有限元法在纳米光子学中的应用研究
2016-10-28孙东慧李坤朱兰孔岩陈志科
孙东慧,李坤,朱兰,孔岩,陈志科
(电子科技大学,四川 成都 611731)
有限元法在纳米光子学中的应用研究
孙东慧,李坤,朱兰,孔岩,陈志科
(电子科技大学,四川 成都 611731)
寻求快速且高效求解偏微分方程的方法对科学未来的发展起来很大的作用。而作为新兴起来的纳米光子学,从被提出就一直广受关注。怎么去求解涉及纳米光子学的模型,也一直备受关注。本文主要研究是用有限元求解纳米光子学中的德鲁德模型,用数值实验进行模拟,求解散射体在纳米级的现象。
有限元;纳米光子学;德鲁德模型
To find a fast and efficient method to solve partial differential equations has a great effect on the development of Science in the future.As a burgeoning nano photonics,was put forward has been widely concerned.How to solve the nano photonics model,has attracted much attention.This paper is using the finite element method to solve Drude model in nano photonics,Numerical experiments are used to simulate,Finding the phenomenon of dissolution of the emitter at the nanometer level.
1 引言
纳米光子学,被定义为纳米技术和光子学的融合学科,是一个新兴的前沿学科。它为基础研究提供了挑战,也为新技术提供了机遇。纳米光子学在市场上已经取得了一定的影响。它是一个多学科交叉的研究领域,为物理学,化学,应用科学,工程学和生物学,以及生物医学技术创造了机遇。
纳米光子学(Nanophotonics)研究光在纳米范畴内的行为。它是处理光或光和粒子,物质相互作用光工程的一个亚波长分支。作为纳米光学的重要部分,等离子体探索了电磁学在小于波长的维度上的定义。纳米光学领域的技术包括近场(near-field)扫描光学显微镜,光助隧道扫描显微镜和表面等离激元(Plasmon)光学。纳米光学有二方面的研究:第一,在纳米范围研究光的性质;第二,为工程应用提高能量效率。
在等离子领域,亚波长的金属被用来散射光,模拟非局部等离子性质已经成为了一项标准,甚至对于复杂的几何体,这些都归功于先进的数值方法和专用的软件技术。
有限元法(finite element method)是一种高效能、常用的数值计算方法。科学计算领域,常常需要求解各类微分方程,而许多微分方程的解析解一般很难得到,使用有限元法将微分方程离散化后,可以编制程序,使用计算机辅助求解。有限元法在早期是以变分原理为基础发展起来的,所以它广泛地应用于以拉普拉斯方程和泊松方程所描述的各类物理场中(这类场与泛函的极值问题有着紧密的联系)。自从1969年以来,某些学者在流体力学中应用加权余数法中的迦辽金法(Galerkin)或最小二乘法等同样获得了有限元方程,因而有限元法可应用于以任何微分方程所描述的各类物理场中,而不再要求这类物理场和泛函的极值问题有所联系。
电传导的德鲁德模型在1900年由保罗·德鲁德提出,以解释电子在物质(特别是金属)中的输运性质。这个模型是分子运动论的一个应用,假设了电子在固体中的微观表现可以用经典的方法处理,很像一个钉球机,其中电子不断在较重的、相对固定的正离子之间来回反弹。用德鲁德模型可以计算超导材料石墨烯的介电常数和电导率以及计算均匀外磁场中的交流电导率等。所以对德鲁德模型的研究有很大的现实意义。
2 德鲁德模型
2.1局部问题德鲁德模型公式
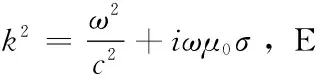
方程第二个式子为一阶吸收边界条件。
对方程进行弱变分,设电场所在的空间为the sobolev space
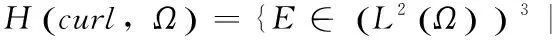
设测试函数Φ∈v=H(curl,Ω)
5)适时冬剪。及时收听天气预报,根据气候变化适当调整冬剪时间,建议在12月下旬至次年1月上中旬修剪;结果母枝选留时切忌选用徒长枝、基部直径大于1.5 cm的发育不充分枝;可适当增加15%~20%的留枝量,避免由于部分枝蔓芽体受冻,影响萌芽率和花芽分化质量。
方程(1)式乘以试探函数得

(3)
利用矢量第一格林公式,(3)式变为
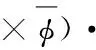
(4)
进一步化简:

(5)
再利用(6)式
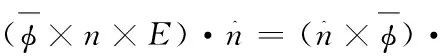
则有:
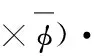
(7)
2.2离散
对公式(7)进行离散:
根据有限元理论,在每个剖分小区域上Ee,φe∈ve=H(curl,Ω)
(8)
将(7)式化为直角坐标形式
(9)
将(8)式代入(9)式则有:
整理成矩阵形式得:
其中i,j=1,2,3…N
3 数值实验
这一部分,我们即将呈现一些关于德鲁德模型的数值结果,有限元方法的数值实验已经用MATLAB代码实现出来。
3.1真空中平面波的传播
我们首先考虑关于平面波在真空中传播的模型,选择的区域为圆域,一阶吸收边界条件强加在边界上面,参数ε1=ε2=1:网格剖分呈现在图(1)。
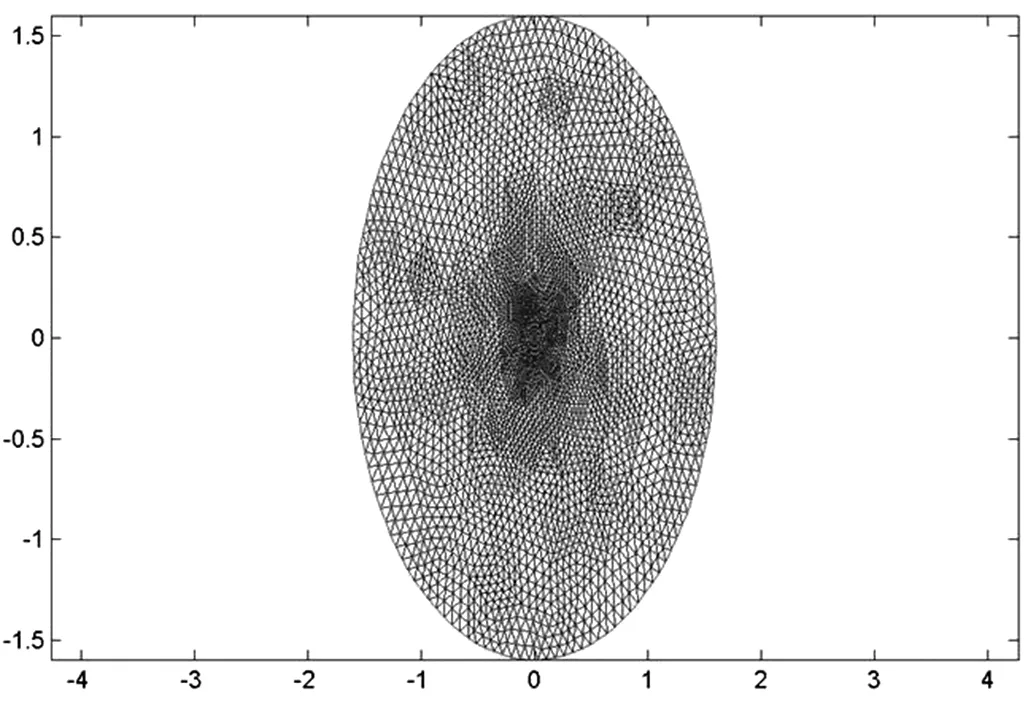
图(1)
数值结果:
接下来分别展示两个区域都为真空状态电场虚部分布图如图(2),电场实部分布图如图(3),电场分布图如图(4)
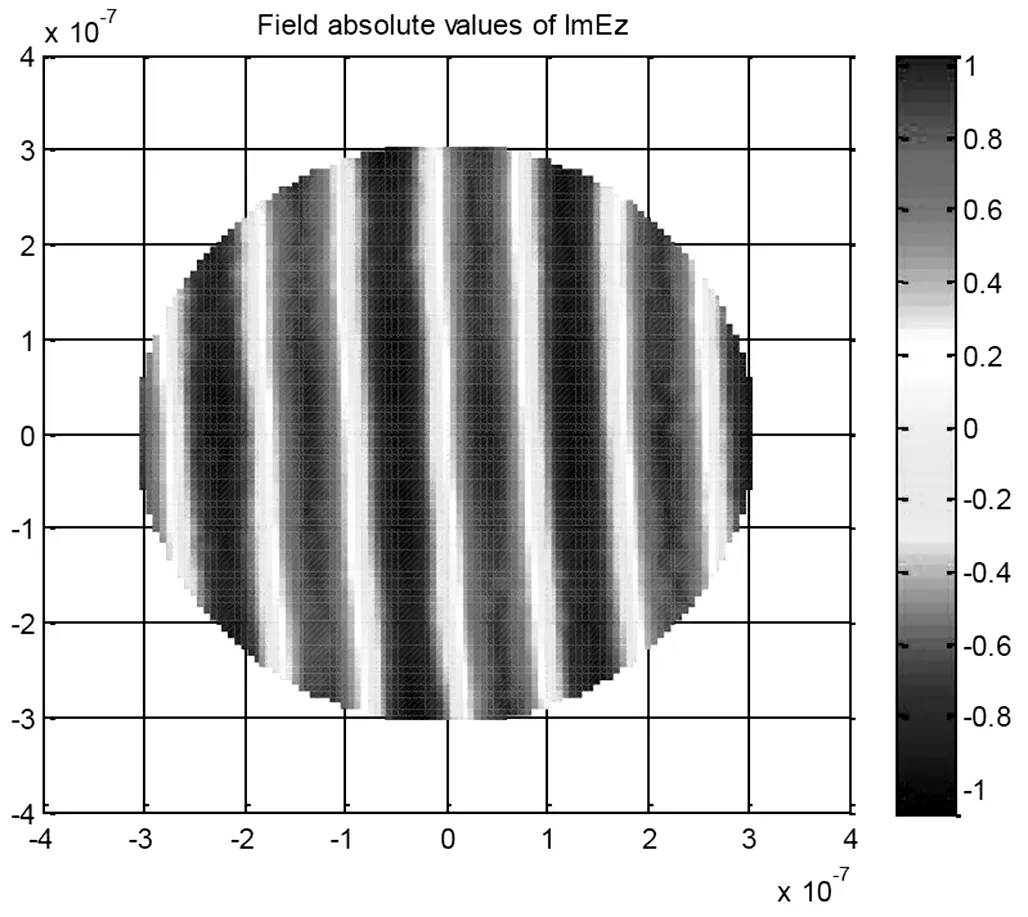
图(2)

图(3)

图(4)
3.2平面波的散射问题
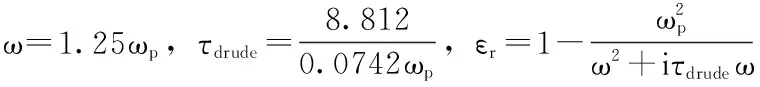
数值结果:
接下来我们展示的是在里面区域是散射体的情况下,磁场与电场的分布情况。
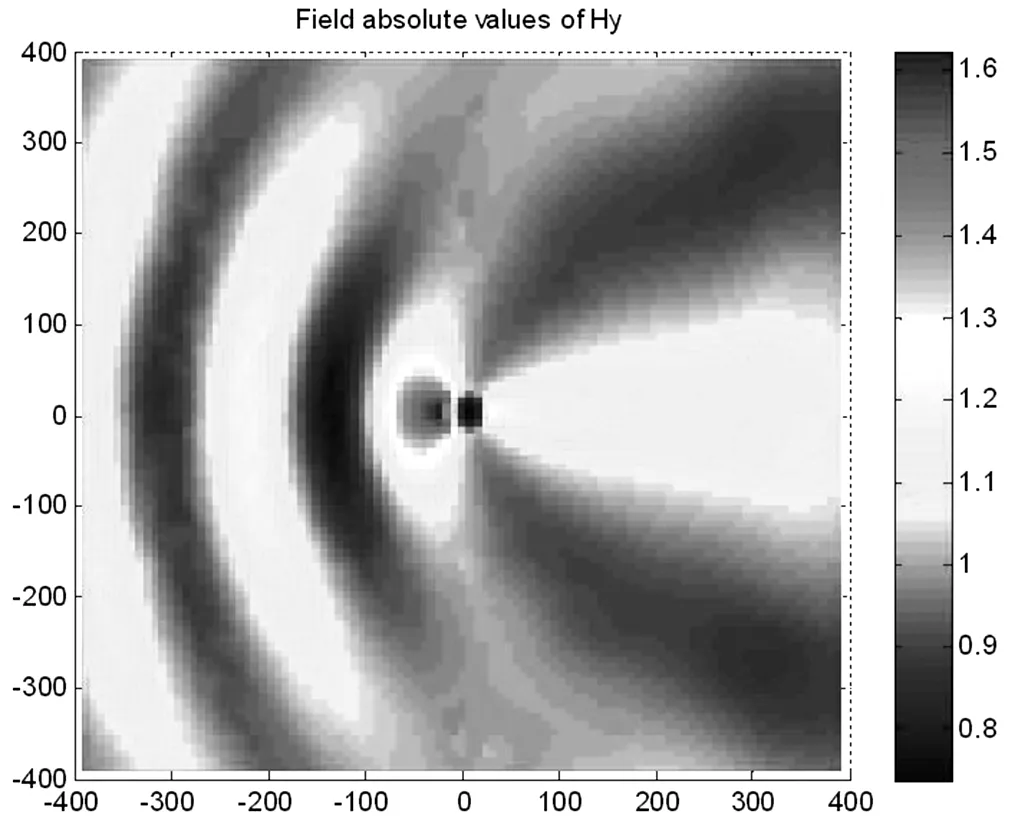
图(5)

图(6)

图(7)
4 结论
在这篇论文中,我们用有限元方法求解纳米光子学的德鲁德模型,并用数值实验验证了平面波在真空中的传播及平面波的散射问题。在不久的将来,我们将利用HDG与FEM耦合的方法求解上述问题。
[1]B.Cockburn, J. Gopalakrishnan, R. Lazarov, Unified hybridization of discon- tinuous Galerkin, mixed, and continuous Galerkin methods for second order elli- ptic problems, SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47 (2) (2009) 1319-1365.
[2]L. Li, S. Lanteri, R. Perrussel, Numerical investigation of a high order hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method for 2d time-harmonic Maxwell’s equations, Compel 2 (3) (2013) 1112-1138.
[3]N. Nguyen, J. Peraire, B. Cockburn, Hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin methods for the time-harmonic Maxwell’s equations, J. Comput. Phys. 230 (19) (2011) 7151-7175.
[4]L.Li, S. Lanteri, R. Perrussel, A Hybridizable Discontinuous Galerkin Method for Solving 3D Time-Harmonic Maxwell’s Equations,numerical mathematics and advanced applications http://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-642-33134-3
[5]L. Li, S. Lanteri, R. Perrussel, A hybridizable discontinuous Galerkin method combined to a Schwarz algorithm for the solution of 3d time-harmonic Maxwell’s equation, Journal of Computational Physics, 256 (2014) 563-581
[6]V. Dolean, S. Lanteri, R. Perrussel, Optimized Schwarz algorithms for solving time-harmonic Maxwell’s equations discretized by a discontinuous Galerkin method, IEEE Trans. Magn. 44 (6) (2008) 954-957.
[7]朱凌雪.高波数Helmholtz方程的连续内罚有限元方法和内罚间断Galerkin方法:[硕士学位论文]. 南京大学,2013-05.
[8]陆金甫,关治. 偏微分方程数值解法(第二版). 清华大学出版社,2004-01.
[9]Reed, W. H. & T. R. Hill. Triangular mesh methods for the neutron transport equation[R]. Los Alamos: Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory,1973.
[10]Houston, I.Perugia, A. Schneebeli & D. Schotzau. Interior penalty method for the indefinite time-harmonic Maxwell equations[J]. Numer. Math., (2005), 100(3): 485-518.
[11]Perugia, D.Schotzau & P. Monk. Stabilized interior penalty methods for the time-harmonic Maxwell equations[J]. Comput. Methods Appl. Meeh. Engrg., (2002), 191(41): 4675-4697.
[12]Perugia, D.Schotzau. The -Local discontinuous Galerkin method for low-frequeney time-harmonic Maxwell equations[J]. Math. Comp., (2002), 72(243): 1179-1214.
[13]S. Raza, S. I. Bozhevolnyi, M. Wubs and A. N. Mortensen, Nonlocal optical response in metallic nanostructures. J. Physics: Condensed Matter, 2015, 27, doi:10.1088/0953-8984/27/18/183204.
[14]K. R. Hiremath, L. Zschiedrich and F. Schmidt, Numerical solution of nonlocal hydrodynamic Drude model for arbitrary shaped nano-plasmonic structures using Ne’de’lec finite elements. J. Comput. Phys., 2012, 31: 5890-5896
[15]K. Busch, M. König, and J. Niegemann, Discontinuous Galerkin methods in nanophotonics. Laser Photonics Rev., 2011, 5(6): 773-809.
[16]D. N. Arnold, F. Brezzi, B. Cockburn, L. D. Marini, Unified analysis of discontinuous Galerkin methods for elliptic problems, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 2002, 39 (5):1749-1779.
[17]Bernardo Cockburn,Clint Dawson, Approximation of the velocity by coupling discontinuous Galerkin and mixed finite element methods for flow problems,Computational Geosciences 6:505-522,202.
[18]Ilaria Perugia,Dominik Schotzau, On the Coupling of Local Discontinuous Galerkin and Conforming Finite Element Methods, Journal of Scientific Computing, Vol.16,No.4,December 2001 (2002).
[19]P. Castillo, B. Cockburn, I. Perugia and D. Schötzau, An a priori error estimate of the local discontinuous Galerkin method for elliptic problems, SIAM J. Numer. Anal., to appear.
[20]I. Perugia and D. Schötzau, The coupling of local discontinuous Galerkin and conforming finite element methods, J. Sci. Comput., to appear.
[21]F. Brezzi, J. Douglas, Jr. and L.D. Marini, Two families of mixed elements for second order elliptic problems, Numer. Math. 88 (1985) 217-235.
[22]F. Brezzi and M. Fortin, Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods (Springer, Berlin,1991).
[23]P. Alotto, A. Bertoni, I. Perugia and D. Schotzau, Discontinuous finite element methods for the simu-lation of rotating electrical machines, COMPEL 20 (2001) 448-462.
[24]C. Dawson and J. Proft, Coupling of continuous and discontinuous Galerkin methods for transport problems, Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering, submitted.
[25]P. Alotto and A. Bertoni, Discontinuous finite element methods for the simulation of rotating electrical machines, COMPEL - The international journal for computation and mathematics in electrical and electronic engineering,Vol. 20 Iss 2 pp.448-462.
[26]B. Cockburn, C.W. Shu, The local discontinuous Galerkin method for time dependent convection-diffusion systems, SIAMJ.Numer. Anal. 35 (1998) 2440-2463.
[27]F. Bassi, S. Rebay, A high-order accurate discontinuous finite element method for the numerical solution of the compressible Navier-Stokes equations, J. Comput. Phys. 131 (1997) 267-279.
[28]B. Cockburn, C. Dawson, Some extensions of the local discontinuous Galerkin method for convection-diffusion equations in multidimensions, in: J.R. Whiteman (Ed.), The Proceedings of the Conference on the Mathematics of Finite Elements and Applications: MAFELAP X, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2000, pp. 225-238.
国家自然基金(数学);G0501100111301057
孙东慧(1991-),女,汉族,河南新乡人,硕士研究生,电子科技大学数学科学学院,研究方向:有限元。
TB115
A
1671-1602(2016)18-0024-04
