基于PSO-SVM算法的梯级泵站管道振动响应预测
2017-07-12张建伟刘轩然马晓君
张建伟,江 琦,刘轩然,马晓君
(华北水利水电大学水利学院,郑州 450011)
基于PSO-SVM算法的梯级泵站管道振动响应预测
张建伟,江 琦,刘轩然,马晓君
(华北水利水电大学水利学院,郑州 450011)
泵站管道振动响应信号实测比较困难,为实现利用较少机组数据预测管道振动状况,提出基于粒子群(particle swarm optimization, PSO)的支持向量机(support vector machine, SVM)预测方法。利用粒子群全局跟踪搜索算法优化SVM核函数和惩罚因子,弱化SVM参数优化不足导致预测精度低的问题。以景电梯级二期3泵站2号管道为研究对象,基于机组和管道的振动实测数据,首先利用频谱分析和数理统计方法确定管道振动的振源贡献率,并计算机组和管道振动相关系数,确定机组和管道之间的强耦合关系。然后建立泵站管道振动的PSO-SVM预测模型,选取机组不同时段振动实测数据作为输入因子,相应时段管道振动数据作为输出因子进行训练和振动预测,并将管道振动预测结果与BP神经网络预测结果进行对比。与BP网络神经预测结果相比,该方法预测结果与实测值吻合度高,其平均相对误差最大为6.8%,根均方误差最大为0.261,预测精度更高。能够有效实现管道的振动响应预测,从而达到管道实时在线安全运行监测的目的。
泵;振动;优化;管道;粒子群;支持向量机;预测
0 引 言
管道结构不仅在水利工程上广泛应用,在军事、化工、石油、消防工程等诸多领域也广泛应用。管道使用寿命有限、制造技术落后、管理不当以及外界环境等影响,导致管道缺陷愈加严重,且管道失效事故时有发生。管道作为各种输送物体的载体,管道长期强烈振动会使管道、管道与附属物之间的连接处等部位发生松动或磨损,振动附加在管道上的交变动荷载引起管道和支吊架材料的结构损伤,甚至发生断裂等严重后果[1-5]。
泵站管道通过厂房与机组直接连接,机组运行过程中,前池高速水流直接进入机组,导致水流冲击转轮叶片,包括蜗壳的复杂结构和水体-蜗壳结构耦合作用进而引起一系列复杂脉冲振动,比如叶片汽蚀、涡流振动、导叶水流不均匀、水体-管道耦合等复杂的水力因素;机械因素包括转频倍频、高次谐波、轴不对称等[6-9]。在多种振动因素共同作用下导致管道振动复杂,其振动属于泵体-管道耦合非线性振动,振动机理也一直是工程界和学术界的研究热点和难点。
鉴于管道结构的复杂性和多样性,目前在水利行业实现管道振动监测比较麻烦。管道振动激励源复杂,且各种激励源大小也无法确定,通过建立精确的数值模拟仿真模型分析管道激励和响应也十分困难,考虑泵站与管道之间的耦合作用和相关关系,为实现利用较少的监测数据整体把握和控制管道振动的目的,基于泵站管道原型观测数据,建立一种预测管道振动响应的基于粒子群算法(particle swarm optimization,PSO)的支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)模型,针对支持向量机预测的不足,引入粒子群优化算法,保证模型预测中的参数更加准确,降低误差、提高预测精度。
1 基本理论
1.1 支持向量机
支持向量机[10]是建立在统计学VC维理论和结构风险最小化基础上的机器学习方法,在解决小样本、非线性和高维模式识别中表现出许多特有的优势,并在很大程度上克服了“维数灾难”和“过学习”等问题。此外,在模式识别、回归分析、函数估计和时间序列预测等领域都得到很好的发展。SVM目的是寻找一个满足分类要求的最优分类超平面,使得该超平面两侧的空白区域最大化,理论上支持向量机能够实现对线性可分数据的最优分类[11]。
以两类数据分类为例,给定训练样本集(xi,yi, i=1,2,…l, x∈Rn, y∈{±1}),超平面记作(ω,x)+b=0,为使分类面对所有样本正确分类且具备分类间隔,要求它满足以下约束条件:
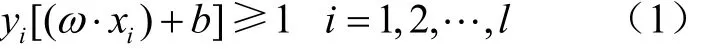
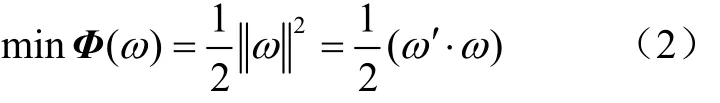
为解决约束最优化问题,引入Lagrange函数:
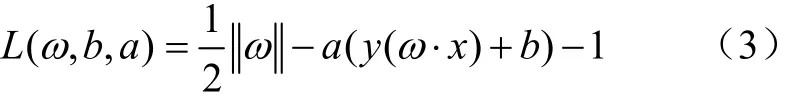
式中ai>0为Lagrange乘数。约束最优化问题的解由Lagrange函数的鞍点决定,并且最优化问题的解在鞍点处满足对ω和b的偏导数为0,将该问题转化为相应的对偶问题,即:
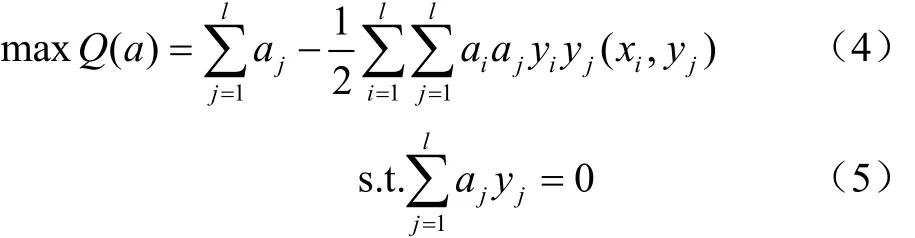
式中j=1,2,…l, aj>0。
计算最优权值向量ω*和最优偏置b*,分别为:
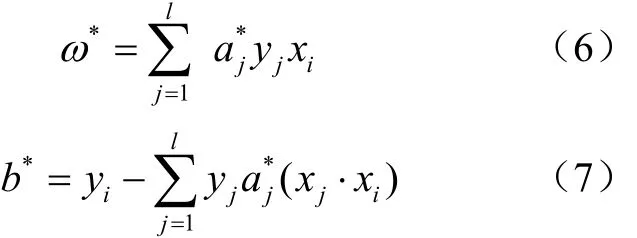
式中j∈{j a*>0}。
j
因此得到最优分类超平面(ω*·x)+b*=0,最优分类函数为:
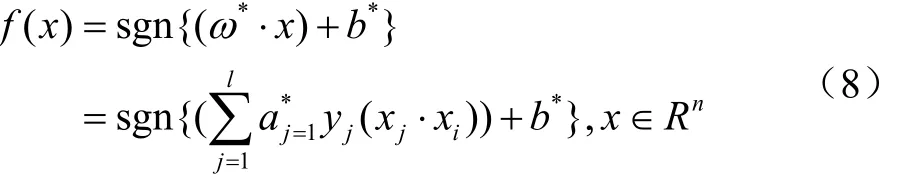
1.2 粒子群算法
粒子群算法(particle swarm optimization,PSO)是一种基于群智能与适应度的全局优化算法。其基本思想源于对鸟群觅食过程中群聚和迁徙行为的研究,并对这种社会行为进行建模和仿真[12-15]。
PSO初始状态为一群粒子,每一个粒子代表一解,粒子通过不断的环境适应和学习,不断更新粒子的位置速度,从而逼近最优解。PSO本质是利用群体中每个粒子之间的相互竞争和协作进而进行每一步迭代搜索,它特有的记忆功能使粒子动态追踪搜索状态,从而达到最优值。基于粒子群的寻优特点,其在多种领域都有广泛应用[16-21]。
2 粒子群优化的支持向量机
工程实践应用中为解决SVM非线性以及维数灾难问题,常使用核函数代替最优分类中的内积运算提高其运算精度[22]。但以往核函数选取常常人为确定,主观因素干扰过多会引起过拟合或者欠学习现象[23]。为提高SVM运算精度,需要合理选取优化算法对其内部运算参数进行调整,进而获取高精度的分类器。结合PSO独特的记忆功能和动态跟踪全局搜索寻优的特点,在建立SVM模型过程中,利用PSO算法对核函数和惩罚因子进行全局优化。从而建立基于粒子群的支持向量机识别算法,步骤如下所示:
1)根据原型观测数据,依据SVM算法筛选出支持向量组成的样本训练集;
2)依据训练集中的每个支持向量,获得一组SVM分类器的参数组成一个粒子,从而获得粒子群;
3)对粒子群进行初始化设置,即设定粒子群的初始参数C1、C2,初始速度矩阵V和每一个初始粒子个体最优位置Pi和全局最优位置Pg;
5)由计算得到的适应度函数值来调整粒子个体的最优位置Pi和全局最优位置Pg;
6)利用调整后的位置更新粒子的状态,从而得到一组新的SVM分类器的参数;
7)重复步骤4)-6)直至获得满足要求的粒子适应度函数值,或者达到所设定的最大迭代次数时终止迭代,输出结果。
3 工程实例应用
3.1 景泰工程简介
甘肃景泰电力提灌二期工程(简称景电工程)是一项高扬程、大流量、多梯级电力提水灌溉工程。选取3泵站2号管道作为原型观测试验对象,与2号管道连接的4机组和5机组均为1200S-56型卧式离心泵,设计流量3 m3/s,额定转速为600 r/min,设计扬程56 m。4、5机组各布置3个测点,分别位于机组蜗壳顶部和蜗壳尾部两侧,每个测点均放置水平方向和垂直方向2个拾振器,拾振器编号依次为#1、#2…#12,机组拾振器现场测试图和平面布置图如图1、2所示。

图1 机组拾振器现场测试图Fig.1 Field test diagram of vibration sensor of units

图2 机组拾振器平面布置图Fig.2 Layout of vibration sensor of units
管道共布置6个测点,各测点均放置3个拾振器(x、y、z 共3个方向,#1、#2、#3拾振器为测点1,#4、#5、#6拾振器为测点2,以此类推,共6个测点18个拾振器),6个测点分别位于2号主管端部和A、B支管的端部和中部,2号管道平面布置图如图3所示。试验采用中国地震局工程力学研究所研制的891-2型拾振器,根据泵站管道工作振动特点,选用中速度档位。该档位下水平方向拾振器的灵敏度范围在7.394~7.543 V·s/m之间,垂直方向拾振器的灵敏度范围在6.729~6.920 V·s/m之间。
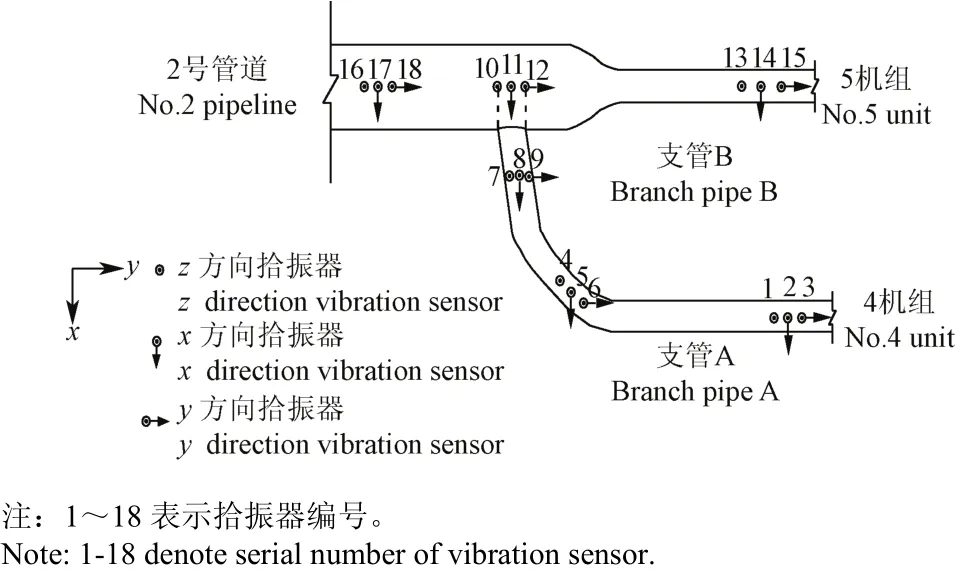
图3 2号管道拾振器布置平面图Fig.3 Vibration sensors layout of No.2 pipeline
3.2 机组和管道振动响应关系
根据景电泵站管道现场实测数据进行振源分析,确定机组运行对管道振动的影响贡献率。原型观测试验测试工况为4机组稳定运行、5机组关闭,测试时间为900 s,采样频率为512 Hz。
选取位于4机组顶部的#5、#6拾振器采样数据进行频谱分析,机组振动信号频谱分析见图4所示。由图4分析机组振动信号频谱可知,其主要振动频率为60、40、50、10、0.5 Hz,主要为机组叶频和转频倍频引起的振动,以及水流脉动的影响,其中50 Hz为电信号频率,不予考虑。选取靠近4机组的支管A上#1、#2和#3拾振器数据进行频谱分析,频谱图见图5,由图5可知,管道3个方向振动主要频率为60、40、30、20、0.5 Hz,主要是机组叶频和转频倍频引起的频率以及低频水流脉动引起的振动。
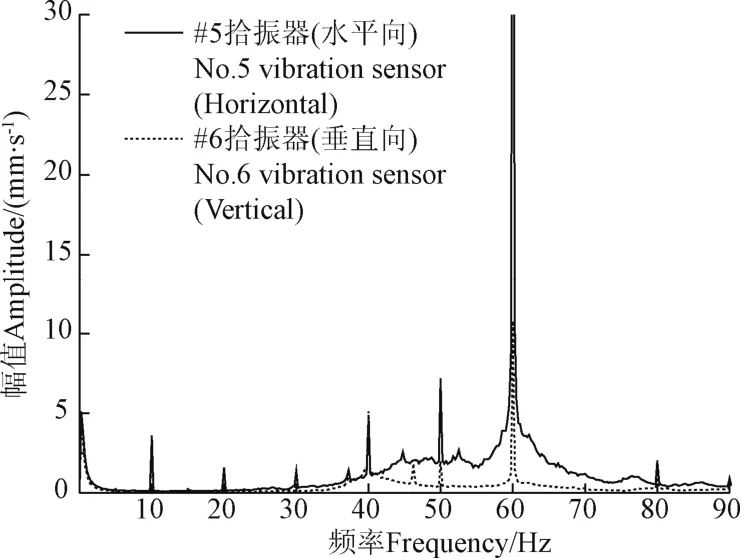
图4 机组#5、#6拾振器振动信号频谱图Fig.4 Spectrum graph of No.5 and No.6 vibration sensor signal of unit
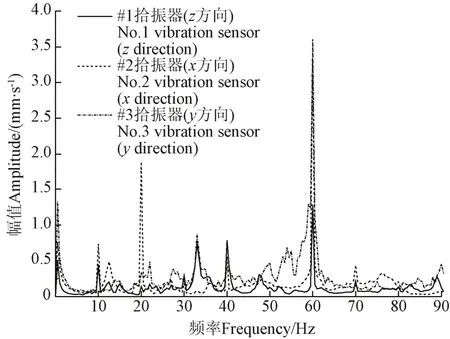
图5 管道#1、#2和#3拾振器振信号频谱图Fig.5 Spectrum graph of No.1, No.2 and No.3 vibration sensor signal of pipeline
依据频谱图计算各主频引起振动的能量百分比,从而确定振源分布,振源分析结果见表1,由表1可知,管道水平x、y向振动,叶频引起的振动所占总能量的比例在50%左右,其次是转频倍频引起的振动,占比例达22%;管道垂直方向振动叶频所占比例较水平方向有所降低,接近40%,转频倍频所占比例与水平方向一致;管道3个方向振动中叶频和转频倍频占比例在70%左右,说明机组运行是引起管道振动的主要原因。
由于机组水平方向只布置一个方向拾振器,管道水平方向布置2个拾振器,由表1中3个方向分频比例数据可知,管道水平x、y方向各主频所占比例接近,说明机组振动对管道水平x、y方向振动影响基本一致。管道水平x向振动数据可反映管道水平向振动趋势,故选取管道x向振动数据代表水平振动响应,与机组水平单方向对应。
机组运行是引起管道振动的主要原因,机组和管道振动的相关系数在一定程度上也可以反映两者之间的耦联振动特性。表2列出了机组与管道在水平方向和垂直方向不同测点的相关性系数。
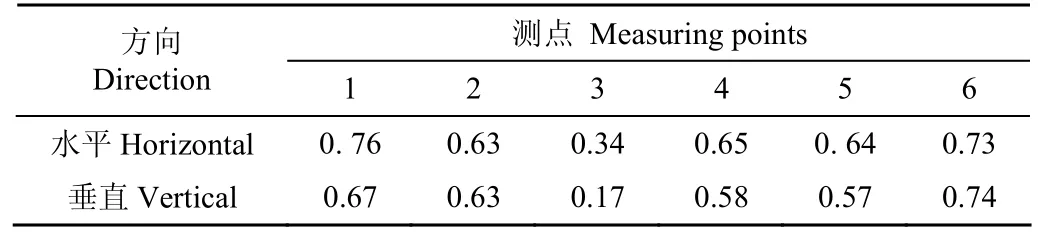
表2 机组与管道振动相关性系数Table 2 Related coefficient of vibration of unit and pipeline
由表2可知,针对4机组运行、5机组关闭工况,机组与管道振动相关系数在1、2、4、5、6测点相关系数均在0.57以上,最大相关系数为0.74。3号测点位于支管A与主管相连接的支管中部,受两端支墩作用,在一定程度上限制了振动能量的传递,且管道系统结构复杂,从而造成3号测点处相关系数较小,尤其在垂直方向。其他5个测点相关性大小不一,且水平方向相关系数普遍大于垂直方向,说明机组和管道之间有一定的耦联关系,且两者耦联振动特性比较复杂,机组与管道之间的振动有较强的耦合关系,利用在线监测的机组数据预测管道振动是比较合理的。
3.3 模型建立与训练
选取4机组#1至#6拾振器振动幅值作为输入因子,同一测点不同时间振动幅值虽不同,但统计意义上的测点振动幅值是反映了信号振动的平均能量。为反映数据全面性,机组振动信号每隔100个数据取30个数据作为样本,共抽取机组振动样本900个。根据上述机组和管道相关系数分析,管道1号测点和6号测点与机组振动相关性较大,相关系数最小为0.67,因此选取2号管道上#1、#2、#16、#17拾振器振动数据作为输出因子,分别代表2号管道支管和主管振动情况。同样振动数据每隔100个取30个,共抽取900个数据作为样本输出。将900个样本数据随机选取870个作为训练数据,剩余30个作为测试数据。训练数据用来进行预测和对比分析。
根据PSO-SVM流程图,在MATLAB平台上建立机组管道模型。粒子群参数选取决定粒子自身寻优信息和其他粒子对寻优轨迹的影响,根据大量理论研究和试验对比,设置初始学习因子C1=1.5,C2=1.7,各测点最优位置和全局最优位置参数见表3,将表3中得到的最优参数作为SVM算法中核函数参数和惩罚因子,内部运算参数的终止代数为200,种群数量为20。将870个训练样本数据代数模型进行训练。
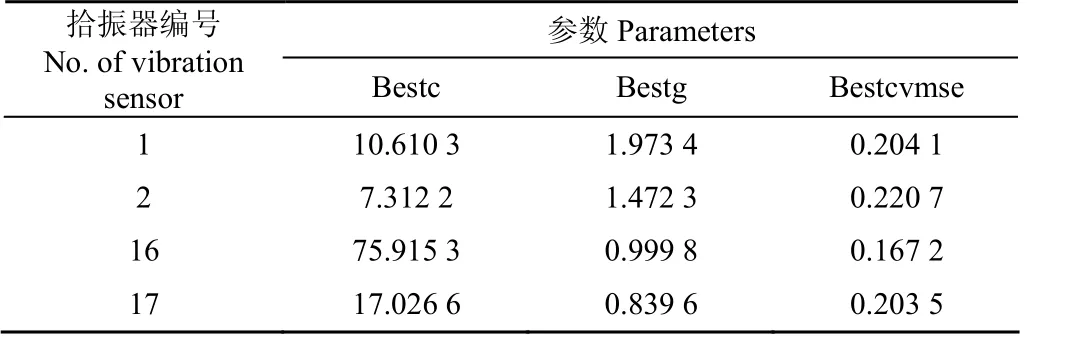
表3 PSO最优化参数Table 3 Optimization parameters of PSO
3.4 预测结果及对比分析
根据训练好的机组管道模型,将30个测试样本代入预测模型进行振动响应仿真并得到预测结果。BP神经网络作为一种精度较高的预测方法,在农业、机械、桥梁结构等领域应用较广[24-29]。为说明本方法的正确性和优越性,将BP网络神经预测作为对比方法。建立泵站管道BP神经网络模型,870个样本数据代入BP神经网络进行训练,剩余30个预测样本进行模型预测获得预测结果。两种方法预测结果与实际值对比如图6所示。
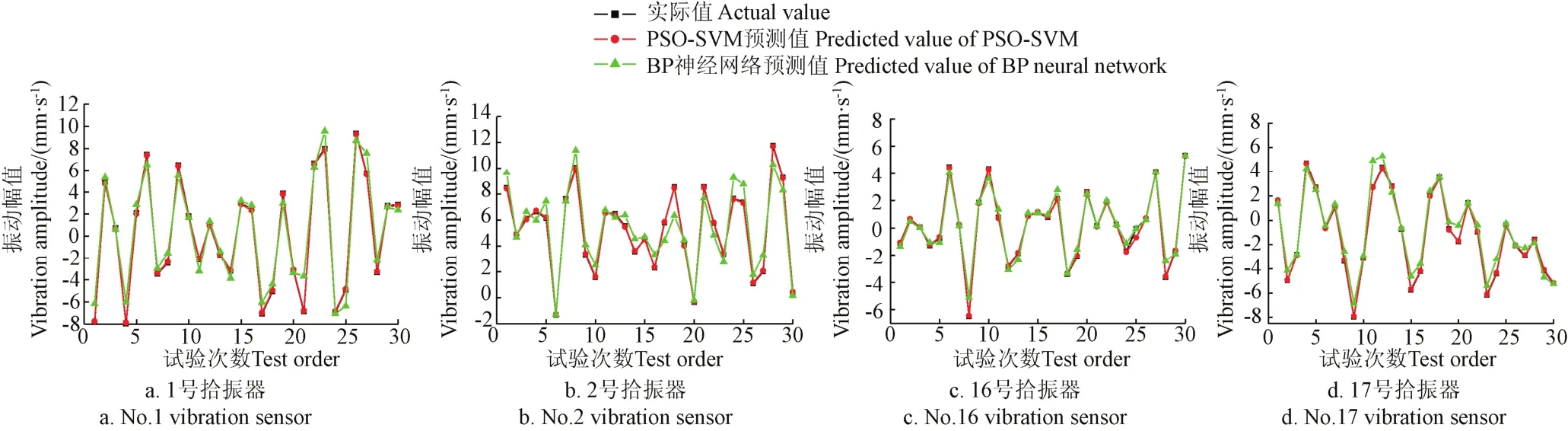
图6 各拾振器PSO-SVM预测结果和BP神经网络预测结果、实际值对比Fig.6 Comparison of predicted results of PSO-SVM, BP neural network and actual for each sensor
由图6中各拾振器PSO-SVM预测结果与BP神经网络预测结果和真实值对比可知,2种预测方法计算结果与实际值都比较接近,但PSO-SVM预测结果相对BP神经网络结果与实际值更接近,基本吻合,BP神经网络预测结果可以反映结构振动趋势,但峰值处与实际值相差较多,导致误差较大,不能准确预测结构振动响应。而本文方法得到的结果不仅能反映管道振动趋势,并且振动峰值与实际值非常接近,保证了预测精度。PSO-SVM方法通过粒子群法优化支持向量机参数,保证了SVM核函数选取的客观性和科学性,提高了计算精度。
图6中2种模型预测结果对比,从横向对比中评价了PSO-SVM预测效果,突出本文方法的优越性。其次可通过评价指标,直观反映2种方法预测结果与真实值误差。常用的评价指标有平均相对误差(mean relative error, MRE)和根均方误差(root mean square error,RMSE)[30]。MRE是指样本中预测值与实际值之间相对误差的平均值,反映了预测值与真实值之间的总体差异。RMSE是指真实值与预测值偏差与真实值比值的平方和样本总数n比值的平方根,根均方误差对一组数据中的特大或者特小误差反映非常敏感,可以很好反映出实际值与预测值之间的差异精密度。MRE和RMSE越接近0,说明模型预测效果越好,预测精度越高。式中k表示样本次序,k=1,2,3…n;n表示预测样本量;Tk表示实际值;ˆKT表示预测值。

表4根据式(9)和式(10)分别计算了BP神经网络和PSO-SVM模型预测值与实际值的平均相对误差和根均方误差。
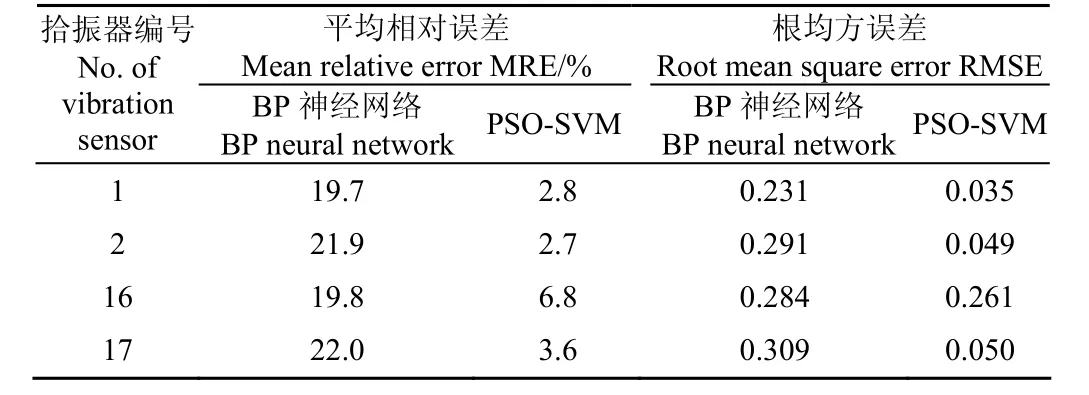
表4 各预测方法评价指标计算结果Table 4 Evaluation index calculation results of each predicted method
由表4可知,利用粒子群优化的支持向量机管道预测值与实际值基本一致,平均相对误差最大值为6.8%,其他3个测点平均相对误差均控制在4%以内,根均方误差接近于0,最大为0.261。BP神经网络预测值与实际值误差相对较大,相对误差在20%左右。就该测试工况而言,当机组与管道相关系数在0.67以上时,基于粒子群优化的支持向量机预测方法有效,泛化能力更强,可以得到较好的预测结果。
4 结 论
1)提出一种基于粒子群的支持向量机预测方法,SVM核函数选取主观因素干扰过多导致预测不准确,利用粒子群算法特有的记忆功能和动态跟踪全局优化特点,优化SVM核函数和惩罚因子,从而提高其预测准确度和精度。结合景电二期工程2号管道机组和管道现场实测数据,验证该方法的准确性和可行性。
2)根据原型观测数据,对振动信号进行频谱分析,计算各振源引起管道振动所占比重。由振源组成知,机组运行引起的管道振动所占比例在70%左右,表明机组运行是管道振动的主要原因。除管道3号测点外,管道其余5个测点振动信号与机组振动信号相关系数0.57以上,说明两者之间的振动响应有强耦合性。
3)针对该工程泵站测试工况,当机组与管道相关系数在0.67以上时,基于粒子群优化的支持向量机预测方法有效,对比PSO-SVM和BP神经网络预测结果和评价指标,PSO-SVM计算结果与真实值基本一致,平均相对误差最大为6.8%,根均方误差相对BP神经网络小一个数量级,更逼近于0,大大降低了预测误差。说明该方法克服了SVM计算缺陷,提高了模型计算精度。本文研究可为大型梯级泵站管道振动预测提供参考。
[1] 周邵萍,郝占峰,韩红飞,等. 基于应变模态差和神经网络的管道损伤识别[J]. 振动、测试与诊断,2015,35(2):334-338. Zhou Shaoping, Hao Zhanfeng, Han Hongfei, et al. Damage identification in straight pipeline using strain modal difference and neural network[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement and Diagnosis, 2015, 35(2): 334-338. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 张建伟,江琦,朱良欢,等. 基于改进HHT的泵站管道工作模态辨识[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(2):71-76. Zhang Jianwei, Jiang Qi, Zhu Lianghuan, et al. Modal parameter identification for pipeline of pumping station based on improved Hilbert-Huang transform[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(2): 71-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 张东山,张志忠,刘瑜,等. 基于压电阻抗方法的油气管道裂纹损伤定量研究[J]. 工程力学,2016,33(1):232-237. Zhang Dongshan, Zhang Zhizhong, Liu Yu, et al. Piezoelectric impedance-based quantitative study on oil and gas pipeline crack damage[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 33(1): 232-237. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 杜国锋,吴方红,周博,等. 基于压电阻抗方法的钢管裂纹损伤识别试验[J]. 武汉大学学报:工学版,2014,47(2):226―229. Du Guofeng, Wu Fanghong, Zhou Bo, et al. Experiment on crack damage identification of steel pipeline based on piezoelectric impedance method[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2014, 47(2): 226―229. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 刘晓霞. 基于有限元分析双层海底管道断裂失效问题[J].管道技术与设备,2016(7):14-16. Liu Xiaoxia. Subsea pipe-in-pipe fracture failure problem based on finite element method[J]. Pipeline Technique and Equipment, 2016(7): 14-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 马震岳,董毓新. 水轮发电机组动力学[M]. 大连:大连理工大学出版社,2003.
[7] 练继建,张辉东,王海军. 水电站厂房接哦故振动响应的神经网络预测[J]. 水力学报,2007,38(3):361-364. Lian Jijian, Zhang Huidong, Wang Haijun. Predication of vibration response of powerhouse structures by means of artificial neural network method[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007, 38(3): 361-364. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张龑,练继建,刘昉,等. 基于原型观测的厂顶溢流式水电站厂房结构振动特性研究[J]. 天津大学学报:自然科学与工程技术版,2015,48(7):584-590. Zhang Yan, Lian Jijian, Liu Fang, et al. Vibration characteristics of powerhouse structure of roof overflow hydropower station based on prototype observation[J]. Journal of Tianjin University: Science and Technology, 2015, 48(7): 584-590. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王海军,毛柳丹,练继建. 基于RVM方法的水电站厂房结构振动预测研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2015,34(3):23-27. Wang Haijun, Mao Liudan, Lian Jijian. Structural vibration prediction for a hydropower house based on RVM method[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(3): 23-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 张松兰. 支持向量机的算法及应用综述[J]. 江苏理工学院学报,2016,22(2):14-17. Zhang Songlan. A survey of improved algorithm and application on support vector machine[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University of Technology, 2016, 22(2): 14-17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 戴卫国,李海涛,颜恒平,等. 基于支持向量机改进算法的船舶类型识别研究[J]. 声学技术,2015,34(3):203-208. Dai Weiguo, Li Haitao, Yan Hengping, et al. Application of an improved support vector machine classification algorithmto underwater targets recognition[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2015, 34(3): 203-208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 辛斌,陈杰. 粒子群优化与差分进化混合算法的综述和分类[J]. 系统科学与数学,2011,31(9):1130-1150. Xin Bin, Chen Jie. A survey and taxonomy on hybrid algorithms based on particle swarm optimization and differential evolution[J]. Journal of Systems Science and Mathematical Sciences, 2011, 31(9): 1130-1150. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 李锋,吴华瑞,朱华吉,等. 基于改进粒子群算法的农产品召回优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(7):238-245. Li Feng, Wu Huarui, Zhu Huaji, et al. Optimization of agricultural products recall based on modified particle swarm algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(7): 238-245. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 郭澎涛,苏艺,茶正早,等. 基于BP 神经网络的橡胶苗叶片磷含量高光谱预测[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(增刊1):177-183. Guo Pengtao, Su Yi, Cha Zhengzao, et al. Prediction of leaf phosphorus contents for rubber seedlings based on hyperspectral sensitive bands and back propagation artificial neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(Supp.1): 177-183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 陈啸,王红英,孔丹丹,等. 基于粒子群参数优化和BP 神经网络的颗粒饲料质量预测模型[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(14):306-314. Chen Xiao, Wang Hongying, Kong Dandan, et al. Quality prediction model of pellet feed basing on BP network using PSO parameters optimization method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(14): 306-314. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 陈黎卿,张栋,陈无畏,等. 基于微粒子群优化算法的 差速器壳体轻量化设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(9):24-31. Chen Liqing, Zhang Dong, Chen Wuwei, et al. Lightweight design of differential case based on particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(9): 24-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李继猛,陈雪峰,何正嘉,等. 采用粒子群算法的冲击信号自适应单稳态随机共振检测方法[J]. 机械工程学报,2011,47(21):58-63. Li Jimeng, Chen Xuefeng, He Zhengjia, et al. Adaptive monostable stochastic resonance based on PSO with application in impact signal detection[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 47(21): 58-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 王华,刘耀林,姬盈利. 基于多目标微粒群优化算法的土地利用分区模型[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(12):237-244. Wang Hua, Liu Yaolin, Ji Yingli. Land use zoning model based on multi-objective particle swami optimization algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(12): 237-244. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 陈教料,陈教选,杨将新,等. 基于自加速遗传粒子群算法的半封闭式温室能耗预测[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(24):186-193. Chen Jiaoliao, Chen Jiaoxuan, Yang Jiangxin, et al. Prediction on energy consumption of semi-closed greenhouses based on self-accelerating PSO-GA[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(24): 186-193. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 冯晓莉,仇宝云. 考虑河道输水损失的大型泵站系统运行优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(17):35-41. Feng Xiaoli, Qiu Baoyun. Optimal operation for large pumping station system based on water transferring losses of river[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(17): 35-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 肖艳,姜琦刚,王斌,等. 基于Relief F 和PSO 混合特征选择的面向对象土地利用分类[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(4):211-216. Xiao Yan, Jiang Qigang, Wang Bin, et al. Object based land-use classification based on hybrid feature selection method of combining Relief F and PSO[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(4): 211-216. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 梁威,景博,焦晓璇,等. 基于进化支持向量机的机载燃油泵故障诊断及试验研究[J]. 机械强度,2016,38(5):933-939. Liang Wei, Jing Bo, Jiao Xiaoxuan, et al. Onboard fuel pump fault diagnosis based on improved support vector machine and experimental research[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2016, 38(5): 933-939. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 杨望灿,张培林,任国全,等. 基于模糊熵与LS-SVM 的轴承故障诊断[J]. 机械强度,2014,36(5):666-670. Yang Wangcan, Zhang Peilin, Ren Guoquan, et al. Bearing fault diagnosis based on fuzzy entropy and LS-SVM[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2014, 36(5): 666-670. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 杜福银. 基于神经网络的风力辅助提水系统自适应PID解耦控制[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(4):165-168. Du Fuyin. Adaptive PID decouple control strategy for wind power aided pumping water system based on neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(4): 165-168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 李震,洪添胜,Ning Wang,等. 基于神经网络预测的无线传感器网络田间射频信号路径损耗[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(12):178-181. Li Zhen, Hong Tiansheng, Ning Wang, et al. Path-loss prediction for radio frequency signal of wireless sensor network in field based on artificial neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(12): 178-181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] Tumenbayar Badrakh-Yeruul,夏安雄,张建华,等. 基于遗传算法的神经网络在爆破振动预测中的应用[J]. 爆破,2014,31(3):140-144. Tumenbayar Badrakh-Yeruul, Xia Anxiong, Zhang Jianhua, et al. Application of neural network based on genetic algorithm in prediction of blasting vibration[J]. Blasting, 2014, 31(3): 140-144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 黎明,何玉林,金鑫. 基于神经网络的风力机结构耦合振动预测模型[J]. 系统仿真学报,2009,21(2):413-417. Li Ming, He Yulin, Jin Xin. Coupled vibration forecasting of wind turbine based on artificial neural network[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2009, 21(2): 413-417. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 冯国胜,贾素梅,周玮. 基于BP神经网络的电控单体泵柴油机标定方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(15):21-26. Feng Guosheng, Jia Sumei, Zhou Wei. Calibration method for EUP diesel engine based on BP neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(15): 21-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 孙宗光,高赞明,倪一清. 基于神经网络的桥梁损伤位置识别[J]. 工程力学,2004,21(1):42-47. Sun Zongming, Ko Jianming, Ni Yiqing. Identification of damage location in bridge deck by neural network[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2004, 21(1): 42-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 刘鹏,范立云,白云,等. 高速电磁阀电磁力近似模型的构建与分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(16):96-101. Liu Peng, Fan Liyun, Bai Yun, et al. Modeling analysis of electromagnetic force approximate model of high-speed solenoid valve[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(16): 96-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Prediction of vibration response for pipeline of cascade pumping station based on PSO-SVM algorithm
Zhang Jianwei, Jiang Qi, Liu Xuanran, Ma Xiaojun
(College of Water Conservancy, North China University of Water Conservancy and Electric Power, Zhengzhou 450011, China)
Pipeline is a carrier of cascade pumping station with long distance water conveyance. Therefore, it is particularly important to keep the stable operation of pipeline structure. Because of the complexity and diversity of pipeline structure, it is difficult to measure vibration response signal of pipeline of pumping station. In order to minimize risks and ensure safe operation of pipeline, it is significant to search for some methods that use fewer unit monitoring data to forecast pipeline vibration state. Support vector machine (SVM) was designed as the core for the proposed prediction model considering its advantages in solving the small sample size, nonlinear and high dimensional pattern recognition, and so on. For the purpose of the improvement of data utilization efficiency, particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm was applied because of its advantage of special memory function. Combining advantages of PSO algorithm and SVM, a PSO-SVM prediction model was proposed in this paper. Global search tracking algorithm of PSO was used to optimize the kernel functions and penalty factors of SVM, which weakened the problem of low accuracy of prediction caused by SVM parameters optimization deficiency. The No.2 pipeline of Pumping Station 3 in Jindian River pumping irrigation was selected as the research object, which was connected with No.4 and No.5 units, and 3 points were set up at the top of the volute of the unit and on both sides of the tail of the volute respectively for these 2 units. First of all, based on the vibration monitoring data of units and pipeline, with the mathematical statistics theory and spectrum analysis, the dominant frequencies of pipeline structure were counted and the contribution rates of vibration sources were determined for pipeline vibration. At the same time, correlation coefficients of vibration between unit and pipeline were calculated. Except No.3 measuring point, the correlation coefficients of the other 5 measuring points were greater than 0.57, of which the correlation coefficients of No.1 and No.6 measuring points were relatively large. Strong coupling relationship between units and pipeline was determined. Selecting the unit monitoring vibration data in the different periods as input factors, and the pipeline vibration response data of vibration sensors #1, #2, #16 and #17 during corresponding periods as output factors, the PSO-SVM prediction model of pump station was established. In order to compare prediction accuracy, back propagation (BP) neural network was established with the same data for training and test. The results showed that the PSO-SVM prediction result coincided highly with actually measured data, and BP neural network only reflected the trend of pipeline vibration response. PSO-SVM prediction model had a fairly high promotion in prediction compared to BP neural network. Aiming to quantitatively compare 2 methods, mean relative error (MRE) and root mean square error (RMSE) were introduced as the evaluation indices. The maximum values of MRE and RMSE for PSO-SVM were 6.8% and 0.261, respectively, much lower than BP neural network. The research shows that, in this test condition, when the correlation coefficient between unit and pipeline is above 0.67, this proposed method can realize effectively vibration prediction of pipeline, which has stronger generalization ability so as to achieve the purpose of pipeline safe operation and online monitoring.
pumps; vibrations; optimization; pipeline; particle swarm; support vector machine; prediction
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.010
TV93; TB53
A
1002-6819(2017)-11-0075-07
张建伟,江 琦,刘轩然,马晓君. 基于PSO-SVM算法的梯级泵站管道振动响应预测[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(11):75-81.
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.010 http://www.tcsae.org
Zhang Jianwei, Jiang Qi, Liu Xuanran, Ma Xiaojun. Prediction of vibration response for pipeline of cascade pumping station based on PSO-SVM algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(11): 75-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.010 http://www.tcsae.org
2016-12-11
2017-05-14
国家自然科学基金(51679091);华北水利水电大学研究生教育创新计划基金(YK2015-02)
张建伟,男,河南洛阳,副教授,博士,主要从事水利水电工程的研究与教学工作。郑州 华北水利水电大学水利学院,450011。
Email:zjwcivil@126.com
