miRNAs在食管鳞癌中的功能、机制及治疗前景
2017-03-02崔曼莉周苏娜张明鑫王景杰第四军医大学唐都医院消化内科放疗科陕西西安70038
崔曼莉,周苏娜,张明鑫,王景杰(第四军医大学唐都医院:消化内科,放疗科,陕西西安70038)
miRNAs在食管鳞癌中的功能、机制及治疗前景
崔曼莉1,周苏娜2,张明鑫1,王景杰1(第四军医大学唐都医院:1消化内科,2放疗科,陕西西安710038)
目的:食管鳞癌(ESCC)在东亚地区占主要地位,大约一半的ESCC病例发生在中国.虽然食管鳞癌的诊断和治疗取得了较大的进步,但预后仍不理想,其精确调控机制仍有待于进一步研究和探索.MicroRNAs(miRNAs)是一组能够在转录后水平调控基因表达的非编码小RNA,不同的肿瘤类型和致癌途径中,miRNAs表达失调控,呈现出表达上调、下调或缺失,显现出类似于癌基因或抑癌基因的功能.本研究综述了miRNAs在ESCC中的表达、功能、机制及治疗前景的相关进展.
功能;机制;治疗前景;miRNAs;食管鳞癌
0 引言
食管癌(esophageal cancer,EC)是全球常见八大恶性肿瘤之一,其死亡率居于全球相关肿瘤的第六位.虽然食管腺癌(esophageal adenocarcinoma,EAC)在西方国家因发病率逐年升高而备受关注,但食管鳞癌(esophageal squamous cell carcinoma,ESCC)在东亚地区仍占主要地位,大约一半的ESCC病例发生在中国[1-2].虽然近三十年来ESCC的诊断和治疗取得了较大的进步,但预后仍不理想,5年生存率仅为15%~25%[3].近年来,大量研究[4]发现了一系列ESCC相关的基因异常,如p53、p21、Cyclin D1等,但其精确调控机制仍有待进一步研究和探索.
MicroRNAs(miRNAs)是一组能够在转录后水平调控基因表达的非编码小RNA,在一系列病理生理过程中发挥着重要的作用.近来的研究发现,不同的肿瘤类型和致癌途径中,miRNAs表达失调,呈现出表达上调、下调或缺失,显现出类似于癌基因或抑癌基因的功能.进一步的研究提示,miRNAs还能够作为肿瘤显像、诊断、治疗以及预后的生物标记.由于西方食管癌以EAC为主,故早期的食管癌miRNAs文献主要集中在EAC,ESCC尤其是我国西部高发地区的相关数据不多.虽然国外已有相关综述探讨了miRNAs在EC中的作用及研究进展,但多数均局限于EAC.近年来,包括我们课题组在内的国内学者逐渐重视ESCC与miRNAs的关系,发表了一系列文章.本研究对近年miRNAs与ESCC研究的相关进展进行综述,现报道如下.
1 miRNAs
miRNAs是一类长度介于(18~25)nt的单链RNA,其本身不具有开放阅读框(ORF),不编码任何蛋白质,成熟miRNA的5'端带有磷酸基团(-HPO4),3'端带有羟基(-OH).miRNAs由基因组编码,并由RNA聚合酶II转录为长的转录本,即初始miRNAs(pri-miRNAs),一般长为几千个碱基大小.成熟的miRNAs便由pri-miRNAs通过下述步骤生成:通过在细胞核中的RNase-III酶Drosha以及其结合伴侣DGCR8组成的复合体识别,将pri-miRNAs处理成含成熟miRNAs的60~80个核苷酸的前体miRNAs(pre-miRNAs).pre-miRNAs很快由核输出因子Exportin-5识别并协同Ran-GTP被运送至细胞浆,之后被另外一个RNA聚合酶III Dicer识别并切割为长18~24个核苷酸长度的双链.其中的一条链被称为引导链,将双链引导至含Argonaute蛋白的RISC复合体中,使其中仅一条链和RNA诱导的沉默复合物(RNA-induced silencing complex,RISC)稳定结合,从而成为成熟miRNAs.miRNAs引导RISC复合物结合靶mRNA的3’-UTR的结合序列,从而将之清除或进行转录后抑制[5-7].
截止2014年6月,miRBase最新21.0版正式发布,新版数据库收录miRNAs总数量已突破35000条,相比上一版本(20.0版)增长近20%,新增4196条发夹前体序列和5441条成熟体miRNAs.miRNAs主要是通过抑制它的靶基因而发挥调控作用,至今尚未发现有上调能力的miRNAs,其在发育、细胞增殖、凋亡、脂类代谢、激素分泌及肿瘤发生等多种生理和病理过程中发挥重要作用.本研究主要关注miRNAs在ESCC中的表达、功能、机制及治疗前景.
2 miRNAs与ESCC
2.1 ESCC的miRNAs表达谱通过ESCC及癌旁或者中间过程(如炎症、不典型增生等)的miRNAs表达谱的变化,明确上调或下调的miRNAs,对于进行进一步的功能研究意义重大.Guo等[8]应用芯片技术探讨了我国ESCC中miRNAs的表达谱情况,首先采用31例配对的ESCC及癌旁组织进行芯片检测,筛选出差异表达的miRNAs,设计检测模型;再应用24例配对资料和1例非配对资料进行验证,最后应用22例含完整预后信息的组织进行预后分析,得出miR-103/107的高表达是不良预后的独立风险因子.Feber等[9]应用芯片技术研究了美国ESCC的表达变化,发现miR-21的高表达,以及miR-203与miR-205的低表达.Mathé等[10]利用收集的美国和日本的ESCC患者的组织,发现癌旁中miR-21的高表达与不良预后密切相关.Ogawa[11]则应用实时定量荧光PCR技术检测了鳞癌组织中73种miRNAs的表达变化,发现了与临床病理相关连的miRNAs,且证实miR-129的高表达是预后不良的独立风险因子.Lee等[12]在研究miR-373的功能时对5例ESCC的表达谱进行分析,发现let-7d、miR-330、miR-340以及miR-373高表达.有研究报道应用含较新miRNAs数据库版本的芯片,获得了我国ESCC的表达谱[13-15].这些基于组织的表达谱变化,既有重叠(如miR-21的上调和miR-203下调),也有不同,其根本原因是标本的病理特征存在差异,同时还有肿瘤间质细胞的干扰.因此,Zhu等[16]应用激光捕获显微切割技术选取组织中的正常、变异及肿瘤细胞进行ESCC表达谱研究,发现了miR-21、miR-25、miR-106b的高表达以及miR-145和miR-203的低表达,为ESCC组织表达谱研究提供了新的思路.
由于细胞株更容易获得并进行相关的处理,之后,学术界又开始探讨ESCC细胞株中miRNAs表达谱.郑志范等[17]对比了放疗抵抗株的KYSE-150R和亲本细胞的miRNAs表达谱的差异,并应用生物信息学寻找可能的靶基因,为探讨ESCC的放疗耐受机制提供了参考.Kimura等[18]通过对比8种ESCC细胞株和正常食管粘膜上皮细胞株之间miRNAs表达谱的差异,证实miR-205和miR-21是ESCC的特异性标志.具体的细节及参数请参照表1.
miRNAs检测技术的不断进步及人们对miRNAs生物学行为认识的不断增加,使得ESCC患者循环miRNAs表达谱在诊断中的价值也逐渐受到重视,一些具有诊断或预后价值的循环miRNAs[19-20]被发现.Liu等[21]新近发表的一篇荟萃分析总结了已发表的ESCC中的循环miRNAs研究,发现其在ESCC中的敏感性、特异性、阳性似然比、阴性似然比和诊断优势比分别为79.9%、81.3%、4.27、0.25和17.29,提示其可作为早期诊断ESCC的潜在标志物,但仍需大量患者数据来验证.
2.2 ESCC中miRNAs的功能如前所述,miRNAs能够在转录后水平调控基因的表达,根据表达谱中其表达水平的变化以及其对癌基因或抑癌基因的表达调控,便可以确定ESCC中miRNAs的可能功能.因此,揭示ESCC中miRNAs功能的方法有很多.以具有癌基因功能的miRNAs为例,一种是在表达谱的基础之上,将具有显著性的高表达的miRNAs作为候选的具有癌基因功能的miRNAs,通过构建其表达质粒和设计抑制剂,探讨其分别在过表达和抑制表达的情况下对ESCC生物学行为的影响,从而判定功能,进一步在生物信息学基础之上寻找可能的靶标,应用报告基因,明确其可信的调控机制;另外一种为通过已知抑癌基因,通过生物信息学反查可能的miRNAs,再通过过表达和抑制观察其生物学功能;此外,针对特殊miRNAs,应用生物信息学方法寻找可能的靶标,文献检索可能的靶标的功能,再重复实验,明确功能;还可以选取其他肿瘤中已经证实的具有抑癌基因功能的miRNAs,探讨其在ESCC中是否仍发挥相似的功能和调控相同的靶标.
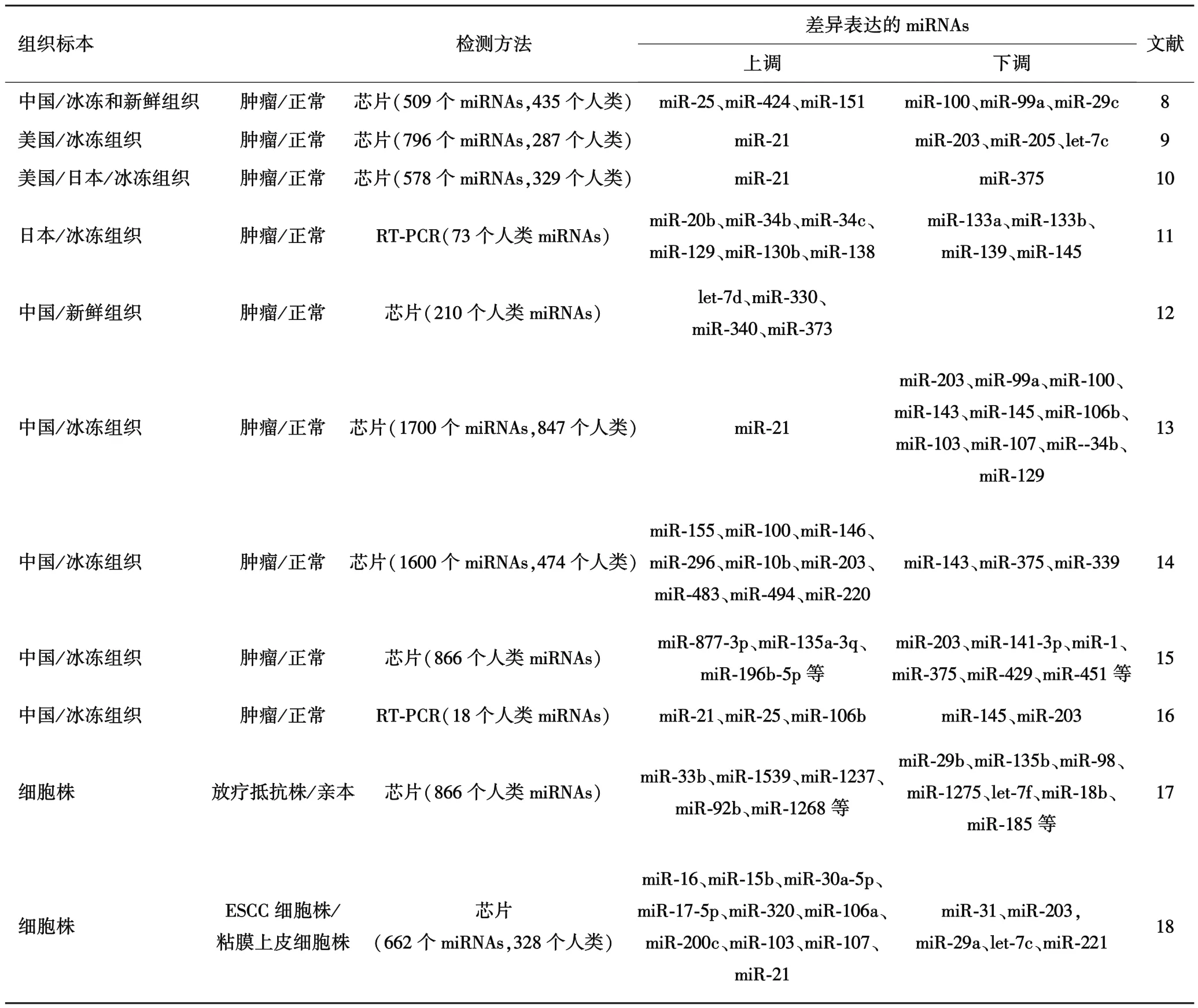
表1 ESCC的miRNAs表达谱研究一览
(1)具有癌基因功能的miRNAs
研究最多且结果最为一致的类癌基因的miRNAs是miR-21.Mori、Hiyoshi和Ma的团队都证实了miR-21在ESCC中的癌基因功能,相关的靶标分别是程序性细胞凋亡因子4(programmed cell death 4,PDCD4)和PTEN等,进而影响ERK信号通路等,促进肿瘤细胞的增殖和侵袭,参与了ESCC的发生及发展[22-26],miR-21也成为ESCC治疗的潜在靶点[27].此外,miR-373、miR-92a、miR-25、miR-10b、miR-130b、miR-1290、miR-330-3p、miR-224都与增殖或侵袭转移相关,靶标参见表2[12,28-36].
结合ESCC的诊治现状,越来越多的研究开始关注治疗耐受与抵抗的困境,虽然已有的研究发现了大量与耐药相关的基因,但是有关的精确调控机制仍未了解,miRNAs的研究为耐药的调控提供了新的视野和思路.多药耐药基因1(multidrug resistance gene 1,MDR1)及蛋白是诱发肿瘤细胞耐药的重要原因,miR-296和miR-27a被证实能够调控MDR1从而参与耐药,同时也与ESCC增殖、凋亡对抗相关[37-38];Imanaka等[39]报道高表达miR-141能够通过调控Yes相关蛋白1(Yes-associated protein 1,YAP1)的表达使ESCC细胞株耐受顺铂诱导的凋亡;Hamano[41]则发现miR-200c在ESCC耐药中的作用与Akt信号通路的激活相关,其靶标为protein phosphatase 2(formerly2A),regulatorysubunitA,betaisoform(PPP2R1B)[40];miR-483-3p则通过靶向EI24与增殖、细胞周期、侵袭以及耐药均有关系(表2).

表2 ESCC中具有癌基因功能的miRNAs
(2)具有抑癌基因功能的miRNAs
相较于具有癌基因功能的miRNAs,更多在ESCC中具有抑癌基因功能的miRNAs被鉴定出来(表3)[42-94].大部分miRNAs都通过靶向特定的靶基因发挥抑制增殖和侵袭转移的功能,从而发挥抑癌基因功能.Kano等[42]研究发现三种具有抑癌基因功能的miRNAs,包含miR-145、miR-133a和miR-133b,可共同调控actin-binding protein,Fascin homolog 1(FSCN1)的表达,参与对ESCC的增殖和侵袭的抑制.miR-29c、miR-200b、miR-577、miR-1、miR-495和miR-181d可通过调控cyclin E、CDK2、TSGA10、cyclin D1,CDK4、Akt1、DERL1细胞周期相关的靶基因调控细胞周期.miR-145、miR-133a、miR-143和miR-200b可通过靶向众多靶基因参与调控EMT从而抑制肿瘤的迁移、侵袭和转移,miR-375和miR-29b则直接通过靶向基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinases,MMPs)如MMP13和MMP2抑制侵袭.本研究也持续关注miRNAs在ESCC中的作用:明确了miR-518b、miR-302b和miR-520a通过调控Rap1、CXCR4,IRF2和ERBB4发挥抑癌基因功能,影响ESCC的增殖、凋亡和侵袭能力.更重要的是,miR-302b可通过靶向多个靶基因调控ESCC肿瘤相关性炎症(cancer related inflammation,CRI)信号通路.我们还明确了miR-381与ESCC的放疗敏感显著相关,潜在的靶基因包括XIAP、CDK1、LEF1、CTNNB1,放疗是ESCC治疗的重要方式,提高放疗敏感性意义重大,除了miR-381外,其他课题组报道了miR-22和miR-98也可以增加放疗敏感性,可能的靶基因包括Rad51和BCL2;而miR-218则可以通过靶向BMI1发挥化疗增敏的作用,miR-100的下游靶基因是mTOR,而mTOR信号途径在包括ESCC在内的多种肿瘤中介导耐药[95],因此我们推测miR-100也可能具有治疗增敏的功能,值得进一步研究.
3 治疗前景
相较于其他肿瘤类型,现有的有关ESCC中miRNAs功能研究的相关报道并不多见,主要受限于以下几个方面的原因.第一,受限于ESCC的地理分布.欧美研究的重点是EAC及Barrett食管[96-97],因为miRNAs作为新近发现的调控因子,进行相关研究的科研经费较大,实验技术要求较高,限制了其快速发展.但是随着miRNAs相关实验技术的不断发展和我国科研实力的不断增强,ESCC与miRNAs的相关研究的报道也不断增加,以“microRNAs”和“esophageal squamous cell carcinoma”作为关键词在PubMed上进行搜索,仅有259篇文献,且大多为我国科研人员的文章;第二,更为重要的是miRNAs研究本身存在的问题.miRNAs本身的产生机制及调控机制仍未完全揭示,存在很多未知之处,尤其是其对靶基因的调控机制及算法上仍存在争议;其次,因为单个miRNAs可以调控多个基因的表达,而单个基因也同时受多个miRNAs的调控,而现行的研究结果都是在单一调控因素的基础上得出的,其准确性有待进一步考证.而该问题受我们所处时代的研究方法及思路的限制,即缺乏高通量的研究模式或叫做整体研究的思路,即便如此,现有的数据也已为ESCC的预防、诊断、治疗以及预后提供了一定的依据.

表3 ESCC中具有抑癌基因功能的miRNAs
既然miRNAs在ESCC中表达失调控,且发挥抑癌基因或癌基因功能,那是否可以应用于ESCC的治疗呢?很遗憾,在ESCC中未见相关报道,但其他肿瘤中的一些研究则具有提示意义.在标准治疗失败的恶性胸膜间皮瘤和晚期非小细胞肺癌患者中,开展了一项应用miR-15/16类似物治疗的临床Ⅰ期研究,将miR-16类似物与EGFR抗体偶联,并应用纳米细胞EDV(EngeneIC delivery vehicle)包装后静脉注射,TAT2015大会的摘要数据显示,5例进行试验的患者耐受良好,仅显示出一过性的细胞因子相关的副反应,更多的结果有待进一步观察[98].当然,miRNAs应用于治疗还有一段很长的路要走,现阶段需要克服的问题主要包括:优化配送系统、改进miRNAs的稳定性、了解miRNAs疗法的脱靶效应等,才可以使miRNAs的治疗实践从实验室过渡到临床应用[99].也期待开展miRNAs应用于ESCC治疗的临床研究,这也依赖于对miRNAs本身生理过程的明晰和呼唤更多更基础的研究证据.
4 结语
综合以上所述,miRNAs在ESCC中表达失调控,并通过多种靶基因发挥抑癌基因或癌基因功能,其临床应用的潜在价值已被充分证实,虽然缺乏应用研究工作,但我国学者的相关研究也取得了一定的进展.相较于其他肿瘤,miRNAs在ESCC中仍处在起始阶段,结合其他肿瘤的相关研究,仍待进一步的发掘.随着miRNAs研究的不断深入、ESCC发病机制的不断明确及相关分子生物技术的不断革新,相信在不久的将来,miRNAs无论是作为诊断或判断预后的标志物,还是作为治疗的靶点,必将更好的服务于ESCC的诊断及治疗.
[1]Torre LA,Bray F,Siegel RL,et al.Global cancer statistics,2012[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2015,65(2):87-108.
[2]Chen W,Zheng R,Baade PD,et al.Cancer statistics in China,2015[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2016,66(2):115-132.
[3]Domper Arnal MJ,Ferrández Arenas Á,Lanas Arbeloa Á.Esophageal cancer:Risk factors,screening and endoscopic treatment in Western and Eastern countries[J].World J Gastroenterol,2015,21(26):7933-7943.
[4]Tétreault MP.Esophageal Cancer:Insights From Mouse Models[J].Cancer Growth Metastasis,2015,8(Suppl 1):37-46.
[5]Li Z,Rana TM.Therapeutic targeting of microRNAs:current status and future challenges[J].Nat Rev Drug Discov,2014,13(8): 622-638.
[6]Calin GA,Sevignani C,Dumitru CD,et al.Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2004,101(9): 2999-3004.
[7]Hayes J,Peruzzi PP,Lawler S.MicroRNAs in cancer:biomarkers, functions and therapy[J].Trends Mol Med,2014,20(8):460-469.
[8]Guo Y,Chen Z,Zhang L,et al.Distinctive microRNA profiles relating to patient survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Cancer Res,2008,68(1):26-33.
[9]Feber A,Xi L,Luketich JD,et al.MicroRNA expression profiles of esophageal cancer[J].J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,2008,135(2): 255-260.
[10]Mathé EA,Nguyen GH,Bowman ED,et al.MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: associations with survival[J].Clin Cancer Res,2009,15(19): 6192-6200.
[11]Ogawa R,Ishiguro H,Kuwabara Y,et al.Expression profiling of micro-RNAs in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using RT-PCR[J].Med Mol Morphol,2009,42(2):102-129.
[12]Lee KH,Goan YG,Hsiao M,et al.MicroRNA-373(miR-373)post-transcriptionally regulates large tumor suppressor,homolog 2(LATS2)and stimulates proliferation in human esophageal cancer[J].Exp Cell Res,2009,315(15):2529-2538.
[13]Wu BL,Xu LY,Du ZP,et al.MiRNA profile in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma:downregulation of miR-143 and miR-145[J].World J Gastroenterol,2011,17(1):79-88.
[14]Hong L,Han Y,Zhang H,et al.The prognostic and chemotherapeutic value of miR-296 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Ann Surg,2010,251(6):1056-1063.
[15]Zang W,Wang Y,Du Y,et al.Differential expression profiling of microRNAs and their potential involvement in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Tumour Biol,2014,35(4):3295-3304.
[16]Zhu L,Yan W,Rodriguez-Canales J,et al.MicroRNA analysis of microdissected normal squamous esophageal epithelium and tumor cells[J].Am J Cancer Res,2011,1(5):574-584.
[17]郑志范,苏华芳,邹 燕,等.microRNA在食管癌放射抵抗细胞表达谱研究[J].中华医学杂志,2011,91(9):639-642.
[18]Kimura S,Naganuma S,Susuki D,et al.Expression of microRNAs in squamous cell carcinoma of human head and neck and the esophagus:miR-205 and miR-21 are specific markers for HNSCC and ESCC[J].Oncol Rep,2010,23(6):1625-1633.
[19]Zhang C,Wang C,Chen X,et al.Expression profile of microRNAs in serum:a fingerprint for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Clin Chem,2010,56(12):1871-1879.
[20]Takeshita N,Hoshino I,Mori M,et al.Serum microRNA expression profile:miR-1246 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Br J Cancer,2013,108(3):644-652.
[21]Liu F,Tian T,Xia LL,et al.Circulating miRNAs as novel potential biomarkers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis:a meta-analysis update[J].Dis Esophagus,2016.
[22]Mori Y,Ishiguro H,Kuwabara Y,et al.MicroRNA-21 induces cell proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Mol Med Rep,2009,2(2):235-239.
[23]Hiyoshi Y,Kamohara H,Karashima R,et al.MicroRNA-21 regu-lates the proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Clin Cancer Res,2009,15(6):1915-1922.
[24]Ma WJ,Lv GD,Tuersun A,et al.Role of microRNA-21 and effect on PTEN in Kazakh's esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Mol Biol Rep,2011,38(5):3253-3260.
[25]Liu T,Liu Q,Zheng S,et al.MicroRNA-21 promotes cell growth and migration by targeting programmed cell death 4 gene in Kazakh's esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Dis Markers,2014:232837.
[26]Liu F,Zheng S,Liu T,et al.MicroRNA-21 promotes the proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in Eca109 via activating ERK1/2/MAPK pathway[J].Mol Cell Biochem,2013,381(1-2):115-125.
[27]Huang S,Li XQ,Chen X,et al.Inhibition of microRNA-21 increases radiosensitivity of esophageal cancer cells through phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 activation[J].Dis Esophagus,2013,26(8):823-831.
[28]Liu W,Li M,Chen X,et al.MicroRNA-373 promotes migration and invasion in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting TIMP3 expression[J].Am J Cancer Res,2015,6(1):1-14.
[29]Chen ZL,Zhao XH,Wang JW,et al.microRNA-92a promotes lymph node metastasis of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via E-cadherin[J].J Biol Chem,2011,286(12):10725-10734.
[30]Xu X,Chen Z,Zhao X,et al.MicroRNA-25 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2012,421(4):640-645.
[31]Tian Y,Luo A,Cai Y,et al.MicroRNA-10b promotes migration and invasion through KLF4 in human esophageal cancer cell lines[J].J Biol Chem,2010,285(11):7986-7894.
[32]Yu T,Cao R,Li S,et al.MiR-130b plays an oncogenic role by repressing PTEN expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells[J].BMC Cancer,2015,15:29.
[33]Li M,He XY,Zhang ZM,et al.MicroRNA-1290 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis[J].World J Gastroenterol,2015,21(11):3245-3255.
[34]Mao Y,Liu J,Zhang D,et al.MiR-1290 promotes cancer progression by targeting nuclear factor I/X(NFIX)in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma(ESCC)[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2015,76: 82-93.
[35]Meng H,Wang K,Chen X,et al.MicroRNA-330-3p functions as an oncogene in human esophageal cancer by targeting programmed cell death 4[J].Am J Cancer Res,2015,5(3):1062-1075.
[36]He X,Zhang Z,Li M,et al.Expression and role of oncogenic miRNA-224 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].BMC Cancer,2015,15:575.
[37]Hong L,Han Y,Zhang H,et al.The prognostic and chemotherapeutic value of miR-296 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Ann Surg,2010,251(6):1056-1063.
[38]Zhang H,Li M,Han Y,et al.Down-regulation of miR-27a might reverse multidrug resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Dig Dis Sci,2010,55(9):2545-2551.
[39]Imanaka Y,Tsuchiya S,Sato F,et al.MicroRNA-141 confers resistance to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by targeting YAP1 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Hum Genet,2011,56(4):270-276.
[40]Hamano R,Miyata H,Yamasaki M,et al.Overexpression of miR-200c induces chemoresistanceinesophagealcancersmediated through activation of the Akt signaling pathway[J].Clin Cancer Res,2011,17(9):3029-3038.
[41]Ma J,Hong L,Xu G,et al.miR-483-3p plays an oncogenic role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting tumor suppressor EI24[J].Cell Biol Int,2016,40(4):448-455.
[42]Kano M,Seki N,Kikkawa N,et al.miR-145,miR-133a and miR-133b:Tumor-suppressive miRNAs target FSCN1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Int J Cancer,2010,127(12):2804-2814.
[43]Wang F,Xia J,Wang N,et al.miR-145 inhibits proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in part by targeting c-Myc[J].Onkologie,2013,36(12):754-758.
[44]Han Q,Zhang HY,Zhong BL,et al.MicroRNA-145 Inhibits Cell Migration and Invasion and Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition(EMT)by Targeting Connective Tissue Growth Factor(CTGF)in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma[J].Med Sci Monit,2016,22:3925-3934.
[45]Cui XB,Li S,Li TT,et al.Targeting oncogenic PLCE1 by miR-145 impairs tumor proliferation and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(2):1777-1795.
[46]Akanuma N,Hoshino I,Akutsu Y,et al.MicroRNA-133a regulates themRNAsoftwoinvadopodia-relatedproteins,FSCN1and MMP14,in esophageal cancer[J].Br J Cancer,2014,110(1): 189-198.
[47]Li S,Qin X,Li Y,et al.MiR-133a suppresses the migration and invasion of esophageal cancer cells by targeting the EMT regulator SOX4[J].Am J Transl Res,2015,7(8):1390-1403.
[48]Yuan Y,Zeng ZY,Liu XH,et al.MicroRNA-203 inhibits cell proliferation by repressing ΔNp63 expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].BMC Cancer,2011,11:57.
[49]Takeshita N,Mori M,Kano M,et al.miR-203 inhibits the migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating LASP1[J].Int J Oncol,2012,41(5):1653-1661.
[50]Yu X,Jiang X,Li H,et al.miR-203 inhibits the proliferation and self-renewal of esophageal cancer stem-like cells by suppressing stem renewal factor Bmi-1[J].Stem Cells Dev,2014,23(6):576-585.
[51]Liu Q,Lv GD,Qin X,et al.Role of microRNA let-7 and effect to HMGA2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Mol Biol Rep,2012,39(2):1239-1246.
[52]Ding DP,Chen ZL,Zhao XH,et al.miR-29c induces cell cycle arrest in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating cyclin E expression[J].Carcinogenesis,2011,32(7):1025-1032.
[53]Matsushima K,Isomoto H,Yamaguchi N,et al.MiRNA-205 modulates cellular invasion and migration via regulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells[J].J Transl Med,2011,9:30.
[54]Zhang M,Zhou S,Zhang L,et al.miR-518b is down-regulated,and involved in cell proliferation and invasion by targeting Rap1b in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].FEBS Lett,2012,586(19):3508-3521.
[55]Zhang M,Yang Q,Zhang L,et al.miR-302b is a potential molecular marker of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting ErbB4[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2014,33(1):10.
[56]Zhang M,Zhang P,Zhang L,et al.miR-302b regulates cancer related inflammation by targeting CXCR4 and IRF2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2015,30(Suppl 4):89-90.
[57]张鹏江,崔曼莉,张 超,等.炎症相关细胞因子对食管癌细胞株miR-302b表达的影响[J].现代肿瘤医学,2016,24(5):690-693.
[58]叶文广,姚青林,张明鑫,等.miR-520a调控ErbB4的表达并抑制食管鳞癌细胞的增殖与侵袭[J].南方医科大学学报,2014,34(2):164-168.
[59]张 超,张 蓉,樊晴伶,等.miR-520a在食管鳞癌组织中的表达及意义[J].现代肿瘤医学,2015,23(20):2923-2925.
[60]Zhou S,Ye W,Ren J,et al.MicroRNA-381 increases radiosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Am J Cancer Res,2015,5(1):267-277.
[61]Kong KL,Kwong DL,Chan TH,et al.MicroRNA-375 inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma through repressing insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor[J].Gut,2012,61(1):33-42.
[62]Isozaki Y,Hoshino I,Nohata N,et al.Identification of novel molecular targets regulated by tumor suppressive miR-375 induced by histone acetylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Int J Oncol,2012,41(3):985-994.
[63]Osako Y,Seki N,Kita Y,et al.Regulation of MMP13 by antitumor microRNA-375 markedly inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Int J Oncol,2016,49(6):2255-2264.
[64]Wang XC,Zhang ZB,Wang YY,et al.Increased miRNA-22 expression sensitizes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to irradiation[J].J Radiat Res,2013,54(3):401-408.
[65]Ni Y,Meng L,Wang L,et al.MicroRNA-143 functions as a tumor suppressor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Gene,2013,517(2):197-204.
[66]Mao Y,Liu J,Zhang D,et al.miR-143 inhibits tumor progression by targeting FAM83F in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Tumour Biol,2016,37(7):9009-9022.
[67]Liu J,Mao Y,Zhang D,et al.MiR-143 inhibits tumor cell proliferation and invasion by targeting STAT3 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Cancer Lett,2016,373(1):97-108.
[68]Fu MG,Li S,Yu TT,et al.Differential expression of miR-195 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and miR-195 expression inhibits tumor cell proliferation and invasion by targeting of Cdc42[J].FEBS Lett,2013,587(21):3471-3479.
[69]Zhang HF,Zhang K,Liao LD,et al.miR-200b suppresses invasiveness and modulates the cytoskeletal and adhesive machinery in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting Kindlin-2[J].Carcinogenesis,2014,35(2):292-301.
[70]Zhang HF,Alshareef A,Wu C,et al.Loss of miR-200b promotes invasion via activating the Kindlin-2/integrin β1/AKT pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma:An E-cadherin-independent mechanism[J].Oncotarget,2015,6(30):28949-28960.
[71]He Z,Yi J,Liu X,et al.MiR-143-3p functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating cell proliferation,invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting QKI-5 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Mol Cancer,2016,15(1):51.
[72]Zhang HF,Alshareef A,Wu C,et al.miR-200b induces cell cycle arrest and represses cell growth in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Carcinogenesis,2016,37(9):858-869.
[73]Zhu L,Wang Z,Fan Q,et al.microRNA-27a functions as a tumor suppressor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting KRAS[J].Oncol Rep,2014,31(1):280-286.
[74]Jiang Y,Duan Y,Zhou H.MicroRNA-27a directly targets KRAS to inhibit cell proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Oncol Lett,2015,9(1):471-477.
[75]Liu R,Yang M,Meng Y,et al.Tumor-suppressive function of miR-139-5p in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].PLoS One,2013,8(10):e77068.
[76]Yuan X,He J,Sun F,et al.Effects and interactions of MiR-577 and TSGA10 in regulating esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2013,6(12):2651-2667.
[77]Wang Y,Zang W,Du Y,et al.Mir-655 up-regulation suppresses cell invasion by targeting pituitary tumor-transforming gene-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Transl Med,2013,11:301.
[78]Li H,Meng F,Ma J,et al.Insulin receptor substrate-1 and Golgi phosphoprotein 3 are downstream targets of miR-126 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Oncol Rep,2014,32(3):1225-1233.
[79]Nie ZC,Weng WH,Shang YS,et al.MicroRNA-126 is down-regulated in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and inhibits the proliferation and migration in EC109 cell via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J].Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2015,8(5):4745-4754.
[80]Liu R,Gu J,Jiang P,et al.DNMT1-microRNA126 epigenetic circuit contributes to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth via ADAM9-EGFR-AKT signaling[J].Clin Cancer Res,2015,21(4): 854-863.
[81]Zhang N,Fu H,Song L,et al.MicroRNA-100 promotes migration and invasion through mammalian target of rapamycin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Oncol Rep,2014,32(4):1409-1418.
[82]Tian H,Hou L,Xiong YM,et al.miR-218 suppresses tumor growth and enhances the chemosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin[J].Oncol Rep,2015,33(2):981-989.
[83]Wang T,Chen T,Niu H,et al.MicroRNA-218 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting BMI1[J].Int J Mol Med,2015,36(1):93-102.
[84]Qi Y,Li X,Zhao S.miR-29b inhibits the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting MMP-2[J].Neoplasma,2015,62(3):384-390.
[85]Yan S,Jiang H,Fang S,et al.MicroRNA-340 Inhibits Esophageal Cancer Cell Growth and Invasion by Targeting Phosphoserine Aminotransferase 1[J].Cell Physiol Biochem,2015,37(1):375-386.
[86]He W,Feng J,Zhang Y,et al.microRNA-186 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting SKP2[J].Lab Invest,2016,96(3):317-324.
[87]Meng X,Chen X,Lu P,et al.MicroRNA-202 inhibits tumor progression by targeting LAMA1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2016,473(4):821-827.
[88]Jiang S,Zhao C,Yang X,et al.miR-1 suppresses the growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in vivo and in vitro through the downregulation of MET,cyclin D1 and CDK4 expression[J].Int J Mol Med,2016,38(1):113-122.
[89]Mao Y,Li L,Liu J,et al.MiR-495 inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting Akt1[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(32):51223-51236.
[90]Jin L,Yi J,Gao Y,et al.MiR-630 inhibits invasion and metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Acta Biochim Biophys Sin(Shanghai),2016,48(9):810-819.
[91]Li D,Shi M,Ji H,et al.MicroRNA-181d is a tumor suppressor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma inversely regulating Derlin-1[J].Oncol Rep,2016,36(4):2041-2048.
[92]Song C,Lu P,Shi W,et al.MiR-622 functions as a tumor suppressor and directly targets E2F1 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2016,83:843-849.
[93]Gao X,Wang X,Cai K,et al.MicroRNA-127 is a tumor suppressor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through the regulation of oncogene FMNL3[J].Eur J Pharmacol,2016,791:603-610.
[94]Jin YY,Chen QJ,Wei Y,et al.Upregulation of microRNA-98 increases radiosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].J Radiat Res,2016,57(5):468-476.
[95]Hou G,Yang S,Zhou Y,et al.Targeted inhibition of mTOR signaling improves sensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin[J].J Immunol Res,2014,2014:845763.
[96]Mallick R,Patnaik SK,Wani S,et al.A Systematic Review of Esophageal MicroRNA Markers for Diagnosis and Monitoring of Barrett's Esophagus[J].Dig Dis Sci,2016,61(4):1039-1050.
[97]Bobryshev YV,Orekhov AN,Chistiakov DA.MicroRNAs in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma:Functional Significance and Potential for the Development of New Molecular Disease Markers[J].Curr Pharm Des,2015,21(23):3402-3416.
[98]Van ZN,Pavlakis N,Kao S,et al.MesomiR 1:a phase I study of TargomiRs in patients with refractory malignant pleural mesothelioma(MPM)and lung cancer(NSCLC)[J].Ann Oncol,2015,26(suppl 2):ii16-ii19.
[99]Shah MY,Ferrajoli A,Sood AK,et al.microRNA Therapeutics in Cancer-An Emerging Concept[J].EBioMedicine,2016,12:34-42.
Function,mechanism and therapeutic prospect of miRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
CUI Man-Li1,ZHOU Su-Na2,ZHANG Ming-Xin1,WANG Jing-Jie1
1Department of Gastroenterology,2Department of Radiotherapy,Tangdu Hospital,Fourth Military Medical University,Xi'an 710038,China
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma(ESCC)dominates in East Asia,and almost one-half of ESCC cases in the world occur in China.Despite improvements in both diagnostic and therapeutic techniques,ESCC continues to show a poor prognosis.Therefore,the molecular mechanisms responsible for the deregulation in ESCC needs further research and investigation.MicroRNAs(miRNAs)represent a class of small,non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional levels.Studies showed that the dysregulation of miRNAs presents up-or down-regulation and deletion in different oncogenic pathways and/or various types of cancers,indicating that some miRNAs may serve as oncogenic or tumor suppressor genes.In this review,we summarize the related research progress on expression,function,mechanism and therapeutic prospect of miRNAs in ESCC.
function;mechanism;therapeuticprospect;miRNAs;esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
R735.1
A
2095-6894(2017)01-11-09
2016-11-21;接受日期:2016-12-10
国家自然基金(81302055,81301922),唐都医院精英才人计划后备人才项目
崔曼莉.硕士,主治医师.研究方向:消化道肿瘤.E-mail: cuiml1587@163.com
张明鑫.博士,副主任医师.研究方向:消化道肿瘤临床及基础研究.E-mail:zmx3115@163.com
