高浓度葡萄糖对人胃腺癌SGC-7901细胞增殖迁移和侵袭的影响*
2017-01-11张术恋杨梅松竹
张术恋,杨梅松竹,杨 瀚,白 霞,吴 丹
(吉首大学医学院,湖南吉首416000)
高浓度葡萄糖对人胃腺癌SGC-7901细胞增殖迁移和侵袭的影响*
张术恋,杨梅松竹△,杨 瀚,白 霞,吴 丹
(吉首大学医学院,湖南吉首416000)
目的探讨高浓度葡萄糖(高糖)对人胃腺癌SGC-7901细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响。方法体外培养人胃腺癌SGC-7901细胞,在不同浓度葡萄糖(5.5、11.0、22.0 mmol/L)培养基进行处理,采用四甲基偶氮唑蓝比色法(MTT)检测SGC-7901细胞的增殖率,采用划痕实验检测SGC-7901细胞的迁移指数(MI),采用Transwell实验检测SGC-7901细胞的侵袭力。结果24、48、72 h各时间点5.5、11.0、22.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组光密度值均有不同程度上升,22.0、11.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组明显高于5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),随葡萄糖浓度的增高和作用时间的延长,SGC-7901细胞增殖率逐渐增大。5.5、11.0、22.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组24 h MI分别为 0.394±0.058、0.510±0.044、0.615± 0.039,48 h MI分别为0.548±0.058、0.685±0.009、0.782±0.038;随葡萄糖浓度的增高和作用时间的延长,SGC-7901细胞MI逐渐增大,22.0、11.0mmol/L葡萄糖组明显高于5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。5.5、11.0、22.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组的穿膜细胞数量分别为(45±5)、(71±4)、(90±10)个,随葡萄糖浓度的增高,发生侵袭的SGC-7901细胞数量逐渐增多,22.0、11.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组明显高于5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论高糖环境可促进SGC-7901细胞增殖,提高细胞迁移、侵袭能力。
胃肿瘤; 比色法; 细胞增殖; 细胞运动; 肿瘤侵润; 葡萄糖; 培养基
胃癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,占恶性肿瘤总发病率的10%,死亡率的8%[1]。胃癌被认为是一种多因素疾病,其发生与多种病因有关。近年来,流行病学研究发现,2型糖尿病与肿瘤之间存在密切联系[2-3]。有相关研究显示,糖尿病或高浓度葡萄糖(高糖)对肿瘤的发生发展、治疗及预后等产生一定的影响[4],其中包括胃癌相关物质代谢、耐药性、患者生存率等方面的研究[5-7],但糖尿病或高糖与胃癌细胞生物学特性的研究甚少。本研究通过体外实验,探讨高糖对人胃腺癌SGC-7901细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响,为阐明高糖与胃癌发生发展的关系提供实验依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 细胞株 人胃腺癌SGC-7901细胞株购自中南大学湘雅中心实验室细胞库。
1.1.2 试剂 胎牛血清(浙江天杭生物科技有限公司),无糖型RPMI-1640培养基(Gibco公司),葡萄糖、甘露醇(石药银湖制药有限公司),青-链霉素溶液、胰酶细胞消化液[赛默飞世尔生物化学制品(北京)有限公司],四甲基偶氮唑蓝(MTT)(江苏碧云天生物科技有限公司),Transwell小室(康宁公司),matrigel基质胶(BD公司)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 实验分组及细胞培养 根据文献[8]应用5.5、11.0、22.0 mmol/L 3种葡萄糖浓度的培养基进行处理。其中5.5 mmol/L代表生理葡萄糖浓度,11.0、22.0 mmol/L代表高糖浓度。SGC-7901细胞使用含10%胎牛血清、葡萄糖浓度为5.5 mmol/L的RPMI-1640培养基于37℃、5% CO2的培养箱中,取对数生长期的细胞进行实验。
1.2.2 MTT实验检测 SGC-7901细胞增殖情况 将SGC-7901细胞消化后制成细胞悬液接种于96孔板,每孔细胞浓度为5×104mL-1,培养至细胞贴壁。每组设5个复孔,并设空白对照组。分别用不同因素处理,继续培养24~72 h。每孔加入20 μL MTT液,继续培养4 h。弃上清液,每孔加200μL二甲基亚砜,振荡10min,使结晶充分溶解。于酶标仪490nm波长测定光密度(OD)值,计算各组细胞的增殖率,细胞增殖率=(处理组/对照组-1)×100%。
1.2.3 划痕实验检测 SGC-7901细胞迁移能力 将SGC-7901细胞消化后制成细胞悬液接种于6孔板,每孔细胞浓度为1×106mL-1,每组设3个复孔。待细胞长满后,用10 μl Tip头在培养板底部划痕,磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)洗掉脱落细胞,测量划痕两侧的细胞间距,拍照并记为0 h。加入不同因素处理后继续培养,于24、48 h测量并拍照。计算迁移指数(MI),MI=1-各时间点划痕距离/0 h划痕距离。
1.2.4 Transwell实验检测SGC-7901细胞侵袭情况 将Matrigel胶稀释铺于Transwell板上层小室内,SGC-7901细胞消化后制成细胞悬液接种于上室内,每孔细胞浓度为1×105mL-1,培养至细胞贴壁。分别于下室中加入不同处理因素继续培养24 h,用棉签擦拭掉上室内的细胞,4%多聚甲醛固定,0.1%结晶紫染色15 min,PBS漂洗3次,倒置显微镜下观察,随机选取5个视野拍照并计数。
1.3 统计学处理 应用SPSS 19.0统计软件进行数据分析,计量资料以±s表示,采用重复测量方差分析或单因素方差分析,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 高糖对SGC-7901细胞增殖的影响 MTT实验结果显示,24、48、72 h各时间点5.5、11.0、22.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组的OD值均有不同程度上升,22.0、11.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组与5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖组比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。随着培养基葡萄糖浓度的增高和作用时间的延长,SGC-7901细胞增殖率逐渐增大。见表1、图1。
2.2 高糖对SGC-7901细胞迁移的影响 划痕实验结果显示,5.5、11.0、22.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组24 h平均MI分别为0.394±0.058、0.510±0.044、0.615±0.039,48 h分别为0.548±0.058、0.685±0.009、0.782±0.038。随着培养基中葡萄糖浓度的增高和作用时间的延长,SGC-7901细胞MI逐渐增大,22.0、11.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组与5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖组比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见图2、3。
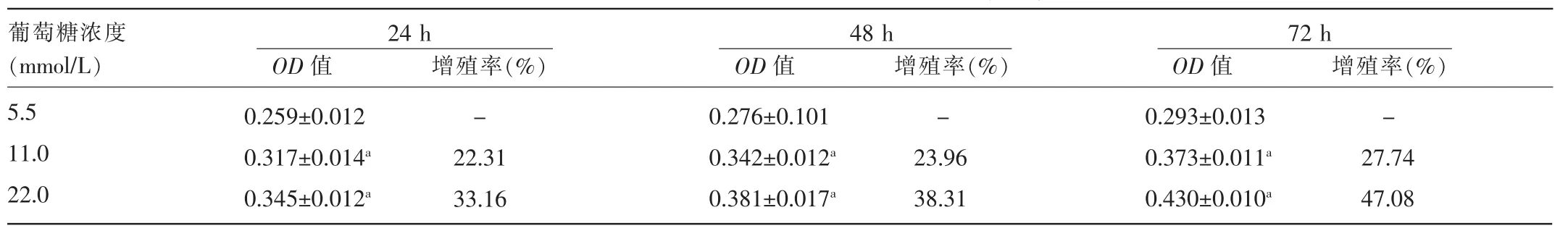
表1 高糖对SGC-7901细胞增殖的影响(n=3)
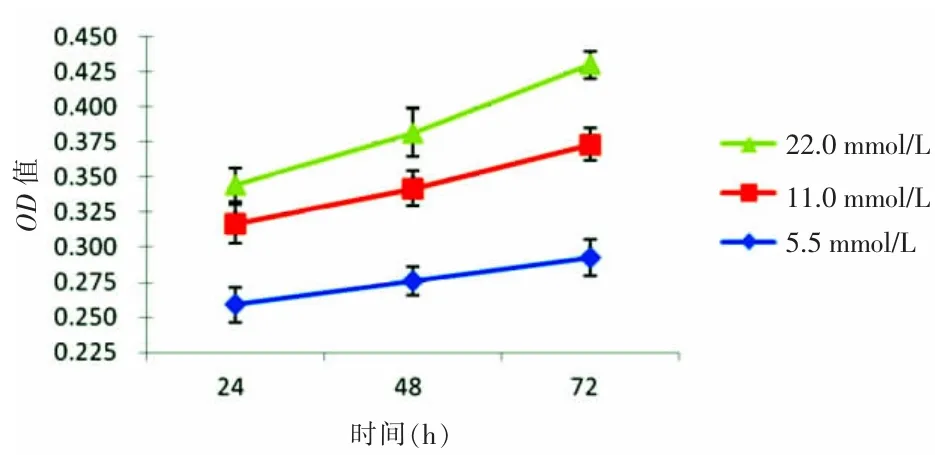
图1 高糖对SGC-7901细胞增殖的影响(n=3)

图2 高糖对SGC-7901细胞迁移的影响(n=3)
2.3 高糖对SGC-7901细胞侵袭的影响 Transwell实验结果显示,5.5、11.0、22.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组的平均穿膜细胞数量分别为(45±5)、(71±4)、(90±10)个,随着培养基中葡萄糖浓度的增高,发生侵袭的SGC-7901细胞数量显著增加,22.0、11.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组与5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖组比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见图4、5。

图3 高糖对SGC-7901细胞迁移的影响(n=3)
图4 高糖对SGC-7901细胞侵袭的影响(n=3)
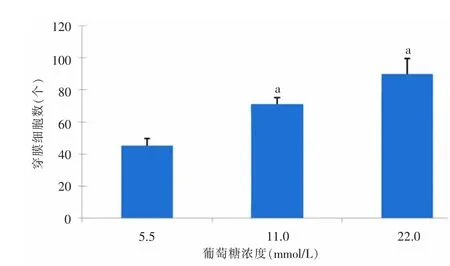
图5 高糖对SGC-7901细胞侵袭的影响(n=3)
3 讨 论
糖尿病已成为严重危害人类健康的全身性代谢疾病,其患病率呈逐年上升趋势[9]。流行病学调查表明,糖尿病或高糖可增加机体罹患结肠癌、直肠癌、前列腺癌、膀胱癌、子宫癌、乳腺癌等肿瘤的风险[10-11]。近年研究发现,2型糖尿病是胃癌的危险因素之一[12-13],糖尿病患者胃癌的发生率显著高于健康人群[14]。增殖、迁移、侵袭能力是肿瘤细胞的重要生物学特性,与肿瘤的发生发展和恶性进展密切相关。本研究检测高糖环境下人胃腺癌SGC-7901细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭等生物学特性的变化。
研究表明,高糖环境下,胃癌SGC-7901细胞的增殖能力明显增加,其机制可能是高糖通过增加胃癌细胞的热能产生,促进细胞新陈代谢[15]。高糖作用24、48、72 h均可促进乳腺癌MCF-7细胞增殖,作用72h时细胞增殖率明显高于对照组[16]。Zhao等[17]在高糖条件下胃癌对化疗耐药性的研究中发现,高糖条件可促进胃癌SGC-7901细胞增殖,并降低对化疗药物的敏感性。随着葡萄糖浓度的升高,5-氟尿嘧啶对胃癌SGC-7901细胞的增殖抑制率逐渐下降,尤其以高浓度组(9000mg/L)效果最明显[18]。本研究中,MTT实验显示,24、48、72 h各时间点22.0、11.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组的OD值均明显高于5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖组。随葡萄糖浓度从5.5 mmol/L升高至22.0 mmol/L,SGC-7901细胞24 h增殖率由22.31%上升至33.16%,48 h增殖率由23.96%上升至38.31%,72 h增殖率由27.74%上升至47.08%,表明高糖条件可促进SGC-7901细胞增殖,与上述文献报道相似。
恶性肿瘤的一个显著特征是具有迁移和侵袭能力。有研究发现,高糖通过上调水通道蛋白3的表达促进胃癌MGC-803、SGC-7901细胞迁移,从而调控胃癌恶性进展[19]。高糖能够通过上调人基质金属蛋白酶-9(MMP-9)和MMP-2的表达、下调上皮细胞钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)的表达,从而促进乳腺癌MDA-MB-435细胞的远处侵袭能力[20]。本研究应用划痕实验检测高糖环境下SGC-7901细胞的迁移情况,结果显示,随葡萄糖浓度从5.5 mmol/L升高至 22.0mmol/L,SGC-7901细胞24 h MI由0.394± 0.058上升至0.615±0.039,48 h MI由0.548±0.058上升至0.782±0.038,各时间点22.0、11.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组MI均明显高于5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖组,表明高糖条件可促进SGC-7901细胞迁移能力的提高。Transwell实验显示,24h时穿膜细胞数量由5.5mmol/L葡萄糖组的(45±5)个上升至22 mmol/L葡萄糖组的(90±10)个,22.0、11.0 mmol/L葡萄糖组的穿膜细胞数量明显高于5.5 mmol/L葡萄糖组,SGC-7901细胞侵袭能力随着葡萄糖浓度的增高而上升,高糖条件可促进SGC-7901细胞侵袭能力的提高。
综上所述,高糖环境可促进人胃腺癌SGC-7901细胞增殖,提高细胞迁移、侵袭能力,为说明高糖促进胃癌发生及进展提供了实验依据,但其作用机制有待进一步深入研究。
[1]Ferlay J,Shin HR,Bray F,et al.Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008:GLOBOCAN[J].Int J Cancer,2010,127(12):2893-2917.
[2]Azoulay L,Yin H,Filion KB,et al.The use of pioglitazone and the risk of bladder cancer in people with type 2 diabetes:nested case-control study[J]. BMJ,2012,344(5):827-829.
[3]Burnol AF,Morzyglod L,Popineau L.Cross-talk between insulin signaling and cell proliferation pathways[J].Ann Endocrinol(Paris),2013,74(2):74-78.
[4]Richardson LC,Pollack LA.Therapy insight:Influence of type 2 diabetes on the development,treatment and outcomes of cancer[J].Nat Clin Pract Oncol,2005,2(1):48-53.
[5]Zhou YC,Wang Y,Wang SL,et al.Hyperglycemia promotes human gastric carcinoma progression via aquaporin 3[J].Dig Dis Sci,2015,60(8):2338-2345.
[6]Zhao W,Chen R,Zhao M,et al.High glucose promotes gastric cancer chemoresistance in vivo and in vitro[J].Mol Med Rep,2015,12(1):843-850.
[7]Kawamura T,Kusakabe T,Sugino T,et al.Expression of glucose transporter-1 in human gastric carcinoma:association with tumor aggressiveness,metastasis,and patient survival[J].Cancer,2001,92(3):634-641.
[8]Hodgson WC,King RG.Effects of glucose,insulin or aldose reductase inhibition on responses to endothelin-1 of aortic rings from streptozotocininduced diabetic rats[J].Br J Pharmacol,1992,106(3):644-649.
[9]Zelenko Z,Gallagher EJ.Diabetes and cancer[J].Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am,2014,43(1):167-185.
[10]Yang X,So WY,Ma RC,et al.Diabetes and cancer:theme chanistic implications of epidemiological analysesfrom the Hong Kong diabetes registry[J].Diabetes Metab Res Rev,2012,28(5):379-387.
[11]Xu HL,Fang H,Xu WH,et al.Cancer incidence in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus:a population-based cohort study in Shanghai[J].BMC Cancer,2015,15(1):1-8.
[12]Sekikawa A,Fukui H,Maruo T,et al.Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of early gastric cancer development[J].Eur J Cancer,2014,50(12):2065-2071.
[13]Ikeda F,Kiyohara Y.Helicobacter pylori infection and hyperglyeemia/diabetes are associated with an increased risk of gastric cancer[J].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho,2015,42(5):529-533.
[14]Inoue M,Iwasaki M,Otani T,et al.Diabetes mellitus and the risk of caner:results from a large-seale population based cohort study in Japan[J].Arch Intern Med,2006,166(17):1871-1877.
[15]陈锐,王展,黄寿奖,等.高血糖环境对胃癌组织及胃癌细胞P-糖蛋白和拓扑异构酶2α表达的影响[J].浙江医学,2015,37(23):1887-1890,1894.
[16]孙启天,高宇,刘晓燕,等.高糖、高胰岛素及二甲双胍对人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞增殖的影响[J].承德医学院学报,2014,31(1):1-3.
[17]Zhao W,Chen R,Zhao M,et al.High glucose promotes gastric cancer chemoresistance in vivo and in vitro[J].Mol Med Rep,2015,12(1):843-850.
[18]张全武,刘芮菡,娄欣.高糖环境对胃癌组织、胃癌SGC7901细胞株P-糖蛋白表达及5-Fu敏感性的影响[J].山东医药,2016,56(24):20-22.
[19]Zhou YC,Wang Y,Wang SL,et al.Hyperglycemia promotes human gastric carcinoma progression via aquaporin 3[J].Dig Dis Sci,2015,60(8):2338-2345.
[20]李军涛,张恒伟,郭旭辉,等.高糖对人乳腺癌细胞体外侵袭能力的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2013,93(2):89-92.
Effects of high glucose on proliferation,migration and invasion of gastric gland carcinoma SGC-7901 cells*
Zhang Shulian,Yang Meisongzhu△,Yang Han,Bai Xia,Wu Dan
(Medical College of Jishou University,Jishou,Hunan 416000,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of high glucose on the proliferation,migration and invasion of gastric gland carcinoma SGC-7901 cells.MethodsSGC-7901 cells were cultured in vitro and treated by medium at different glucose concentrations of 5.5,11.0,22.0 mmol/L.MTT method was applied to detect the proliferation rate,the scratch test was performed to test the migrate index(MI),and the Transwell test was used to evaluate the invasiveness.ResultsThe optical density(OD)values were increased in each time point(24,48,72 h)and each glucose group(5.5,11.0,22.0 mmol/L).The OD values in 24,48,72 h in the 22.0,11.0 mmol/L glucose groups were obviously higher than those in the 5.5 mmol/L glucose group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).With the glucose concentration increase and action time prolongation,the SGC-7901 cell proliferation rate was increased gradually.The 24 h MI in the 5.5,11.0,22.0 mmol/L glucose groups were 0.394±0.058,0.510± 0.044 and 0.615±0.039 respectively,and the 48 h MI were 0.548±0.058,0.685±0.009 and 0.782±0.038 respectively.With the glucose concentration increase and action time prolongation,the SGC-7901 cell MI was increased gradually.The MI in the 22.0,11.0 mmol/Lglucose groups were obviously higher than those in the 5.5mmol/L glucose group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).The numbers of transmembrane cells in the 5.5,11.0 and 22.0 mmol/L glucose groups were 45±5,71±4 and 90±10 respectively.With the increase of glucose concentration,the invasive SGC-7901 cells number was increased gradually.The invasive cells number in the 22.0 and 11.0 mmol/L glucose groups were obviously higher than those in the 5.5 mmol/L group glu cose group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).ConclusionThe high glucose environment could promote the proliferation of SGC-7901 cells,and improve their migration and invasion abilities.
Stomach neoplasms; Colorimetry; Cell proliferation; Cell movement; Neoplasm invasiveness;Glucose; Culture media
10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2016.24.009
:A
:1009-5519(2016)24-3767-03
2016-10-28)
吉首大学2013年大学生研究性学习与创新性实验计划项目(JSU-CX-2013-29);吉首大学2013年度校级科研项目(13JDX009);2014年度湖南省卫生厅科研基金项目(C2014-14)。
张术恋(1993-),本科,主要从事临床医学工作。
△通讯作者,E-mail:yangmeisongzhu@163.com。
