吲哚胺2,3-双加氧化酶1及其抑制剂的研究
2017-03-01张胜男
张胜男 刘 鑫 杨 青
(复旦大学生命科学学院生物化学系 上海 200438)

吲哚胺2,3-双加氧化酶1及其抑制剂的研究
张胜男 刘 鑫 杨 青△
(复旦大学生命科学学院生物化学系 上海 200438)
吲哚胺2,3-双加氧化酶1( indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1,IDO1)是肝脏以外催化色氨酸沿着犬尿氨酸途径(kynurenine pathway,KP)分解代谢的限速酶。IDO1过度活化而引起KP的神经毒性产物喹啉酸(quinolinic acid,QUIN)的蓄积,是导致神经紊乱和神经退行性疾病的重要原因。IDO1同时又是免疫耐受酶,在诱导母胎免疫耐受和肿瘤免疫逃逸中均发挥重要作用,被视为新的免疫检查点。IDO1与阿尔茨海默病、老年性白内障、癌症等多种疾病发病机制的相关性已被证实,因此IDO1抑制剂作为极具潜能的药物受到日益广泛的关注。本文就IDO1的生物活性及其抑制剂的研究作一综述。
吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶 1; 抑制剂; 肿瘤免疫治疗
吲哚胺2,3-双加氧化酶1( indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1,IDO1) 可催化L-色氨酸(L-tryptophan,L-Trp)沿着犬尿氨酸途径(kynurenine pathway,KP)分解代谢生成包括神经毒素喹啉酸(quinolinic acid,QUIN)在内的一些代谢产物[1]。IDO1的过度活化及其引起的QUIN含量的增多,与神经系统炎症、抑郁、神经退行性疾病的发病机制密切相关[2-3]。IDO1还具有免疫耐受功能,被视为新的免疫检查点[4-5]。肿瘤细胞、抗原呈递细胞如巨噬细胞、树突状细胞上的IDO1均可诱导T细胞对肿瘤抗原的免疫耐受[6]。
IDO1有2个同工酶,即色氨酸双加氧酶 (tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase,TDO)和吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶2(indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2,IDO2)[7]。TDO在多种肿瘤的免疫逃逸中起一定作用[8-9],而IDO2在T细胞对肿瘤抗原的免疫耐受中的角色和机制还有待深入研究[7,10-13]。
IDO1已被证实是一个重要的药物发现靶标,IDO1抑制剂作为具有新药靶、新机制的药物,可应用于治疗肿瘤、阿尔茨海默病、抑郁症等多种疾病,社会和经济效益显著,应用前景广阔[14-15]。
本文对IDO1的生物活性及其抑制剂的研究现状作一介绍,以促进IDO1抑制剂类药物的研发。
催化L-色氨酸分解代谢的限速酶 哺乳动物体内催化必需氨基酸L-Trp循KP分解代谢的首个反应的限速酶有3个,即TDO、IDO1和IDO2[7,16-17](图1)。
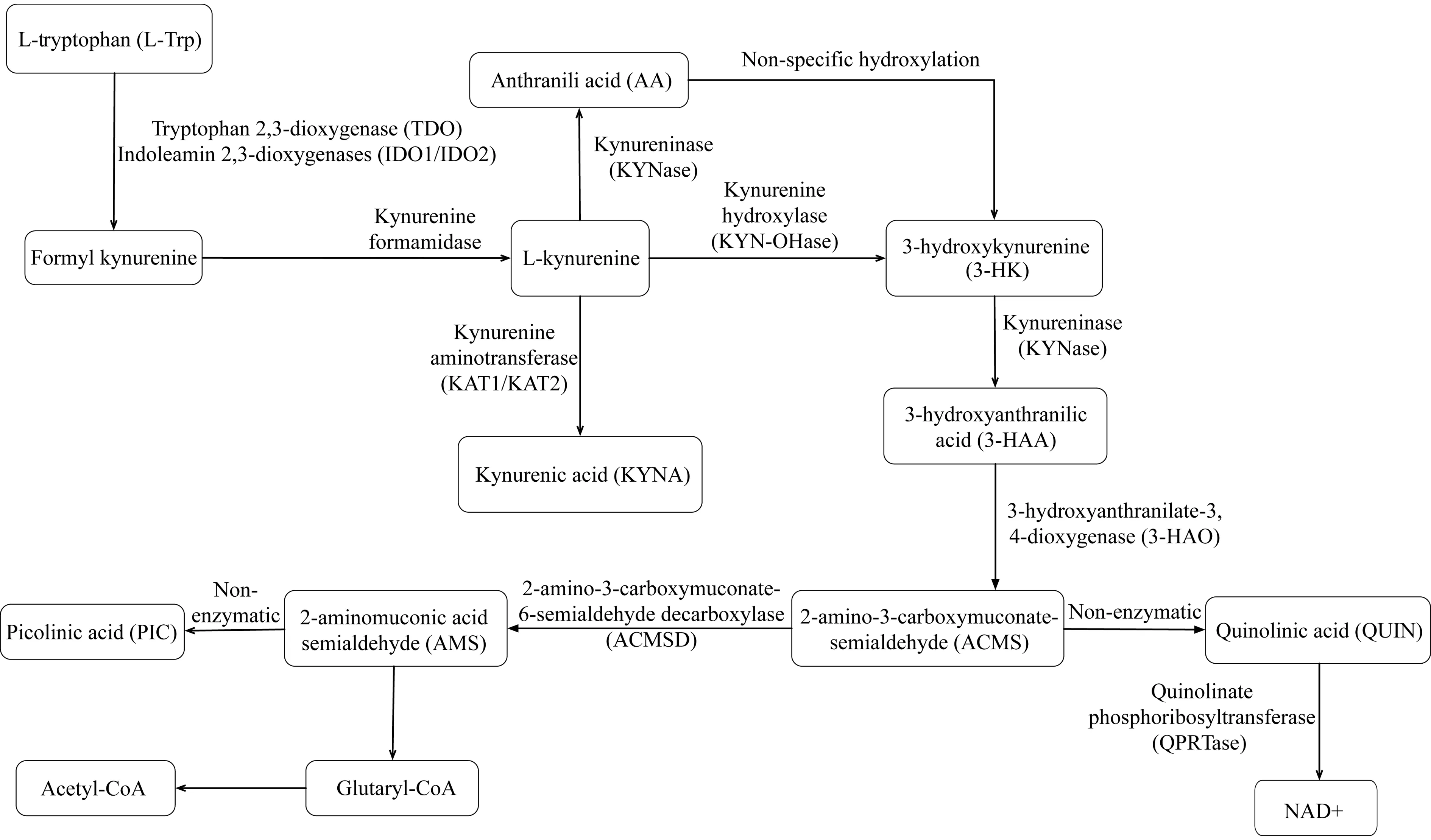
图1 L-色氨酸的犬尿氨酸代谢途径
Fig 1 The kynurenine pathway of L-tryptophan metabolism
TDO(或TDO 2,EC.1.13.11.11)是存在于细胞内的含血红素的多聚体双加氧酶[18],由4个含血红素的相同亚基组成[19],于1936年首次被发现于兔肝脏中[20],主要分布在哺乳动物的肝脏,经过刺激后在其他部位如皮肤、胎盘和脑中也有表达[21]。外源的色氨酸、犬尿氨酸(kynurenine,Kyn)以及糖皮质激素可诱导内源TDO2基因的表达[18,22]。人TDO的编码基因(Tdo或Tdo2)位于4号染色体上(4q32.1 )[23],全长约16 kb,包含12个外显子和6个内含子,其单体蛋白质产物分子量约46.7 kD,由406个氨基酸构成[7,24]。 真核和原核TDO都对L-Trp具有较高催化活性,而对D-Trp的催化活性很低[25-26]。TDO与IDO序列相似性很低,但是TDO与IDO其含亚铁血红素的活性部位高度相似[27]。近年研究发现TDO与肿瘤免疫逃逸有关[9,28],TDO活性的增强,造成Kyn等色氨酸代谢产物的含量显著上升,进而提高体内调节性T细胞的水平并随之产生免疫耐受[29],Kyn可以结合并激活芳香烃受体,增加肿瘤细胞存活率来帮助肿瘤细胞进行免疫逃逸[8]。
IDO1(或INDO,EC 1.13.11.52)是存在于细胞内的含亚铁血红素的单体蛋白质类酶,于1967年首次被发现于兔小肠中[30],广泛分布于哺乳动物肝脏以外的多种组织,尤其是淋巴组织和胎盘[31]。IDO1是肝脏外可催化色氨酸分子中吲哚环氧化裂解,使其循KP分解代谢的限速酶[32]。人IDO1的编码基因(Ido1,INDO)为单拷贝,全长约15 kb,由10个外显子和9个内含子组成[33], 其蛋白质产物分子量约42 kD, 由403个氨基酸构成[34]。肿瘤细胞、抗原呈递细胞如巨噬细胞、树突状细胞上的IDO1均可诱导T细胞对肿瘤抗原的免疫耐受。首先,IDO1通过降解色氨酸,造成缺乏色氨酸的微环境,使色氨酸依赖的T细胞增殖滞留在G1期[35]。其次,KP的一些代谢产物对T细胞有毒性,阻碍其功能[36-37]。最后,IDO1可以诱导调节性T细胞的扩增,而调节性T细胞的上调是肿瘤免疫治疗的重要阻碍[38-40]。
IDO2(EC 1.13.11)于2007年首次被发现[41-43]。与IDO1的广泛分布相比,IDO2分布范围相对较小,如在小鼠的器官中,肾脏的IDO2 含量最高, 其次是副睾、肝脏[42-43]。与IDO1相比,IDO2催化L-Trp降解的酶活性很弱[44]。在人类和小鼠体内,IDO1 和IDO2 的编码基因均位于8号染色体上(8p11.21),IDO2的基因位于IDO1的下游,二者呈头-尾相连的串联形式排列。人的IDO2基因(Ido2,INDOL1)全长约81 kb,包含11个外显子和10个内含子,翻译得到的蛋白质由420个氨基酸组成,分子量略大于46 kD[41-42,13]。研究表明IDO2也具有抑制T细胞增殖的作用[12,45]。提高色氨酸浓度或加入抑制剂1-甲基色氨酸(1-methyl-tryptophan,1-MT)可以逆转由IDO1所引起的对T细胞增殖的抑制作用;与之明显不同的是,由IDO2引起的T细胞增殖抑制作用即使补充高浓度色氨酸或1-MT也不能逆转[45]。由此推测在T细胞参与的免疫调节反应中,IDO2与IDO1可能具有不同的信号调控通路,发挥不同的作用。氨基酸序列比对发现在人和小鼠体内,IDO1和 IDO2具有43%的序列同源性,但与TDO的同源序列均很少;蛋白质水平上IDO2与IDO1的空间结构类似,核心催化残基相同,并且二者在功能上是保守的[42,46]。
IDO1抑制剂研发历程 尽管TDO、IDO1和IDO2都具有催化色氨酸循KP代谢的功能,但是其组织分布以及催化底物能力有所不同,参与肿瘤免疫逃逸的作用及机制也不尽相同,在神经系统疾病发病机制中的作用被确认和认知的程度也不相同,其中IDO1受到较早的关注以及广泛的重视,被认为是重要的药物研发靶标[47-49]。
自1967年被发现至2000年,IDO1抑制剂的研发主要以治疗神经紊乱和神经退行性疾病为目的,以合成化学为手段,以IDO1的底物色氨酸为模板,在研究构效关系的基础上对其进行结构修饰。发表的文章和注册的专利几乎覆盖了所有能修饰的基团[50-51],但是收效甚微。两个比较有代表性的IDO1抑制剂分别是3-丁基-β咔啉(3-butyl-β-carboline,非竞争性抑制剂,Ki=3.3 μmol/L)[52]和1-MT(竞争性抑制剂,Ki=34 μmol/L)[53],后者被广泛应用于体内外实验。
2000年前后,随着IDO1的免疫抑制作用被发现,IDO1抑制剂的研发掀起高潮。2006年,人IDO1与配体抑制剂4-苯基咪唑(4-phenylimidazole,4-PI )的复合物的晶体结构被解明[54],为IDO1抑制剂的设计提供了可贵的信息。IDO1抑制剂的研发不再局限于色氨酸衍生物的设计合成,而是天然产物提取、结构修饰、计算机模拟设计等多种手段并存,产生了许多种不同结构骨架的IDO1抑制剂。 来自海洋生物的Exiguamine A (Ki=0.21 μmol/L)[55]和Annulin C (Ki=0.14 μmol/L)[56-57],来自十字花科植物的Brassinin (Ki=97.7 μmol/L)[58],吲哚衍生物MTH-trp (细胞水平IC50=0.5 μmol/L)[47],苯醌衍生物Quinone (Ki=0.58 μmol/L)[48,57],抑制效率提高了10倍的4-PI的衍生物[59], 咪唑类化合物NLG919 (IC50=38 nmol/L)[60-62],三氮唑衍生物MMG-0358(IC50=0.33 μmol/L)[63],N-羟基眯类INCB024360(IC50=72 nmol/L)[64-67],Amg-1(IC50=3 μmol/L)[46],细胞水平IC50达到pmol/L的2-氨基苯脲类化合物[68-71]等是比较典型的代表。
尽管不同结构的IDO1抑制剂不断被发现,但是许多结构骨架在进一步的研究中表现出的活性或者特异性并不确定,因此未进行药物研发。目前世界上还未有IDO1抑制剂药物问世,只有NewLink Genetics公司的NLG919和Incyte公司的INCB024360两个化合物进入临床试验[49]。2014年9月罗氏公司以头款1.5亿美元的价格收购了NLG919,接着在2015年4月又以头款2 300万美元获得Curadev公司处于临床前开发阶段的IDO1和TDO抑制剂[72-73],从此开启了IDO1抑制剂研发白热化的竞赛。
IDO1在被发现之后较长时间里没有商品化出售,这给建立酶活检测体系进行IDO1抑制剂筛选带来一定难度,药物学家不太容易在自己的实验室里进行活性检测指导下的分离提取或者设计合成。因此,IDO1抑制剂筛选工作在国内鲜有开展[74]。
从2006年开始,本课题组运用基因工程技术,制备不同种源(人、小鼠和大鼠)的IDO1、IDO2、TDO,在体外和细胞水平上建立了酶活性检测体系,系统地测定抑制类型、抑制常数Ki、酶以及细胞水平IC50,建立了国内首个IDO1抑制剂筛选平台。采取天然提取和化学合成的手段在数百个化合物中筛选出(E)-4-(β-溴乙烯基)苯氧酰基、4-苯基-1,2,3-三氮唑、黄连生物碱、吲哚生物碱等结构骨架的数十个优良的IDO1抑制剂;完成酶动力学测试、细胞水平抑制活性测试及IDO1蛋白质的三维对接试验;运用获得的IDO1抑制剂进行抗肿瘤、抗阿尔茨海默病的药效学研究,并探索其相应的机制[15,75-78]。申请了多项IDO1抑制剂的中国发明专利和1项PCT国际专利。2016年3月,PCT专利的海外权利已经成功授权给美国沪亚生物国际有限公司(HUYA),业界评价是“中国知识产权成功转化的一个案例”。
IDO1抑制剂评价方法 要完整系统地评价一个化合物的IDO1抑制活性,一般要测定抑制剂类型、抑制常数、酶以及细胞水平的 IC50等。
酶水平活性检测 在Takikawa等[79]研究的基础上进行优化。在500 μL的检测体系中,将50 mmol/L磷酸钾缓冲液、400 μg/mL 过氧化氢酶、40 mmol/L维生素C、20 μmol/L亚甲基蓝、L-Trp以及待测样品混合,混合液37 ℃保温3~5 min, 再向上述混合液内加入重组人IDO1,37 ℃反应30 min,后加入质量浓度为300 g/L的三氯乙酸200 μL终止反应,并在65 ℃水浴锅中加热15 min,使之完成从N-甲酰犬尿氨酸到犬尿氨酸的转化,然后12 000 r/min离心10 min(离心半径为5.5 cm)。吸取上清100 μL与等体积的质量浓度为2 g/L的对二甲氨基苯甲醛的乙酸溶液混合,犬尿氨酸与该溶液产生反应,并使溶液变为黄色,使用酶标仪在492 nm处检测其吸光度。
抑制类型及Ki、IC50值测定 利用上述反应体系,加入50 μmol/L 抑制剂和不同浓度的IDO1 酶,其他处理方法同上,最后以v ~ [E]作图,根据所得曲线的关系判断抑制剂类型。抑制常数 Ki 及 IC50值的测定同样利用上述反应体系,加入不同浓度底物 L-Trp,在一个底物浓度下,加入不同浓度的抑制剂,其他处理方法同上,最后以 Dixon 作图法得到Ki值[71],利用改良寇氏法计算出 IC50值。
细胞水平IDO 抑制活性测定 将HEK 293细胞以 2.5 × 104/孔的密度接种于96孔板中, DMEM 培养基培养(含10% 胎牛血清、50 U/mL青霉素、50 mg/mL 链霉素),置于37 ℃、湿度 95%、5% CO2的培养箱中培养。24 h后使用脂质体 Lipofectamin 2000 介导 pcDNA3.1-hIDO 质粒转染。转染24 h后加入待测药物,孵育5 h 后,取 140 μL上清到另一 96 孔板中,加入10 μL质量浓度为300 g/L的三氯乙酸,在65 ℃加热15 min,然后12 000 r/min离心10 min(离心半径为5.5 cm),取等体积质量浓度为20 g/L的对-二甲氨基苯甲醛的乙酸溶液混合显色,最后采用酶标仪检测492 nm处的吸光值。
结语 在肿瘤免疫治疗被日渐重视的今天,IDO1作为继程序性死亡蛋白1 (programmed death protein-1,PD-1)和细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关抗原4 (cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4,CTLA4)之后又一被关注的新免疫检查点,其成为药物发现靶标的价值和前景已经毋庸置疑。IDO1抑制剂研发过程中由于三维结构未明、IDO1未商品化、活性筛选体系不完善所带来的壁垒被逐个攻破,人们已经对IDO1抑制剂的关键药效基团有所了解和认识,并对IDO1抑制剂的作用机制不断发掘和阐明。可以期待在不久的将来IDO1抑制剂作为药物问世,为世人带来健康的福音。
[1] MYINTAM,KIM YK.Network beyond IDO in psychiatric disorders:revisiting neuro-degeneration hypothesis[J].ProgNeuro-Psychoph,2014,48:304-313.
[2] LOPRESTI AL,MAKER GL,HOOD SD,etal.A review of peripheral biomarkers in major depression:the potential of inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers[J].ProgNeuro-Psychoph,2014,48:102-111.
[3] O’CONNOR JC,SALAZAR A,GONZALEZ-RIVERA BL,etal.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase mediates anhedonia and anxiety-like behaviors caused by peripheral lipopolysaccharide immune challenge[J].HormBehav,2012,62(3):202-209.
[4] BADAWY AA.The tryptophan utilization concept in pregnancy[J].ObstetGynecolSci,2014,57(4):249-259.
[5] PRENDERGAST GC,SMITH C,THOMAS S,etal.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase pathways of pathogenic inflammation and immune escape in cancer[J].CancerImmunolImmunother,2014,63(7):721-735.
[6] HOLMGAARD RB,ZAMARIN D,LI Y,etal.Tumor-expressed IDO recruits and activates MDSCs in a Treg-dependent manner[J].CellRep,2015,13(2):412-424.
[7] BALL HJ,JUSOF FF,BAKMIWEWA SM,etal.Tryptophan-catabolizing enzymes-party of three[J].FrontImmunol, 2014,5:485.
[8] OPITZ C A,LITZENBURGER UM,SAHM F,etal.An endogenous tumour promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor[J].Nature,2011,478(7368):197-203.
[9] PILOTTE L,LARRIEU P,STROOBANT V,etal. Reversal of tumoral immune resistance by inhibition of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase[J].ProcNatlAcadSci, 2012,109(7):2497-2502.
[10] VAN BAREN N,VAN DEN EYNDE BJ.Tryptophan-degrading enzymes in tumoral immune resistance[J].FrontImmunol,2015,6:34.
[11] FATOKUN AA,HUNT NH,BALL HJ.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 (IDO2) and the kynurenine pathway:characteristics and potential roles in health and disease[J].AminoAcids,2013,45(6):1319-1329.
[12] METZ R,SMITH C,DUHADAWAY JB,etal.IDO2 is critical for IDO1-mediated T-cell regulation and exerts a non-redundant function in inflammation[J].IntImmunol, 2014,26(7):357-367.
[13] PRENDERGAST GC,METZ R,MULLER AJ,etal.IDO2 in immune-modulation and autoimmune disease[J].FrontImmunol,2014,5:585.
[14] 孔令雷,匡春香,杨青.IDO 抑制剂的研究进展[J].中国药物化学杂志,2009,19(2):147-154.
[15] YANG S,LI X,HU F,etal.Discovery of tryptanthrin derivatives as potent inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase with therapeutic activity in Lewis lung cancer (LLC) tumor-bearing mice[J].JMedChem,2013,56(21):8321-8331.
[16] BAKMIWEWA SM,FATOKUN AA,Tran A,etal.Identification of selective inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2[J].BioorgMedChemLett,2012,22(24):7641-7646.
[17] YUASA HJ,TAKUBO M,TAKAHASHI A,etal.Evolution of vertebrate indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases[J].JMolEvol,2007,65(6):705-714.
[18] SONO M,ROACH MP,COULTER ED,etal.Heme-containing oxygenases[J].ChemRev,1996,96(7):2841-2888.
[19] SCHUTZ G,FEIGELSON P.Purification and properties of rat liver tryptophan oxygenase[J].JBiolChem, 1972,247(17):5327-5332.
[20] KOTAKE Y,MASAYAMA I.The intermediary metabolism of tryptophan.XVIII.The mechanism of formation of kynurenine from tryptophan[J].ZPhysiolChem,1936,243:237-244.
[21] ISHIGURO I,NAITO J,SAITO K,etal.Skin l-tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase and rat hair growth[J].FEBSLett,1993,329(1-2):178-182.
[22] KATZ JB,MULLER AJ,PRENDERGAST GC.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in T-cell tolerance and tumoral immune escape[J].ImmunolRev, 2008,222(1):206-221.
[23] COMINGS DE,MUHLEMAN D,DIETZ GW,etal.Human tryptophan oxygenase localized to 4q31:Possible implications for alcoholism and other behavioral disorders[J].Genomics,1991,9(2):301-308.
[24] MENG B,WU D,GU J,etal.Structural and functional analyses of human tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase[J].ProteinStructFunctGenet,2014,82(11):3210-3216.
[25] CAPECE L,ARRAR M,ROITBERG AE,etal.Substrate stereo-specificity in tryptophan dioxygenase and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase[J].ProteinStructFunctGenet, 2010,78(14):2961-2972.
[26] BASRAN J,RAFICE SA,CHAUHAN N,etal. A kinetic,spectroscopic,and redox study of human tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase[J].Biochemistry,2008,47(16):4752-4760.
[27] THACKRAY SJ,MOWAT CG,CHAPMAN SK.Exploring the mechanism of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase[J].BiochemSocTrans, 2008,36(6):1120-1123.
[28] VAN DEN EYNDE B,PILOTTE L,DE PLAEN E.Tryptophan catabolism in cancer treatment and diagnosis[P].WO 2010/008427,2010-01-21.
[29] STONE TW,STOY N,DARLINGTON LG.An expanding range of targets for kynurenine metabolites of tryptophan[J].TrendsPharmacolSci,2013,34(2):136-143.
[30] YAMAMOTO S,HAYAISHI O.Tryptophan pyrrolase of rabbit intestine d-and l-tryptophan-cleaving enzyme or enzymes[J].JBiolChem,1967,242(22):5260-5266.
[31] YAMAZAKI F,KUROIWA T,TAKIKAWA O,etal.Human indolylamine 2,3-dioxygenase.Its tissue distribution,and characterization of the placental enzyme[J].BiochemJ, 1985,230(3):635-638.
[32] SHIMIZU T,NOMIYAMA S,HIRATA F,etal.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.Purification and some properties[J].JBiolChem,1978,253(13):4700-4706.
[33] DAI W,GUPTA SL.Molecular cloning,sequencing and expression of human interferon-γ-inducible indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase cDNA[J].BiochemBiophysResCommun,1990,168(1):1-8.
[34] HIRATA F,OHNISHI T,HAYAISHI O.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.Characterization and properties of enzyme.O2- complex [J]JBiolChem,1977,252(13):4637-4642.
[35] MELLOR A.IMELLOR A.Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase and regulation of T cell immunity[J].BiochemBiophysResCommun,2005,338(1):20-24.
[36] MUNN DH,MELLOR AL.IDO and tolerance to tumors[J].TrendsMolMed,2004,10(1):15-18.
[37] FRUMENTO G,ROTONDO R,TONETTI M,etal.Tryptophan-derived catabolites are responsible for inhibition of T and natural killer cell proliferation induced by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase[J].JExpMed,2002,196(4):459-468.
[38] MUNN DH,MELLOR AL.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tumor-induced tolerance[J].JClinInvest, 2007,117(5):1147-1154.
[39] COLOMBO MP,PICONESE S.Regulatory T-cell inhibition versus depletion:the right choice in cancer immunotherapy[J].NatRevCancer, 2007,7(11):880-887.
[40] FALLARINO F,GROHMANN U,YOU S,etal.Tryptophan catabolism generates autoimmune-preventive regulatory T cells[J].TransplImmunol, 2006,17(1):58-60.
[41] BALL HJ,SANCHEZ-PEREZ A,WEISER S,etal.Characterization of an indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-like protein found in humans and mice[J].Gene,2007,396(1):203-213.
[42] METZ R,DUHADAWAY J B,KAMASANI U,etal.Novel tryptophan catabolic enzyme IDO2 is the preferred biochemical target of the antitumor indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitory compound D-1-methyl-tryptophan[J].CancerRes,2007,67(15):7082-7087.
[43] MURRAY MF.The human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase gene and related human genes[J].CurrDrugMetab,2007,8(3):197-200.
[44] BALL HJ,YUASA HJ,AUSTIN C JD,etal. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2; a new enzyme in the kynurenine pathway[J].IntJBiochemCellBiol,2009,41(3):467-471.
[45] QIAN F,LIAO J,VILLELLA J,etal.Effects of 1-methyltryptophan stereoisomers on IDO2 enzyme activity and IDO2-mediated arrest of human T cell proliferation[J].CancerImmunolImmunother,2012,61(11):2013-2020.
[46] MEININGER D,ZALAMEDA L,LIU Y,etal.Purification and kinetic characterization of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases 1 and 2 (IDO1 and IDO2) and discovery of elective IDO1 inhibitors[J].BiochimBiophysActa,2011,1814(12):1947-1954.
[47] MULLER AJ,DUHADAWAY JB,DONOVER PS,etal.Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase,an immunoregulatory target of the cancer suppression gene Bin1,potentiates cancer chemotherapy[J].NatMed, 2005,11(3):312-319.
[48] KUMAR S,MALACHOWSKI WP,DUHADAWAY JB,etal.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is the anticancer target for a novel series of potent naphthoquinone-based inhibitors[J].JMedChem,2008,51(6):1706-1718.
[49] RÖHRIG UF,MAJJIGAPU SR,VOGEL P,etal.Challenges in the discovery of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) inhibitors[J].JMedChem,2015,58(24):9421-9437.
[50] LI X,YIN W,SRIRAMA SARMA PVV,etal. Synthesis of optically active ring-A substituted tryptophans as IDO inhibitors[J].TetrahedronLett, 2004,45(46):8569-8573.
[51] MA C,LIU X,YU S,etal.Concise synthesis of optically active ring-A substituted tryptophans[J].TetrahedronLett,1999,40(4):657-660.
[52] PETERSON AC,LA LOGGIA AJ,HAMAKER LK,etal.Evaluation of substituted β‐carbolines as noncompetitive indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors[J].MedChemRes,1993,3(14):473-482.
[53] CADY SG,SONO M.1-Methyl-dl-tryptophan,β-(3-benzofuranyl)-dl-alanine (the oxygen analog of tryptophan),and β-[3-benzo (b) thienyl]-dl-alanine (the sulfur analog of tryptophan) are competitive inhibitors for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase[J].ArchBiochemBiophys,1991,291(2):326-333.
[54] SUGIMOTO H,ODA S,OTSUKI T,etal.Crystal structure of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase:catalytic mechanism of O2 incorporation by a heme-containing dioxygenase[J].ProcNatlAcadSciUSA,2006,103(8):2611-2616.
[55] BRASTIANOS HC,VOTTERO E,PATRICK BO,etal.Exiguamine A,an indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor isolated from the marine sponge Neopetrosia exigua[J].JAmChemSoc,2006,128(50):16046-16047.
[56] PEREIRA A,VOTTERO E,ROBERGE M,etal.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors from the northeastern Pacific marine hydroid Garveia annulata[J].JNatProdResour,2006,69(10):1496-1499.
[57] ANDERSEN RJ,PEREIRA A,HUANG XH,etal.Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitors,and their therapeutic use[P].WO 2006/005185,2006-01-19.
[58] GASPARI P,BANERJEE T,MALACHOWSKI WP,etal.Structure-activity study of brassinin derivatives as indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors[J].JMedChem,2006,49(2):684-692.
[59] KUMAR S,JALLER D,PATEL B,etal.Structure based development of phenylimidazole-derived inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase[J].JMedChem,2008,51(16):4968-4977.
[60] MAUTINO M R,JAIPURI FA,WALDO J,etal.NLG919,a novel indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-pathway inhibitor drug candidate for cancer therapy[J].CancerRes,2013,73(8):491.
[61] NAYAK A,HAO Z,SADEK R,etal. A Phase I study of NLG919 for adult patients with recurrent advanced solid tumors[J].JImmunotherCancer,2014,2(Suppl 3):250.
[62] KHLEIF S,MUNN D,NYAK-KAPOOR A,etal.First-in-human phase 1 study of the novel indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor NLG-919[J].JClinOncol,2014,32(15 Suppl):TPS3121.
[63] RÖHRIG UF,MAJJIGAPU SR,GROSDIDIER A,etal.Rational design of 4-aryl-1,2,3-triazoles for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 inhibition[J].JMedChem,2012,55(11):5270-5290.
[64] COMBS A,YUE E,SPARKS R,etal. 1,2,5-Oxadiazoles as inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase[P].WO 2010/005958,2010-06-24.
[65] LIU X,SHIN N,KOBLISH HK,etal.Selective inhibition of IDO1 effectively regulates mediators of antitumor immunity[J].Blood,2010,115(17):3520-3530.
[66] YUE EW,DOUTY B,WAYLAND B,etal. Discovery of potent competitive inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase with in vivo pharmacodynamic activity and efficacy in a mouse melanoma model[J].JMedChem,2009,52(23):7364-7367.
[67] KOBLISH HK,HANSBURY MJ,BOWMAN KJ,etal.Hydroxyamidine inhibitors of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase potently suppress systemic tryptophan catabolism and the growth of IDO-expressing tumors[J].MolCancerTher,2010,9(2):489-498.
[68] BALOG J,HUANG A,CHEN B,etal.IDO inhibitors[P].WO 2014/150646,2014-09-25.
[69] BALOG J,HUANG A,CHEN B,etal.Markwalder,J.Inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)[P].WO 2014/150677,2014-09-25.
[70] MARKWALDER J,SEITZ S,BALOG J,etal.IDO inhibitors[P].WO2015/ 002918,2015-01-08.
[71] MARKWALDER JA,SEITZ SP,BALOG JA,etal.IDO inhibitors[P].WO 2015/006520,2015.
[72] BANERJEE M,MIDDYA S,SHRIVASTAVA R,etal.Aminonitriles as kynurenine pathway inhibitors[P].WO 2014/141110,2014-09-18.
[73] BANERJEE M,MIDDYA S,SHRIVASTAVA R,etal.Inhibitors of the kynurenine pathway[P].WO 2014/186035,2014-11-20.
[74] 徐跃洋,吴俊军.吲哚胺-2,3-双加氧酶IDO1抑制剂研究进展[J].中国新药杂志,2016,25(4):425-432.
[75] YU D,TAO BB,YANG YY,etal.The IDO inhibitor coptisine ameliorates cognitive impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer′s disease[J].JAlzheimersDis,2015,43(1):291-302.
[76] YU CJ,ZHENG MF,KUANG CX,etal.Oren-gedoku-to and its constituents with therapeutic potential in Alzheimer′s disease inhibit indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity in vitro[J].JAlzheimersDis,2010,22(1):257-266.
[77] LI J,LI Y,YANG D,etal.Establishment of a human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 (hIDO2) bioassay system and discovery of tryptanthrin derivatives as potent hIDO2 inhibitors[J].EurJMedChem,2016,123:171-179.
[78] HUANG Q,ZHENG M,YANG S,etal.Structure-activity relationship and enzyme kinetic studies on 4-aryl-1H-1,2,3-triazoles as indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitors[J].EurJMedChem,2011,46(11):5680-5687.
[79] TAKIKAWA O,KUROIWA T,YAMAZAKI F,etal.Mechanism of interferon-gamma action.Characterization of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in cultured human cells induced by interferon-gamma and evaluation of the enzyme-mediated tryptophan degradation in its anticellular activity[J].JBiolChem,1988,263(4):2041-2048.
The study of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 and its inhibitors
ZHANG Sheng-nan, LIU Xin, YANG Qing△
(DepartmentofBiochemistry,SchoolofLifeSciences,FudanUniversity,Shanghai200438,China)
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) is an extrahepatic enzyme that catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the catabolism of the essential amino acid tryptophan (Trp) along the kynurenine pathway (KP).The overexpression or overactivation of IDO1 leads to the accumulation of downstream neurotoxic metabolite,quinolinic acid (QUIN),which is the main reason of nervous disorder and neurodegenerative disease.As an immunotolerant enzyme,IDO1 is regarded as a new immune checkpoint due to vital role in both the induction of maternal-fetal immune tolerance and tumor immune escape.Furthermore,the correlation between IDO1 and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer′s disease (AD),age-related cataracts and cancer has been confirmed,which brings IDO1 inhibitors increasingly widespread attention as promising drugs.This paper reviews the biological activity and development of IDO1 inhibitors.
indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; inhibitor; cancer immunotherapy
国家自然科学基金 (81373396,81573310);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金 (20130071110037);上海市科委生物医药重点课题 (12431900204) ;复旦大学遗传工程国家重点实验室开放课题
专家简介 杨青,复旦大学生命科学学院教授,博士生导师。上海市生化与分子生物学学会理事,上海市药学会生化药物专委会委员。先后主持国家自然基金、教育部博士点基金博导类项目、教育部留学回国人员基金、上海市浦江计划、上海市生物医药重点课题等研究课题。主要进行疾病发生的分子机制研究及相关药物的研发,2006年起从事吲哚胺2,3-双加氧化酶(IDO)抑制剂的研究工作。重点研究IDO代谢通路失调与疾病的关系,筛选发现IDO抑制剂及相应的信号传导网络;以及药物转运蛋白 (drug transporter) 在药物代谢中的功能及其表达、定位的调控机制。研究成果先后发表于国际知名期刊。拥有自主知识产权的新型IDO抑制剂的PCT专利,海外权利已成功转化给美国企业。
R730.3
B
10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2017.01.001
2016-08-10;编辑:张秀峰)
△Corresponding author E-mail:yangqing68@fudan.edu.cn
*This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81373396,81573310),the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education in China (20130071110037),the Key Medical Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (12431900204) and the Research Fund for the State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering,Fudan University.
