缺氧/好氧时间变化对SBBR处理海水养殖废水过程中胞外聚合物特性的影响❋
2017-04-10王雪礁高孟春
赵 堃, 王 哲, 王 森, 郑 栋, 王雪礁, 高孟春❋❋
(1.中国海洋大学海洋环境与生态教育部重点实验室,山东 青岛 266100; 2.中国海洋大学环境科学与工程学院,山东 青岛 266100)
缺氧/好氧时间变化对SBBR处理海水养殖废水过程中胞外聚合物特性的影响❋
赵 堃1,2, 王 哲1,2, 王 森1, 郑 栋1, 王雪礁1, 高孟春1,2❋❋
(1.中国海洋大学海洋环境与生态教育部重点实验室,山东 青岛 266100; 2.中国海洋大学环境科学与工程学院,山东 青岛 266100)
本文系统地评价了缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对处理海水养殖废水的序批式生物膜反应器(SBBR)中胞外聚合物(EPS)特性的影响。研究结果表明,在SBBR运行过程中好氧时间的缩短能抑制生物膜中微生物分泌EPS,从而导致松散附着EPS(LB-EPS)和紧密附着EPS(TB-EPS)中蛋白质(PN)和多糖(PS)含量随着好氧时间的缩短而降低。随着缺氧时间/好氧时间的变化,LB-EPS和TB-EPS的三维荧光(3D-EEM)光谱中代表不同化学组分的荧光峰位置发生了移动,荧光峰强度也发生了变化,部分荧光峰在缺氧时间/好氧时间为9.5 h/0.5 h和8 h/1 h时消失。LB-EPS和TB-EPS的傅里叶红外(FTIR)光谱中不同吸收峰的强度随着缺氧时间/好氧时间变化而变化,好氧时间的缩短对生物膜中LB-EPS和TB-EPS的PN和PS中官能团有明显的影响。
缺氧时间;好氧时间;序批式生物膜反应器;海水养殖废水;胞外聚合物

在生物法处理海水养殖废水的过程中活性污泥或生物膜中微生物分泌的胞外聚合物(Extracellular Polymeric Substances,简称EPS)能够影响反应器内微生物聚集体的特性,对活性污泥或生物膜的絮凝、沉降和脱水性能起关键作用[8-10]。EPS的化学成分比较复杂,主要包括蛋白质、糖类、核酸、脂类、腐殖酸以及一些无机组分。其中,EPS中蛋白质(PN)和多糖(PS)是主要组分,约占总量的70%~80%[11]。在废水生物处理工艺中EPS产量和组分与进水水质、污染物负荷、运行模式、溶解氧状态、有毒物质存在和环境温度是密切相关的[12-15]。为了有效地去除海水养殖废水中氮化合物,生物处理工艺中硝化过程和反硝化过程分别在好氧条件和厌氧(或缺氧)条件下进行。好氧/缺氧时间的变化能够影响生物处理工艺内微生物群落的活性,从而影响微生物分泌EPS的量和组分。然而,目前尚未发现有关缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对SBBR处理海水养殖废水过程中胞外聚合物特性影响的相关报道。因此,本文研究了缺氧/好氧时间变化对生物膜中紧密附着EPS(TB-EPS)和松散附着EPS(TB-EPS)中PN和PS含量的影响,通过三维荧光光谱(3D-EEM)和傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)分析LB-EPS和TB-EPS化学组成的变化。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置及运行条件
装有悬挂式组合填料的SBBR由有机玻璃柱制成,高度和直径分别为550和350 mm。组合式填料由醛化纤维压于双圈塑料环上,使纤维呈雪花状分布,可有效进行气体切割,提高氧转移效率。填料直径是150 mm,塑料环之间距离为100 mm,反应器内放置4片填料。进水通过蠕动泵进入SBBR,排水由电磁阀控制,采用重力排水,容积交换率为50%。好氧阶段通过电磁式空气压缩机由反应器底部砂芯曝气头曝气,维持溶解氧在2 mg/L以上。缺氧阶段通过磁力搅拌器使混合液与生物膜接触。进水、曝气、搅拌、沉淀和排水通过时间继电器实现自动控制。在SBBR运行过程中,缺氧阶段的DO低于0.5 mg/L,好氧阶段的DO高于2 mg/L。在本研究中SBBR的缺氧时间/好氧时间变化情况如表1所示。

表1 不同运行阶段的运行参数Table 1 Operation parameters of different operational stage
1.2 接种污泥和进水水质

1.3 常规指标分析方法
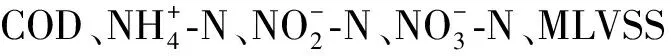
1.4 胞外聚合物提取和分析方法
1.4.1 胞外聚合物提取和测定 胞外聚合物(EPS)在细胞外的分布呈现为具有流变性的双层结构,内层称为紧密附着EPS(TB-EPS),外层称为松散附着EPS(LB-EPS)。依据Li和Yang[10]的方法适当修改后提取LB-EPS和TB-EPS。具体步骤如下:取反应器中生物膜样品40 mL,将其在6 000 r/min下离心5 min,弃去上清夜,得到浓缩的生物膜样品;用预热到70 ℃的NaCl溶液(盐度为3%)稀释至40 mL,盖紧盖子并快速振荡1 min;将提取后的混合液于6 000 r/min离心10 min;收集上清液,即为LB-EPS。用盐度为3%NaCl溶液稀释至40 mL,60 ℃水浴30min后6 000 r/min离心15 min,收集上清液,即为TB-EPS。
上清液经过0.45 μm醋酸纤维素膜过滤后分析LB-EPS和TB-EPS中蛋白质(PN)和多糖(PS)含量,PN含量采用Folin酚法测定[17],PS含量采用蒽酮比色法测定[18]。
1.4.2三维荧光光谱分析 LB-EPS和TB-EPS三维荧光光谱(3D-EEM)采用荧光分光光度计(F-4600,Hitachi,日本)测定。激发波长(Ex)范围200~400 nm,扫描间隔5 nm;发射波长(Em)范围200~500 nm,扫描间隔5 nm;激发光和发射光的狭缝均为10 nm,扫描速度为1 200 nm/min。采用Origin 8.1软件绘制光谱图。
1.4.3傅里叶变换红外光谱分析 LB-EPS和TB-EPS红外光谱(FTIR)采用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Tensor 27,Bruker Optics,德国)测定,LB-EPS和TB-EPS提取液经过冷冻干燥处理后与光谱纯KBr按照1∶100研磨混合,并于一定压力下保持若干分钟制成半透明薄片,在400~4 000 cm-1波数范围内扫描,检测器分辨率为4 cm-1。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对SBBR性能的影响


表2 缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对SBBR处理海水养殖废水性能的影响Table 2 Effect of anoxic time/aerobic time on the performance of SBBR treating mariculture wastewater
2.2 缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对生物膜中LB-EPS和TB-EPS主要组分的影响
图1表示缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对生物膜中LB-EPS和TB-EPS的PN和PS含量影响。

图1 缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对生物膜中LB-EPS和TB-EPS的PN和PS含量影响
在缺氧时间和好氧时间之和为10 h情况下,当好氧时间从3 h逐渐缩短到0.5 h时,生物膜中LB-EPS的PN含量从10.26 mg·g-1MLVSS逐渐降低到5.57 mg·g-1MLVSS,生物膜中LB-EPS的PS含量从6.93 mg·g-1MLVSS逐渐降低到2.84 mg·g-1MLVSS。同样地,生物膜中TB-EPS的PN含量从12.20 mg·g-1MLVSS逐渐降低到6.79 mg·g-1MLVSS,TB-EPS中PS含量从9.32 mg·g-1MLVSS逐渐降低到4.07 mg·g-1MLVSS。这些研究结果表明,在SBBR一个运行周期中好氧时间的增加能够促进生物膜中微生物对LB-EPS和TB-EPS的分泌量。为了进一步验证上述研究结果,本研究中将SBBR缺氧时间/好氧时间又依次变为8h/1h和7h/1h。由图1可知,缺氧时间/好氧时间为7h/1h时生物膜中LB-EPS(或TB-EPS)中PN和PS含量均高于缺氧时间/好氧时间为8h/1h时生物膜的LB-EPS(或TB-EPS)中PN和PS含量,也很好地说明了好氧时间的延长有利于生物膜中微生物分泌EPS。
2.3 缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对LB-EPS和TB-EPS的3D-EEM光谱影响
为了考察缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对LB-EPS和TB-EPS化学组成的影响,考察了缺氧时间/好氧时间分别为7 h/3 h、9.5 h/0.5 h、8 h/1 h和7 h/1 h时EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱变化情况(见图2)。在3D-EEM光谱中,X轴和Y轴分别代表发射光谱(Em)和激发光谱(Ex),荧光峰的位置通过Em/Ex来表示。每个3D-EEM荧光光谱峰能够表征LB-EPS和TB-EPS的化学组成。由图2可知,LB-EPS和TB-EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱中出现了荧光峰A(275~280/330~345 nm)、荧光峰B(220~230/330~345 nm)、C(270~275/440~465 nm)和D(310~360/370~450 nm)。根据以往的文献报道[19-21],荧光峰A、B、C和D分别与色氨酸蛋白类物质、芳环蛋白类物质、胡敏酸类物质和富里酸类物质有关。在缺氧时间/好氧时间为7 h/3 h时LB-EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱中出现了荧光峰A、B、C和D,荧光峰C在缺氧时间/好氧时间为9.5 h/0.5 h时在LB-EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱中消失,荧光峰B和D未出现在缺氧时间/好氧时间为8 h/1 h和7 h/1 h时LB-EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱。生物膜中TB-EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱在不同缺氧时间/好氧时间时均仅出现了荧光峰A和B,未发现荧光峰消失或新荧光峰出现。
表3表示缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对生物膜中LB-EPS和TB-EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱中不同荧光峰位置和荧光强度的影响。荧光峰的位置沿着Ex轴(或Em轴)增长(称为红移)或减少(称为蓝移)。与缺氧时间/好氧时间为7 h/3 h时相比,缺氧时间/好氧时间为9.5 h/0.5 h、8 h/1 h和和7 h/1 h时荧光峰A的位置在LB-EPS、TB-EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱均沿着Em轴红移了10 nm。LB-EPS的荧光峰B在缺氧时间/好氧时间为9.5 h/0.5 h和8 h/1 h时分别沿Ex/Em轴蓝移/红移了10 nm/10 nm,在缺氧时间/好氧时间为7 h/1 h时LB-EPS的荧光峰B沿着Ex轴蓝移了10 nm。缺氧时间/好氧时间为9.5 h/0.5 h和8 h/1 h


((a)LB-EPS (7h/3h); (b)TB-EPS (7h/3h); (c)LB-EPS (9.5 h/0.5 h); (d)TB-EPS (9.5 h/0.5 h); (e)LB-EPS (8 h/1 h); (f)TB-EPS (8 h/1 h); (g)LB-EPS (7 h/1 h); (h)TB-EPS (7 h/1 h).)

表3 不同缺氧时间/好氧时间下LB-EPS和TB-EPS的荧光峰位置和强度Table 3 Fluorescence peak location and intensity of LB-EPS and TB-EPS at different anoxic time/aerobic time
时荧光峰B在TB-EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱中均未发生位移,但在缺氧时间/好氧时间为7 h/1 h时荧光峰B在在TB-EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱沿着Em轴红移了10 nm。荧光峰D的位置在缺氧时间/好氧时间为9.5 h/0.5 h时沿着Ex轴蓝移了10 nm。由表3可知,荧光峰A、B、C和D的强度在不同缺氧时间/好氧时间时或增大或降低。荧光峰的红移与荧光基团中羰基、羧基、羟基和胺基的增加有关[19],蓝移与芳香环的减少有关[22-23]。
2.4 缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对生物膜中LB-EPS和TB-EPS的FTIR光谱影响
为了评价缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对生物膜的LB-EPS和TB-EPS中PN和PS的官能团影响,分别考察了缺氧时间/好氧时间为7 h/3 h、8 h/2 h、9.5 h/0.5 h、8 h/1 h和7 h/1 h时生物膜中LB-EPS和TB-EPS的FTIR光谱变化情况(见图3)。3 415 cm-1处的宽吸收峰是与来自多糖类化合物中羟基和来自蛋白质中氨基的伸缩振动导致[24]。1 637 cm-1附近的吸收峰是与蛋白质二级结构中β-sheets的C=O伸缩振动相关[25-26]。1 402 cm-1附近吸收峰是甲基中C—H键振动产生的[27],1 137 cm-1附近吸收峰是多糖类化合物和芳香族化合物中C—O键的伸缩振动导致[28]。615 cm-1附近属于指纹区,表明样品中存在着不饱和键[29]。在LB-EPS和TB-EPS的FTIR光谱中3 415、1 637和1 137 cm-1处均有明显的吸收峰存在,进一步说明了表明LB-EPS和TB-EPS中蛋白质类和多糖类化合物的存在。在不同的缺氧时间/好氧时间下,LB-EPS和TB-EPS的FTIR光谱是相似的,但是每个峰的相对强度却表现出不同的变化。在缺氧时间和好氧时间之和为10 h情况下,当好氧时间从3 h逐渐缩短到0.5 h时,3 415和1 637 cm-1处吸收峰的相对强度在LB-EPS和TB-EPS的FTIR光谱中均逐渐降低。与缺氧时间/好氧时间为8 h/1 h时相比,LB-EPS中3 415和1 637 cm-1处吸收峰的相对强度在缺氧时间和好氧时间为7 h/1 h时变强,但该两吸收峰的相对强度在LB-EPS傅里叶红外光谱中变化不大。1 402和1 137 cm-1附近吸收峰的相对强度在不同缺氧时间和好氧时间下或增强或变弱。研究结果表明,缺氧时间/好氧时间变化对生物膜的LB-EPS中蛋白质和TB-EPS中多糖的官能团有更明显的影响。

((I) 7 h/3 h; (II) 8h/2h; (III) 9 h/ 1h; (IV) 9.5 h/0.5 h; (V) 8 h/1 h; (VI) 7 h/1 h.)图3 不同缺氧时间/好氧时间下生物膜中LB-EPS (a)和TB-EPS (b)的FTIR光谱
3 结论
(1)在好氧时间和缺氧时间之和为定值的情况下,好氧时间的缩短使LB-EPS和TB-EPS中PN和PS含量降低,不利于SBBR内生物膜中微生物分泌更多的EPS。
(2)在LB-EPS和TB-EPS的3D-EEM荧光光谱中代表不同化学组成的荧光峰在不同缺氧时间/好氧时间下部分消失,或者荧光峰位置发生了红移或蓝移,表明缺氧时间/好氧时间变化能够影响LB-EPS和TB-EPS的化学组成。
(3)LB-EPS和TB-EPS的FTIR光谱中不同吸收峰的强度随着缺氧时间/好氧时间变化而变化,说明好氧时间的缩短对LB-EPS和TB-EPS中PN和PS的官能团有明显的影响。
[1] FAO. The state of World Fisheries and Aquaculture[M]. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization, 2014.
[2] Hagopian D S, Riley J G. A closer look at the bacteriology of nitrification [J]. Aquaculture Engineering, 1998, 18: 223-244.
[3] Cripps S J, Bergheim A. Solids management and removal for intensive land-based aquaculture production systems [J]. Aquaculture Engineering, 2000, 22: 33-56.
[4] Gregory S P, Shields R J, Fletcher D J, et al. Bacterial community responses to increasing ammonia concentrations in model recalculating vertical flow saline biofilters [J]. Ecology Engineering, 2010, 36: 1485-1491.
[5] Boopathy R, Bonvillain C, Fontenot Q, et al. Biological treatment of low-salinity shrimp aquaculture wastewater using sequencing batch reactor [J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2007, 59: 16-19.
[6] Matos C T, Sequeira A M, Velizarov S, et al. Nitrate removal in a closed marine system through the ion exchange membrane bioreactor [J]. Journal of Hazardous Material, 2009, 166: 428-434.
[7] Webb J M, Quintã R, Papadimitriou S, et al. The effect of halophyte planting density on the efficiency of constructed wetlands for the treatment of wastewater from marine aquaculture [J]. Ecology Engineering, 2013, 61: 145-153.
[8] 吴志高. 胞外聚合物对污泥沉降性能的影响及其生物除磷中的作用研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2006. Wu Zhi-Gao. Study on the Effect of Extracellular Polymer Substances on the Settleability of the Sludge and Its Role in Biological Removal of Phosphorus [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2006.
[9] Yang S F, Li X Y. Influence of extracellular polymeric substances(EPS) on the characteristics of activated sludge under non-steady-state conditions [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2009, 44(1): 91-96.
[10] Li X Y, Yang S F. Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewater ability of activated sludge [J]. Water Research, 2007, 1(5): 1022-1030.
[11] 杨敏, 胡学伟, 宁平, 等. 废水生物处理中胞外聚合物(EPS)的研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2011, 31(7): 7-12. Yang M, Hu X W, Ning P, et al. Research progress in extracellular polymeric substances applied to biological wastewater treatment [J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2011, 31(7): 7-12.
[12] 操家顺, 朱哲莹, 方芳, 等. 活性污泥处理偶氮染料废水过程中胞外聚合物特性研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(9): 2498-2503. Cao J S, Zhu Z Y, Fang F, et al. Characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in the azo dye wastewater treated by activated sludge [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(9): 2498-2503.
[13] 李莹, 田林, 张宏伟, 等. 膜生物反应器中运行参数对污泥胞外聚合物的影响 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(7): 1562-1566. Li Y, Tian L, Zhang H W, et al. Influence of operation parameters on extracellular polymeric substances from activated sludge in membrane bioreactor [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2011, 5(7): 1562-1566.
[14] Jeong T Y, Cha G C, Yoo I K, et al. Characteristics of bio-fouling in a submerged MBR [J]. Desalination, 2007, 207(1-3): 107-113.
[15] Ji L, Zhou J T. Influence of aeration on microbial polymers and membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2006, 276(1-2): 168-177.
[16] 国家环境保护总局, 水和废水监测分析方法编委会. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. (第四版). 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. Chinese NEPA. Water and Wastewater Monitoring Methods[M]. Fourth ed. Beijing: Chinese Environmental Science Publishing Press, 2002.
[17] Lowry O H, Rosebrough N J, Farr A L, et al. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1951, 193: 265-275.
[18] Dubois M, Gilles K A, Hamilton J K, et al. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substance [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1956, 28: 350-356.
[19] Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer J A, et al. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(24): 5701-5710.
[20] Yamashita Y, Tanoue E. Chemical characterization of protein-like fluorophores in DOM in relation to aromatic amino acids [J]. Marine Chemistry, 2003, 82(3-4): 255-271.
[21] Sheng G P, Yu H Q. Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances of aerobic and anaerobic sludge using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy [J]. Water Research, 2006, 40(6): 1233-9.
[22] Coble P G. Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using matrix excitation-emission spectroscopy [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1996, 51(4): 325-346.
[23] Korshin G V, Kumke M U, Li C W, et al. Influence of chlorination on chromophores and fluorophores in humic substances [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1999, 33(8): 1207-1212.
[24] Ramesh A, Lee D J, Hong S G. Soluble microbial products (SMP) and soluble extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from wastewater sludge [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 73(1): 219-225.
[25] Wang Z, Wu Z, Yin X, et al. Membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor (MBR) under sub-critical flux operation: membrane foulant and gel layer characterization [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008, 325(1): 238-244.
[26] Maruyama T, Katoh S, Nakajima M, et al. FT-IR analysis of BSA fouled on ultrafiltration and microfiltration membranes [J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2001, 192(1): 201-207.
[27] Pongjanyakul T, Puttipipatkhachorn S. Xanthan-alginate composite gel beads: molecular interaction and in vitro characterization [J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2007, 331(1): 61-71.
[28] Zhu L, Lv M L, Dai X, et al. The stability of aerobic granular sludge under 4-chloroaniline shock in a sequential air-lift bioreactor (SABR) [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 140(3): 126-130.
[29] Wang Z, Wu Z, Tang S. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in a submerged membrane bioreactor by using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy [J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(6): 1533-1540.
责任编辑 庞 旻
Effects of Anoxic Time/Aerobic Time on the Characterization of Extracellular Polymeric Substances from a SBBR Treating Mariculture Wastewater
ZHAO Kun1,2, WANG Zhe1,2, WANG Sen1, ZHENG Dong1, WANG Xue-Jiao1, GAO Meng-Chun1,2
(1.Tle Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science and Ecology, Ministry of Education, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China; 2.College of Environmental Science and Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China)
The effects of anoxic time/aerobic time on the characterization of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from the biofilm were evaluated in a sequencing batch biofilm reactor (SBBR) treating mariculture wastewater. The decrease of aerobic time during the SBBR operation could inhibit the EPS secretion of organisms in the biofilm, which could result in the decrease of protein (PN) and polysaccharide (PS) content in the LB-EPS and TB-EPS with the decrease of aerobic time. The locations of the fluorescence peaks representing different chemical compositions of LB-EPS and TB-EPS showed some shifts in three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix (3D-EEM) fluorescence spectra with the variation of anoxic time/aerobic time, and the intensity of fluorescence peaks also varied at different operational stages. Some fluorescence peaks disappeared at the anoxic time/aerobic time of 9.5h/0.5h and 8h/1h. The intensities of different absorption peaks varied with the variation of anoxic time/aerobic time, which suggested that the decrease of aerobic time could obviously affect the functional groups of PN and PS in the LB-EPS and TB-EPS.
Anoxic time; aerobic time; sequencing batch biofilm reactor; mariculture wastewater; extracellular polymeric substances
国家自然科学基金项目(51178437)资助 Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51178437)
2016-04-15;
2016-05-27
赵 堃(1985-),男,博士生。E-mail:dragoon83123@163.com
❋❋ 通讯作者:E-mail:mengchun@ouc.edu.cn
X171
A
1672-5174(2017)05-034-08
10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20160129
赵堃, 王哲, 王森, 等. 缺氧/好氧时间变化对SBBR处理海水养殖废水过程中胞外聚合物特性的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 47(5): 34-41.
ZHAO Kun, WANG Zhe, WANG Sen, et al. Effects of anoxic time/aerobic time on the characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from a SBBR treating mariculture wastewater[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(5): 34-41.
