分子印迹固相萃取技术在食品的农药和兽药残留检测中的应用进展
2017-05-15赵雯彭黔荣冯贵涛杨敏冯淑艳
赵雯,彭黔荣,3*,冯贵涛,杨敏,2*,冯淑艳
(1.贵州大学 化学与化工学院,贵阳 550025;2.贵州大学 药学院,贵阳 550025;3.贵州中烟工业有限责任公司技术中心,贵阳 550009)
分子印迹固相萃取技术在食品的农药和兽药残留检测中的应用进展
赵雯1,彭黔荣1,3*,冯贵涛1,杨敏1,2*,冯淑艳1
(1.贵州大学 化学与化工学院,贵阳 550025;2.贵州大学 药学院,贵阳 550025;3.贵州中烟工业有限责任公司技术中心,贵阳 550009)
分子印迹固相萃取技术是一种高效的样品前处理技术,能从复杂的样品中选择性分离目标物及其结构类似物,现已广泛应用于食品、医药、化工等多个领域。介绍了分子印迹聚合物的合成原理、方法及表征,分子印迹固相萃取的操作模式,并对近几年国内外分子印迹固相萃取技术在食品农药、兽药残留检测中的应用进行了总结。阐述了该技术目前存在的问题,并对其发展趋势进行展望,为其更好地应用于食品的分析检测提供参考。
分子印迹固相萃取;农药残留;兽药残留;食品安全;应用进展
分子印迹固相萃取技术(Molecularly Imprinted Solid-phase Extraction,MISPE)是采用分子印迹聚合物(Molecularly Imprinted Polymers,MIPs)作为选择性吸附剂的样品前处理技术。分子印迹固相萃取技术充分耦合了MIPs的高选择性识别能力和固相萃取(Solid-phase Extraction,SPE)的操作简易自动化的特点,可实现特定目标分子从混合物或与其结构类似的物质中的有效分离,现已广泛应用于食品安全分析测定领域,调味品领域也有MISPE的应用,王会枝等[1]在测定酱油中的防腐剂苯甲酸时,利用苯甲酸MIPs 作为固相萃取剂,通过建立MISPE-高效液相色谱法(High Performance Liquid Chromatography, HPLC)来进行分离和分析,该方法的回收率为98.46%~106.10%,在10~100 mg/L的范围内线性关系良好(r=0.9998),相对标准偏差为2.55%。李春丽等[2]制备出了酪胺MIPs,将其装填成柱制成MISPE,结合HPLC测定了3种酱油样品中的酪胺含量,回收率为86.95%~106.06%,检出限低至0.15 μg/mL,低于杨红梅等[3]采用传统SPE法测得的1.0 μg/mL和王新运等[4]采用HPLC法测得的0.35 μg/mL。Wang等[5]建立了MISPE-HPLC测定辣椒面样品中的4种苏丹红,其中苏丹红I号的线性范围为0.005~50 μg/L,5次重复测定的RSD为3.66%,检测限(S/N=3)为1.2 ng/L,显著低于苏日辉等[6]利用超声辅助液液萃取测得的检测限3×103ng/L(S/N=3),说明MISPE具有更高选择性和灵敏度。本文介绍了MIPs的合成原理、方法和表征以及MISPE技术的操作模式,重点对近2年来MISPE技术在食品农药残留、兽药残留分析检测中的应用进行了概述。
1 MISPE技术
1.1 MIPs的合成
1.1.1 MIPs的合成原理
MIPs是一种高度交联的有机聚合物,由于具有特异的识别位点和空间结构,故MIPs对目标分子具有高度的选择识别能力。MIPs的合成主要分为3个步骤[7]:模板分子与功能单体在一定介质中相互作用形成复合物;加入交联剂,发生交联聚合反应形成刚性聚合物;用适当的方法将模板分子从聚合物中除去,就合成了仅对目标分子具有特异识别能力的MIPs。MIPs的合成原理见图1。
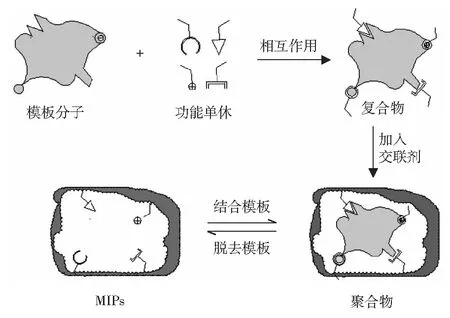
图1 分子印迹聚合物(MIPs)的制备原理图
1.1.2 MIPs的合成方法及表征
按照功能单体与模板分子之间的作用方式来分,MIPs的制备方法包括:共价法[8]、非共价法[9]、半共价法[10]和一些新型的方法如片段印迹法[11]、虚拟模板法[12,13]、化学印迹法[14,15]、循环伏安法[16,17]等;MIPs有块状、薄膜状、微球状和棒状等,按照其形貌和粒径的不同,MIPs的制备方法有:本体聚合法[18,19]、原位聚合法[20]、乳液聚合法[21]、悬浮聚合法[22]、沉淀聚合法[23]、表面印迹法[24]等。
MIPs作为一种选择吸附材料,其表征类型主要包括形貌表征、化学表征和分子识别性能表征。但由于MIPs的应用范围较广,不同的领域中有不同的表征方法,目前尚无一个统一的方法。MISPE中,一般采用饱和吸附量Q、保留时间tR、分离度α、富集因子等作为表征参数来评价MIPs的性能。
1.2 MISPE的操作模式
MISPE的操作模式可分为在线模式(on-line)和离线模式(off-line)两种。两种模式的区别在于:on-line模式中萃取和分析测定是同步完成的,而在off-line模式中萃取和分析测定是依次完成的,但两种模式在原理上是一致的。两种方法各有裨益,off-line模式具有简单、方便、选择性好和富集因子高的特点,但存在着耗时长的缺点;而on-line模式大大降低了样品预处理的时间,精密度、准确性也明显提高,但仪器成本高昂[25]。
Wang课题组[26-28]先后采用off-line MISPE 模式结合HPLC分析检测海水及海产品样品中的结晶紫和塔玛亚历山大藻样品中的膝沟藻毒素2,3(GTX 2,3)。检测到2个海水样品中的结晶紫浓度分别为0.92,0.52 g/L,2种海鲜样品中分别为0.36,0.27 g/kg;经过MISPE检测塔玛亚历山大藻提取物中的干扰基质明显减少,测得GTX 2,3的检测限和定量限分别低至0.1,0.35 μg/L。
Liu等[29]建立了on-line MISPE-HPLC法并用于测定环境水样中四环素类残留,加标回收率为83.2%~111%,相对标准偏差(RSD)小于5.3%,线性范围为1~200 mg/L,检测限和定量限分别为0.08~1.02 ,0.41~3.56 mg/L。结果表明:该方法具有良好的灵敏度和较高的检测效率,可用于测定环境水样中四环素类抗生素。Qiu等[30]利用off-line MISPE 模式结合HPLC测定环境水样中的4个酚类化合物,测得2,4,6-三氯酚、2,6-二氯酚、4-氯酚和苯酚的检测限分别为0.19,0.20,0.75,0.73 mg/L,实验结果表明该方法具有快速、准确、选择性高的特点,可用于环境样品中痕量酚类物质的测定。
2 MISPE在食品药物残留分析检测中的应用
2.1 MISPE在食品农药残留检测中的应用
MISPE在食品中农药残留分析检测的应用中,绝大多数是对嘧啶类杀菌剂、三嗪类除草剂等残留的测定。样品测定存在着基质复杂、干扰物质多和残留物浓度低的难题,但由于MIPs的特异选择识别能力,使得经MISPE处理后的样品的分析检测具有选择性高、富集率好、检出限低等特点。
Khan等[31]利用氯苯嘧啶醇(一种嘧啶类杀菌剂)为模板分子,甲基丙烯酸为功能单体,二甲基丙烯酸乙二醇酯为交联剂,偶氮二异丁腈为引发剂,通过沉淀聚合法制备出均匀的微球型MIPs,通过静态吸附-动态吸附试验对MIPs和空白NIPs(非印迹聚合物)两者的吸附性能进行研究,实验表明该MIPs对氯苯嘧啶醇吸附性能优于NIPs。然后将MIPs作为固相萃取剂,利用MISPE结合HPLC对苹果、香蕉和番茄这3种样品中的氯苯嘧啶醇进行测定,其检测限和定量限分别为0.03~0.06,0.12~0.21 μg/mL,回收率可达91.16%~99.52%,显著低于欧洲食品安全局规定的氯苯嘧啶醇的最大残留限度(MRL),番茄0.5 μg/g,苹果0.1 μg/g和香蕉0.01 μg/g,表明该方法可有效分析实际样品中残留的氯苯嘧啶醇。
Li等[32]研究采用MISPE技术结合HPLC富集并测定葡萄籽中的莠去通、西草净、莠去津和扑草净这4种三嗪类除草剂,他们首先制备出三嗪类MIPs,以聚合物和目标物的结合率为重要参数考察了洗脱液的组成、洗脱时间对聚合物性能的影响,然后用扫描电镜和傅里叶变换红外光谱对其进行表征, 实验结果表明MIPs相对于NIPs而言对目标物具有更好的富集率,最后用该MIPs作为固相萃取剂,同时对这4种目标物进行测定。实验测得该方法的线性范围为0.010~5.0 μg/g(r2为0.9993~0.9999),日内精密度和日间精密度在81.2%~113.0%之间,相对偏差为1.2%~10.7%,该方法的检测限和定量限分别低至0.006~0.013,0.02~0.04 μg/g,其中莠去津的检测限为0.02 μg/g ,低于GB/T 5009.132-2003中莠去津的检测限0.03 μg/g,说明该方法灵敏、准确,能有效地测定样品中的三嗪类物质。
Andrade等[33]利用MISPE on-line模式结合LC(液相色谱)分析玉米样品中的阿特拉津、西玛津、莠灭净、草净、西草净这5种三嗪类除草剂。他们首先以阿特拉津为模板,甲基丙烯酸为功能单体,乙二醇二甲基丙烯酸酯为交联剂,采用沉淀聚合法合成了MIPs。实验测得该方法的加标回收率为80.2%~119.1%,检测限和定量限分别为1.6~3.3,5~10 ng/g,低于Wu等[34]用分子印迹膜结合HPLC的检测限5.8 ng/g,说明该方法更加灵敏高效,可用于实际玉米样品中三嗪类除草剂的测定。
2.2 MISPE在食品兽药残留检测中的应用
样品预处理是兽药残留分析过程中的关键环节,直接影响检测的准确度和效率。常规的预处理存在着耗时长、操作繁琐和误差大等弊端,而MISPE技术为兽药残留的分析检测提供了一个全新的样品预处理方法。目前利用MISPE对食品中兽药残留检测分析主要包括神经兴奋剂、抗生素类、抗菌类和激素类物质等,并取得了较好的效果。
汤凯洁等[35]建立了MISPE-HPLC测定猪肝中盐酸克伦特罗(一种肾上腺类神经兴奋剂)残留的方法,对GB/T 5009.192-2003《动物性食品中克伦特罗残留量的测定》中HPLC法的流动相做出了调整,优化了MISPE条件,优化后测得盐酸克伦特罗的线性范围为0.432~4.32 μg/mL(r2=0.9990),加标回收率为84.7%~92.0%,相对标准偏差为1.5%~1.8%,检出限和定量限分别低至0.02,0.34 μg/mL,该方法的准确度和精密度均满足兽药残留分析检测要求,可用于检测实际样品中较低浓度的盐酸克伦特罗残留。
Song等[36]以泰乐菌素(一种内酯类抗生素)为模板,甲基丙烯酸为功能单体,合成了MIPs并建立了MISPE-LC-MS/MS法用于猪、牛、鸡肉这3种肉制样品中10种大环内酯类抗生素药物(阿奇霉素、泰拉霉素、螺旋霉素、替米考星、红霉素、克拉霉素、罗红霉素、麦迪霉素、交沙霉素和北果霉素)的测定。考察了MIP,C18,HLB,SCX这4种类型的SPE柱对10种大环内酯类药物加标回收率的影响,实验结果表明:MIP制成的固相萃取柱的任一目标物的加标回收率均明显高于其他SPE柱60.7%~100.3%,相对标准偏差为2.4%~14%,说明MISPE精密度更高、准确度更好、性能更加稳定。用该方法测定3种动物肌肉中的这10种环内酯类药物的检测限为0.1~0.4 ng/g,定量限为0.3~1.0 ng/g,显著低于王凤美等[37]用超高效液相色谱-质谱/质谱(UPLC-MS/MS)的检测限5.0 ng/g和定量限10.0 ng/g,说明MISPE法具有更高的灵敏度,可用于动物肌肉中的大环内酯类药物残留监测。
Lima等[38]采用表面印迹法制备出伊维菌素(一种抗生素)MIPs,然后在MIPs的表面覆盖上牛血清蛋白(BSA)制成MIPs-BSA,通过扫描电镜在5万倍下观察MIPs和MIPs-BSA的形貌,发现在涂覆BSA后MIPs-BSA粒径变大,红外扫描发现涂覆牛血清蛋白对MIPs并无大的影响。将同样量BSA标液注入分别装有MISPE柱和MISPE-BSA柱的HPLC系统中,测得BSA柱和非BSA柱峰面积分别为2543和2391(n=3),表明BSA柱具有更好地与蛋白质结合的能力。然后,他们采用on-line 模式并结合LC-UV对牛肉样品中的伊维菌素的残留进行测定。该方法的线性浓度范围为50~500 ng/g(r=0.996),定量限为50 ng/g,低于国家规定的允许伊维菌素的最高限量100 ng/g,说明该方法可用于牛肉样品中伊维菌素的测定。
林冬等[39]采用MISPE结合HPLC对牛奶样品中的氯霉素进行测定,测得氯霉素出峰时间为8.42 min,其他杂质出峰时间为2.5~5.0 min,可实现目标物与杂质的基本分离。实验结果表明该方法可用于筛选和分离基质复杂的牛奶提取液中的氯霉素。
Victorla等[40]制备了氯霉素分别将MISPE与LC-UV和LC-MS联用, MISPE-LC-MS测定5个牛奶样品的日内和日间精密度分别为88.7%~97.1%(n=5)和85.2%~106.1%(n=3)。两种方法的检测限分别为17,0.1 ng/g,其中LC-MS的定量限低至0.3 ng/g,低于蒋定国等[41]用HPLC法测得的定量限1.1 ng/g。实验结果表明:该方法可用于快速灵敏检测牛奶样品中的氯霉素。
Tang等[42]建立了采用MISPE-HPLC法测定鱼样品中的恩诺沙星(一种喹诺酮类抗菌药物)的方法。首先,他们以恩诺沙星为模板,合成了纳米级hollow MIPs(h-MIPs,即具有中空结构的MIPs),考察了不同摩尔比的模板分子、功能单体和交联剂对MIPs吸附性能的影响,分别与相应的NIPs进行了对比,试验表明MIPs比NIPs具有更大的吸附容量,然后采用傅立叶变换红外光谱、X射线粉末衍射和扫描电镜对其结构和形貌进行表征,扫描电镜图显示h-MIPs比MIPs比表面积更大、厚度更薄,这些都有助于目标物在聚合物中的运输,说明h-MIPs性能优越于普通的MIPs。将h-MIPs制成MISPE测定鱼样品中的恩诺沙星,测得其线性范围是0.5~16 ng/mL(r=0.9912),回收率为68.88%~100.29%,相对标准偏差(n=3)为1.6%~4.4%,检测限低至0.24 ng/mL(S/N=3),说明该方法具有更高的灵敏度。
He等[43,44]采用悬浮聚合法先后制备己烯雌酚(非甾体类雌激素物质)MIPs和磺胺嘧啶(一种磺胺类抗菌药物)MIPs,采用扫描电镜对其形貌进行表征,发现MIPs与NIPs在同等倍数的电镜图中具有更多的空隙结构,正是这些结构使得MIPs具有良好的选择识别能力。采用MISPE off-line模式结合HPLC分别对水产养殖区的4个海水样品中残留的己烯雌酚和鸡蛋中残留的磺胺嘧啶进行测定,测得己烯雌酚的检测限和定量限分别为1.8,6.0 ng/mL,磺胺嘧啶的检测限和定量限分别为0.3,1 ng/g,远远低于GB/T 21316-2007《动物源性食品中磺胺类药物残留量的测定》中定量限为50 ng/g,说明经MISPE处理后的样品的分析检测具有选择性高和检出限低等特点。
3 展望
随着生活水平的提高,食品安全问题逐渐成为全球关注的焦点,特别是食品中农药、兽药残留问题,无论是食品生产部门还是质量检验部门都迫切需要一种高效的食品分析检测方法。食品检测的难度在于:样品成分复杂,有害物质含量低、种类多,存在杂质干扰。因此,在分析检测之前采用MISPE技术来进行样品前处理能有效解决传统方法分离效率低、选择性差等不足。同时,MISPE技术还具有稳定性高和可重复利用等特性,使得该技术广泛应用于食品安全分析领域。但对于MISPE技术的研究多集中在实际运用方面,对其理论研究较少,MISPE技术要想得到长足的发展,还需要做好理论研究。MIPs的制备是MISPE技术的核心部分,虽然MIPs的制备方法有多种,但现有的方法仍存在着一些弊端,如洗脱液渗漏、功能单体和交联剂的选择存在局限性等,因此需要开发出一种新型的、清洁的、高效的MIPs的制备方法,同时将其他新型技术(如计算机技术)应用于MIPs的制备,模拟不同单体与模板分子之间的相互作用,使MIPs的合成技术更具科学性和绿色环保性。由此可见,MISPE技术理论进一步深层次的研究是该技术的一个重要方向。相信随着科技的不断发展、MIPs材料研究的深入,MISPE技术将会在包括调味品在内的食品科学的各个领域分析检测的应用中大放异彩。
[1]王会枝,杨柳,沈妍铮,等.印迹固相萃取-HPLC对酱油中防腐剂的选择分析[J].河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2011,32(2):40-44.
[2]李春丽,严守雷.分子印迹固相萃取-高效液相色谱法测定酱油中酪胺含量[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2014(9):2728-2734.
[3]杨红梅,刘艳琴,王浩,等.固相萃取-高效液相色谱法测定酱油中10种防腐剂[J].中国调味品,2011,36(5):94-96.
[4]王新运,万新军,程乐华,等.高效液相色谱法同时测定酱油中的苯甲酸和山梨酸[J].应用化工,2010,39(9):1413-1416.
[5]Wang S, Xu Z X, Fang G Z,et al. Synthesis and characterization of a molecularly imprinted silica-gel sorbent for the on-line determination of trace sudan I in chilli powder through high-performance liquid chromatography[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(10):3869-3876.
[6]苏日辉,阮贵华,曾令镇,等.超声辅助分散乳液微萃取/高效液相色谱法同时测定辣椒粉中的5种染色剂[J].分析测试学报,2015,34(5):546-551.
[7]Haupt K, Mosbach K. Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors[J].Chemical Reviews,2000,100(7):2495-2504.
[8]Wulff G,Sarhan A,Zabrocki K.Enzyme-analogue built polymers and their use for the resolution of raeemates[J].Tetrahedron Letters,1973,14(44):4329-4332.
[9]Li Ji, Hu Xiaoling, Guan Ping. Synthesis and application of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles combined ultrasonic assisted for highly selective solid phase extraction trace amount of celecoxib from human plasma samples using design expert(DXB)software[J].Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2016,33:67-76.
[10]Whitcombe M J, Rodriguez M E, Villar P, et al. A new method for the introduction of recognition site functionality into polymers prepared by molecular imprinting: synthesis and characterization of polymeric receptors for cholesterol[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,1995,117(27):7105-7111.
[11]Ndunda E N,Mizaikoff B. Synthesis of stationary phases that provide group recognition for polychlorinated biphenyls by porogenic fragment template imprinting[J].Journal of Separation Science,2016,39(5):939-946.
[12]Sun Guangying, Wang Chao, Luo Yuqin, et al. Cost-effective imprinting combining macromolecular crowding and a dummy template for the fast purification of punicalagin from pomegranate husk extract[J].Journal of Separation Science,2016,39(10):1963-1970.
[13]Arabi M, Ghaedi M, Ostovan A. Development of dummy molecularly imprinted based on functionalized silica nano-particles for determination of acrylamide in processed food by matrix solid phase dispersion[J].Food Chemistry,2016,210:78-84.
[14]Xu Zhifeng, Deng Peihong, Li Junhua, et al. Construction of imprint sites in mesopores of SBA-15 via thiol-ene click reaction[J].Food Chemistry,2016,210:78-84.
[15]Luliński P, Klejn D, Maciejewska D. Stoichiometric molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of anti-cancer pro-drug tegafur[J].Materials Science and Engineering C,2016,65:400-407.
[16]马明明,刘承龙,苏新科,等.基于分子印迹聚合物零流电位法识别邻甲苯胺[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版),2016,55(1):9-15.
[17]戴芳芳,周瑶,马良,等.间苯氧基苯甲酸分子印迹膜的电化学聚合制备及其应用[J].食品科学,2015,36(20):232-238.
[18]Ersoya S K, Tutemb E, Baskan K S, et al.Preparation, characterization and usage of molecularly imprinted polymer for the isolation of quercetin from hydrolyzed nettle extract[J].Journal of Chromatography B,2016,210:78-84.
[19]P Luliński,D Klejn,D Maciejewska. Synthesis and characterization of imprinted sorbent for separation of gramine from bovine serum albumin[J].Journal of Chromatography B,2016,65:400.
[20]苏子豪.分子印迹固相萃取芯片的构建及其分析应用的研究[D].广州:广东药学院,2015.
[21]Li Ji, Hu Xiaoling, Guan Ping. Preparation of L-phenylalanine imprinted solid-phase extraction sorbent by pickering emulsion polymerization and the selective enrichment of L-phenylalanine from human urine[J].Journal of Separation Science,2016,39(10):1863-1872.
[22]周菊英,张玲玉,李鹏飞,等.以马来松香丙烯酸乙二醇酯为交联剂的分子印迹聚合物对槲皮素的选择吸附性能[J].精细化工,2016,33(3):314-319.
[23]Li Hong, He Hongliang, Huang Jiaojiao, et al. A novel molecularly imprinted method with computational simulation for the affinity isolation and knockout of baicalein from Scutellaria baicalensis[J].Biomedical Chromatography,2015,30(2):117-125.
[24]Song Renyuan, Hu Xiaoling, Guan Ping, et al. Surface modification of imprinted polymer microspheres with ultrathin hydrophilic shells to improve selective recognition of glutathione in aqueous media[J].Materials Science and Engineering C,2016,60:1-6.
[25]吴宗远,李小燕,苏晓濛,等.分子印迹固相萃取在线检测技术在食品安全分析中的研究进展[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2014(5):1297-1304.
[26]Lian Ziru, Wang Jiangtao. Determination of crystal violet in seawater and seafood samples through off-line molecularly imprinted SPE followed by HPLC with diode-array detection[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2013,36(5):980-985.
[27]Lian Ziru, Wang Jiangtao. Study of molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction of gonyautoxins 2,3 in the cultured dinoflagellateAlexandriumtamarenseby high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection [J].Environmental Pollution,2013,182(6):385-391.
[28]Lian Ziru, Li Haibei, Wang Jiangtao. Experimental and computational studies on molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for gonyautoxins 2,3 from dinoflagellateAlexandriumminutum[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2016,408(20):5527-5535.
[29]Liu Meijiao, Li Yongna, Lin Shen, et al. Determination of tetracycline residues in lake water by on-line coupling of molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction with high performance liquid chromatography[J].Analytical Methods,2014,6(23):9446-9452.
[30]Qiu Xiuzhen, Liang Yong, Guo Huishi, et al. Determination of phenolic compounds in environmental water by HPLC combination with on-line solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymers[J].Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology,2015,15(12):9578-9584.
[31]Khan S, Bhatia T, Trivedi P, et al. Selective solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer as a sorbent for the analysis of fenarimol in food samples[J].Food Chemistry,2016,199:870-875.
[32]Li Xinpei, Wang Yuanpeng, Sun Qun, et al. Molecularly imprinted dispersive solid-phase extraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in grape seeds by high-performance liquid chromatography[J].Chromatographic Science,2016,54(5):871-877.
[33]Andrade F N, Nazario C E D, Santos-neto A J, et al. Development of on-line molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography mass spectrometry for triazine analysis in corn samples[J].Analytical Methods,2016,8(5):1181-1186.
[34]Wu Suqin,Xu Zhiguang,Yuan Qionghui,et al. Recognition characteristics of molecularly imprinted microspheres for triazine herbicides using hydrogen-bond array strategy and their analytical applications for corn and soil samples[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2011,1218(10):1340-1346.
[35]汤凯洁,罗秋水,余瑞龙,等.分子印迹固相萃取/高效液相色谱法测定猪肝中盐酸克伦特罗的方法研究[J].分析测试学报,2016,35(1):115-118.
[36]Song Xuqin, Zhou Tong,Liu Qingying, et al. Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for the determination of ten macrolide drugs residues in animal muscles by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J].Food Chemistry, 2016, 208:169-176.
[37]王凤美,陈军辉,林黎明,等.UPLC- MS /MS法对动物源性食品中12种大环内酯类抗生素残留的测定[J].分析测试学报,2009,28(7):784-788.
[38]Lima M D, Vieira A C, Martins I, et al. On-line restricted access molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction of ivermectin in meat samples followed by HPLC-UV analysis[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,197:7-13.
[39]林冬,郭晶晶.氯霉素分子印迹整体柱的制备和表征[J].环境监测管理与技术,2016,28(1):50-53.
[40]Samanidou V,Kehagia M, Kabir A, et al. Matrix molecularly imprinted mesoporous sol-gel sorbent for efficient solid-phase extraction of chloramphenicol from milk[J].Analytica Chimica Acta,2016,914:62-74.
[41]蒋定国,杨大进,方从容,等.高效液相色谱法测定牛奶中氯霉素残留量的研究[J].中国食品卫生杂志,2003,15(1):35-36.
[42]Tang Yimei, Li Min, Gao Xue, et al. Preconcentration of the antibiotic enrofloxacin using a hollow molecularly imprinted polymer, and its quantitation by HPLC[J].Microchim Acta,2016,183(2):589-596.
[43]He Xiuping,Mei Xiaoqi, Wang Jiangtao, et al. Determination of diethylstilbestrol in seawater by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2016,102:142-147.
[44]He Xiuping,Tan Liju, Wu Wei. Determination of sulfadiazine in eggs using molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2016,39(11):2204-2212.
Application of Molecularly Imprinted Solid-phase Extraction Technique on Detection of Pesticides and Veterinary Drugs Residues in Food
ZHAO Wen1, PENG Qian-rong1,3*, FENG Gui-tao1,YANG Min1,2*, FENG Shu-yan1
(1.School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China;2.School of Medicine, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China;3.Technology Center of China Tobacco Guizhou Industrial Co., Ltd., Guiyang 550009, China)
Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction technique is a sample pretreatment technique with high performance, which can separate target molecules and structurally similar molecules from complex samples. It is widely used in multiple fields, such as food, medicine and chemical engineering. Introduce the synthesis principle, methods and characterization of MIPs, the operating mode of molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction, and its application in the determination of pesticides and veterinary drugs residues in food in recent years. Besides, the current problems in application progress of the technology and the future development are discussed. It provides references for analysis and detection of food.
molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction(MISPE);pesticides residues; veterinary drugs residues;food safety; application progress
2016-11-18 *通讯作者
国家自然科学基金项目(21562014)
赵雯(1991-),女,硕士,主要从事食品药品方面的研究; 彭黔荣(1963-),男,副教授,硕士生导师,博士,主要从事烟草化学与工程方面的研究; 杨敏(1962-),女,教授,硕士生导师,博士,主要从事活性化合物分析方法方面的研究。
TS207.53
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2017.05.036
1000-9973(2017)05-0157-06
