秀丽隐杆线虫衰老与衰老相关神经退行性疾病模型及药物筛选研究进展
2017-06-05薛晓利张建琴宋少娟李震宇秦雪梅
薛晓利,张建琴,宋少娟,李震宇,秦雪梅
(山西大学1.中医药现代研究中心,2.化学化工学院,山西太原 030006;3.长治医学院基础医学院,山西长治 046000)
·综 述·
秀丽隐杆线虫衰老与衰老相关神经退行性疾病模型及药物筛选研究进展
薛晓利1,2,张建琴1,宋少娟3,李震宇1,秦雪梅1
(山西大学1.中医药现代研究中心,2.化学化工学院,山西太原 030006;3.长治医学院基础医学院,山西长治 046000)
秀丽隐杆线虫(C.elegans)是生命科学领域非常重要的模式生物,具有寿命短、世代周期短、易于培养与观察等特点,因而被广泛用于生命科学研究,特别是在药物筛选和药物作用机制研究等方面。衰老是一个复杂的过程,是多因素共同作用的结果。在C.elegans中的抗衰老信号通路主要有3种,包括胰岛素-胰岛素样生长因子1信号通路、饮食限制信号通路和线粒体呼吸链/ATP合成信号通路。本文主要综述了基于以上3种信号通路的衰老模型以及基于以上衰老模型的抗衰老药物研究进展。此外,通过转基因或化学诱变可获得一些与衰老相关神经退行性疾病的C.elegans模型,包括帕金森病的α-突触核蛋白转基因模型、阿尔茨海默病的β-淀粉样蛋白沉积模型和亨廷顿舞蹈病的多聚谷氨酰胺聚集的转基因模型,总结了基于以上C.elegans疾病模型筛选的有效药物。
秀丽隐杆线虫;衰老;神经退行性疾病;药物筛选
随着当今社会人口老龄化的日益加重,人口老龄化已对我国社会经济的稳定和发展产生了深远影响,与此同时与衰老相关的疾病也引起了人们的广泛关注,如何安全有效地延缓衰老已成为医学界和社会关注的焦点,因而衰老机制的探索以及抗衰老药物的研究已成为当今社会研究的一大热点。在衰老与抗衰老研究中人们遴选出了各种动物衰老模型,如D-半乳糖(D-galactose,D-Gal)所致的亚急性大鼠衰老模型[1]、β淀粉样蛋白(β-amyloid protein,Aβ)致衰老模型[2]、去胸腺致衰老模型[3]、快速老化模型小鼠[4]、自然衰老鼠模型[5]、鱼类衰老模型[6]和果蝇衰老模型[7]等,都已广泛应用于抗衰老实验研究中。而秀丽隐杆线虫(Caenorhabditis ele⁃gans,C.elegans)是一种营自由生活的多细胞蠕虫,在20℃营养充足条件下从卵发育为成虫只需3 d。此外,C.elegans其遗传背景清楚,个体微小,身体透明,易于在实验室培养,生活周期短,基因组测序完成等特点,也可用于衰老与寿命的研究。
C.elegans作为模式生物研究寿命与衰老具有以下优点:①C.elegans生活周期短可模拟自然衰老,简化和缩短了实验周期。②对C.elegans做同步化处理,能严格控制实验条件提高可比性。③C.elegans体积较小便于收集和分析,有助于全面认识疾病的本质等。④C.elegans60%~80%基因与人类的相关基因是高度保守,因此可通过观察C.elegans的衰老通路来为人类的衰老疾病做更大的贡献。C.elegans衰老的生理与分子调控主要涉及3个信号通路,即胰岛素-胰岛素样生长因子1(insulin like growth factor 1,IGF-1)信号通路(insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway,IIS)、饮食限制信号通路和线粒体呼吸链/ATP合成信号通路[8]。
1 C.elegans的衰老模型
1.1 IIS模型
IIS是一个参与调控寿命的途径。在多种生物体如C.elegans、果蝇和哺乳动物中,衰老是通过IIS调控的,这表明IIS是一个进化保守的长寿调节器[9-11]。诸多研究表明,IIS可调控C.elegans寿命[12]。IIS能调控多尔(dauer)幼虫的形成[13],多尔幼虫能对抗逆境且不会老化[14]。IIS能影响C.elegans寿命,以胰岛素信号减弱、胰岛素敏感性增强和血浆IGF-1水平降低为共同特征,由于此过程涉及到多尔幼虫的形成,所以相关基因以daf命名。IIS作为一个调节寿命的关键调节器,在C.elegans衰老模型中强调特定基因突变后,C.elegans寿命能大幅度地延长。这些基因包括daf-2[15],age-1[16]和daf-16等[17]。目前通过C.elegans的IIS发现的抗衰老药物有绿原酸[18]、9种氨基酸(组氨酸、脯氨酸、丙氨酸、色氨酸、丝氨酸、谷氨酸、半胱氨酸、酪氨酸、赖氨酸)[19]、阿司匹林[20]、黄芪多糖[16]、蔓越橘提取物[21]、华茶藨子(Ribes fasciculatum)的乙酸乙酯提取部位[22]和睡茄素A(withanolide A)[23]等。
1.2 饮食限制的模型
饮食限制(dietary restriction,DR)是指在保证不过度饥饿前提下减少进食量。保持充足营养的情况下,减少热量的摄入能延长许多生物的寿命,这是目前比较公认的延长生物体寿命的理论。DR也可理解为热量限制,热量限制可通过沉默信息调节因子(silent information regulator,SIRT)介导的信号通路来延缓衰老,SIRT在果蝇中是最接近哺乳动物SIRT2的同源基因。SIRT起初被确定为基因沉默因子,但后来的研究表明,当它们高表达时,还能延长寿命[24]。此外,与物质能量代谢有关的基因(nac-2,nac-3和nhx-2)等在介导长寿进程中的调控机制也有研究。有3种方法可以在C.elegans中实现DR的处理:减少大肠杆菌OP50的喂饲量、使用因神经或肌肉受损而有进食缺陷的突变体(如eat-2突变型C.elegans)或在无大肠杆菌OP50的液体培养基中进行培养[14]。有研究表明,rBTI就是通过模仿DR来延长C.elegans的寿命[25]。
1.3 抑制线粒体呼吸链/ATP合成体系
对影响C.elegans寿命的突变体研究表明,线粒体产生的活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)对机体老化起着重要的作用,即C.elegans中ROS的水平是影响衰老的重要因素。齐墩果酸即通过降低ROS的水平延长C.elegans寿命[26]。尽管线粒体中的电子传递链非常高效,但还是有少部分的分子氧被部分还原,产生超氧阴离子,随后产生羟基自由基等其他氧自由基。如体内的ROS数量增多,就会造成脂质过氧化,导致机体器官的损伤,从而导致衰老的发生[27]。研究据此推测,适当抑制电子传递链可能有延长C.elegans寿命的作用。
1.4 基于C.elegans衰老模型的药物筛选进展
目前,已有116篇文献报道基于C.elegans发现潜在抗衰老药物,其中化学药所占比例为80%,植物药单体所占比例为15%,植物药提取物所占比例为5%。植物药单体包括绿原酸[18]、黄芩素[28]、槲皮素、白藜芦醇[29]、咖啡因[30]、咖啡酸、单宁酸、杨梅素[31]、茶氨酸、姜黄素[32]、迷迭香酸、菊苣酸(chicoric acid)[33]、金合欢素[34]、叶绿素[35]、叶酸[36]、松果菊苷(echinacoside)[37]和黄金树苷(specioside)[38]。植物药提取物包括rBTI[25]、黄芪多糖[16]、酪醇(tyro⁃sol)[39]、海藻糖、砂生槐乙醇提取物[40]、牡荆素(vi⁃texin)[41]、白及多糖[42]和三七多糖[43]。
2 与衰老相关的神经退行性疾病
神经退行性疾病(neurodegenerative diseases,ND)的发病原因是神经元进行性变性死亡,导致人体中枢神经系统等受损。ND的特点具有致病性蛋白的异常积累,如在阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer disease,AD)中的淀粉样蛋白的积累、亨廷顿舞蹈病(Huntington disease,HD)中的多聚谷氨酰胺(polyglutamine, PolyQ)的累积[44]等,导致渐进性神经功能障碍与特定的神经回路结构和功能的丧失,从而导致行为症状的出现。随着全球人口老龄化的逐年增加,ND发病率持续升高,给社会和家庭带来极大负担,鉴于迫切需要治疗这些毁灭性的疾病,许多研究人员已开发了用动物模型来筛选治疗ND的潜在新药物。
哺乳动物疾病模型可提供类似人的体内环境和大脑,直观地反映出药物的治疗效果、不良反应及毒副作用。但在哺乳动物模型系统中筛选药物非常昂贵,需要耗时的实验设计。此外,动物模型个体差异较大、数据采集干扰因素多、研究周期长、不能进行高通量药物筛选及成本高等使得用哺乳动物疾病模型筛选药物受到了限制。C.elegans作为整体动物模型,因其世代周期短、易进行操作、独特的病理行为、病理缺陷和简单的神经系统,被广泛运用于ND的潜在临床药物的筛选。C.elegans的神经系统结构虽比较简单,但它的神经元的功能和神经递质(如乙酰胆碱、5-羟色胺和多巴胺等)与其他高等动物类似,与ND相关的C.elegans疾病模型已构建[45]。下面简单介绍与ND有关的C.elegans模型。
2.1 帕金森病C.elegans模型
帕金森病(Parkinson disease,PD),是中老年人常见的神经系统变性疾病。随着年龄增高,发病率升高且男性稍多于女性。PD的病因现在还不很清楚,公认的病因是神经细胞的退行性病变,主要病变是多巴胺能神经元(dopaminergic neurons,DA)的减少和路易小体(Lewy bodies,LB)的聚集。在C.elegans中已成功制备了化学药物等所致的多巴胺神经元损伤模型和转基因路易小体聚集模型。
2.1.1 化学损伤模型
研究表明,1-甲基-4-苯基-1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶(1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine,MPTP)作用于人类可产生类似PD的症状、慢行性的进行性过程和变化。MPTP进入体内通过血脑屏障在神经胶质细胞中的单胺氧化酶(mono⁃amine oxidase,MAO)的作用下转化为有效成分1-甲基4-苯基吡啶离子(1-methyl-4-pehnylpyridine,MPP+),MPP+能选择性地破坏中脑中的黑质DA,从而诱导PD发生,因而MPTP被认为是诱导PD模型的有效药物。C.elegans暴露在MPTP/MPP+环境下,会出现C.elegans的活动力减弱和DA损伤等表型。再给予治疗PD的药物如麦角乙脲(lisuride)和阿扑吗啡等后,C.elegans上的PD表型会有所减弱[46]。
选择性损伤中脑黑质细胞的神经毒素6-羟多巴胺(6-hydroxydopamine,6-OHDA)是多巴胺递质羟基化的类似物。由于6-OHDA能在灵长类及较低等动物体内模拟类似PD的生理及病理特征,因此被广泛用于PD模型的制备,是目前体内外研究DA退变机制的常用毒素之一。C.elegans暴露在6-OHDA环境下,会表现出DA损伤的表型。在给予多巴胺D2受体激动剂后C.elegans上的PD表型会有所减弱[47]。此外,丹参酮I也可缓解这一症状[48]。有研究表明[49],黄芪甲苷不仅可抑制6-OHDA诱导的DA减少,同时可促进神经突增生、增加一氧化氮合酶(nitric oxide synthase,NOS)和酪氨酸酶(tyrosine enzyme,TE)免疫反应DA的数量。这一发现提示黄芪甲苷可开发成潜在治疗PD的临床用药。
2.1.2 α-突触核蛋白转基因C.elegans模型
α-突触核蛋白是路易小体中最为重要的蛋白,也是现今研究治疗PD的主要靶点之一。PD的主要病理特征是LB的聚集,因此PD的动物模型应以α-突触核蛋白的表达及其所产生的毒性为考察指标。因C.elegans自身不能表达α-突触核蛋白,所以必须通过人为地导入α-突触核蛋白基因建立转基因α-突触核蛋白C.elegansPD理想模型。有研究表明[50],丹参酮对α-突触核蛋白聚集有抑制作用,表明丹参酮可作为防治PD的潜在药物。以α-突触核蛋白基因建立转基因α-突触核蛋白C.elegans的PD模型有8类。导入的α-突触核蛋白基因主要在多巴胺神经元、组成型神经元和运动神经元中表达。且通过这种转基因模型已筛选出5种有效的抗衰老化合物(表1)。
2.2 阿尔茨海默病C.elegans模型
AD的发病机制不明确,病程呈慢性进行性,是老年期痴呆最常见的一种类型。AD的病因及发病机制尚未阐明,特征性病理变化为Aβ沉积形成的细胞外老年斑(senile plaque,SP)[56]和Tau蛋白过度磷酸化形成的神经细胞内神经原纤维缠结(neurofibrillary tangle,NFT)。这两种机制虽导致神经元凋亡或死亡的机制尚不明确,但这两个蛋白现已被确定是治疗AD的关键因素。有研究表明[57],黄酮和槲皮素可改善C.elegans和啮齿类中AD的表型。
2.2.1 淀粉样蛋白沉积C.elegans模型
Aβ是构成AD患者脑中老年斑块的主要成分。与Aβ形成相关的基因有早老素1(presenilin 1,PSEN1)、PSEN2以及淀粉样蛋白前体蛋白(amy⁃loid precursor protein,App)。C.elegans虽具有App同源基因apl-1,但由于apl-1表达的Apl-1蛋白缺乏Aβ[58],所以采用人源Aβ基因建立C.elegans的Aβ沉积模型。Aβ诱导的病理特征已在肌肉特异性的转基因C.elegans中被观察到,这为直接量化Aβ的毒性和验证潜在治疗AD的药物提供了一个良好的表型[59]。有研究表明[60],黄精多糖能预防Aβ诱导的神经毒性作用。
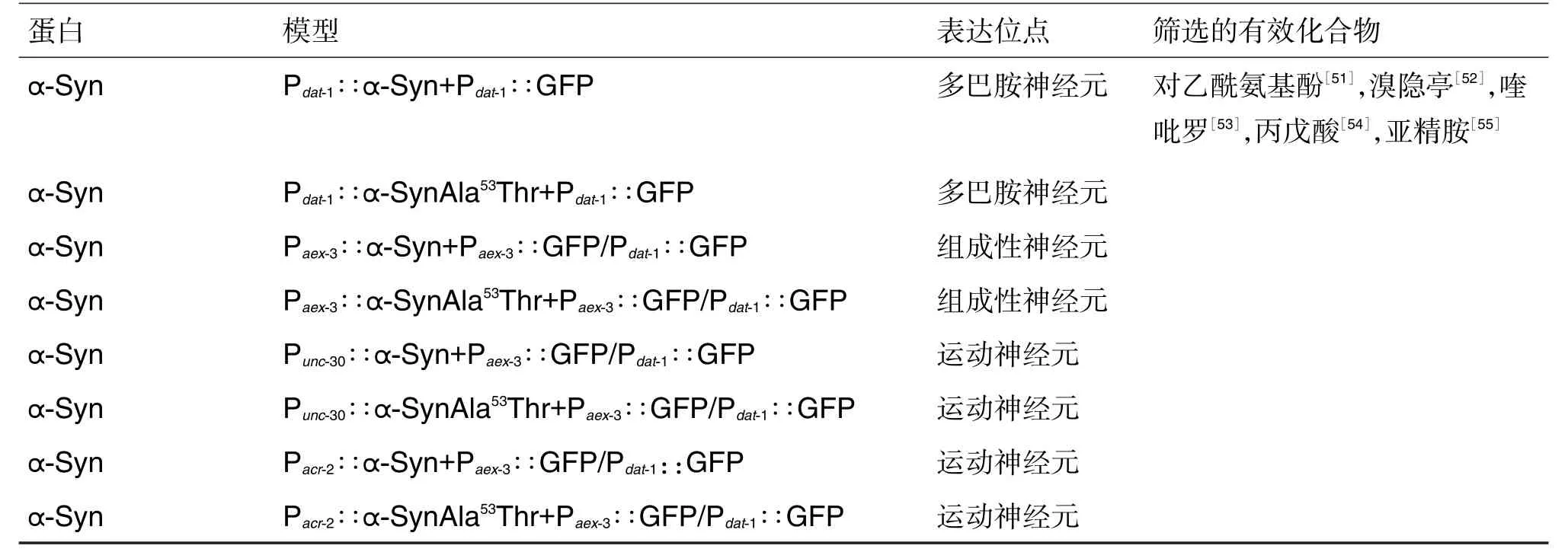
表1 帕金森病α-突触核蛋白(α-Syn)转基因秀丽隐杆线虫(C.elegans)模型
利用unc-54,myo-3和snb-1基因作为启动子的C.elegans的AD模型可产生有毒性的Aβ沉积。Link[61]首先在C.elegans中建立转unc-54/人Aβ1-42基因的模型CL2006。通过CL2006C.elegans模型已发现了一些具有神经保护作用的化合物。包括自然产物银杏内酯、大豆异黄酮、绿茶成分表没食子儿茶素、没食子酸酯和咖啡提取物。通过CL2006C.elegans发现这些老药还具有神经保护的作用,实现了老药的二次开发,对老药新用的发展起了极大的推动作用。美国FDA批准的药品单宁酸、杆菌肽、利福平、硫磺素T、利血平和抗抑郁药氟西汀[62]。此外,还有研究表明[63],番茄红素能缓解Aβ1-42蛋白积累导致的毒性。单宁酸主要用于抗炎和治疗痔疮、湿疹;利血平是一种降血压药物。此外,还有姜黄素和阿魏酸多酚类化合物。姜黄素具有抗炎、抗氧化和治疗心血管疾病的作用。Florez-McClure和Link的研究团队建立了转myo-3/人Aβ1-42基因的C.elegans模型CL4176[64],最近的研究表明,蔓越橘提取物也能缓解CL4176模型中Aβ沉积的毒性[65]。此外,还有转snb-1/Aβ1-42基因的CL2241C.elegans线虫模型[64]。
2.2.2 Tau蛋白过度磷酸化C.elegans模型
Tau蛋白为含磷酸基的蛋白,正常成熟脑中的Tau蛋白分子含2~3个磷酸基。而AD患者脑的Tau蛋白则异常过度磷酸化,每分子Tau蛋白可含5~9个磷酸基,并丧失正常生物功能。Tau蛋白的沉积是AD的常见特征。
C.elegans中虽有单一的与Tau同源的基因ptl-1,但因ptl-1功能的缺失并不能完整表达Tau蛋白的病理特征,所以通常采用人源Tau蛋白基因建立转基因的Tau蛋白C.elegans模型。在C.elegans中,转入异常磷酸化的人源Tau蛋白可造成AD模型,研究人员可通过这个模型以间接方式进行AD疾病的评估,如运动受损和寿命缩短等;也可通过这个模型以直接方式进行AD疾病评估,如通过介入荧光蛋白直接观察神经元的损失过程。随着年龄增长,Tau蛋白过度磷酸化C.elegans模型表现出不溶性磷酸化Tau蛋白逐渐增多、神经元细胞的退化和减少以及运动的不协调性。
通过Tau蛋白C.elegans模型已经发现了一些化合物能改善神经元的活性和C.elegans的运动能力,如姜黄素[66]。还有研究表明,多巴胺D2受体拮抗剂可被确定为针对Tau蛋白诱导的神经毒性的一种有效策略,它可减少不溶性Tau蛋白的水平,提高C.elegans的蠕动能力[67]。如抗精神病药,阿扎哌隆(氮哌酮,azaperone)、奋乃静(perphenazine)和佐替平(泽坦平,zotepine)均能改进Tau蛋白C.elegans模型的表型特征。最近的一项研究报告表明[68],抗癫痫药物乙琥胺(ethosuximide)能改善Tau V337 MC.elegans受损的运动能力并延长其寿命。
通过在肌肉和神经元中导入人源Aβ基因建立的Aβ沉积C.elegans模型有8种,分别为CL2006,CL2010,CL2109,CL3115,CL4176,CL2241,CL2355和CL2337,其中通过CL2006模型筛选出10种化合物,通过CL2010模型筛选出1种化合物,通过CL4176模型筛选出5种化合物,CL2355模型筛选出1种化合物(表2)。
2.3 亨廷顿舞蹈病C.elegans模型
HD是一种最为常见的polyQ疾病,是由位于亨廷顿蛋白(Huntingtin protein,Htt)N端的一段重复的谷氨酰胺序列过度延长引起的,其对周围神经组织造成严重影响,甚至会使神经元丧失功能。不同长度的polyQ蛋白能在特定的神经元,肌细胞,甚至肠细胞中表达,从而成为被广泛用于polyQ神经毒性几个方面的模型,特别是解决底层聚集倾向的蛋白质对细胞的影响机制和确定新的疾病的潜在指示物[80]。在C.elegansHD模型中,polyQ介导的神经毒性与年龄和poly Q长度相关。有研究表明,红景天苷能减弱polyQ蛋白介导的ND[81]。
由于C.elegans自身无相应基因,不能表达Htt蛋白,所以通常采用人源htt基因建立转基因HDC.elegans模型。在C.elegans中过表达变异的Htt,就能模拟HD的表型。Hart的科研小组建立了osm-10/Htt-Q150的C.elegans模型。该模型利用osm-10作为启动子,引入含有重复表达150个多聚谷氨酰胺的htt基因片段,可在C.elegans的感受神经元中表达Htt-Q150,从而导致神经元功能的失调[82]。
通过polyQ聚集构建的模型主要分为3类:第一类是polyQ在肌细胞中聚集(AM141),通过该模型筛选出1种有效化合物;第二类是polyQ在神经元细胞中聚集(HA759),通过该模型筛选出7种有效化合物;第三类是polyQ在触觉细胞中聚集(ID24),通过该模型筛选出1种化合物(表3)。

表2 阿尔茨海默病转基因C.elegans模型
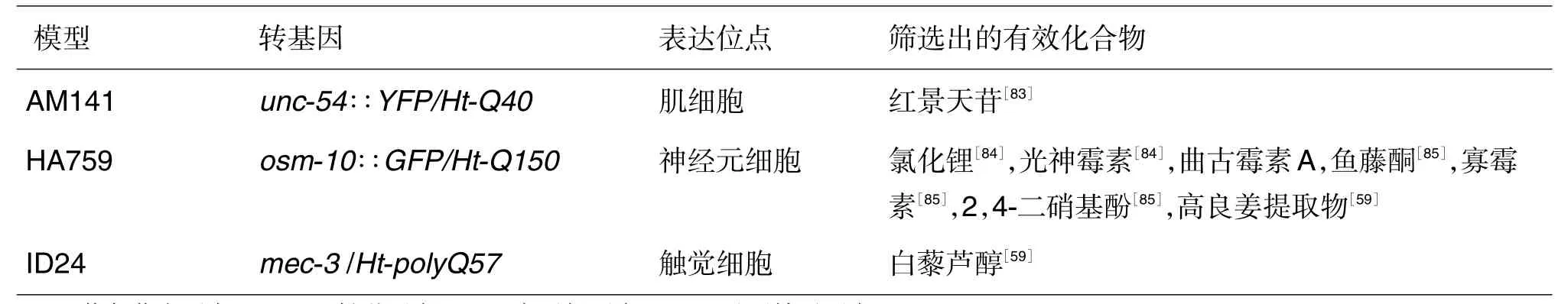
表3 亨廷顿舞蹈病转基因C.elegans模型
2.4 C.elegans与衰老相关神经退行性疾病模型及药物筛选比例研究
目前,已有大量文献报道了基于C.elegans模型发现潜在治疗人类ND的药物,其中治疗AD的药物占比为35%,治疗HD的药物占比为21%,治疗PD药物占比为13%,其他相关疾病占比为31%。由此可见,目前学者主要研究热点还是利用C.elegans模型筛选潜在的治疗人类3种常见ND的药物。基于C.elegans已发现潜在治疗AD的药物中,化学药占比为48%,植物药单体为33%和植物药提取物为19%。基于C.elegans已发现的潜在治疗HD的药物中,三者分别为75%,19%和6%。基于C.elegans已发现的潜在治疗PD的药物均为化学药。由于化学药的成分单一,结构清晰,因此采用C.elegans模型筛选潜在治疗人类ND的化药以及进一步深入研究药物发挥药效的机制是目前该研究方向的热点,借鉴化学药的研究理念,科研工作者也在不断努力将C.elegans模型用于植物药的快速筛选中,尤其是植物药单体的快速筛选取得了可喜的进展。
3 结语
模式生物C.elegans可通过同步化处理排除个体间的差异,数据采集的干扰因素少,生活周期短,表型易观察,可实现药物的高通量筛选,成本低且其基因组测序早已完成,许多信号通路与人类是同源的。因此,以C.elegans为研究对象可进行药物的快速筛选也可便捷地了解许多人类疾病的发病机制,从而能更好地采取相应措施来预防疾病。C.elegans的研究数据也可预测药物-靶标相互作用和确证靶点。目前,已有大量的文献报道基于C.elegans筛选的潜在抗衰老药物及与衰老相关的ND药物,其中化学药占比为74%,植物药单体为14%,植物药提取物为12%。由此可见,采用C.elegans快速筛选化学药的药效和药理是加快研发新药的成功典范,而将C.elegans用于植物药的快速筛选才刚起步,未来在科研工作者的不断探索和努力下,将C.elegans成功地应用于植物药的快速筛选中,会加快推进植物药的“老药新用”的新药研发进程,为植物药的开发和利用提供一种更加快速、便捷的动物模型。同时也将促进我国中草药行业的发展。
[1]Haider S,Liaquat L,Shahzad S,Sadir S,Madiha S,Batool Z,et al.A high dose of short term exoge⁃nous D-galactose administration in young male rats produces symptoms simulating the natural aging process[J].Life Sci,2015,124:110-119.
[2]Liu L,Zhao YH,Zeng CQ,Zeng Y.Research progress in pharmacological effects ofUncariaon Alzheimer disease models[J].Acta Pharm Sin(药学学报),2016,51(4):536-542.
[3]Novoseletskaya AV,Kiseleva NM,Zimina IV,Bystrova OV,Belova OV,Inozemtsev AN,et al. Thymus polypeptide preparation tactivin restores learning and memory in thymectomied rats[J].Bull Exp Biol Med,2015,159(5):623-625.
[4]Sasaki K,Han J,Shimozono H,Villareal MO,Isoda H.Caffeoylquinic acid-rich purple sweet potato extract,with or without anthocyanin,imparts neuro⁃protection and contributes to the improvement of spatial learning and memory of SAMP8 mouse[J].J Agric Food Chem,2013,61(21):5037-5045.
[5]Salazar C,Valdivia G,Ardiles ÁO,Ewer J,Palacios AG.Genetic variants associated with neurodegenerative Alzheimer disease in natural models[J].Biol Res,2016,49:14.
[6]Bailey JM,Oliveri AN,Levin ED.Pharmacological analyses of learning and memory in zebrafish(Danio rerio)[J].Pharmacol Biochem Behav,2015,139(Pt B):103-111.
[7]Yan ML,Zhou YZ,Li MH,Gao L,Qin XM,Du GH. Metabonomic study of alcohol extract from Radix Scutellariae in prolonging lifespan ofDrosophila melanogasterbased on1H-NMR[J].Chin Tradit Herb Drugs(中草药),2016,47(10):1714-1722.
[8]Chen D,Pan KZ,Palter JE,Kapahi P.Longevity determinedbydevelopmentalarrestgenesinCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Aging Cell,2007,6(4):525-533.
[9]Hesp K,Smant G,Kammenga JE.Caenorhabditis elegansDAF-16/FOXO transcription factor and its mammalian homologs associate with age-related disease[J].Exp Gerontol,2015,72:1-7.
[10]Altintas O,Park S,Lee SJ.The role of insulin/IGF-1 signaling in the longevity of model invertebrates,C. elegansandD.melanogaster[J].BMB Rep,2016,49(2):81-92.
[11]Xu T,Li P,Wu S,Li D,Wu J,Raley-Susman KM,et al.Chronic exposure to perfluorooctane sulfo⁃nate reduces lifespan ofCaenorhabditis elegansthrough insulin/IGF-1 signaling[J].Bull Environ Contam Toxicol,2016,97(1):119-123.
[12]Chen Y,Onken B,Chen H,Xiao S,Liu X,Driscoll M,et al.Mechanism of longevity exten⁃sion ofCaenorhabditis elegansinduced by penta⁃galloyl glucose isolated fromEucalyptusleaves[J].J Agric Food Chem,2014,62(15):3422-3431.
[13]Ewald CY,Landis JN,Porter Abate J,Murphy CT,Blackwell TK.Dauer-independent insulin/IGF-1-signal⁃ling implicates collagen remodelling in longevity[J].Nature,2015,519(7541):97-101.
[14]Rodrigues RP, Kaul TK, Ho JH, Lucanic M,Burkewitz K,Mair WB,et al.Synthetic ligands of cannabinoid receptors affect dauer formation in the nematodeCaenorhabditis elegans[J].G3(Bethesda),2016,6(6):1695-1705.
[15]Hu JP,Xu XY,Huang LY,Wang LS,Fang NY. Freeze-thawCaenorhabditis elegansfreeze-thaw stress response is regulated by the insulin/IGF-1 receptor DAF-2[J].BMC Genet,2015,16:139.
[16]Zhang H,Pan N,Xiong S,Zou S,Li H,Xiao L,et al.Inhibition of polyglutamine-mediated proteo⁃toxicity byAstragalus membranaceuspolysaccha⁃ride through the DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor inCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Biochem J,2012,441(1):417-424.
[17]Zamberlan DC,Amaral GP,Arantes LP,Machado ML,Mizdal CR,Campos MM,et al.Rosmarinus officinalisL.increasesCaenorhabditiselegansstress resistance and longevity in a DAF-16,HSF-1 and SKN-1-dependent manner[J].Braz J Med Biol Res,2016,49(9):e5235.
[18]ZhengSQ,HuangXB,XingTK,DingAJ,Wu GS,Luo HR.Chlorogenic acid extends the lifespan ofCaenorhabditis elegansvia insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway[J].J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci,2017,72(4):464-472.
[19]Edwards C,Canfield J,Copes N,Brito A,Rehan M5,Lipps D,et al.Mechanisms of amino acidmediated lifespan extension inCaenorhabditis ele⁃gans[J].BMC Genet,2015,16:8.
[20] Ayyadevara S,Bharill P,Dandapat A,Hu C,Khaidakov M,Mitra S,et al.Aspirin inhibits oxidant stress,reduces age-associated functional declines,and extends lifespan ofCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Antioxid Redox Signal,2013,18(5):481-490.
[21]Guha S,Cao M,Kane RM,Savino AM,Zou S,Dong Y.The longevity effect of cranberry extract inCaenorhabditis elegansis modulated by DAF-16 and OSR-1[J].Age(Dordr),2013,35(5):1559-1574.
[22] Jeon H,Cha DS.Anti-aging properties ofRibes fasciculatuminCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Chin J Nat Med,2016,14(5):335-342.
[23] Akhoon BA,Pandey S,Tiwari S,Pandey R.With⁃anolide A offers neuroprotection,ameliorates stress resistance and prolongs the life expectancy ofCaenorhabditiselegans[J].ExpGerontol,2016,78:47-56.
[24]Bamps S,Wirtz J,Savory FR,Lake D,Hope IA. TheCaenorhabditis eleganssirtuin gene,sir-2.1,is widely expressed and induced upon caloric restriction[J].Mech Ageing Dev,2009,130(11-12):762-770.
[25] LiJ,CuiX,WangZ,LiY.rBTIExtendsCaenorhabditiseleganslifespan bymimicking calorie restriction[J].Exp Gerontol,2015,67:62-71.
[26] Zhang J,Lu L,Zhou L.Oleanolic acid activates DAF-16 to increase lifespan inCaenorhabditis elegans[J].BiochemBiophysResCommun,2015,468(4):843-849.
[27] Zhao J,Chen C,Wang YF,Wang H,Huang J,Wang H.Protective effect of hawthorn fruht extract on the acute oxidative damage inCaenorhabditis elegans[J].China Food Addit(中国食品添加剂),2015,10:53-57.
[28] Havermann S,Humpf HU,Wätjen W.Baicalein modulates stress-resistance and life span inC.elegansvia SKN-1 but not DAF-16[J].Fitoterapia,2016,113:123-127.
[29]Lee J,Kwon G,Park J,Kim JK,Lim YH.Brief communication:SIR-2.1-dependent lifespan exten⁃sion ofCaenorhabditis elegansby oxyresveratrol and resveratrol[J].Exp Biol Med(Maywood),2016,241(16):1757-1763.
[30]Bridi JC,Barros AG,Sampaio LR,Ferreira JC,Antunes Soares FA,Romano-Silva MA.Lifespan extension induced by caffeine inCaenorhabditis elegansis partially dependent on adenosine signaling[J].Front Aging Neurosci,2015,7:220.
[31]Büchter C,Ackermann D,Havermann S,Honnen S,Chovolou Y,Fritz G,et al.Myricetin-mediated lifespan extension inCaenorhabditis elegansis modulated by DAF-16[J].Int J Mol Sci,2013,14(6):11895-11914.
[32]Liao VH,Yu CW,Chu YJ,Li WH,Hsieh YC,Wang TT.Curcumin-mediated lifespan extension inCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Mech Ageing Dev,2011,132(10):480-487.
[33] Schlernitzauer A,Oiry C,Hamad R,Galas S,Cortade F,Chabi B,et al.Chicoric acid is an anti⁃oxidant molecule that stimulates AMP kinase pathway in L6 myotubes and extends lifespan inCaenorhab⁃ditis elegans[J].PLoS One,2013,8(11):e78788.
[34]Asthana J,Mishra BN,Pandey R.Acacetin pro⁃motes healthy aging by altering stress response inCaenorhabditiselegans[J].FreeRadicRes,2016,50(8):861-874.
[35]Wang E,Wink M.Chlorophyll enhances oxidative stress tolerance inCaenorhabditis elegansand extends its lifespan[J].Peer J,2016,4:e1879.
[36]Rathor L,Akhoon BA,Pandey S,Srivastava S,Pandey R.Folic acid supplementation at lower doses increases oxidative stress resistance and longevity inCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Age(Dordr),2015,37(6):113.
[37]Wang X,Zhang J,Lu L,Zhou L.The longevity effect of echinacoside inCaenorhabditis elegansmediated through DAF-16[J].Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,2015,79(10):1676-1683.
[38]Asthana J,Yadav AK,Pant A,Pandey S,Gupta MM,Pandey R.Specioside ameliorates oxidative stress and promotes longevity inCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol,2015,169:25-34.
[39]Cañuelo A,Esteban FJ,Peragón J.Gene expression profiling to investigate tyrosol-induced lifespan exten⁃sion inCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Eur J Nutr,2016,55(2):639-650.
[40]Li X,Han J,Zhu R,Cui R,Ma X,Dong K.Life span and motility effects of ethanolic extracts fromSophora moorcroftianaseeds onCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Pharmacogn Mag,2016,12(Suppl 2):S228-S230.
[41]Lee EB,Kim JH,Cha YS,Kim M,Song SB,Cha DS,et al.Lifespan extending and stress resis⁃tant properties of vitexin fromVigna angularisinCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Biomol Ther(Seoul),2015,23(6):582-589.
[42]Zhang Y,Lv T,Li M,Xue T,Liu H,Zhang W,et al.Anti-aging effect of polysaccharide fromBletilla striataon nematodeCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Pharmacogn Mag,2015,11(43):449-454.
[43]Feng S,Cheng H,Xu Z,Shen S,Yuan M,Liu J,et al.Thermal stress resistance and aging effects ofPanax notoginsengpolysaccharides onCaenorhab⁃ditis elegans[J].Int J Biol Macromol,2015,81:188-194.
[44] BourdenxM, KoulakiotisNS, SanoudouD,Bezard E,Dehay B,Tsarbopoulos A.Protein aggregation and neurodegeneration in prototypical neurodegenerative diseases:examples of amy⁃loidopathies,tauopathies and synucleinopathies[J/OL].Prog Neurobiol,[2016-08-10].http://dx. doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.07.003.
[45]Nussbaum-Krammer CI,Morimoto RI.Caenorhab⁃ditis elegansas a model system for studying non-cellautonomous mechanisms in protein-misfolding diseases[J].Dis Model Mech,2014,7(1):31-39.
[46]Zhang N,Li Y,Gao T,Li GJ.The review of human disease model studies usingCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Chin J Food Hyg(中国食品卫生杂志),2014,26(4):398-403.
[47]Marvanova M,Nichols CD.Identification of neuro⁃protective compounds ofCaenorhabditis elegansdopaminergic neurons against 6-OHDA[J].J Mol Neurosci,2007,31(2):127-137.
[48]Jing X,Wei X,Ren M,Wang L,Zhang X,Lou H. Neuroprotective effects of tanshinoneⅠ against 6-OHDA-induced oxidative stress in cellular and mouse model of Parkinson′s disease through upregulating Nrf2[J].Neurochem Res,2016,41(4):779-786.
[49]Chan WS,Durairajan SS,Lu JH,Wang Y,Xie LX,Kum WF,et al.Neuroprotective effects of astragalosideⅣin 6-hydroxydopamine-treated primary nigral cell culture[J].Neurochem Int,2009,55(6):414-422.
[50]Ji K,Zhao Y,Yu T,Wang Z,Gong H,Yang X,et al. Inhibition effects of tanshinone on the aggre-gation of α-synuclein[J].Food Funct,2016,7(1):409-416.
[51] Lakso M,Vartiainen S,Moilanen AM,Sirviö J,Thomas JH,Nass R,et al.Dopaminergic neuronal loss and motor deficits inCaenorhabditis elegansoverexpressing human alpha-synuclein[J].J Neuro⁃chem,2003,86(1):165-172.
[52]Settivari R,Levora J,Nass R.The divalent metal transporter homologues SMF-1/2 mediate dopamine neuron sensitivity inCaenorhabditis elegansmodels of manganism and Parkinson disease[J].J Biol Chem,2009,284(51):35758-35768.
[53]Cao S,Gelwix CC,Caldwell KA,Caldwell GA. Torsin-mediated protection from cellular stress in the dopaminergic neurons ofCaenorhabditis elegans[J].J Neurosci,2005,25(15):3801-3812.
[54]Kuwahara T,Koyama A,Gengyo-Ando K,Masuda M,Kowa H,Tsunoda M,et al.Familial Parkinson mutant alpha-synuclein causes dopamine neuron dysfunction in transgenicCaenorhabditis elegans[J].J Biol Chem,2006,281(1):334-340.
[55]Büttner S,Broeskamp F,Sommer C,Markaki M,Habernig L,Alavian-Ghavanini A,et al.Spermi⁃dine protects against α-synuclein neurotoxicity[J].Cell Cycle,2014,13(24):3903-3908.
[56]Selkoe DJ,Hardy J.The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer′s disease at 25 years[J].EMBO Mol Med,2016,8(6):595-608.
[57]Kong Y,Li K,Fu T,Wan C,Zhang D,Song H,et al.Quercetin ameliorates Aβ toxicity inDrosophilaAD model by modulating cell cycle-related proteinex⁃pression[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(42):67716-67731.
[58]Ewald CY,Marfil V,Li C.Alzheimer-related protein APL-1 modulates lifespan through heterochronic gene regulation inCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Aging Cell,2016,15(6):1051-1062
[59]Chen X,Barclay JW,Burgoyne RD,Morgan A. UsingC.elegansto discover therapeutic compounds for ageing-associated neurodegenerative diseases[J].Chem Cent J,2015,9:65.
[60]Zhang H,Cao Y,Chen L3 Wang J,Tian Q,Wang N,et al.A polysaccharide fromPolygonatum sibiricumattenuates amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells[J].Carbohydr Polym,2015,117:879-886.
[61]Link CD.Expression of human beta-amyloid peptide in transgenicCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1995,92(20):9368-9372.
[62]Chen X,Barclay JW,Burgoyne RD,Morgan A. UsingC.elegansto discover therapeutic compounds for ageing-associated neurodegenerative diseases[J].Chem Cent J,2015,9:65.
[63]Chen W,Mao L,Xing H,Xu L,Fu X,Huang L,et al.Lycopene attenuates Aβ1-42secretion and its toxicity in human cell andCaenorhabditis elegansmodels of Alzheimer disease[J].Neurosci Lett,2015,608:28-33.
[64]Link CD.C.elegansmodels of age-associatedneurodegenerative diseases:lessons from trans⁃genic worm modelsof Alzheimer′s disease[J].Exp Gerontol,2006,41(10):1007-1013.
[65]Guo H,Dong YQ,Ye BP.Cranberry extract supple⁃mentation exerts preventive effects through alleviating Aβ toxicity inCaenorhabditis elegansmodel of Alzheimer′s disease[J].Chin J Nat Med,2016,14(6):427-433.
[66] Miyasaka T,Xie C,Yoshimura S,Shinzaki Y,Yoshina S, Kage-Nakadai E,et al.Curcumin improves tau-induced neuronaldysfunction of nematodes[J].Neurobiol Aging,2016,39:69-81.
[67]McCormick AV, WheelerJM, Guthrie CR,Liachko NF,Kraemer BC.Dopamine D2 receptor antagonism suppresses tau aggregation and neuro⁃toxicity[J].Biol Psychiatry,2013,73(5):464-471.
[68] Chen X,McCue HV,Wong SQ,Kashyap SS,Kraemer BC,Barclay JW,et al.Ethosuximide ameliorates neurodegenerative disease pheno⁃types by modulating DAF-16/FOXO target gene expression[J].Mol Neurodegener,2015,10:51.
[69]Diomede L,Rigacci S,Romeo M,Stefani M,Salmona M.Oleuropein aglycone protects trans⁃genicC.elegansstrains expressing Aβ42by reduc⁃ing plaque load and motor deficit[J].PLoS One,2013,8(3):e58893.
[70]Gutierrez-Zepeda A,Santell R,Wu Z,Brown M,Wu Y,Khan I,et al.Soy isoflavone glycitein protects against beta amyloid-induced toxicity and oxidative stress in transgenicCaenorhabditis elegans[J].BMC Neurosci,2005,6:54.
[71]Abbas S,Wink M.Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits betaamyloidoligomerizationinCaenorhabditis elegansand affects the DAF-2/insulin-like signaling pathway[J].Phytomedicine,2010,17(11):902-909.
[72]Dostal V,Roberts CM,Link CD.Genetic mecha⁃nisms of coffee extract protection in aCaenorhabditis elegansmodel of β-amyloid peptide toxicity[J].Genetics,2010,186(3):857-866.
[73] Lublin A,Isoda F,Patel H,Yen K,Nguyen L,Hajje D,et al.FDA-Approved drugs that protect mammalian neurons from glucose toxicity slow aging dependent on Cbp and protect against pro⁃teotoxicity[J].PLoS One,2011,6(11):e27762.
[74]Arya U,Dwivedi H,Subramaniam JR.Reserpine ameliorates Abeta toxicity in the Alzheimer′s disease model inCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Exp Gerontol,2009,44(6-7):462-466.
[75] Alavez S,Vantipalli MC,Zucker DJ,Klang IM, Lithgow GJ.Amyloid-binding compounds maintain protein homeostasis during ageing and extend lifespan[J].Nature,2011,472(7342):226-229.
[76]Keowkase R,Aboukhatwa M,Luo Y.Fluoxetine protects against amyloid-beta toxicity,in part via DAF-16 mediated cell signaling pathway,inCaenorhabditis elegans[J].Neuropharmacology,2010,59(4-5):358-365.
[77] Schneider LS,Dagerman KS,Insel P.Risk of death with atypical antipsychotic drug treatment for dementia:meta-analysis of randomized place⁃bo-controlled trials[J].JAMA,2005,294(15):1934-1943.
[78]Sangha JS,Sun X,Wally OS,Zhang K,Ji X,Wang Z,et al.Liuwei Dihuang(LWDH),a tradi⁃tional Chinese medicinal formula,protects against β-amyloid toxicity in transgenicCaenorhabditis elegans[J].PLoS One,2012,7(8):e43990.
[79] Diomede L,Cassata G,Fiordaliso F,Salio M,Ami D,Natalello A,et al.Tetracycline and its analogues protectCaenorhabditis elegansfrom β amyloid-induced toxicity by target in goligomers[J].Neurobiol Dis,2010,40(2):424-431.
[80]Machiela E,Dues DJ,Senchuk MM,Van Raams⁃donk JM.Oxidative stress is increased inC.elegansmodels of Huntington′s disease but does not con⁃tribute to polyglutamine toxicity phenotypes[J].Neurobiol Dis,2016,96:1-11.
[81]Xiao L,Li H,Zhang J,Yang F,Huang A,Deng J,et al.Salidroside protectsCaenorhabditis elegansneurons from polyglutamine-mediated toxicity by reducing oxidative stress[J].Molecules,2014,19(6):7757-7769.
[82]Calamini B,Lo DC,Kaltenbach LS.Experimental models for identifying modifiers of polyglutamineinduced aggregation and neurodegeneration[J].Neurotherapeutics,2013,10(3):400-415.
[83]Silva DF,Esteves AR,Oliveira CR,Cardoso SM. Mitochondria:the common upstream driver of amyloid-β and tau pathology in Alzheimer′s disease[J].Curr Alzheimer Res,2011,8(5):563-572.
[84]Voisine C,Varma H,Walker N,Bates EA,Stockwell BR,Hart AC.Identification of potential therapeutic drugs for Huntington′s disease usingCae⁃norhabditis elegans[J].PLoS One,2007,2(6):e504.
[85]VarmaH,ChengR,VoisineC,HartAC,Stockwell BR.Inhibitors of metabolism rescue cell death in Huntington′s disease models[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2007,104(36):14525-14530.
Aging and aging related neurodegenerative disease models and drug screening based on Caenorhabditis elegans:research progress
XUE Xiao-li1,2,ZHANG Jian-qin1,SONG Shao-juan3,LI Zhen-yu1,QIN Xue-mei1
(1.Modern Research Center for Traditional Chinese Medicine,2.College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Shanxi University,Taiyuan 030006,China;3.Basic Medical School,Changzhi Medical College,Changzhi 046000,China)
Caenorhabditis elegansis a very important model organism in life sciences.C.eleganshas been widely used in research on life sciences,especially in drug screening and the mechanism of drugs,thanks to some of their prominent characteristics,including a short life,short generation cycle, and easy culture and observation.Aging is a complex process,which is the result of multiple factors. There are mainly three types of anti-aging signal pathways inC.elegans,including insulin-insulin-like growth factor-1 signal pathway,diet-restricted signaling pathway and mitochondrial respiratory chain/ ATP synthesis pathway.In this paper,we reviewed the aging models based on the above three signaling pathways and the progress in anti-aging drugs based on the above aging models.In addition,a number ofC.elegansmodels of aging-related neurodegenerative diseases can be obtained by using transgenic or chemical mutagenesis.Thus,this paper reviewed the transgenic models ofC.elegansassociated with neurodegenerative diseases,including the α-synuclein transgenic model of Parkinson disease,the β-amyloid deposition model of Alzheimer disease,and the polyQ of Huntington disease,and summa⁃rized the effective drugs based on the above disease models.This review will provide reference for the study ofC.elegansin the future screening of anti-aging drugs and drug screening for the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Caenorhabditis elegans;aging;neurodegenerative disease;drug screening
The project supported by Program of Science and Technology of Higher Education of Shanxi Province (2015119);Shanxi Provincial Key Team of Scientific and Technological Innovation(201605D131045-18);and Program of Applied Basic Research of Shanxi Province(201601D202058)
ZHANG Jiang-qin,E-mail:jiangqinzh3@sxu.edu.cn,Tel:(0351)7018379;QIN Xue-mei,E-mail: qinxm@sxu.edu.cn
R965
:A
:1000-3002-(2017)05-0429-10
10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2017.05.008
2016-09-10 接受日期:2017-02-10)
(本文编辑:乔 虹)
山西省高等学校科技创新项目(2015119);山西省科技创新重点团队(201605D131045-18);山西省应用基础研究项目(201601D202058)
薛晓利,女,硕士研究生,主要从事基于模式生物的中药活性成分筛选研究,Tel:15735175892,E-mail:695029166@qq.com;张建琴,女,博士,讲师,硕士生导师,主要从事基于模式生物的中药活性成分筛选研究。
张建琴,E-mail:jiangqinzh3@sxu.edu.cn,Tel:(0351)7018379;秦雪梅,E-mail:qinxm@sxu.edu.cn
