SCORTEN评分对中毒性表皮坏死松解症和Stevens⁃Johnson综合征评估分析
2016-11-06王昱璐左亚刚刘洁刘跃华李丽孙秋宁晋红中
王昱璐 左亚刚 刘洁 刘跃华 李丽 孙秋宁 晋红中
100730 北京,中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院皮肤科
SCORTEN评分对中毒性表皮坏死松解症和Stevens⁃Johnson综合征评估分析
王昱璐 左亚刚 刘洁 刘跃华 李丽 孙秋宁 晋红中
100730 北京,中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院皮肤科
目的分析SCORTEN评分对中毒性表皮坏死松解症和Stevens⁃Johnson综合征患者预后评估的准确性。方法回顾性分析1992年4月至2014年3月期间在北京协和医院收治的中毒性表皮坏死松解症和Stevens⁃Johnson综合征39例,其中死亡病例13例,按照年龄分层1∶2匹配诊断明确好转出院26例。39例患者用SCORTEN评分系统评分,计算预期死亡数,比较39例各级分层的预期死亡数与实际死亡数,绘制受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线),评估SCORTEN评分的判断力。结果39例患者中,按SCORTEN评分系统评为1分15例,2分14例,3分6例,4分4例,总预期死亡6.808例,实际死亡13例。每个积分层预期死亡数与实际死亡数差异无统计学意义。SCORTEN评分系统的ROC曲线下面积=0.832 8,表明有较好的预测能力。结论SCORTEN评分系统可在早期对中毒性表皮坏死松解症和Stevens⁃Johnson综合征患者死亡率作出评估。
表皮坏死松解症,中毒性;药疹;Stevens⁃Johnson综合征;SCORTEN评分
Stevens⁃Johnson综合征(SJS)和中毒性表皮坏死松解症(toxic epidermal necrolysis,TEN)是一组药物过敏反应,可引起特征性的皮损、严重的黏膜和系统受累。临床表现为红斑、松弛性水疱及表皮松解、Nikolsky征阳性、黏膜也有坏死剥脱。受累皮肤的体表面积(body surface area,BSA)<10%体表面积为SJS,>30%为TEN,介于两者之间的为SJS/TEN重叠征。SJS死亡率为5%,SJS/TEN重叠征为10%~15%,TEN 为 30%~40%[1]。SCORTEN(score of toxic epidermal necrolysis)评分量表是对TEN/SJS严重程度的特异性评分[2]。通过记录入院24 h内的7个临床指标,预测患者的死亡率。SCORTE评分量表简单易用,适用于所有TEN患者,已被应用于预测TEN和SJS患者的死亡率。但有报道[3]证实,在某些验证SCORTEN评分的研究中存在方法学错误,亦有研究[4]认为,SCORTEN评分过高预测了死亡率。还有研究报道证实,该评分量表的准确性可能会受到人口分布概况和研究人群特点的影响[1],尚需对其准确性做进一步验证。为探讨此评分表在国内患者应用的准确性,我们回顾性分析了39例TEN/SJS患者的临床资料。
一、对象和方法
1.对象:1992年4月至2014年3月,在北京协和医院收治的诊断明确的TEN/SJS患者39例。其中死亡13例(11例TEN,2例SJS),按照年龄分层1∶2匹配诊断明确的TEN/SJS好转出院病例26例(24例TEN,1例SJS/TEN重叠,1例SJS)。诊断依据临床表现和 Bastuji⁃Garin[5]提出的分类诊断标准。年龄(41.77±18.3)岁(2~80岁),13例死亡病例的死亡原因:感染性休克9例,肺部感染6例,电解质失衡1例,慢性肾衰2例,呼吸衰竭7例,急性心梗1例,急性肾衰4例,败血症2例,气胸1例,皮肤感染2例,消化道出血1例,循环衰竭4例。
2.SCORTEN评分:记录入院24 h内7个临床指标(年龄>40岁,并发恶性肿瘤,心率>120次,血糖>14 mmol/L,碳酸氢盐<20 mmol/L,表皮剥脱>10%体表面积,血尿素氮>10 mmol/L),每项1分,无上述临床指标记为0。采用Bastuji⁃Garin等[2]研究预测死亡率:符合0~7个指标患者死亡可能性分别为0.012、0.039、0.122、0.324、0.622、0.85、0.951和0.985。计算患者SCORTEN评分和预期死亡率,比较预期死亡数与实际死亡例数。
3.统计学方法:各评分间预期死亡数与实际死亡数的比较采用Fisher精确检验,检验水准为0.05。SCORTEN评分的准确性通过受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)评估,曲线下面积(area under curve,AUG)越接近于1,说明诊断效果越好。AUC在0.5~0.7时有较低准确性,0.7~0.9时有一定准确性,>0.9时有较高准确性,AUC=0.5时,无诊断价值。
二、结果
1.SCORTEN评分结果和死亡数比较:39例患者中,按SCORTEN评分系统评为1分15例,2分14例,3分6例,4分4例,总预期死亡6.808例,实际死亡13例。各评分预期死亡数与实际死亡数差异无统计学意义(表1)。
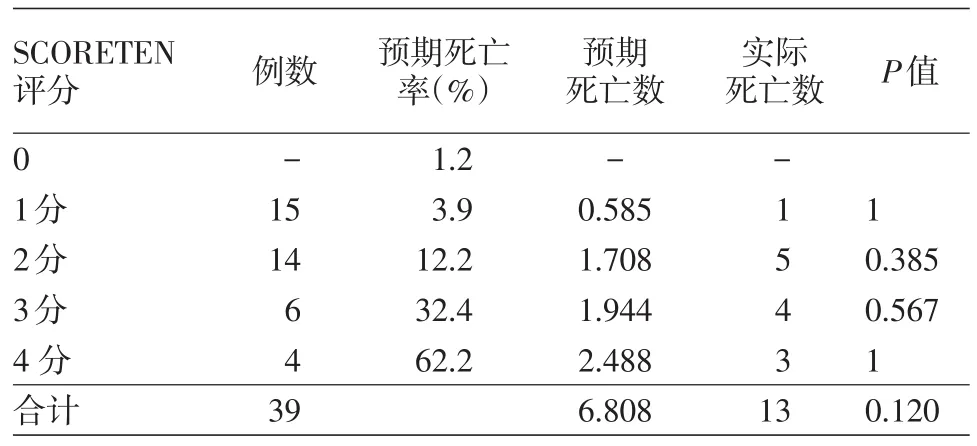
表1 39例中毒性表皮坏死松解症和Stevens⁃Johnson综合征患者SCORTEN评分结果和死亡数比较
2.ROC曲线:根据SCORTEN评分结果绘制ROC曲线(图1)。AUC=0.832 8,标准误0.0912,95%置信区间为0.65~1.00,置信区间不包含0.5,按α=0.05水平,可以认为SCORTEN评分对SJS和TEN具有判断力。0.7<AUC=0.832 8<0.9,可认为价值中等。
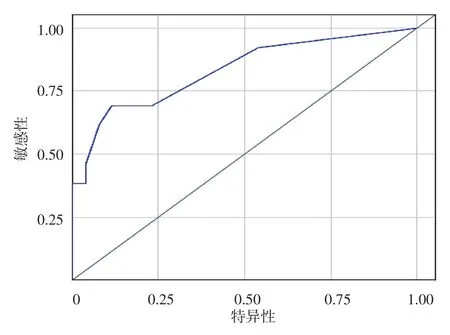
图1 ROC曲线评估SCORTEN评分系统判断中毒性表皮坏死松解症和Stevens⁃Johnson综合征患者死亡率的敏感性和特异性。0.7<AUC=0.832 8<0.9,价值中等
三、讨论
本研究对39例TEN/SJS患者进行SCORTEN评分,ROC分析SCORTEN评分系统的评估准确性,发现AUC为0.832 8,表明SCORTEN评分系统总体来说具有较好的预测能力,与文献结果一致[1,6⁃10],可在早期即对患者严重程度作出评估。Guégan等[11]发现,在入院前5天SCORTEN评分的价值较高,尤其是第3天,其预测价值最高。Cartotto等[3]和Bansal等[1]也得出了相似的结论。Ho等[12]发现,SCORTEN评分系统具有很好的判断力,在患者入院第1天价值最高。George等[13]对145例TEN患者进行评分,发现SCORTEN评分的准确性高于 APACHE Ⅱ(acute physiology and chronic health evaluation)评分,但低于ICNARC(intensive care national audit and research center)评分。有作者[1]提出,应加入新指标去预测死亡率,其中包括皮肤、血、尿培养阳性,呼吸系统受累,高钠血症,BSA>30%和住院天数。杨永生等[10]研究了60例TEN/SJS患者,发现SCORTEN评分系统对TEN/SJS病情预测评估有判断力。总之,SCORTEN评分系统的评价时机尚待进一步完善,是否需要新附加因素需进一步研究。
[1]Bansal S,Garg VK,Sardana K,et al.A clinicotherapeutic analysis of Stevens⁃Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis with an emphasis on the predictive value and accuracy of score of toxic epidermal necrolysis[J].Int J Dermatol,2015,54(1):e18 ⁃26.DOI:10.1111/ijd.12466.
[2]Bastuji⁃Garin S,Fouchard N,Bertocchi M,et al.SCORTEN:a severity⁃of⁃illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis[J].J Invest Dermatol,2000,115(2):149 ⁃153.DOI:10.1046/j.1523 ⁃1747.2000.00061.x.
[3]Cartotto R,Mayich M,Nickerson D,et al.SCORTEN accurately predicts mortality among toxic epidermal necrolysis patients treated in a burn center[J].J Burn Care Res,2008,29(1):141⁃146.DOI:10.1097/BCR.0b013e31815f3865.
[4]Imahara SD,Holmes JH,Heimbach DM,et al.SCORTEN overestimates mortality in the setting of a standardized treatment protocol[J].J Burn Care Res,2006,27(3):270 ⁃275.DOI:10.1097/01.BCR.0000216532.71360.9B.
[5]Bastuji⁃Garin S,Rzany B,Stern RS,et al.Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis,Stevens⁃Johnson syndrome,and erythema multiforme[J].Arch Dermatol,1993,129(1):92⁃96.
[6]Sekula P,Liss Y,Davidovici B,et al.Evaluation of SCORTEN on a cohort of patients with Stevens⁃Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis included in the RegiSCAR study[J].J Burn CareRes,2011,32(2):237 ⁃245.DOI:10.1097/BCR.0b013e31820aafbc.
[7]Vaishampayan SS,Das AL,Verma R.SCORTEN:does it need modification?[J].Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol,2008,74(1):35⁃37.
[8]Trent JT,Kirsner RS,Romanelli P,et al.Use of SCORTEN to accurately predict mortality in patients with toxic epidermal necrolysis in the United States[J].Arch Dermatol,2004,140(7):890⁃892.DOI:10.1001/archderm.140.7.890.
[9]MoralesME,Purdue GF,Verity SM,etal.Ophthalmic manifestations of Stevens⁃Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis and relation to SCORTEN[J].Am J Ophthalmol,2010,150(4):505⁃510.e1.DOI:10.1016/j.ajo.2010.04.026.
[10]杨永生,徐金华,朱小华,等.SCORTEN评分系统评估重症大疱性药疹的可行性分析[J].临床皮肤科杂志,2011,40(1):19⁃20.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000⁃4963.2011.01.008.Yang YS,Xu JH,Zhu XH,et al.Performance of the SCORTEN on patients with severe bullous drug eruption[J].J Clin Dermatol,2011,40(1):19⁃20.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000⁃4963.2011.01.008.
[11]Guégan S,Bastuji⁃Garin S,Poszepczynska⁃Guigné E,et al.Performance of the SCORTEN during the first five days of hospitalization to predict the prognosis of epidermal necrolysis[J].J Invest Dermatol,2006,126(2):272⁃276.DOI:10.1038/sj.jid.5700068.
[12]Ho YL,Chang YT,Chu YT,et al.Performance of the SCORTEN in Taiwanese patients with Stevens⁃Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis[J].Dermatologica Sinica,2010,28(1):15⁃20.DOI:10.1016/S1027⁃8117(10)60002⁃x.
[13]George SM,Harrison DA,Welch CA,et al.Dermatological conditions in intensive care:a secondary analysis of the Intensive Care National Audit and Research Centre(ICNARC)case mix programme database[J].Crit Care,2008,12 Suppl 1:S1.DOI:10.1186/cc6141.
Prognostic accuracy of the SCORTEN scoring system in patients with toxic epidermal necrolysis or Stevens⁃Johnson syndrome
Wang Yulu,Zuo Yagang,Liu Jie,Liu Yuehua,Li Li,Sun Qiuning,Jin Hongzhong
Department of Dermatology,Peking Union Medical College Hospital,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College,Beijing 100730,China
ObjectiveToevaluatetheprognosticaccuracyofthescoreoftoxicepidermalnecrolysis(SCORTEN)scoring system in patients with toxic epidermal necrolysis(TEN)or Stevens⁃Johnson syndrome(SJS).Methods Clinical data were collected from 39 patients with SJS/TEN hospitalized in Peking Union Medical College Hospital during April 1992 and March 2014,and retrospectively analyzed.Among the 39 patients,13 had died,and the other 26 patients,who were matched to the dead patients in a ratio of 2∶1 for age,all had a definite diagnosis and were discharged with improved conditions.The SCORTEN scoring system was used to evaluate the 39 patients with SJS/TEN and calculate expected mortality.The expected mortality and actual mortality were compared between different groups stratified by age in the 39 patients.The receiver operating characteristic(ROC)curve was drawn to assess the prognostic accuracy of the SCORTEN scoring system.ResultsAccording to the SCORTEN scoring system,15 out of the 39 patients scored 1 point,14 scored 2 points,6 scored 3 points,and 4 scored 4 points.The total number of expected deaths was 6.808,while that of actual deaths was 13.There was no significant difference between the expected mortality and actual mortality in every SCORTEN score⁃based group.The area under curve(AUC)was 0.832 8,indicating a good predictive ability of the SCORTEN scoring system.ConclusionThe SCORTEN scoring system can predict mortality in TEN/SJS patients at early stage.
Epidermal necrolysis,toxic;Drug eruptions;Stevens⁃Johnson syndrome;SCORTEN
Zuo Yagang,Email:zuoyagang@263.net
2015⁃11⁃10)
(本文编辑:颜艳)
左亚刚,Email:zuoyagang@263.net
10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412⁃4030.2016.09.011
国家自然科学基金(81071301);北京市自然科学基金(7132203)
Fund programs:National Natural Science Foundation of China(81071301);Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation(7132203)
