类风湿关节炎患者血清IL-37和可溶性PD-1分子的表达水平及临床意义①
2017-04-10陈栖栖
陈栖栖 田 娟 张 晶 苏 江
(四川省医学科学院·四川省人民医院风湿免疫科,成都610072)
类风湿关节炎患者血清IL-37和可溶性PD-1分子的表达水平及临床意义①
陈栖栖 田 娟 张 晶 苏 江
(四川省医学科学院·四川省人民医院风湿免疫科,成都610072)
目的:通过研究类风湿关节炎(RA)患者血清IL-37和可溶性PD-1分子的表达水平,初步探讨其与RA的相关性以及临床意义。方法:收集RA患者及对照组人群的外周血,然后采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测30例RA患者(RA标准评分≥6)和30名健康对照组血清中IL-37、sPD-1的表达水平,结合分析两组人群外周血IL-18、IL-6和IL-18BP三种细胞因子的表达,并通过Pearson相关分析其相关性。结果:经ELISA检测发现,RA组患者外周血中IL-37和sPD-1以及其他几种炎症相关细胞因子IL-18、IL-18BP、IL-6的表达水平均高于健康对照组(P<0.05);且IL-37与细胞因子IL-18、IL-18BP、IL-6均呈正相关,sPD-1仅与细胞因子IL-6呈正相关,IL-37、sPD-1均与患者病情程度评分呈正相关。结论:IL-37、sPD-1在RA患者中表达水平升高,且与其他炎性细胞因子及疾病严重程度具有相关性,两者在RA的进展中可能发挥着重要的调控作用,为今后RA治疗提供新的依据。
类风湿关节炎; 白介素-37; 可溶性PD-1; 细胞因子
类风湿关节炎(Rheumatoid arthritis,RA)是以累及周围关节为主的多系统炎症的自身免疫疾病[1]。主要临床表现为慢性、对称性。多滑膜关节炎和关节外病变,是我国最为常见的风湿病之一,患病率约为0.4%[2]。白细胞介素-37(Interleukin-37,IL-37),归属IL-1家族,属于一类抗炎性的细胞因子,其在机体自身免疫疾病中能起到保护作用,主要机制是抑制过度的炎症反应[3]。可溶性PD-1(soluble PD-1,sPD-1)是新近发现的一个协同刺激分子。研究表明可溶性协同刺激分子参与血液循环,并在免疫应答中发挥重要调节作用,目前国内对其在自身免疫性疾病中的研究较少[4]。我们通过检测和比较RA患者及健康对照人群血清中IL-37、sPD-1的表达水平,结合分析两组人群外周血IL-18、IL-6和IL-18BP三种细胞因子的表达,探讨IL-37、sPD-1与RA的相关性及其临床意义,为临床治疗RA提供新依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
1.1.1 RA组 依据欧洲风湿病防治联合会(EULAR)和美国风湿病学院(ACR)在2010年联合修改制定的诊断标准,即通过评估患者其得分≥6分者,即可诊断为类风湿关节炎,选取2014年1月~2015年1月在本院住院及门诊确诊的类风湿关节炎患者30例。其中男16例,女性14例,平均年龄(48.94±5.1)岁。所有患者均无系统性红斑狼疮,无感染性疾病,无急慢性疾病史。
1.1.2 对照组 随机选择在本院体检中心进行健康体检的30名健康者作为对照组,其中男性健康体检者12例,女性健康体检者18例,平均年龄(50.34±7.1)岁。且该组除无类风湿关节炎外,在研究对象的年龄、性别、其他基础疾病等方面均与RA组具有可比性,且两组在上述各方面经统计学分析,差异无统计学意义。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 标本采集 病例组与对照组在采血前空腹12 h,采集外周静脉血2 ml静置半小时后采用离心机进行离心(2 000 r/min离心5 min),离心后用抗凝素管收集上层血浆,并置于-80℃冰箱保存备用。
1.2.2 检测方法 运用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)试剂盒检测IL-37、sPD-1、IL-18、IL-6和IL-18BP等细胞因子表达情况,严格按照试剂盒内的说明书进行实验。直线回归方程的计算:根据标准品的浓度以及对应的A值计算出标准曲线,再用回归方程根据样品的A值,计算出对应的样品浓度。每个标本均需重复测量3次,以减少误差。仪器为ELX800酶标仪,由美国BioTech公司生产。
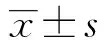
2 结果
2.1 两组血清IL-37和sPD-1分子的表达水平 经ELISA检测结果发现,RA组患者血清中IL-37和sPD-1的表达水平均高于健康对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图1、2。
2.2 RA相关细胞因子IL-18、IL-18BP、IL-6分子的表达水平 经ELISA检测结果发现,RA组患者血清中3种炎症相关细胞因子IL-18、IL-18BP、IL-6的表达水平均高于健康对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。
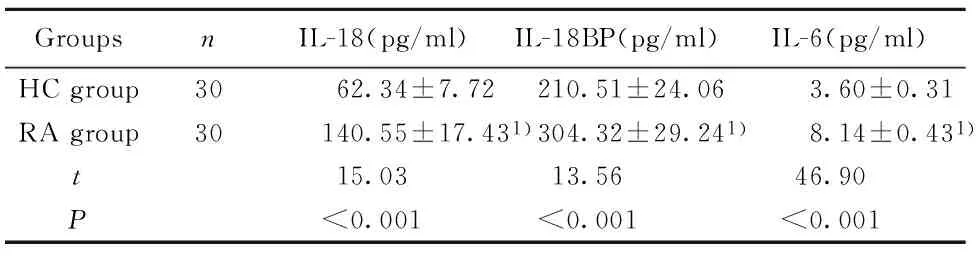
2.3 IL-37、sPD-1与3种细胞因子相关性分析 经相关性统计分析结果发现,IL-37与细胞因子IL-18(r=0.928,P=0.004)、IL-18BP(r=0.931,P=0.002)、IL-6(r=0.851,P=0.010)均呈正相关;sPD-1仅与细胞因子IL-6呈正相关(r=0.881,P=0.010),见表2。
2.4 RA与血清IL-37、sPD-1相关性分析 对按照ACR及EULAP联合制定的RA评分标准(表3)所获得的患者评分与RA患者血清中IL-37、sPD-1水平进行相关性分析发现,血清IL-37与患者病情程度评分呈正相关(r=0.863,P=0.004),sPD-1与患者病情程度评分呈正相关(r=0.939,P=0.001),见表4。
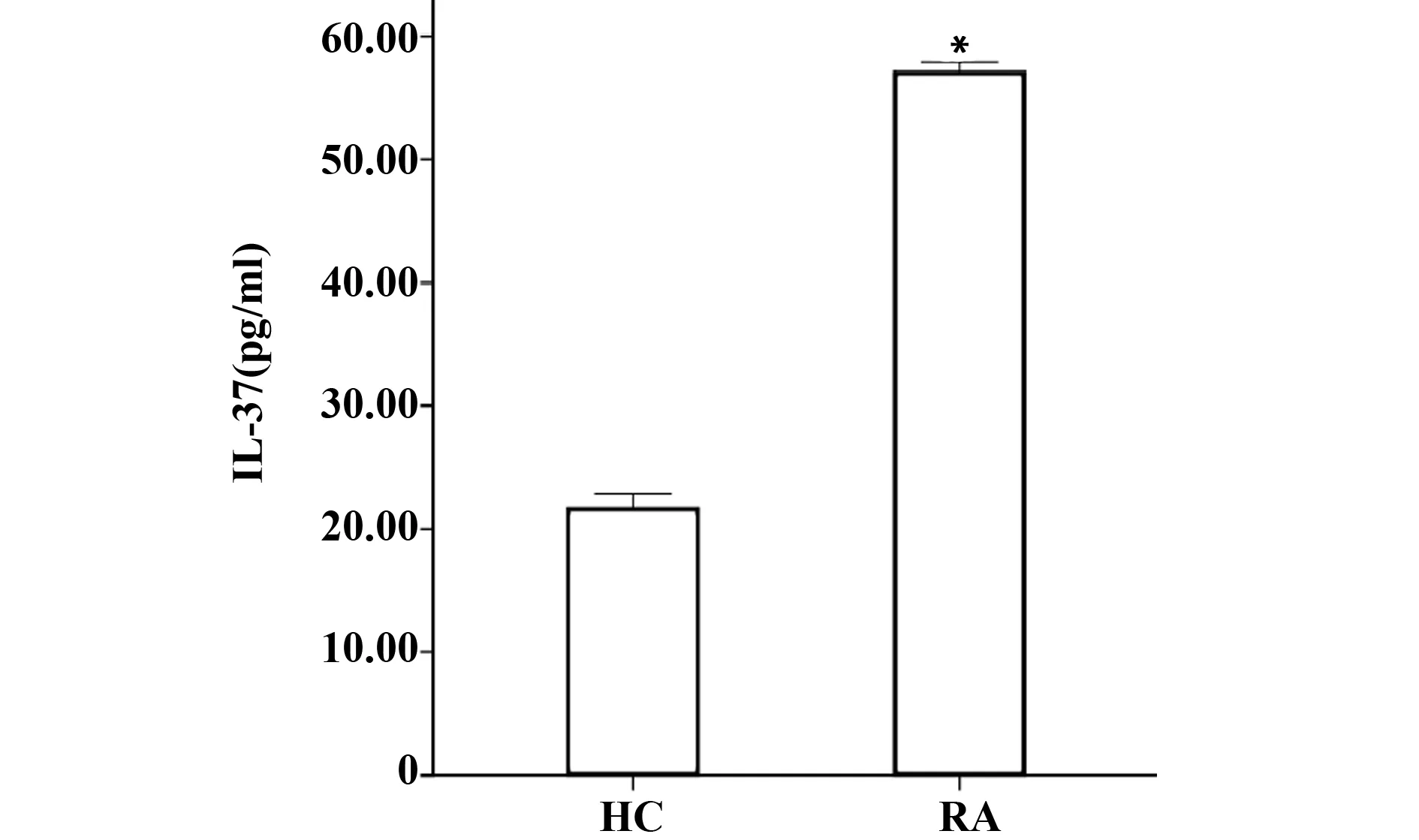
图1 两组血清IL-37分子的表达水平Fig.1 Expression of serum IL-37 in two groupsNote: Significantly different from group HC,*.P<0.05.
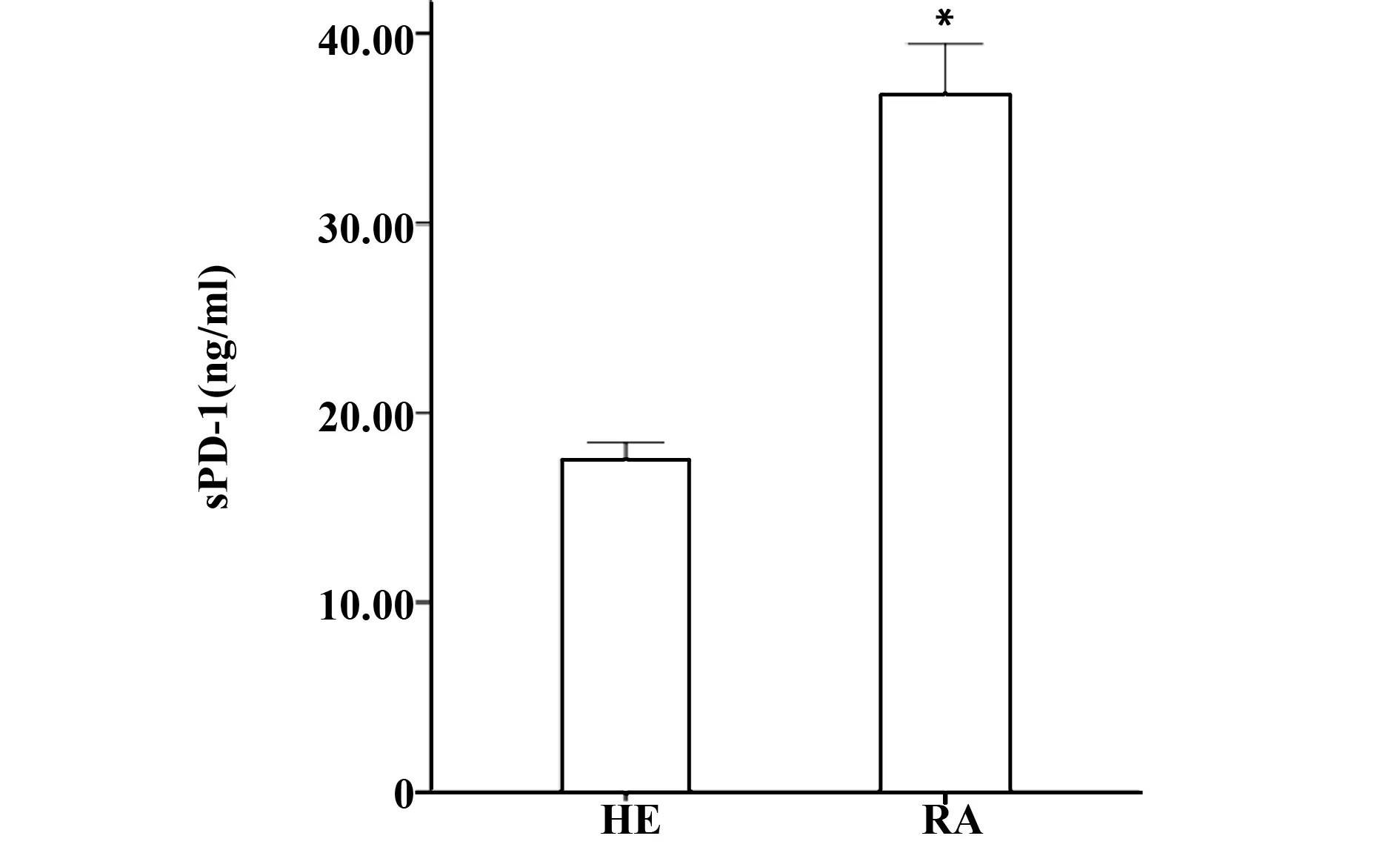
图2 两组血清sPD-1分子的表达水平Fig.2 Expression of serum sPD-1 in two groupsNote: Significantly different from group HC,*.P<0.05.
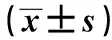
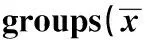
GroupsnIL-18(pg/ml)IL-18BP(pg/ml)IL-6(pg/ml)HCgroup3062.34±7.72210.51±24.063.60±0.31RAgroup30140.55±17.431)304.32±29.241)8.14±0.431)t15.0313.5646.90P<0.001<0.001<0.001
Note:Significantly different from group HC,1)P<0.05.
表2 IL-37、sPD-1与细胞因子IL-18、IL-18BP、IL-6相关性分析
Tab.2 Correlation between IL-37,sPD-1 expression level and serum IL-8,IL-18BP,IL-6
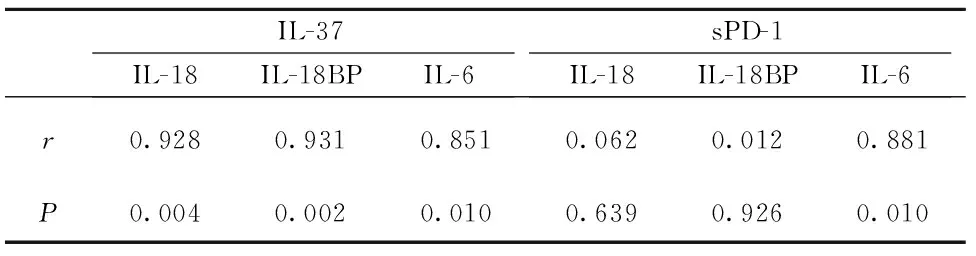
IL-37IL-18IL-18BPIL-6sPD-1IL-18IL-18BPIL-6r0.9280.9310.8510.0620.0120.881P0.0040.0020.0100.6390.9260.010
表3 类风湿关节炎诊断评分标准
Tab.3 Diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis
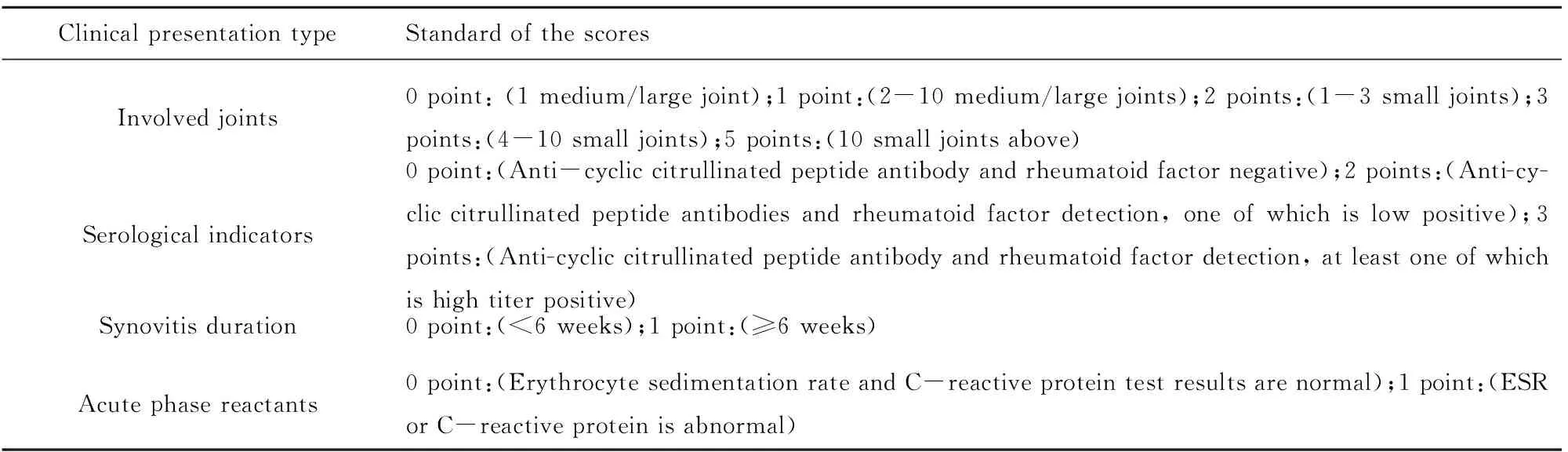
ClinicalpresentationtypeStandardofthescoresInvolvedjoints0point:(1medium/largejoint);1point:(2-10medium/largejoints);2points:(1-3smalljoints);3points:(4-10smalljoints);5points:(10smalljointsabove)Serologicalindicators0point:(Anti-cycliccitrullinatedpeptideantibodyandrheumatoidfactornegative);2points:(Anti-cy-cliccitrullinatedpeptideantibodiesandrheumatoidfactordetection,oneofwhichislowpositive);3points:(Anti-cycliccitrullinatedpeptideantibodyandrheumatoidfactordetection,atleastoneofwhichishightiterpositive)Synovitisduration0point:(<6weeks);1point:(≥6weeks)Acutephasereactants0point:(ErythrocytesedimentationrateandC-reactiveproteintestresultsarenormal);1point:(ESRorC-reactiveproteinisabnormal)
表4 患者血清IL-37、sPD-1水平与RA评分相关性分析
Tab.4 Correlation between IL-13,sPD-1 expression level and RA score
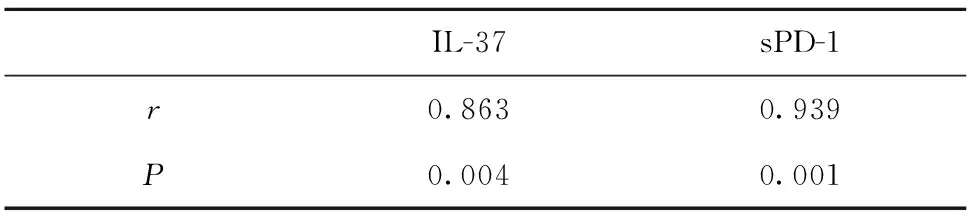
IL-37sPD-1r0.8630.939P0.0040.001
3 讨论
RA是一种自身免疫系统疾病,主要病理表现为慢性血管炎和滑膜炎,严重损害患者关节腔血供,目前其病因学机制尚不明确,主要病理表现为慢性血管炎和滑膜炎[5]。RA患者滑膜组织中存在众多巨噬细胞及其分泌的IL-1、TNF-α、TNF-β等细胞因子。越来越多的研究表明这些细胞因子在RA的发生、发展过程中起到了不可或缺的作用[6-9]。IL-37是IL-1家族的新成员,具有抑制先天性炎症反应和调节免疫应答的作用[10]。IL-37在正常机体组织中的表达较少,但在发生炎症的组织中高表达,如系统性红斑狼疮患者体内IL-37表达水平较高。本次实验亦观察到RA组患者外周血中IL-37的表达水平高于健康对照组。提示IL-37同RA的发生具有一定相关性。
由于IL-37发现时间较晚,其抑制机制的研究尚处于初级阶段,但受到越来越多学者的关注,力图寻找其在自身免疫性疾病治疗中的作用。研究表明[11],细胞因子IL-18、IL-18BP和IL-6均参与了RA的疾病进程,且IL-37与这几种细胞因子具有相关性。IL-18是IL-1家族中一类致炎性细胞因子,其在促进NK细胞活性及Th1类炎症反应中发挥着重要作用。IL-37通过与IL-18BP结合形成的复合物增强了抑制IL-18诱导生成IFN-γ的能力。IL-6在RA的发生发展进程中发挥重要作用[12,13]。本次实验发现,RA组患者外周血中IL-37以及其他几种炎症相关细胞因子IL-18、IL-18BP、IL-6的表达水平均高于健康对照组;且IL-37与IL-18、IL-18BP、IL-6均呈正相关。另外,通过与RA患者疾病程度的评分的相关性研究,亦证实了IL-37与患者病情严重程度呈正相关。这与其他学者的研究结果相一致[14]。提示IL-37作为炎症抑制因子因受炎症因子刺激而代偿性增加,参与了RA的病程发展,并且IL-37与炎性相关因子之间相互影响。
虽然,目前RA的病因及发病机制尚不十分清楚,但大多数学者认为[15-17],RA是由T细胞介导的自身免疫性疾病,在RA免疫病理过程中,T淋巴细胞的过度活化起着重要作用。目前研究表明[18,19],功能异常的T细胞介导的自身免疫损伤与RA密切相关,RA病程中T淋巴细胞的过度活化是其中一个环节。T细胞的活化需要双信号,其中第二信号需由T细胞和APC间协同刺激分子的相互作用启动。而新近发现的协同刺激分子PD-1在自身免疫反应疾病中,起到保护机体的作用,其表达可缓解促炎症T细胞在自身免疫反应疾病中的过度反应,减缓其对人体自身组织细胞的伤害。Wan等[20]研究发现,sPD-1在类风湿性关节炎患者的血清、滑膜液中的表达水平显著升高。本次研究发现,RA组患者外周血中sPD-1的表达水平高于健康对照组,且sPD-1与患者病情程度评分呈正相关,但其与IL-18、IL-18BP、IL-6三种细胞因子的相关性分析发现,除IL-6细胞因子外,均无相关性。提示sPD-1在RA的免疫病理进程中发挥了重要作用,这为进一步研究sPD-1在类风湿性关节炎病程中的作用和意义提供了实验基础。
综上所述,健康人体内IL-37、sPD-1表达较少,而在RA患者中表达水平升高,且与疾病严重程度相关。IL-37与其他炎性细胞因子IL-6、IL-18、IL-18BP具有相关性。两者在RA的进展中可能发挥着重要的调控作用。RA患者体内,炎性因子之间形成一个复杂的网络体系,作用机制亦较为复杂,通过对这些因子的检测可初步评估RA患者体内免疫功能,对预后做出判断,也为今后RA治疗提供新的依据。
[1] 杨 超,刘荣臻,张晓延,等.类风湿性关节炎患者血清中 IL-37 水平变化的探索研究[J].中华全科医学,2014,12(7):1035-1037.
[2] 冯 佳,夏 燕,袁 林,等.类风湿性关节炎及骨关节炎患者外周血单个核细胞及滑膜成纤维细胞中白细胞介素27水平增高[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2015,31(12):1673-1676.
[3] Yang T,Lin Q,Zhao M,etal.IL-37 is a novel proangiogenic factor of developmental and pathological angiogenesis[J].ATVB,2015,35(12):2638-2646.
[4] Ye L,Jiang B,Deng J,etal.IL-37 Alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing IL-17 and IL-17-triggering cytokine production and limiting Th17 cell proliferation[J].J Immunol,2015,194(11):5110-5119.
[5] Chen B,Huang K,Ye L,etal.Interleukin-37 is increased in ankylosing spondylitis patients and associated with disease activity[J].J Translational Medicine,2015,13(1):1.
[6] Zhao PW,Jiang WG,Wang L,etal.Plasma levels of IL-37 and correlation with TNF-α,IL-17A,and disease activity during DMARD treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J].PLoS One,2014,9(5):e95346.
[7] 吉春玲,瞿 洋,任亦频,等.右美托咪定对脓毒症大鼠心肌组织水通道蛋白-1及炎症细胞因子水平的干预作用[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2014,21(14):266-269.
[8] Ye Z,Wang C,Tang J,etal.Decreased interleukin-37 expression in vogt-koyanagi-harada disease and upregulation following immunosuppressive treatment[J].J Interferon Cytokine Res,2015,35(4):265-272.
[9] Magyari L,Varszegi D,Kovesdi E,etal.Interleukins and interleukin receptors in rheumatoid arthritis:Research,diagnostics and clinical implications[J].World J Orthopedics,2014,5(4):516.
[10] Xia T,Zheng X,Qian B,etal.Plasma interleukin-37 is elevated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis:its correlation with disease activity and Th1/Th2/Th17-related cytokines[J].Disease markers,2015,6(10):1-6.
[11] Boutet MA,Bart G,Penhoat M,etal.Distinct expression of interleukin (IL)-36α,β and γ,their antagonist IL-36Ra and IL-38 in psoriasis,rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn′s disease[J].Clin Exp Immunol,2016,184(2):159-173.
[13] Greisen SR,Rasmussen TK,Stengaard-Pedersen K,etal.Increased soluble programmed death-1 (sPD-1) is associated with disease activity and radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis[J].Scandinavian J Rheumatol,2014,43(2):101-108.
[14] Pen JJ,Keersmaecker BD,Heirman C,etal.Interference with PD-L1/PD-1 co-stimulation during antigen presentation enhances the multifunctionality of antigen-specific T cells[J].Gene Therapy,2014,21(3):262-271.
[15] Hassan WA,Baraka EA,Fouad NA.Clinical significance of soluble programmed death-1 (sPD-1) in rheumatoid arthritis patients:Relation to disease activity and functional status[J].Egyptian Rheumatologist,2015,37(4):165-169.
[16] Dolff S,Quandt D,Feldkamp T,etal.Increased percentages of PD-1 on CD4+T cells is associated with higher INF-γ production and altered IL-17 production in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Scandinavian J Rheumatol,2014,43(4):307-313.
[17] Fadda S,Abolkheir E,Afifi R,etal.Serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 in rheumatoid arthritis patients:Correlation with disease activity and joint destruction[J].Egy Rheumatol,2016,43(4):852-858.
[18] Ikebuchi R,Konnai S,Okagawa T,etal.Blockade of bovine PD-1 increases T cell function and inhibits bovine leukemia virus expression in B cells in vitro[J].Veterinary Res,2013,44(1):1.
[19] Yang L,Zhang J,Tao J,etal.Elevated serum levels of Interleukin-37 are associated with inflammatory cytokines and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis[J].Apmis,2015,123(12):1025-1031.
[20] Wan ZY,Sun Z,Song F,etal.Downregulated interleukin 37 expression associated with aggravation of intervertebral disc degeneration[J].Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2014,7(2):656-662.
[收稿2016-08-05 修回2016-08-26]
(编辑 倪 鹏)
Expression and clinical significance of serum IL-37 and soluble PD-1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
CHENXi-Xi,TIANJuan,ZHANGJing,SUJiang.
DepartmentofRheumatologyandImmunology,SichuanAcademyofMedicalSciences&SichuanProvincialPeople′sHospital,Chengdu610072,China
Objective:To investigate the relationship between IL-37 and soluble PD-1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and investigate the relationship between IL-37 and soluble PD-1.Methods: Peripheral blood was collected from RA patients and control group.The levels of IL-37 and sPD-1 in 30 RA patients (RA standard score ≥ 6) and 30 healthy controls were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The expression of IL-18, IL-6 and IL-18BP in the peripheral blood of two groups was analyzed and the correlation was analyzed by Pearson correlation analysis.Results: The results of ELISA detection showed that the expression levels of IL-37 and sPD-1 in the peripheral blood of patients with RA and other inflammatory cytokines such as IL-18, IL-18BP and IL-6 were higher than those of healthy controls (P<0.05).IL-37 was positively correlated with cytokines IL-18, IL-18BP and IL-6;sPD-1 was positively correlated with cytokine IL-6.IL-37 and sPD-1 were positively correlated with the severity of patients.Conclusion: IL-37 and sPD-1 are elevated in RA patients and associated with other inflammatory cytokines and disease severity.Both of them may play an important regulatory role in the progress of RA, and provide a new basis for future RA therapy.
Rheumatoid arthritis;Interleukin-37;Soluble PD-1;Cytokines
10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2017.03.022
①本文受四川省卫计委科研课题资助(No.120071)。
陈栖栖(1980年-),女,硕士,主治医师,主要从事风湿免疫方面研究,E-mail:44475135@qq.com。
R593.22
A
1000-484X(2017)03-0422-04
