海水氨氮检测技术研究进展
2017-06-01刘淑文丁家旺
于 涵,丁 兰,刘淑文,丁家旺,秦 伟*
(1.中国科学院 海岸带环境过程与生态修复重点实验室 山东省海岸带环境过程重点实验室 中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所,山东 烟台 264003;2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049;3.大连理工大学,辽宁 大连 116024)
海水氨氮检测技术研究进展
于 涵1,2,丁 兰3,刘淑文1,2,丁家旺1,秦 伟1*
(1.中国科学院 海岸带环境过程与生态修复重点实验室 山东省海岸带环境过程重点实验室 中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所,山东 烟台 264003;2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049;3.大连理工大学,辽宁 大连 116024)
氨氮(NH3-N)是溶解无机氮的重要组成之一,其含量是重要的营养盐指标。海水氨氮是上层海洋氮循环的重要组成部分,也是海洋浮游植物所必需的营养物质之一。氨氮浓度与海洋生物生命活动密切相关,可直接影响海洋生物的正常生命活动,因此快速准确地检测海水氨氮浓度及其变化对研究海洋氮循环及开展海洋生态环境监测至关重要。介绍了近年来海水氨氮的检测方法,如靛酚蓝分光光度法、荧光光谱法、化学发光法、色谱法、表面等离子共振法及电化学分析法,分析了不同方法的灵敏度、准确性等特性,并对各类方法进行了比较与展望。
氨氮;海水分析;检测方法

近年来,国内外许多研究者一直致力于探索更灵敏、快速的测定方法,这些方法包括靛酚蓝分光光度法、荧光光谱法、化学发光法、色谱法、表面等离子共振法、电化学分析法等。作者针对这些方法进行探讨。
1 分子光谱法
1.1 靛酚蓝分光光度法
靛酚蓝分光光度法是海水氨氮测定的经典方法[3],其原理为:在次氯酸作用下氨氧化生成氯胺,氯胺与苯酚反应生成靛酚蓝络合物,利用分光光度计检测该络合物在640 nm处的吸光度。该方法已成为我国海洋检测规范中使用的标准方法,但不足之处是显色反应时间长,不便于海上调查分析。近年来,不少研究者对反应试剂、反应条件、分离富集及分析自动化等方面进行了改进。表1列举了靛酚蓝分光光度法检测海水氨氮的改进技术。
表1 靛酚蓝分光光度法检测海水氨氮的改进技术
Tab.1 Improved technologies of indophenol blue spectrophotometry for determination of ammonia nitrogen in seawater

反应物分离富集/自动化技术检出限/(nmol·L-1)参考文献邻苯基苯酚、次氯酸盐、氨气体分段/流动注射4.0[2]水杨酸、次氯酸盐、氨气体扩散离子交换/流动注射14.3[4]萘酚、二氯异氰尿酸盐、氨PTFE滤膜138.9[5]苯酚、次氯酸盐、氨固相萃取/流动分析3.5[6]
1.1.1 反应试剂的选择
苯酚具有腐蚀性气味和毒性,室温下固液态之间可相互转化,为了消除苯酚在使用过程中的不便,可使用邻苯基苯酚、水杨酸、萘酚等代替苯酚。由表1可知,用邻苯基苯酚代替苯酚对其检测灵敏度没有大的影响,而使用萘酚大大降低了检测灵敏度。此外,为了防止碱性条件下海水中Ca2+、Mg2+等离子形成沉淀[5,7],常采用柠檬酸三钠、EDTA等作为掩蔽剂;亚硝基铁氰化钠、Mn2+则作为反应催化剂,加快反应速率[8-9]。需要注意的是,试剂的加入顺序对显色反应至关重要。次氯酸盐应在苯酚和样品溶液未碱化前加入,以消除加热碱性溶液时氨气的损失。
1.1.2 预分离或富集技术
与传统的分光光度法相比,气体扩散分离、液液萃取、固相萃取等预分离富集技术的使用大大提高了检测灵敏度。气体扩散分离易于实现自动化、可消除基体干扰,但质量转化效率受温度和盐度的影响,气体渗透膜也需定期清洗或更换。液液萃取需要大量有机试剂甚至有毒有机试剂,至今未被广泛采用。固相萃取技术具有富集倍数高、溶剂消耗少及方便在线萃取等优点,因而受到广泛关注[6,10]。Chen等[6]采用HLB固相萃取柱分离富集生成的靛酚蓝染料,用乙醇水溶液洗脱后测其在640 nm处的吸光度,检出限为3.5 nmol·L-1,线性范围为0~428 nmol·L-1。该方法不需要复杂的样品处理操作,可用于野外分析。
1.1.3 检测方法的改进
由朗伯-比尔定律可知,吸光度与吸光物质浓度及比色池厚度成正比,基于此,人们通过增加光程来提高检测灵敏度。Li等[11]利用2 m的长光程测定海水样品中痕量铵离子,检出限为5 nmol·L-1,精密度为5%(10~100 nmol·L-1);Zhu等[12]进一步增加光程,采用2.5 m长的波导纤维为样品流通池,检出限为3.6 nmol·L-1,线性范围为10~500 nmol·L-1,相对标准偏差为4.4%(n=7)。该方法灵敏度高、检测范围宽、分析速度快,且试剂消耗量少,适用于河湾及表层海水中氨氮的野外在线检测,但毛细管内径小,容易发生堵塞。Hashihama等[2]进一步改进实验方案增大毛细管内径,采用2 m长的多路径毛细管(UltraPath,内径2 mm)代替长通路液芯波导毛细管(LWCC,内径0.5 mm),检出限为4 nmol·L-1。光程的增加在一定程度上增强了分析物的检测信号,但空白响应也随之同比例增强,因此增加光程理论上并不能提高信噪比,只能在试剂空白极低的前提下有限地改善灵敏度。Li等[11]通过优化实验条件,发现当加入54 mmol·L-1柠檬酸盐(5.4 mmol·L-1EDTA)、8.0~9.0 mmol·L-1苯酚、1.0~2.0 mmol·L-1NaDTT,且pH值为11~12时,空白响应最小。
1.1.4 分析的自动化
流动注射分析(FIA)具有高精密度、高样品处理量、低样品与试剂消耗量等特点,可实现样品在线处理与检测,已越来越多地应用于海洋检测领域[13-17]。一些学者将其用于改进靛酚蓝分光光度法,实现了海水氨氮的快速、可靠、实时监测。Azzaro等[18]改进循环流动分析反应器(LFA),设计了一种多参数分析仪(MicroMAC FAST MP3)自动检测海水中铵离子、硝态氮和正磷酸盐,检出限分别为2.5μg·L-1、2.5μg·L-1、5μg·L-1,相对标准偏差≤4%。该方法船上在线检测时,不需要人工操作。 Shoji等[19]将流动注射分析技术和改进的靛酚蓝分光光度法相结合测定环境水样中铵离子浓度,检出限为0.013μg·mL-1,线性范围为0~4.0μg·mL-1,测定海水中的铵离子回收率在92.5%~99.0%。此外,流动注射分析技术已实现与多种检测方法的联用。
1.2 荧光光谱法



Tab.2 OPA--determination of ammonia nitrogen in seawater


1.3 化学发光法
Meseguer-Lloret等[30]基于次氯酸盐氧化鲁米诺化学发光反应,间接测定铵离子含量。碱性条件下氨和次氯酸盐反应生成氯胺,加入鲁米诺后,鲁米诺能与溶液中的次氯酸盐反应产生化学发光信号,发射波长为425 nm,强度随氨浓度的增大而减弱,检出限为0.07 mg·L-1。由于次氯酸盐是不稳定试剂,可以通过电化学反应在线生成[31]。该方法发光体系灵敏度不高,达不到痕量分析的要求,因而需寻找很好的增敏剂来辅助增加灵敏度。
2 色谱法
色谱分析法是基于被分析样品物理或物理化学性质不同而进行的分离分析法,组分分子在流动相和固定相间进行多次“分配”,从而使各组分得到分离。色谱法具有分离效率高、分析速度快、样品用量少及分离与测定可一次完成等优点,目前已广泛应用于海水样品的检测[32-34]。
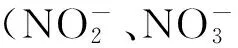
3 表面等离子共振法
表面等离子共振(SPR)是一种非常灵敏的表面光谱技术,通过测定金属表面附近折射率或介电常数的变化来研究物质的性质。自Liedberg等将SPR技术用于化学传感器研究领域以来[38-39],SPR传感器逐渐成为国际传感器领域的研究热点。Fujii等[40]设计了一种SPR铵离子传感器,用以检测海水中铵离子浓度。他们在离子光极膜中加入铵离子选择性离子载体TD19C6和亲脂性阳离子染料KD-M11,TD19C6选择性地使铵离子进入光极膜,为了保持膜的电中性,KD-M11染料发生去质子化。该阳离子交换过程使敏感膜吸收光谱强度发生改变,通过检测信号的变化实现铵离子的定量分析。但该方法线性范围小、灵敏度低,并且对测试环境要求高,不利于海水氨氮的在线分析。
4 电化学分析法
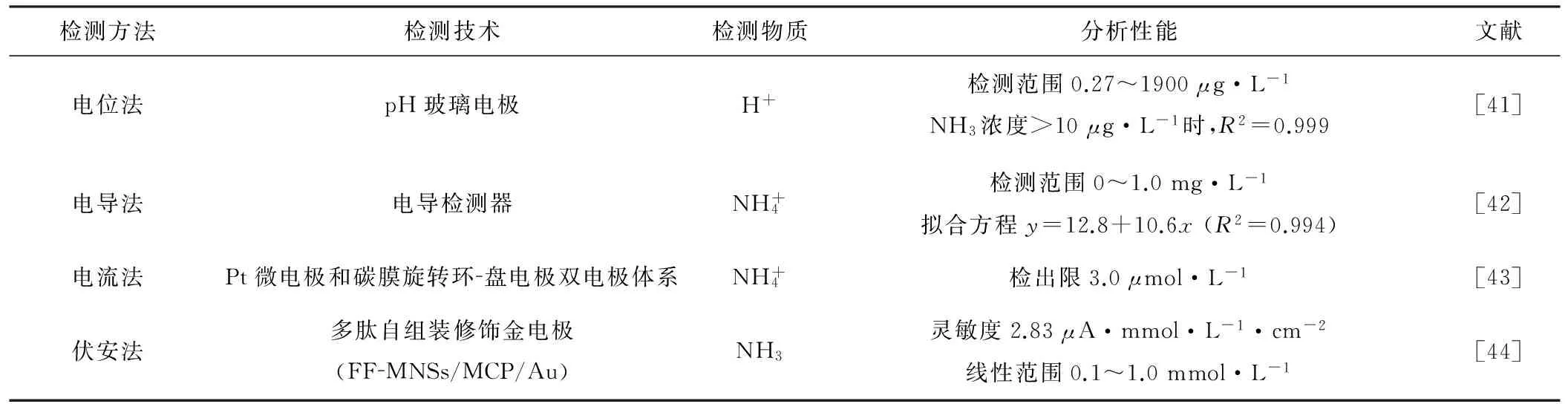
海洋环境研究的发展趋势是现场获取数据,电化学分析法具有操作简单、携带方便、易于微型化等特点,因此特别适于水质连续自动监测和现场快速分析。基于电位法、电导法、电流法、伏安法等电化学分析法检测海水氨氮的技术得到快速发展。表3列举了检测海水氨氮的电化学分析法。
表3 检测海水氨氮的电化学分析法
Tab.3Electrochemical analysis method for determination of ammonia nitrogen in seawater
4.1 电位法
离子选择性电极是一类利用相界面电位变化来指示待测离子活度的电化学传感器,广泛应用于环境监测、食品安全和工业分析等领域。氨气敏电极是一种基于pH玻璃电极的海水氨氮检测离子选择性电极,由疏水性气体渗透膜、pH玻璃电极和AgCl/Ag参比电极组成[45]。氨的水解平衡方程为:

[OH-]/[NH3]=K′
氨气敏电极法操作简单、耗费低、空白响应小、试剂消耗量少,受样品颜色、浊度及其它含氮化合物的干扰小[46],但使用氨气敏电极检测氨氮时,需要向水样中添加氢氧化钠溶液来调节水样的pH值。由于氢氧化钠溶液具有很强的腐蚀性,操作时有一定危险性,而且排放到环境中会造成环境污染。陈晓东[46]设计了一种基于电渗析离子转型的氨氮在线自动监测技术,通过电渗析电解去离子水产生的强碱性溶液来取代传统氨气敏电极法中的氢氧化钠溶液,线性范围为0.1~10 mg·L-1,相关系数R2=0.997。该方法无需添加任何化学试剂,只需要消耗去离子水和电能,绿色环保,与国标法测定结果相比,相对误差在5%以内,达到了氨氮在线检测的要求。
4.2 电导法
刘增东等[42]设计了一种新型的海水氨氮连续监测仪,该仪器利用氨反应器将铵盐转化为氨,氨在载气的带动下进入冷凝气液分离器,脱水后与酸试剂反应转化为铵盐,再注入电导检测器测定,以吸收气态氨前后溶液电导率的变化来计算待测水样中氨氮浓度。实际海水样品检测结果与分光光度法检测结果相比,线性相关系数R2高达0.994。该方法采用冷凝气液分离器代替气体渗透膜实现气液分析,从而避免了生物淤积或膜堵塞,且该方法能够克服海水中金属离子、氯离子、颜色等的干扰,可长时间可靠地测定海水氨氮浓度。
4.3 电流法
Takahashi等[43]基于HBrO和铵离子发生氧化还原反应,采用Pt微电极和碳膜旋转环-盘电极双电极体系,提出了一种间接电化学氨氮检测法。在pH值为7的磷酸缓冲液中,阳极电解产生的Br2水解后生成HBrO,与水样中铵离子相互反应,使得阴极还原电流减小,阴极还原电流的减小与铵离子浓度存在定量关系,检出限为3.0 μmol·L-1。实验所需Br2可通过阳极电解实时产生,避免了试剂稳定性对实验的影响,适用于各种环境水体的检测。
4.4 伏安法
Bianchi等[44]在金电极表面修饰上4-巯基吡啶(MCP),通过自组装修饰微/纳米结构的L,L-苯丙氨酸二肽(FF-MNSs),电极表面的苯环和酰胺基与铵离子形成阳离子-π键和氢键,采用循环伏安法可得到作用前后的CV曲线,从而实现氨和尿素氧化的检测。氨的线性范围为0.1~1.0 mmol·L-1,灵敏度为2.83 μA·mmol·L-1·cm-2。
海洋环境研究的发展趋势是现场实时监测,以避免样品在运输和储存时污染或形态改变。电化学方法易于与流动注射分析技术联用,可更好地用于连续自动检测系统,适于在线、实时环境检测,最大限度地避免了样品采集和运输过程中造成的污染或变质等问题。
5 结语
电化学分析法不受水体浊度和色度影响,具有灵敏度高、选择性好、易于微型化等优点。近年来,固体接触式离子选择性电极检测技术得到快速发展[47-48],并已成功应用于水样中氨氮的检测[49]。固体接触式电极不含内充液,可有效避免从电极膜相流向样品溶液相的稳态主离子通量带来的影响,且不需特别维护保养、易于小型化、便于仪器集成。为了降低成本、简化装置,纸质材料已经成为一种简单、灵活、可靠的分析装置[50]。Ding等[51]已成功地设计了一种三维折纸电位型生物传感装置用于检测酶的活性,因此基于纸芯片的电位检测装置将被广泛地应用于环境分析的现场原位检测,也为海水氨氮原位分析提供了一种新的检测方法。
随着新传感原理的发现和新材料的使用,电极性能将不断改善。我们相信固体接触式离子选择性电极有望成为海水氨氮原位检测的重要工具。此外,近年来可穿戴式传感器已成为一个新的研究领域[52]。Malzahn等[53]设计了一种用于潜水时穿戴的电化学传感器用于海水中离子的实时监测,为可穿戴潜水式海水氨氮检测技术提供了可能。潜水测量装置可测定不同深度海水氨氮的含量,这对研究海洋氨氮分布、氮循环具有重大的意义。
[1] MOLINS-LEGUA C,MESEGUER-LIORET S,MOLINERMA-RTINEZ Y,et al.A guide for selecting the most appropriate method for ammonium determination in water analysis[J].Trac Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2006,25(3):282-290.
[2] HASHIHAMA F,KANDA J,TAUCHI A,et al.Liquid waveg-uide spectrophotometric measurement of nanomolar ammonium in seawater based on the indophenol reaction witho-phenylphenol (OPP)[J].Talanta,2015,143:374-380.
[3] AMINOT A,KIRKWOOD D S,KEROUEL R.Determination of ammonia in seawater by the indophenol-blue method:evaluation of the ICES NUTS I/C 5 questionnaire[J].Marine Chemistry,1997,56(1/2):59-75.
[4] KEISUKE F,SHINSUKE O,KEIRO H,et al.Spectrophotometric flow injection analysis for the determination of trace amount of ammonium ion in seawater coupled with on-line gas diffusion/ion exchange concentration technique[J].Bunseki Kagaku,2007,56(9):757-763.
[5] SHOJI T,NAKAMURA E.Collection of indonaphthol blue on a membrane filter for the spectrophotometric determination of ammonia with 1-naphthol and dichloroisocyanurate[J].Analytical Sciences,2010,26(7):779-783.
[6] CHEN G,ZHANG M,ZHANG Z,et al.On-line solid phase extraction and spectrophotometric detection with flow technique for the determination of nanomolar level ammonium in seawater samples[J].Analytical Letters,2011,44(1/2/3):310-326.
[7] PAI C S,TSAU J Y,YANG T I.pH and buffering capacity problems involved in the determination of ammonia in saline water using the indophenol blue spectrophotometric method[J].Analytica Chimica Acta,2001,434(2):209-216.
[8] MOLINER Y M,FALCO P C,HERNANDEZ R H.Influence of the presence of surfactants and humic acid in waters on the indophenol-type reaction method for ammonium determination[J].Talanta,2006,69(4):1038-1045.
[9] 魏海峰,刘长发,张俊新.靛酚蓝法测定水中氨氮方法的改进[J].实验室研究与探索,2013,32(7):17-19.
[10] HATA N,KASAHARA I,TAGUCHI S.Micro-phase sorbent extraction for trace analysisviainsitusorbent formation:application to the preconcentration and the spectrophotometric determination of trace ammonia[J].Analytical Sciences,2002,18(6):697-699.
[11] LI Q P,ZHANG J Z,MILLERO F J,et al.Continuous colorimetric determination of trace ammonium in seawater with a long-path liquid waveguide capillary cell[J].Marine Chemistry,2005,96(1/2):73-85.
[12] ZHU Y,YUAN D X,HUANG Y M,et al.A modified method for on-line determination of trace ammonium in seawater with a long-path liquid waveguide capillary cell and spectrophotometric detection[J].Marine Chemistry,2014,162(2):114-121.
[13] SRAJ L O,ALMEIDA M I G S,SWEARER S E,et al.Analytical challenges and advantages of using flow-based methodologies for ammonia determination in estuarine and marine waters[J].Trac Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2014,59:83-92.
[14] WORSFOLD P J,CLOUGH R,LOHAN M C,et al.Flow injection analysis as a tool for enhancing oceanographic nutrient measurements—a review[J].Analytica Chimica Acta,2013,803(19):15-40.
[15] FENG S C,ZHANG M,HUANG Y M,et al.Simultaneous determination of nanomolar nitrite and nitrate in seawater using reverse flow injection analysis coupled with a long path length liquid waveguide capillary cell[J].Talanta,2013,117(22):456-462.
[16] MA J,BYRNE R H.Flow injection analysis of nanomolar silicate using long pathlength absorbance spectroscopy[J].Talanta,2013,88:484-489.
[17] KOLEV S D,FERNANDES P R L V,SATINSKY D,et al.Highly sensitive gas-diffusion sequential injection analysis based on flow manipulation[J].Talanta,2009,79(4):1021-1025.
[18] AZZARO F,GALLETTA M.Automatic colorimetric analyzer prototype for high frequency measurement of nutrients in seawater[J].Marine Chemistry,2006,99:191-198.
[19] SHOJI T,NAKAMURA E.Flow injection analysis with spectrophotometry for ammonium ion with 1-naphthol and dichloroisocyanurate[J].Journal of Flow Injection Analysis,2009,26(1):37-41.
[20] WATSON R J,BUTLER E C V,CLEMENTSON L A,et al.Flow-injection analysis with fluorescence detection for the determination of trace levels of ammonium in seawater[J].Journal of Environmental Monitoring,2005,7(1):37-42.
[21] POULIN P,PELLETIER E.Determination of ammonium using a microplate-based fluorometric technique[J].Talanta,2007,71(4):1500-1506.
[22] BEY S K A K,CONNELLY D P,LEGIRET F E,et al.A high-resolution analyser for the measurement of ammonium in oligotrophic seawater[J].Ocean Dynamics,2011,61(10):1555-1565.
[23] HORSTKOTTE B,DUARTE C M,CERDA V.A miniature and field-applicable multipumping flow analyzer for ammonium monitoring in seawater with fluorescence detection[J].Talanta,2011,85(1):380-385.
[24] AMORNTHAMMARONG N,ZHANG J Z,ORTNER P B.An autonomous batch analyzer for the determination of trace ammonium in natural waters using fluorometric detection[J].Analytical Methods,2011,3(7):1501-1506.
[25] AMORNTHAMMARONG N,ZHANG J Z.Shipboard fluorometric flow analyzer for high-resolution underway measurement of ammonium in seawater[J].Analytical Chemistry,2008,80(4):1019-1026.
[26] ZHU Y,YUAN D X,HUANG Y M,et al.A sensitive flow-batch system for on board determination of ultra-trace ammonium in seawater:method development and shipboard application[J].Analytica Chimica Acta,2013,794(17):47-54.
[27] XUE S H,UCHIYAMA K,LI H F.Determination of ammonium on an integrated microchip with LED-induced fluorescence detection[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences,2012,24(3):564-570.
[28] AMORNTHAMMARONG N,ZHANG J Z,ORTNER P B,et al.A portable analyser for the measurement of ammonium in marine waters[J].Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts,2013,15(3):579-584.
[29] ZHU Y,YUAN D X,LIN H Y,et al.Determination of ammonium in seawater by purge-and-trap and flow injection with fluorescence detection[J].Analytical Letters,2016,49(5):665-675.
[30] MESEGUER-LLORET S,MOLINS-LEGUA C,VERDUANA-RES J,et al.Chemiluminescent method for detection of eutrophication sources by estimation of organic amino nitrogen and ammonium in water[J].Analytical Chemitry,2006,78(21):7504-7510.
[31] QIN W,ZHANG Z J,LI B X,et al.Chemiluminescence flow system for the determination of ammonium ion[J].Talanta,1999,48(1):225-229.
[32] SI Q Q,LI F M,GAO C C,et al.Detection of phthalate esters in seawater by stir bar sorptive extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2016,108(1/2):163-170.
[33] LIAN Z R,WANG J T.Determination of ciprofloxacin in Jiao-zhou Bay using molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2016,111(1/2):411-417.
[34] KUO C T,WANG P Y,WU C H.Fluorometric determination of ammonium ion by ion chromatography using postcolumn derivatization witho-phthaldialdehyde[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2005,1085(1):91-97.
[35] MICHALSKI R,KURZVCA I.Determination of nitrogen species (nitrate,nitrite and ammonia ions) in environmental samples by ion chromatography[J].Polish Journal of Environmental Studies,2006,15(1):5-18.
[36] NIEDZIELSKI P,KURZYCA I,SIEPAK J.A new tool for inorganic nitrogen speciation study:simultaneous determination of ammonium ion,nitrite and nitrate by ion chromatography with post-column ammonium derivatization by Nessler reagent and diode-array detection in rain water samples[J].Analytical Chemica Acta,2006,577(2):220-224.
[37] KURZYCA I,NIEDZIELSKI P,FRANKOWSKI M.Simultaneous speciation analysis of inorganic nitrogen with the use of ion chromatography in highly salinated environmental samples[J].Journal of Separation Science,2016,39(18):3482-3487.
[38] NYLANDER C,LIEDBERG B,LIND T.Gas detection by means of surface plasmon[J].Sensors and Actuators,1982,3(82):79-88.
[39] LIEDBERG B,NYLANDER C,LUNDSTROM I.Surface-plasmon resonance for gsa-detection and biosensing[J].Sensors and Actuators,1983,4(2):299-304.
[40] FUJII E,KOIKE T,NAKAMURA K,et al.Application of an absorption-based surface plasmon resonance principle to the development of SPR ammonium ion and enzyme sensors[J].Analytical Chemistry,2002,74(23):6106-6110.
[41] GILBERT T R,CLAY A M.Determination of ammonia in aquaria and in sea-water using ammonia electrode[J].Analytical Chemistry,1973,45(9):1757-1759.
[42] 刘增东,徐滋秋.海水中氨氮连续检测的方法研究[J].科技创新与应用,2015(16):54.
[43] TAKAHASHI M,NAKAMURA K,JIN J.Study on the indirect electrochemical detection of ammonium ion within-situelectrogenerated hypobromous acid[J].Electroanalysis,2008,20(20):2205-2211.
[44] BIANCHI R C,da SILVA E R,DALL′ANTONIA L H,et al.A nonenzymatic biosensor based on gold electrodes modified with peptide self-assemblies for detecting ammonia and urea oxidation[J].Langmuir,2014,30(38):11464-11473.
[45] THOMAS R G,ALICE M C.Determination of ammonia in aquaria and in sea water using the ammonia electrode[J].Analytical Chemistry,1973,45(9):1757-1759.
[46] 陈晓东.基于电渗析离子转型的氨氮在线监测技术研究[D].无锡:江南大学,2015.
[47] ZENG X Z,YU S Y,YUAN Q,et al.Solid-contact K+-selective electrode based on three-dimensional molybdenum sulfide nanoflowers as ion-to-electron transducer[J].Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical,2016,234:80-83.
[48] LI J H,YIN T J,QIN W.An effective solid contact for an all-solid-state polymeric membrane Cd2+-selective electrode:three-dimensional porous graphene-mesoporous platinum nanoparticle composite[J].Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical,2016,239:438-446.
[49] ATHAVALE R,KOKORITE I,DINKEL C,et al.Insituammonium profiling using solid-contact ion-selective electrodes in eutrophic lakes[J].Analytical Chemistry,2015,87(24):11990-11997.
[50] MAHADEVA S K,WALUS K,STOEBER B.Paper as a platform for sensing applications and other devices:a review[J].ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(16):8345-8362.
[51] DING J W,LI B W,CHEN L X,et al.A three-dimensional origami paper-based device for potentiometric biosensing[J].Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2016,55(42):13033-13037.
[52] BAKKER E.Wearable sensor—an exciting area of research for sensor scientists[J].ACS Sensors,2016,1(7):834.
[53] MALZAHN K,WINDMILLER J R,VALDÉS-RAMREZ G,et al.Wearable electrochemical sensors forinsituanalysis in marine environments[J].Analyst,2011,136(14):2912-2917.
Research Progress on Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen in Seawater
YU Han1,2,DING Lan3,LIU Shu-wen1,2,DING Jia-wang1,QIN Wei1*
(1.KeyLaboratoryofCoastalEnvironmentalProcessesandEcologicalRemediation,YantaiInstituteofCoastalZoneResearch(YIC),ChineseAcademyofSciences(CAS),ShandongProvincialKeyLaboratoryofCoastalEnvironmentalProcesses,YICCAS,Yantai264003,China;2.UniversityofChineseAcademyofSciences,Beijing100049,China;3.DalianUniversityofTechnology,Dalian116024,China)
Ammonia nitrogen(NH3-N) is an important component of dissolved inorganic nitrogen,and its content is an important index of nutrition salt.Ammonia nitrogen in seawater is an important part of the upper ocean nitrogen cycle,and also an essential nutrient for marine phytoplankton.Ammonia nitrogen concentration is closely related to life activities of marine organisms,and ammonia nitrogen can affect the normal life activities of marine organisms.Therefore,it is crucial to rapidly and accurately detect ammonia nitrogen concentration and its change in seawater for studying ocean nitrogen cycle and developing oceanic ecology environmental monitoring.Determination methods of ammonia nitrogen in seawater developed in recent years,including indophenol blue spectrophotometry,fluorescence spectrometry,chemiluminescence,chromatography,surface plasmon resonance and electrochemical analysis,are reviewed.The characteristics of sensitivity and accuracy for different methods are analyzed,and they are also compared and prospected.
ammonia nitrogen;seawater analysis;determination method
中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(A类)项目(XDA11020702),山东省泰山学者人才计划项目(TS20081159)
2016-12-22
于涵(1992-),女,河南驻马店人,硕士研究生,研究方向:海岸带环境分析化学,E-mail:hyu@yic.ac.cn;通讯作者:秦伟,研究员,E-mail:wqin@yic.ac.cn。
10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2017.05.001
X830.2 X132
A
1672-5425(2017)05-0001-07
于涵,丁兰,刘淑文,等.海水氨氮检测技术研究进展[J].化学与生物工程,2017,34(5):1-7.
