子宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗效果及远处转移的影响因素研究
2016-10-13程英祝叶晖王爱敏春芽
程英祝 叶晖 王爱敏 春芽
·论著·
子宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗效果及远处转移的影响因素研究
程英祝叶晖王爱敏春芽
目的探讨子宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗的疗效及远处转移的影响因素。方法抽取2007年10月至2010年10月子宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者139例(Ⅱb期~Ⅳa期)进行回顾性分析,通过翻阅病例和电话随访的方法,观察总生存率、远处转移的生存率、无转移的生存率;单因素分析远处转移的影响因素;多因素分析远处转移的影响因素。结果139例患者中,出现复发46例,其中局部复发16例,远处转移23例,局部复发并发远处转移7例。复发患者存活5例,死亡41例;未复发患者存活83例,死亡10例。宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者总生存率为63.30%,远处转移生存率3.57%,5年无转移生存率89.24%。单因素分析结果显示, FIGO临床分期、治疗后SCC-Ag水平、治疗前Hb水平、盆腔淋巴结转移是影响宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者远处转移的影响因素,差异有统计学意义(χ2=9.371、11.245、6.747、5.110,P=0.002、0.000、0.009、0.024)。多因素分析结果显示, FIGO临床分期、治疗后SCC-Ag水平、盆腔淋巴结转移是影响宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者远处转移的独立影响因素,差异有统计学意义(χ2=2.412、4.536、3.553,P=0.011、0.004、0.008)。结论子宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗的疗效较好,总生存率较高,值得进一步推广;FIGO临床分期、治疗后SCC-Ag水平、盆腔淋巴结转移是影响宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者远处转移的独立影响因素。
子宫鳞癌;放化疗;远处转移;影响因子
宫颈癌对于女性的危害性可谓众人皆知,其中鳞状细胞癌在宫颈恶性肿瘤中的比重最大,以致宫颈鳞癌成为女性生命的典型杀手[1,2]。近年来,随着医疗水平的逐步提高,对于宫颈鳞癌的诊断和治疗手段也越来越先进,该病的病死率也在随之下降[3]。手术疗法和放化疗的结合运用对于该病的疗效颇为显著[4],但是对于中晚期的患者而言,仍然存在很多待解决的问题,例如合理放化疗方案的选择、癌症复发和转移的预防等方面[5-7],都有待我们进一步研究。本次研究进一步探讨子宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗的疗效及远处转移的影响因素,报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料抽取2007年10月至2010年10月宝鸡市中医医院妇科子宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者139例进行回顾性分析,年龄32~70岁,平均年龄(44.14±12.83)岁。139例子宫颈鳞癌中晚期患者中,Ⅱb期65例,Ⅲa期7例,Ⅲb期62例,Ⅳa期5例;肿瘤直径>4 cm的66例,肿瘤直径≤4 cm的73例;盆腔淋巴结转移者42例,未出现转移者97例;治疗前,Hb≤110 g/L者48例,Hb>110 g/L者91例;治疗前,SCC-Ag>1.5 μg/L者108例,SCC-Ag≤1.5 μg/L者31例;治疗后,SCC-Ag>1.5 μg/L者40例,SCC-Ag≤1.5 μg/L者99例。
1.2纳入标准(1)病理活检确诊为子宫颈鳞癌患者;(2)根据2009年妇产科联盟FIGO的分期标准[8],所有患者均为Ⅱb~Ⅳa期宫颈癌患者;(3)治疗方案为基础治疗+同步放化疗;(4)知情同意并且愿意签署知情同意书者。
1.3方法
1.3.1治疗方法:所有患者均采用放疗和化疗相结合的方式进行,放疗分为体外放疗和腔内放疗两种。①化疗方案:顺铂30 mg/m2,每周1次,共5次。②放疗:X线盆腔前后对穿野照射,总剂量为45 Gy,分25次进行;当剂量达到30 Gy时,交替进行192Ir后装腔内放疗,每周1次,分6次进行,单次剂量为6 Gy/次。
1.3.2观察方法:主要采用随访和病例查阅的方法对以下资料进行搜集,随访时间为治疗结束后1个月,之后每3个月进行随访,截止时间为患者死亡或者2015年12月30日,平均随访时间(86.35±12.51)个月。观察指标:①观察总生存率、远处转移的生存率、无转移的生存率;②分析单因素分析远处转移的影响因素;③分析多因素分析远处转移的影响因素。

2 结果
2.1宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者生存率139例患者中,出现复发46例,局部复发16例,远处转移23例,局部复发并发远处转移7例。复发患者存活5例,死亡41例;未复发患者存活83例,死亡10例。宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者总生存率63.30%,远处转移生存率3.57%,5年无转移生存率89.24%。见图1。
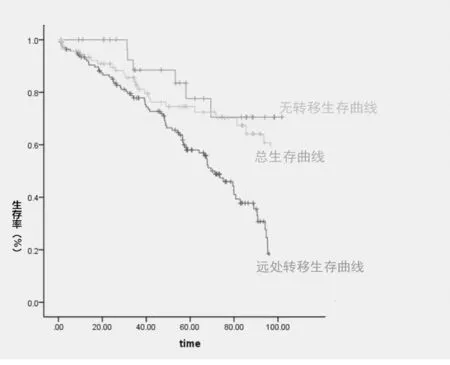
图1 不同类型同步放化疗患者生存曲线
2.2单因素分析远处转移的影响因素FIGO临床分期、治疗后SCC-Ag水平、治疗前Hb水平、盆腔淋巴结转移是影响宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者远处转移的影响因素,差异有统计学意义(χ2=9.371、11.245、6.747、5.110,P=0.002、0.000、0.009、0.024)。见表1。

表1 单因素分析远处转移的影响因素
注:SCC-Ag:鳞状细胞癌抗原
2.3多因素分析远处转移的影响因素FIGO临床分期、治疗后SCC-Ag水平、盆腔淋巴结转移是影响宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者远处转移的独立影响因素,差异有统计学意义(χ2=2.412、4.536、3.553,P=0.011、0.004、0.008)。见表2。

表2 多因素分析远处转移的影响因素
3 讨论
宫颈鳞癌中晚期(Ⅱb期~Ⅳa期)患者目前主要采用的主要治疗方法为放化疗相结合的方法,但是由于放化疗本身副作用大[9,10],因此具体运用起来需要慎重考虑,我科室主要采用体外放疗和腔内放疗、配合化疗的方法来探索该病特定时期的临床疗效。此外,对于中晚期鳞癌的远处转移,我们选择了FIGO临床分期、治疗前后SCC-Ag水平、盆腔淋巴结转移、以及治疗前Hb等作为备选指标,争取找到远处转移的相关因素,希望对于转移的预防和早期诊断起到帮助。
本次研究结果显示,宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者总生存率为63.30%,远处转移生存率为3.57%,5年无转移生存率89.24%。结果提示我科室对于子宫颈鳞癌中晚期进行的同步放化疗的疗效较好,总生存率较高,倘若未发生远处转移,对于该类患者的治疗会体现出更大优势。众所周知,癌症患者一旦出现远端转移,就以目前的医疗水平,还难以达到控制疾病的能力,对于症状的控制和疾病的治疗目前还处于摸索阶段[11,12]。我们得出FIGO临床分期、治疗后SCC-Ag水平、盆腔淋巴结转移是影响宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者远处转移的独立影响因素,从临床分期角度分析,本次研究选择的对象均为Ⅱb期~Ⅳa期范围内的样本,在这样相对病情较重的患者中,Ⅲ~Ⅳ期患者5年内的生存率要小于Ⅱ期的患者,这就提示我们如果能够阻止疾病的发展速度和程度,则对于提高患者的生存率会有一定的价值。而对于鳞状细胞癌抗原SCC-Ag而言,该指标现在已经广泛运用于妇科宫颈鳞癌的学科中[13]。很多学者认为,它在诊断学中可以用于诊断宫颈鳞癌的判定,在治疗学中可以用于评价治疗后放化疗的临床疗效[14]。并且治疗后血清中SCC-Ag很可能与人体内的肿瘤残存量相关,这也与本次研究的结果相吻合,通过本次的结果我们发现,如果治疗后血清中鳞状细胞癌抗原SCC-Ag水平较高的话,则出现远处转移的风险也可能更大。另外,对于盆腔淋巴结转移与否的探索,医学界已经进行了很多探索,淋巴结作为人体重要的免疫器官,在与癌症的抗争中起到不可忽视的作用[15],本次试验只不过对其中一个点进行了细化,发现了盆腔淋巴结转移与治疗后子宫癌远端转移的相关性,这也与以往的医学研究结论保持了一致的方向。所以,三种影响因素都与癌细胞的转移有着千丝万缕的联系,至此,笔者认为,虽然我们的试验得出了较为满意的结论,但是我们还需要在前人的基础上还做更深入的研究,才能得到更为有价值的结论。
综上所述,子宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗的疗效较好,总生存率较高,值得进一步推广, FIGO临床分期、治疗后SCC-Ag水平、盆腔淋巴结转移是影响宫颈鳞癌中晚期同步放化疗患者远处转移的独立影响因素。
1Naemura M,Murasaki C,Inoue Y,et al.Long Noncoding RNA ANRIL Regulates Proliferation of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Cervical Cancer Cells.Anticancer research,2015,35:5377-5382.
2冀淑英.子宫颈癌根治术后高危患者同步放化疗与单纯放疗的疗效比较.中国实用医刊,2015,42:78-80.
3Sakano CR,Ribalta JC,Zucchi P.Tracking of cervical cancer in 7,519 patients: a study of the prevalence of altered cytologies.European journal of gynaecological oncology,2015,36:437-441.
4Pyeon SY,Park JY,Ulak R,et al.Isolated brain metastasis from uterine cervical cancer: a case report and review of literature.European journal of gynaecological oncology,2015,36:602-604.
5Robbins AS,Han X,Ward EM,et al.Association between the affordable care act dependent coverage expansion and cervical cancer stage and treatment in young women.Jama,2015,314:2189-2191.
6张臖,杨金香,王峻峰,等.营养干预对宫颈癌患者同步放化疗耐受性及生活质量的影响.现代肿瘤医学,2015,24:2652-2654.
7Basta P,Jach R,Laskowicz L,et al.Conization and radical vaginal trachelectomy with laparoscopic lymphadenectomy in fertility-sparing surgical treatment of cervical cancer.Ginekologia polska,2015,86:590-597.
8胡元晶,曲芃芃.第19届国际妇产科联盟(FIGO)大会纪要(肿瘤部分).国际妇产科学杂志,2009,36:483-484.
9Salih SM,Albayrak S,Seo S,et al.Diminished utilization of in vitro fertilization following ovarian transposition in cervical cancer patients.The Journal of reproductive medicine,2015,60:345-353.
10刘平,魏子白,于俊岩,等.奈达铂或顺铂联合紫杉醇同步放化疗治疗中晚期宫颈癌的临床疗效观察.中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2015,9:77-81.
11Chiappetta C,Lendaro E,Cacciotti J,et al.Primary HPV test screening in cervical cancer: a two-year experience of a single screening center in Latina (Italy).European journal of gynaecological oncology,2015,36:569-573.
12沈佳惠,李胜泽.预测宫颈癌新辅助化疗敏感性的研究进展.中华全科医学,2014,12:1995-1997.
13佐合拉古丽·木塔力甫,李小文,张云霞.缓释氟尿嘧啶同期放化疗治疗中晚期宫颈癌的临床研究.新疆医科大学学报,2015,38:1265-1267,1273.
14Kong LY,Du W,Wang L,et al.PAX1 Methylation Hallmarks Promising Accuracy for Cervical Cancer Screening in Asians: Results from a Meta-Analysis.Clinical laboratory,2015,61:1471-1479.
15Shmidt AA,Alieva MT,Ivanova LV,et al.The role of the vaccine prophylaxis of cervical cancer among female military personnel.Voenno-meditsinskii zhurnal,2015,336:30-33.
Therapeutic effects of middle-late stage synchronism chemoradiation on cervical squamous cell carcinomas and influencing factors of distant metastasis
CHENGYingzhu,YEHui,WANGAimin,etal.
DepartmentofGynaecology,TCMHospitalofBaojiCity,Shanxi,Baoji721001,China
ObjectiveTo observe the therapeutic effects of middle-late stage synchronism chemoradiation on cervical squamous cell carcinomas and influencing factors of distant metastasis.MethodsThe data about 139 patients with cervical squamous carcinoma (stageⅡb ~Ⅳa) who underwent middle-late stage synchronism chemoradiation in our hospital from October 2007 to October 2010 were retrospectively analyzed. The total survival rate, the survival rate in distant metastasis, the survival rate without metastasis were observed by the method of browse cases and telephone follow-up. The influencing factors of distant metastasis were investigated by single factor analysis and multiple factors analysis, respectively.ResultsAmong 139 patients, there were 46 cases with relapse including 16 cases of local relapse, 23 cases of distant metastasis and 7 cases of local relapse combined with distant metastasis.Among 46 patients with relapse, 5 patients were survived,the other 41 patients died.However among 83 patients without relapse,only 10 patients died.The total survival rate in patients receiving middle-late stage synchronism chemoradiation was 63.30%,the survical rate in patients with distant metastasis was 3.57%, and the survival rate in patients without metastasis within 5 years was 89.24%. The results by single factor analysis showed that FIGO clinical staging,the levels of SCC-Ag after treatment,the levels of Hb before treatment, pelvic lymph node metastasis were the influencing factors on distant metastasis in patients receiving middle-late stage synchronism chemoradiation (χ2=9.371,11.245, 6.747, 5.110, respectively,P<0.01 or P<0.05). The results by multiple factors analysis showed that FIGO clinical staging,the levels of SCC-Ag after treatment, pelvic lymph node metastasis were independent influencing factors on distant metastasis in patients receiving middle-late stage synchronism chemoradiation (χ2=2.412,4.536,3.553,respectively,P<0.05 or P<0.01).ConclusionThe therapeutic effects of middle-late stage synchronism chemoradiation on cervical squamous cell carcinomas are better,and the total survival rate of patients is higher,thus,which is worth using widely in clinical practice. FIGO clinical stage, the levels of SCC Ag after treatment, pelvic lymph node metastasis are independent influencing factors on distant metastasis in patients receiving middle-late stage synchronism chemoradiation.
uterus squamous cell carcinomas; radiation and chemotherapy; distant metastases; influencing factors
10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2016.19.015
721001陕西省宝鸡市中医医院妇科
R 737.33
A
1002-7386(2016)19-2939-03
2016-03-06)
