthroscopic subacromial debridement has advantages in treating the curved acromion.
Impingement syndrome;Curved acromion;Acromioplasty;Debridement
2016-04-22)
(本文编辑:胡桂英;英文编辑:陈建海、张晓萌、张立佳)
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2017.01.008
116023 大连医科大学附属第二医院关节外科
杨梁,Email:yangliangyang@126.com
苏雨亮,杨梁.肩峰撞击征二型肩峰行关节镜下肩峰成形术与关节镜下单纯肩峰下清理术疗效比较 [J/CD].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2017,5(1):47-53.
