负载敏感变量泵结构建模与性能分析
2017-03-04陈随英赵建军毛恩荣宋正河朱忠祥杜岳峰
陈随英,赵建军,毛恩荣,宋正河,朱忠祥,杜岳峰
负载敏感变量泵结构建模与性能分析
陈随英,赵建军,毛恩荣,宋正河,朱忠祥,杜岳峰※
(中国农业大学工学院现代农业装备优化设计北京市重点实验室,北京100083)
作为现代农业装备液压系统关键零部件,负载敏感变量泵为农业绿色生产提供了保障。为深入研究负载敏感变量泵的工作性能,该文重点分析了其内部机械结构和工作机理,充分考虑了各运动部件的有效行程范围,应用现代控制理论状态空间法建立了基于边界条件的负载敏感变量泵非线性数学模型,基于Matlab/Simulink软件,采用四阶龙格-库塔算法对其稳态和动态性能进行了仿真分析,并搭建闭心式负载敏感液压系统试验平台,完成其性能试验,通过对比分析负载敏感变量泵动态特性试验与仿真结果,得到负载补偿压力误差约为0.1 MPa,验证了负载敏感变量泵非线性数学模型的正确性。试验结果表明:负载敏感变量泵输出流量和压力可实时与负载相适应,补偿压力约为1.5 MPa,可有效提高液压系统效率,减少系统发热,满足现代农业装备作业机组的田间作业需求。
泵;计算机仿真;农业装备;负载敏感;变量泵;非线性建模;边界条件
0 引 言
近年来,随着中国农业生产机械化、自动化水平不断提高,农机装备逐步向大型化、复合化、智能化方向发展[1-3]。液压传动系统以其质量功率比大、调速范围广、低速稳定性好、易于布局等优点,在农机产业发展进程中得到了广泛应用[4-5]。以大型农机底盘静液压驱动系 统[6-8]和重型拖拉机电液提升器[9]为例,前者可有效提高驾驶员操作舒适性,降低劳动强度;后者可显著提高拖拉机悬挂作业机组[10-13]的田间作业质量和作业效率。
国外农机装备整机及作业机组配套液压系统为适应田间作业环境复杂、负载波动大、行驶速度低等特点,广泛采用闭心式负载敏感液压系统回路[14-16],该回路主要由变量泵、液压阀、液压执行机构等组成,可根据实际负载工况进行压力和流量补偿,最大限度降低液压系统的功率损失,减少系统发热,达到节能环保的目的。而国内由于缺乏液压关键零部件自主研发能力,农机装备液压系统多数仍采用开心式定量泵液压系统回路,降低了液压系统工作效率,已难以适应现代化农业生产节能增效的发展要求。
目前,国内学者针对农机装备液压系统核心元件及关键技术的研究尚处于起步阶段,且主要集中在液压阀仿真优化及特性分析方面[17-21],而在液压泵建模仿真及性能试验方面研究相对较少[22-24]。为此,本文拟以负载敏感变量泵为研究对象,在对比分析国内外现有液压泵建模方法[25-30],结合变量泵内部结构和工作原理,并充分考虑变量泵非线性因素及流量调节机构有效行程范围的基础上,建立基于边界条件的负载敏感变量泵非线性数学模型,并进行仿真分析与试验研究。
1 负载敏感变量泵数学建模
1.1 负载敏感变量泵结构及工作原理
负载敏感变量泵液压系统原理图如图1所示,主要由斜盘式柱塞泵1、有弹簧变量机构柱塞缸2、无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸3、压力控制阀4、流量控制阀5、负载反馈单向阀6、泄压阻尼孔7和减震阻尼孔8组成,额定压力为25 MPa,公称流量为68 L/min。由图1可知,当系统压力低于压力控制阀调定压力时,压力控制阀右位工作,变量泵通过流量控制阀调整斜盘倾角,为系统提供所需流量,变量泵出口压力始终高出负载压力一定值;当系统压力高于压力控制阀调定压力时,压力控制阀左位工作,切断流量控制阀与无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸之间的油路,变量泵输出的高压油进入无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸的无杆腔,使变量泵斜盘倾角变小,直至接近零排量, 满足变量泵在超载工况下输出高压小流量的功能需求,减少了液压系统的功率损失。
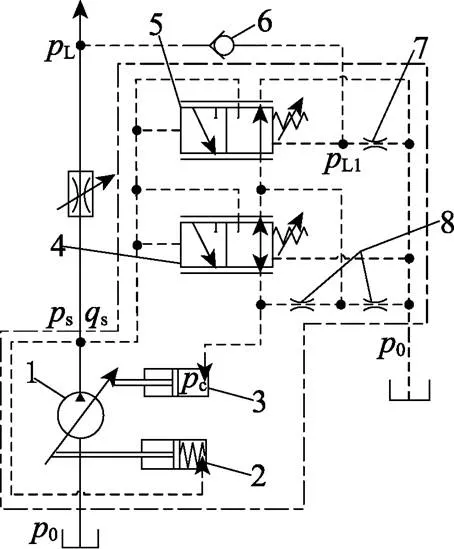
1. 斜盘式柱塞泵 2. 有弹簧变量机构柱塞缸 3. 无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸 4. 压力控制阀 5. 流量控制阀 6. 负载反馈单向阀7. 泄压阻尼孔 8. 减震阻尼孔
1. Swash plate piston pump 2. Plunger cylinder with spring variable mechanism 3. Plunger cylinder without spring variable mechanism 4. Pressure control valve 5. Flow control valve 6. Load-sensing check valve 7. Pressure relief damping orifice 8. Shock absorbing damping orifice
注:L为负载压力,Pa;L1为流量控制阀低压控制油腔压力,Pa;0为回油压力,Pa;s为变量泵出口压力,Pa;s为变量泵出口流量,m3·s-1;c为无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸无杆腔油液压力,Pa。
Note:Lis the load pressure, Pa;L1is the pressure of oil chamber with low pressure control of the flow control valve, Pa;0is the return oil pressure, Pa;sis the variable pump outlet pressure, Pa;sis the variable pump outlet flow, m3·s-1;cis the rodless chamber oil pressure of the plunger cylinder without spring variable mechanism.
图1 负载敏感变量泵液压原理图
Fig.1 Hydraulic schematic diagram of load-sensing variable pump
1.2 负载敏感变量泵数学模型的建立
1.2.1 流量控制阀数学模型
1)主阀口的压力-流量方程
流量控制阀为正重叠双边滑阀,即有2个控制节流口,其内部结构简图如图2所示,假定流入无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸的流量为负,则:
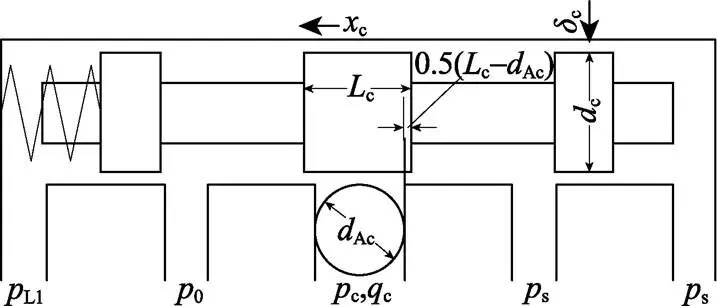
注:xc为流量控制阀阀芯位移,m;Lc为主阀芯控制台肩宽度,m;dAc为流量控制阀通往无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸的油孔直径,m;δc为阀芯与阀套的径向配合间隙,m;dc为流量控制阀阀芯直径,m;qc为变量泵流量控制阀的流量,m3·s-1;其他符号含义见图1。
式中c为变量泵流量控制阀的流量,m3/s;dc为流量控制阀节流口流量系数;为油液密度,kg/m3;Ac为流量控制阀通往无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸的油孔直径,m;c为主阀芯控制台肩宽度,m;c为流量控制阀阀芯位移,向左为正方向,原点取重叠区中点,m;cm1、cm2分别为阀芯左、右最大位移量,m;s为变量泵出口压力,Pa;c为无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸无杆腔油液压力,Pa;0为回油压力,Pa;c(c)为流量控制阀节流口通流截面积,m2。
节流口由阀芯对称布置的2个圆形孔构成,如图3所示,其通流截面积及其对阀芯位移c的导数按下式计算:
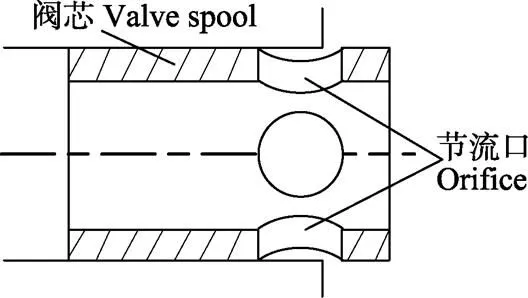
图3 弓形节流口示意图
2)流量控制阀阀芯的力平衡方程
流量控制阀阀芯受力包括:阀芯两端油液压力产生的驱动力、惯性力、黏性阻尼力、弹簧力、稳态液动力(始终指向使流量控制阀阀口趋于关闭的方向)、瞬态液动力(油液流入流量控制阀阀腔时,瞬态液动力起正阻尼作用,流出流量控制阀阀腔时,油液起负阻尼作用)、干摩擦力(由于在阀芯上开有多条均压槽,液压卡紧力很小,干摩擦力可忽略不计)等。
式中c为流量控制阀阀芯直径,m;c0为流量控制阀弹簧的预压缩量,m;L1为流量控制阀低压控制油腔压力,Pa;c为流量控制阀阀芯质量,kg;c为流量控制阀弹簧刚度,N/m;c为阀芯运动阻尼系数,N·s/m;cs为阀芯所受稳态液动力,N;ct为阀芯所受瞬态液动力,N。
式中为液压油动力黏度,Pa·s;cv为流量控制阀阀芯密封长度,m;c为阀芯与阀套的径向配合间隙,m。
式中c为阀芯节流口出射角度,(°);cv为节流口流速系数。
式中ct为流量控制阀的阻尼长度,m。
3)负载反馈单向阀压力-流量特性方程
负载反馈单向阀内部结构如图4所示。
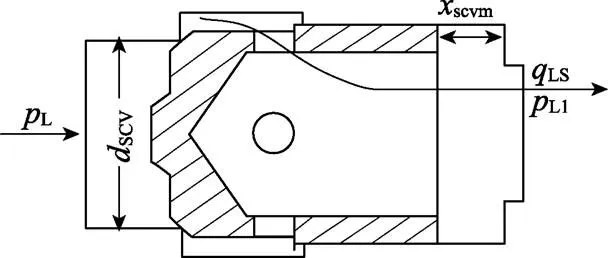
注:xscvm为单向阀阀芯最大位移量,m;dscv为单向阀锥阀式阀座孔直径,m;qLS为负载反馈单向阀流量,m3·s-1;其他符号含义见图1。
式中LS为负载反馈单向阀流量,m3/s;dscv为单向阀节流口流量系数;scv为单向阀锥阀式阀座孔直径,m;scvm为单向阀阀芯最大位移量,m;L为负载压力,Pa;scv为负载反馈单向阀阀芯半锥角,rad。
4)负载敏感变量泵泄压阻尼孔流量-压力方程
式中c3为泄压阻尼孔流量,m3/s;d03为泄压阻尼孔流量系数;03为泄压阻尼孔直径,m。
5)负载反馈单向阀至变量泵泄压阻尼孔间油腔流量连续性方程
忽略流量控制阀阀芯与阀套配合间隙处的泄漏,流入负载反馈单向阀至负载敏感变量泵泄压阻尼孔间油腔的流量,一部分补偿油腔内油液压缩量,一部分补偿流量控制阀阀芯运动引起的油腔容积变化量,其余部分经泄压阻尼孔流回油箱。
式中e为油液体积弹性模量,Pa;L1为流量控制阀阀芯处于原点时,负载反馈单向阀至泄压阻尼孔间油腔容积,m3。
1.2.2 负载敏感变量泵变量控制机构数学模型
1)变量控制机构油腔流量连续性方程
流入无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸控制油腔的流量除推动柱塞运动外,还用来补偿油液压缩量以及通过减震阻尼孔漏入泵腔的流量。
式中c为无弹簧柱塞缸及油道的总容积,m3;Pc为无弹簧柱塞缸柱塞直径,m;Pc为无弹簧柱塞缸柱塞位移量,m;PP为减震阻尼孔长度,m;PP为减震阻尼孔直径,m。
2)变量控制机构的力矩平衡方程
变量泵结构如图5所示。由图5可知,通过无弹簧和有弹簧变量机构柱塞缸控制变量泵斜盘倾角,其中有弹簧变量机构柱塞缸无杆腔与变量泵出口油路相通,其作用力指向使斜盘倾角增大的方向;无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸无杆腔经压力控制阀右位与流量控制阀的控制节流口相通,其作用力指向使斜盘倾角减小的方向,变量泵斜盘受力分析图如图6所示。
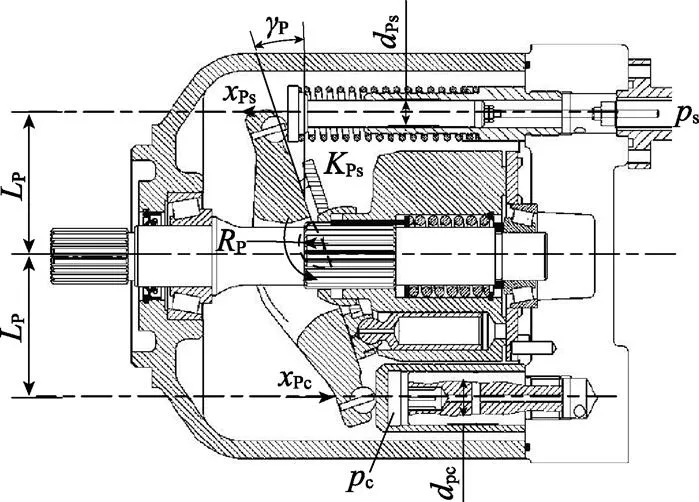
注:LP为有弹簧、无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸轴线至斜盘转动中心的垂直距离,m;γP为变量泵斜盘倾角,rad;xPs为有弹簧变量机构柱塞缸柱塞位移,m;xPc为无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸柱塞位移,m;dPs为有弹簧变量机构柱塞缸柱塞直径,m;dPc为无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸柱塞直径,m;KPs为变量机构压紧弹簧刚度,N·m-1;RP为变量泵斜盘支撑轴颈的半径,m;其他符号含义见图1。
负载敏感变量泵变量机构力矩平衡方程:
式中P为有、无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸轴线至斜盘转动中心的垂直距离,m;Ps为有弹簧柱塞缸柱塞直径,m;P为变量泵斜盘和回程盘对旋转中心的转动惯量,kg·m2;P为变量泵斜盘倾角,rad;Pz为柱塞组轴向惯性力转矩,N·m;Pf1、Pf2分别为变量泵斜盘轴颈处的摩擦转矩、柱塞球铰上的摩擦转矩,N·m;Ps、Pc分别为有、无弹簧柱塞缸质量,kg;Pmin、Pmax分别为变量泵斜盘的最小、最大倾角,rad;Ps为变量机构压紧弹簧刚度,N/m;Ps为有弹簧变量机构柱塞缸柱塞位移,Ps=P·tan(P-Pmax),m;Ps0为斜盘在最大倾角时变量机构弹簧预压缩量,m;Psv、Pcv分别为有、无弹簧柱塞缸的密封长度,m;Ps、Pc分别为有、无弹簧柱塞缸内孔与柱塞的配合间隙,m。
注:Pm为柱塞分布圆直径,m;Pc为无弹簧变量机构柱塞缸对斜盘的支反力,N;Ps为有弹簧变量机构柱塞缸对斜盘的支反力,N;Pz为柱塞球铰支反力,N;Pf1为改变斜盘倾角时变量泵斜盘轴颈处的摩擦转矩,N·m;Pf2为改变斜盘倾角时柱塞球铰上的摩擦转矩,N·m;Pz为变量泵柱塞组轴向惯性力所产生的转矩,N·m;其他符号含义见图5。
Note:Pmis the plunger distribution diameter, m;Pcis the support reaction between the swash plate and the plunger type cylinder without a spring, N;Psis the support reaction between the swash plate and the plunger type cylinder with a spring, N;Pzis the support reaction of the plunger spherical hinge, N;Pf1is the frictional torque of the swash plate shaft neck, N·m;Pf2is the frictional torque of the plunger spherical hinge, N·m;Pzis the torque of the axial inertia force of the plunger group, N·m; the meanings of other symbols are as shown in Fig.5.
图6 变量泵斜盘受力分析图
Fig.6 Force analysis of variable pump swash plate
式中P为变量泵斜盘支撑轴颈的半径,m;Pz为柱塞铰接球头半径,m;Pf1、Pf2分别为变量泵斜盘轴颈处、变量泵柱塞球铰处摩擦系数;P为变量泵柱塞数,P=9,假定泵工作中平均有一半柱塞处于泵油状态;P为变量泵的柱塞直径,m。
式中Pz为单个柱塞及其滑履的质量,kg;P为变量泵的转速,r/s;Pm为柱塞分布圆直径,m。
将式(12)~(13)代入式(11)可得:
其中:
1.2.3 液压泵腔流量连续性方程
负载敏感变量泵腔活塞排出的流量,除了用于负载流量输出外,一部分用于推动有弹簧柱塞缸运动,一部分通过缸体的泄漏流回油箱,还有一部分用于补偿变量泵排油腔及其连接管道内油液的压缩量。
式中s为变量泵出口流量,m3/s;P为变量泵的排量,m3/r;lP为变量泵的泄漏系数,m3/(Pa·s);s为变量泵排油腔及连接管道总容积,m3。
1.2.4 负载敏感变量泵状态方程
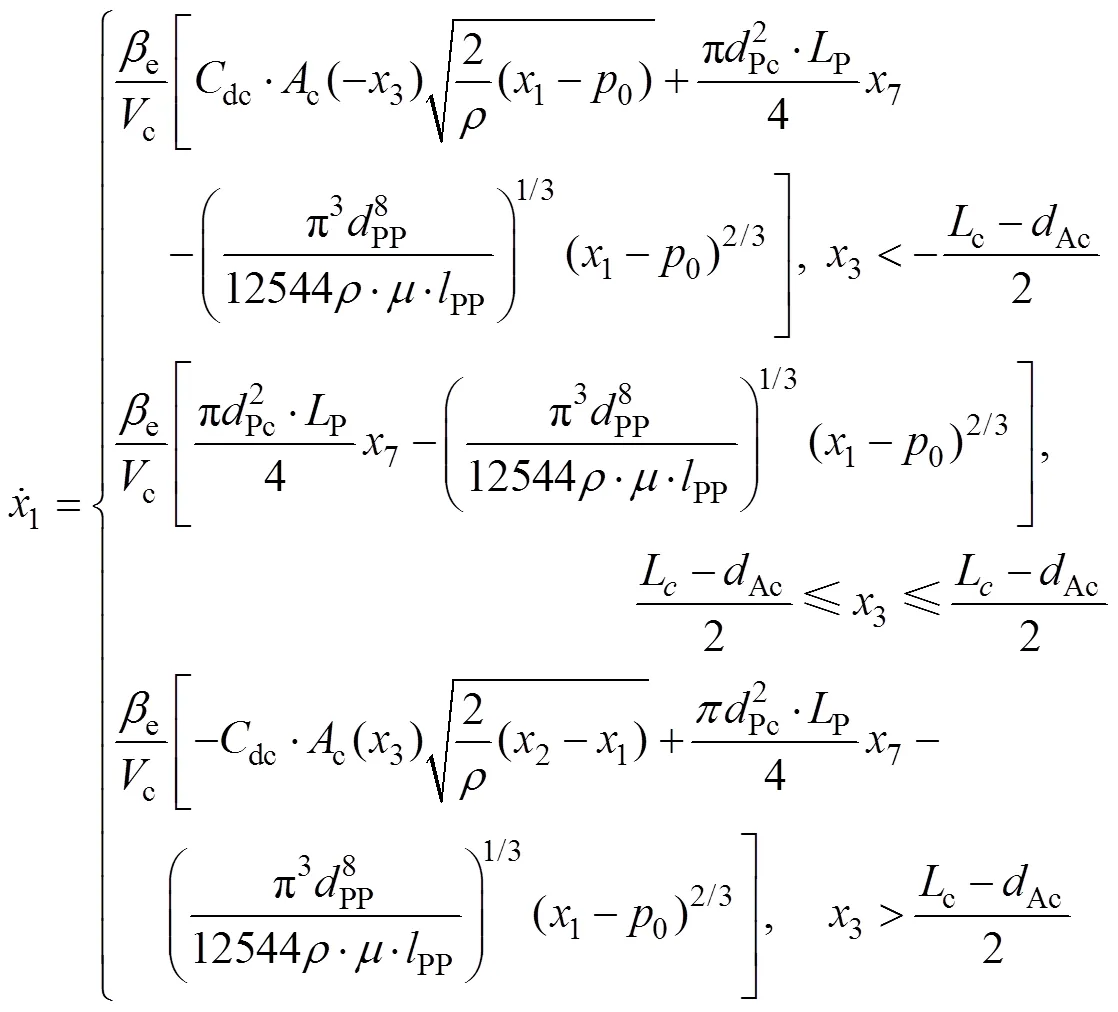

边界条件:
如果3<-cm1,则3=-cm1;如果3>cm2,则3=cm2;
如果6<Pmin,则6=Pmin;如果6>Pmax,则6=Pmax;
如果3=-cm1且4<0,或3=cm2且4>0,则4=0;
如果6=Pmax且7>0,或6=Pmin且7<0,则7=0。
2 负载敏感变量泵仿真分析
2.1 负载敏感变量泵稳态特性仿真分析
基于MATLAB/Simulink建立了负载敏感变量泵仿真模型,其主要参数值如表1所示,给定负载反馈压力 10 MPa,系统流量30 L/min,仿真时间为2 s,得到负载敏感变量泵出口压力和斜盘倾角稳态响应特性曲线分别如图7a、7b所示。
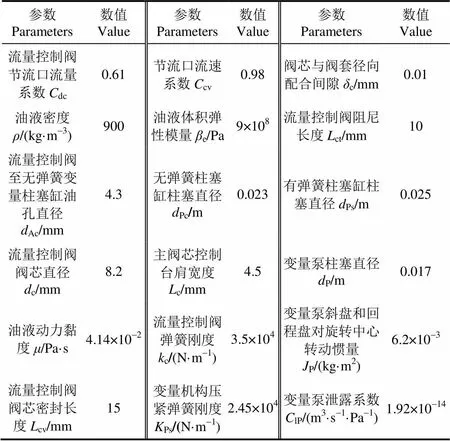
表1 负载敏感变量泵主要参数
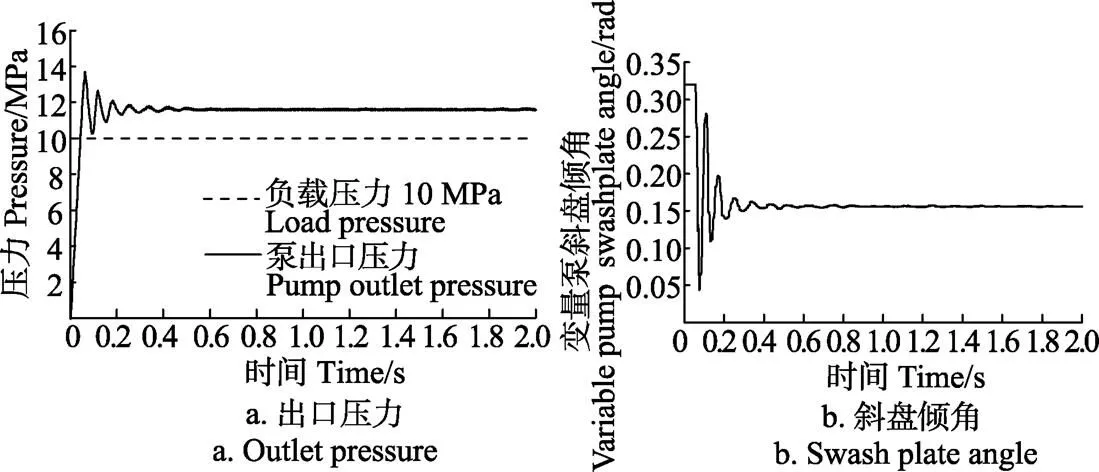
图7 变量泵出口压力和斜盘倾角稳态响应特性
由图7a可知,负载敏感变量泵出口压力经小幅振荡后稳定在11.6 MPa左右,补偿压力约为1.6 MPa,出口压力的超调量约为17.2%,调整时间约为0.5 s,该补偿压力可通过流量控制阀调压弹簧设定,出口压力建立时间约为0.06 s,动态响应性能良好。由图7b可知,负载敏感变量泵斜盘倾角经0.5 s左右振荡后稳定在0.16 rad左右,结合变量泵输出流量理论公式可知,变量泵输出流量与给定系统输入流量相符。
2.2 负载敏感变量泵动态特性仿真分析
给定系统流量为30 L/min,仿真时间为4 s,得到负载敏感变量泵出口压力和斜盘倾角在负载反馈压力由10~15 MPa阶跃变化时的动态响应特性曲线分别如8a、8b所示。
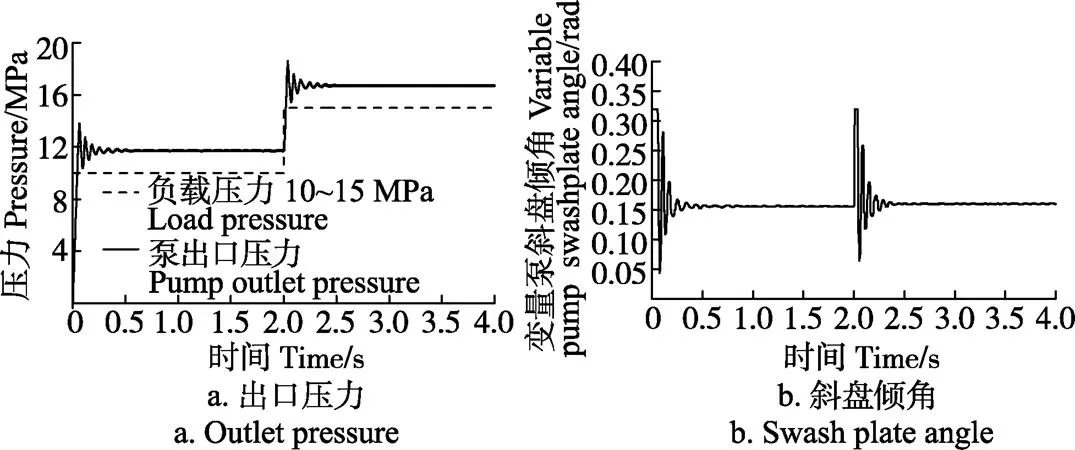
图8 负载阶跃输入变量泵出口压力和斜盘倾角响应特性
由图8a可知,变量泵出口压力建压时间约为0.4 s,稳定后达到11.6 MPa左右,当负载反馈压力阶跃变化到15 MPa后,变量泵出口压力随之增加,建压时间约为 0.4 s,超调量约为12%,稳定后达到16.6 MPa左右,补偿压力约为1.6 MPa,负载敏感变量泵的动态压力补偿特性良好。
由图8b可知,初始状态下变量泵斜盘倾角经一段时间振荡后,稳定在0.16 rad左右,调整时间约为0.5 s,当负载反馈压力阶跃变化时,变量泵斜盘倾角迅速振荡后稳定在0.16 rad左右,调整时间约为0.5 s,系统流量不受负载阶跃变化的影响,变量泵具有良好的稳态流量输出特性。
给定负载反馈压力10 MPa,仿真时间为4 s,得到负载敏感变量泵出口压力和斜盘倾角在系统流量由30~60 L/min阶跃变化时的动态响应特性曲线分别如图9a、9b所示。
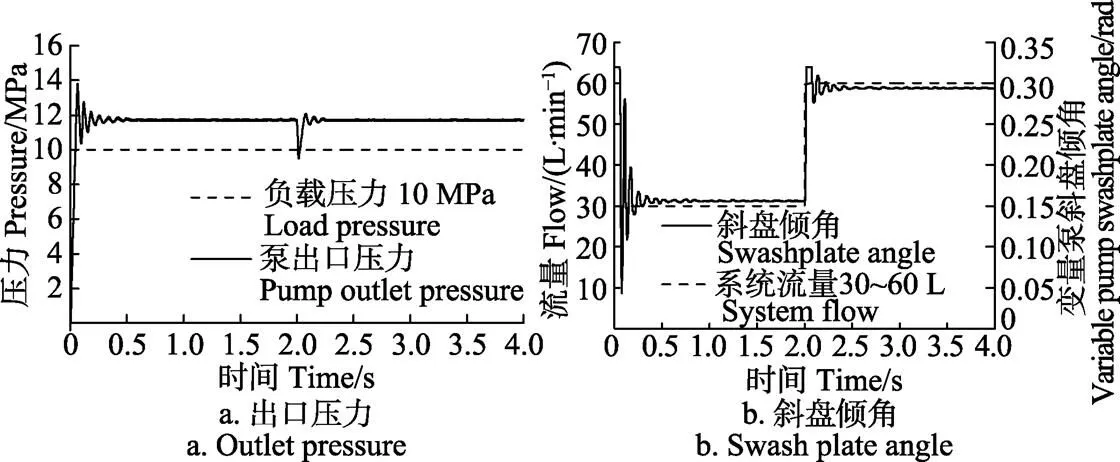
图9 流量阶跃输入变量泵出口压力和斜盘倾角响应特性
由图9a可知,初始状态下变量泵出口压力的建压时间约为0.5 s,稳定后达到11.6 MPa左右;当系统流量阶跃变化到60 L/min后,变量泵出口压力迅速减小,随即快速上升,经一段时间振荡后稳定在11.6 MPa左右,超调量约为17.2%,调整时间约为0.4 s,补偿压力约为 1.6 MPa,变量泵出口压力不受系统流量阶跃变化的影响,具有良好的稳压特性。
由图9b可知,初始状态下变量泵斜盘倾角经一段时间振荡后稳定在0.16 rad左右,调整时间约为0.5 s;当系统流量阶跃变化到60 L/min后,变量泵斜盘倾角迅速增大,经一段时间振荡后稳定在0.29 rad左右,调整时间约为0.5 s,变量泵动态流量输出特性良好。
综上仿真分析可知,负载敏感变量泵可根据负载提供其所需的流量和压力,有效降低了系统功率损失。
3 负载敏感变量泵试验
为了验证负载敏感变量泵数学模型和仿真分析的正确性,搭建了闭心式负载敏感液压系统室内试验平台,如图10所示。

图10 负载敏感液压系统室内试验平台
油压传感器采用德国米科MIK-P300型压力传感器,其技术参数如表2所示,响应时间约为20 ms,而变量泵液压系统压力控制响应时间约为0.5 s,可满足系统油液压力动态测量需求。智能变送仪用于实时显示油压传感器所采集的油压数值,流量传感器采用TLW-15G型涡轮流量传感器,压力范围0~25 MPa,量程为0~ 100 L/min,24 V电源供电,输出信号为4~20 mA电流信号。压力和流量信号可通过NI采集卡实时传输到PC机中,并通过LabVIEW程序界面实时显示传感器输出信号变化曲线。
比例溢流阀选用华德液压生产的DBEM2-30B/ 315YM型锥阀式先导比例溢流阀,通径为25 mm,允许通过的最大流量为600 L/min,可提供的最大开启压力为31.5 MPa。可根据VT-2000BS40G型电液比例控制器无级调节比例溢流阀的开启压力。比例阀控制放大器采用9~32 V电源供电,输入电压范围为2.5~5 V,输出比例线圈驱动电流范围为0~1.2 A,最大输出电流为2 A。

表2 油压传感器技术参数
注:表中FS表示满量程。
Note:FS meanings full scale.
3.1 试验方案
图11为负载敏感变量泵性能试验方案原理图,节流阀与负载敏感变量泵出口相连,用于调节液压系统流量。在节流阀出口位置并联比例溢流阀可为比例控制阀提供所需的负载压力。同时,负载压力经节流阀出口可反馈至泵流量控制阀进行压力补偿,安全溢流阀用于液压系统过载保护,开启压力为20 MPa。其中,比例溢流阀开启压力和比例控制阀阀芯开度可分别通过电液比例控制器和比例阀控制放大器进行实时控制。

1. 负载敏感变量泵 2. 油压传感器 3. 节流阀 4. 两位三通比例换向阀 5. 安全溢流阀 6. 比例溢流阀 7. 流量传感器
3.2 试验结果分析
设定比例控制阀输入电压为4.7 V,保持其阀口开度不变,由电液比例控制器控制比例溢流阀开启压力在10 s时由10 MPa阶跃变化到15 MPa,得到变量泵出口压力、负载压力以及变量泵出口压力仿真值得动态响应特性曲线如图12所示。

图12 负载阶跃时变量泵出口压力响应特性曲线
由图12可知,负载压力在10~15 MPa之间阶跃变化时,负载敏感变量泵建压时间约为0.5 s,变量泵出口压力与负载压力几乎同步变化,由11.5 MPa阶跃变化到16.5 MPa,补偿压力约为1.5 MPa,与变量泵出口压力仿真曲线对比可知,补偿压力的稳态误差约为0.1 MPa,主要受负载敏感液压系统试验管路油液压缩性及压力损失的影响,负载敏感变量泵动态压力补偿特性良好,验证了负载敏感变量泵非线性数学模型的正确性。
设定比例溢流阀开启压力为5 MPa,比例控制阀输入电压在10 s时由4.3 V阶跃变化到4.7 V,得到变量泵出口压力、负载压力以及系统流量的动态响应特性曲线如图13所示。
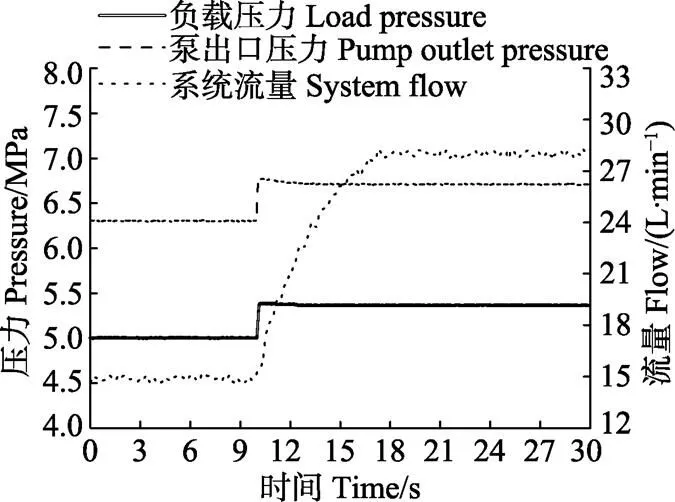
图13 阀芯阶跃时变量泵出口压力及流量响应特性曲线
由图13可知,比例控制阀输入电压在4.3~4.7 V之间阶跃变化时,由于受到系统流量变化及液压系统试验管路压力损失的影响,回油管路背压略微升高,由比例溢流阀设定的负载压力会出现小幅阶跃变化,变量泵出口压力也跟随变化,补偿压力平均值约为1.5 MPa,系统流量由15 L/min阶跃变化到28 L/min,由于负载敏感变量泵机构惯性、内部泄漏、液压系统试验管路油液压缩性等因素影响,液压系统整体惯性增加,导致系统流量响应变慢,调整时间约为7 s,变量泵在保持一定补偿压力时可根据比例控制阀阀芯开度变化为其提供相应流量。
4 结 论
1)充分考虑负载敏感变量泵内部液压元件的有效行程范围,建立了基于边界条件的负载敏感变量泵非线性数学模型,该模型更为准确地描述了负载敏感变量泵的工作特性。
2)搭建了负载敏感变量泵Simulink仿真模型,仿真分析结果表明:变量泵可根据负载所需压力和流量实时调整斜盘倾角大小,进而实现压力-流量补偿功能,补偿压力约为1.6 MPa,负载压力和流量阶跃变化时,变量泵具有良好的动态补偿特性。
3)试验研究结果表明:在给定比例控制阀阀口开度不变的情况下,负载压力阶跃变化时,负载敏感变量泵通过流量控制阀调整斜盘倾角为比例控制阀提供所需流量,此外,变量泵出口压力始终高出负载压力1.5 MPa,通过与仿真结果对比可知,补偿压力稳态误差约为0.1 MPa,主要与液压系统试验管路压力损失有关,验证了负载敏感变量泵非线性数学模型的正确性。当比例控制阀阀芯阶跃变化时,负载敏感变量泵输出其所需流量,满足现代农机装备液压系统对负载敏感变量泵压力-流量补偿功能的需求。
[1] 武建设,陈学庚.新疆兵团棉花生产机械化发展现状问题及对策[J].农业工程学报,2015,31(18):5-10. Wu Jianshe, Chen Xuegeng. Present situation, problems and countermeasures of cotton production mechanization development in Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(18): 5-10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 段向敏,代荣.精确农业背景下我国农业机械发展趋势[J].农机化研究,2013(12):229-232. Duan Xiangmin, Dai Rong. The tendency of China’s agricultural machinery development under precision agriculture[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2013(12): 229-232. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 吴海华,方宪法,杨炳南.国内外农业装备技术发展趋势及进展[J].农业工程,2013,3(6):20-23. Wu Haihua, Fang Xianfa, Yang Bingnan. Development trends and progress of agricultural machinery technology at home and abroad[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 3(6): 20-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 赵剡水,杨为民.农业拖拉机技术发展观察[J].农业机械学报,2010,41(6):42-48. Zhao Yanshui, Yang Weimin. Technological development of agricultural tractor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(6): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 金文胜,安国军.静液压驱动在农业机械行走装置上的应用与发展趋势[J].内蒙古民族大学学报:自然科学版,2001,16(3):252-257. Jin Wensheng, An Guojun. Application and trend of hydraulic driving in agricultural machinery implements running[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University for Nationalities: Natural Sciences, 2001, 16(3): 252-257. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 毛罕平,倪静,韩绿化,等.高地隙液压四轮驱动喷雾机转向防滑控制系统[J].农业机械学报,2012,43(6):58-62. Mao Hanping, Ni Jing, Han Lühua, et al.Turning anti-slip control system of hydraulic four-wheel drive high clearance sprayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(6): 58-62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 武广伟,付卫强,董建军,等.1KY-40型液压驱动农田水渠开沟机设计与试验[J].农业机械学报,2014(增刊1):302-308. Wu Guangwei, Fu Weiqiang, Dong Jianjun, et al. Design and experiment of 1KY-40 hydraulic drive ditcher for farmland conduit[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for AgriculturalMachinery, 2014(Supp.1): 302-308. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 高海涛,邓志刚,高敏强,等.静液压驱动技术在玉米联合收获机行走驱动上的应用[J].农业机械,2013,25:138-140. Gao Haitao, Deng Zhigang, Gao Minqiang, et al. Application of hydrostatic drive technology on the drive system of corn combine harvester[J]. Farm Machinery, 2013, 25: 138-140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 李明生,赵建军,朱忠祥,等.拖拉机电液悬挂系统模糊PID自适应控制方法[J].农业机械学报,2013,44(增刊2):295-300.Li Mingsheng, Zhao Jianjun, Zhu Zhongxiang, et al. Fuzzy-PID self-adaptive control method in electro-hydraulic hitch system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(Supp.2): 295-300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李立.拖拉机后悬挂电液控制系统的研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2012. Li Li. Research on the Electro-hydraulic System in Tractor Rear Suspension[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 杜巧连,熊熙程,魏建华.拖拉机液压悬挂耕深电液控制系统设计与试验[J].农业机械学报,2008,39(8):62-65. Du Qiaolian, Xiong Xicheng, Wei Jianhua. Design and experiment on the control system of electro-hydraulic plow depth of tractor hydraulic hitch mechanism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2008, 39(8): 62-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 王会明,侯加林,赵耀华,等.拖拉机液压悬挂机构自动控制系统[J].农业机械学报,2006,37(10):42-45,49. Wang Huiming, Hou Jialin, Zhao Yaohua, et al. Study on automatic control system for hydraulic hitch equipment of tractor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2006, 37(10): 42-45, 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 乔晓东,王晓燕,颜华,等.后悬挂农具田间试验平台[J].农业机械学报,2013,44(8):63-68. Qiao Xiaodong, Wang Xiaoyan, Yan Hua, et al. Field experiment platform for rear suspension[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(8): 63-68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 鞠卫平.国内外拖拉机悬挂系统的发展现状[J].江苏农机化,2006(6):40. Ju Weiping. The progress status of tractor hitch system of oversea and domestic research[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Mechanization, 2006(6): 40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 吴清分,凌桐森.欧美大中型拖拉机近期技术结构概况[J].拖拉机与农用运输车,2002(5):31-33,40. Wu Qingfen, Ling Tongsen. The survey of present technical structure of large and medium-sized tractor in Europe and America[J]. Tractor & Farm Transporter, 2002(5): 31-33, 40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 袁士豪,殷晨波,刘世豪.机械负载敏感定量泵系统性能分析[J].农业工程学报,2013,29(13):38-45. Yuan Shihao, Yin Chenbo, Liu Shihao. Performance analysis of machinery load sensitive quantitative pump system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(13): 38-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 侯明亮,王方艳,毛恩荣.螺纹插装式液控换向阀的状态变量模型与仿真[J].农业机械学报,2006,37(9):145-148,170.
Hou Mingliang, Wang Fangyan, Mao Enrong. Study onsimulation and state variable model of electro-hydraulic directional control valve[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2006, 37(9): 145-148, 170. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 史增录,赵武云,吴建民,等.4UX-550型马铃薯收获机悬挂机组机液耦合仿真[J].农业机械学报,2011,42(6):98-102,92. Shi Zenglu, Zhao Wuyun, Wu Jianmin, et al. Suspension unit hydraulic-mechanical coupling simulation of 4UX-500 potato harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(6): 98-102, 92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 李明生,朱忠祥,毛恩荣,等.大功率拖拉机电液提升器比例提升阀设计[J].农业机械学报,2012,43(10):31-35. Li Mingsheng, Zhu Zhongxiang, Mao Enrong, et al. Design of proportional raise valve in electro-hydraulic lifting mechanism of big-power tractor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(10): 31-35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 李明生,宋正河,迟瑞娟,等.大功率拖拉机电液提升器比例下降阀仿真与优化[J].农业机械学报,2012,43(增刊1):1-5. Li Mingsheng, Song Zhenghe, Chi Ruijuan, et al. Simulation analysis on proportional lowering valve for high-power tractor[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(Supp.1): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 刘榛,卢堃,陆初觉.负载敏感变量泵中负载敏感阀的设计与分析[J].兰州理工大学学报,2005,31(6):55-58. Liu Zhen, Lu Kun, Lu Chujue. Design and analysis of load-sensitive valve in load-sensible variable displacement pump[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2005, 31(6): 55-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 何智,刘庆庭,区颖刚.甘蔗收获机双向变量柱塞泵动态响应特性仿真[J].农业机械学报,2012,43(增刊1): 329-334,328. He Zhi, Liu Qingting, Qu Yinggang. Dynamic response characteristic simulation of double-action variable displacement plunger pump for sugarcane harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(Supp.1): 329-334, 328. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王进军.电液比例负载敏感控制变量柱塞泵技术研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2006. Wang Jinjun. Research on the Variable Displacement Piston Pump with Electrohydraulic Proportional and Load-sensitive Control[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 来升,穆希辉,杜峰坡,等.负载敏感变量泵稳态特性研究[J].机床与液压,2011,39(9):74-76. Lai Sheng, Mu Xihui, Du Fengpo, et al. Steady state characteristic analysis of the load-sensing pump[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2011, 39(9): 74-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] Capponi C, Ferrante M, Pedroni M, et al. Real data analysis and efficiency of the TEA Mantova Casale (Italy) variable- speed pumping station[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2014, 70: 248-255.
[26] Cheung H, Braun J E. Component-based, gray-box modeling of ductless multi-split heat pump systems[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2014, 38(1): 30-45.
[27] Rakibuzzaman, Suh S H, Kyung-Wuk K, et al. A study on multistage centrifugal pump performance characteristics for variable speed drive system[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015, 105: 270-275.
[28] Kemmetmüller W, Fuchshumer F, Kugi A. Nonlinear pressure control of self-supplied variable displacement axial piston pumps[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2010, 18(1): 84-93.
[29] Casoli P, Anthony A. Gray box modeling of an excavator’s variable displacement hydraulic pump for fast simulation of excavation cycles[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2013, 21(4): 483-494.
[30] Mikami A, Imoto K, Tanabe T, et al. Geometric and kinematic modeling of a variable displacement hydraulic bent-axis piston pump[J]. Journal of Computational & Nonlinear Dynamics, 2010, 5(4): 2040-2049.
Structural modeling and performance analysis of load-sensing variable pump
Chen Suiying, Zhao Jianjun, Mao Enrong, Song Zhenghe, Zhu Zhongxiang, Du Yuefeng※
(100083,)
In recent years, to meet the development requirements of green production and energy efficiency of modern agriculture, the closed-center load-sensing hydraulic system has been widely used in the domestic and overseas agricultural machinery because of its low energy consumption and strong adaptability. As a key power component of the hydraulic system of the modern agricultural equipment, the performance of the load-sensing variable pump plays an important role in the performance of the whole hydraulic system. At present, the domestic scholars have mainly concentrated in the optimization and characteristics analysis of hydraulic valve, while have done little about the hydraulic pump. Therefore, this paper focused on the mathematical modeling, performance simulation and testing of the load-sensing variable pump, which was composed of swashplate piston pump, plunger cylinder, pressure control valve, flow control valve, load feedback check valve, and so on. In order to better analyze the performance of the pump, the mathematical models of these parts were established by using the pressure-flow equation, flow continuity equation, force balance equation, and so on. Taking into account the effective travel range of the moving parts such as valve spool and swashplate, the nonlinear mathematical model of the load-sensing variable pump based on the boundary conditions was constructed by using the state space method. Then, the simulation model of the pump was established using MATLAB/Simulink based on the mathematical model. By using the fourth order Runge-Kutta algorithm, the steady-state and dynamic performances of the pump were simulated. At the steady state, the compensating pressure of the variable pump was about 1.6 MPa. And in the dynamic state, the outlet pressure and swashplate angle of the pump could respectively follow the step changes of the load and system flow very well, the adjustment time of which was about 0.4 and 0.5 s, respectively. The simulation results showed that the load-sensing variable pump could adjust the inclination angle of the swashplate in real time according to the required flow and pressure of the load, and thus had a good pressure-flow compensation characteristic. Finally, to verify the correctness of the mathematical model and the simulation analysis, an indoor test platform of the load-sensing hydraulic system was built, including hydraulic pump station, proportional control valve, proportional relief valve, flowmeter, pressure sensor, and so on. The dynamic performance test of the load-sensing variable pump was carried out by using the platform. Among them, the step change of the load pressure could be achieved by controlling the proportional valve’s opening pressure, while the step change in flow could be achieved by controlling the spool opening of the proportional relief valve. The test results showed that the load-sensitive pump could output its required flow when the proportional valve spool encountered a step change. And when the load made a step change, the outlet pressure of the variable pump changed almost synchronously with the load pressure. Compared with the simulation results, the steady-state error of the compensation pressure was about 0.1 MPa, which verified the correctness of the nonlinear mathematical model of the load-sensing variable pump. It can be seen that the output flow and pressure of the load-sensing variable pump can be adapted to the load in real time, thus effectively improving the efficiency of the hydraulic system and reducing the system heat, which meets the field work demands of the modern agricultural equipment operation unit.
pumps; computer simulation; agricultural equipment; load-sensing; variable pump; mathematical model; boundary condition
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.03.006
S232.3; TH321
A
1002-6819(2017)-03-0040-10
2016-07-21
2016-12-08
中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金项目(2015QC009);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金(20130008110042)
陈随英,女,湖南岳阳人,博士生,主要从事流体传动及静液压驱动车辆技术研究。北京 中国农业大学现代农业装备优化设计北京市重点试验室,100083。Email:chen_suiying@126.com
杜岳峰,男,讲师,博士,主要从事流体传动及农业机械设计研究。北京 中国农业大学现代农业装备优化设计北京市重点试验室,100083。Email:dyf@cau.edu.cn
陈随英,赵建军,毛恩荣,宋正河,朱忠祥,杜岳峰. 负载敏感变量泵结构建模与性能分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(3):40-49. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.03.006 http://www.tcsae.org
Chen Suiying, Zhao Jianjun, Mao Enrong, Song Zhenghe, Zhu Zhongxiang, Du Yuefeng. Structural modeling and performance analysis of load-sensing variable pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(3): 40-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.03.006 http://www.tcsae.org
