部分线性测量误差模型的模拟—推断估计
2016-09-23赵昕
赵 昕
(南京理工大学理学院,南京210094)
部分线性测量误差模型的模拟—推断估计
赵昕
(南京理工大学理学院,南京210094)
该文研究了部分线性测量误差模型,即无法直接观测非参数部分协变量,只能得到其替代变量的模型.利用局部线性估计并结合模拟-推断的方法(SIMEX)得到参数及非参数的估计,并在适当的条件下,得到了所提估计量的渐近偏差及方差.将该文提出的模拟-推断方法与Liang(2000)的估计方法比较,表明模拟-推断法在处理测量误差问题上的有效性.值得一提的是,模拟-推断方法不需要对非参数部分协变量的分布提出假设.
测量误差; 部分线性模型; 替代变量; 模拟-推断方法
1 引 言
(1.1)




本文其余内容安排如下:第二节介绍了模拟-推断(SIMEX)方法并证明了所得估计的渐近性质;第三节通过一些模拟实验以验证该方法的有效性,此外,本文还与Liang(2000)提出的估计方法进行了比较,通过一些数量特征直观地反映出本文方法的优越性.文中定理的证明在附录中给出.
2 模拟-推断法及其渐近性质
本文结合模拟-推断法、局部线性回归及加权最小二乘法构造了参数β及非参数函数g(·)的估计.即先利用局部线性回归对未知函数g(·)进行估计,然后对参数β进行加权最小二乘估计.具体的算法如下:
(i) 模拟


(2.1)
(ii) 估计
假设函数g(·)在x0的邻域内有连续的二阶导数,那么g(x)可被一线性函数逼近,即
g(x)≈g(x0)+g′(x0)(x-x0)=a+b(x-x0),

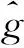

(2.2)

直接计算可得β的估计为

其中


(iii) 推断








参数β及非参数g(·)的估计量的渐近性质如下


定理1表明参数β的模拟-推断估计量比Naive估计量具有更复杂的方差结构.该定理中各记号的定义将在附录中给出.
定理2假设附录中条件(C1)-(C5)成立,当n→∞且B→∞时,有


其中

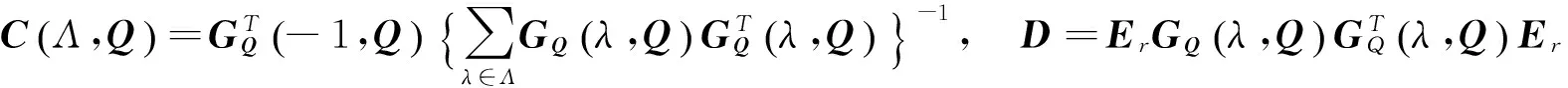
Er是一个除了第一个元素为1,其它元素均为0的r阶方阵,r为参数Q的维数.
3 数值结果
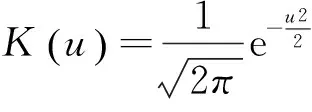
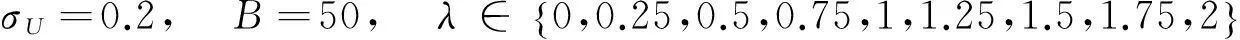
产生500个数据集,每个数据集包含个体数分别为n=50,100,150.
我们使用模拟-推断法及Naive方法(即忽略测量误差的估计)来构造参数β的估计,其结果列在表1中.

表1 参数β的SIMEX及Naive估计及其标准差SD
此外,取不同的测量误差方差σU=0.2,0.4,0.8,比较模拟-推断估计与忽略测量误差的Naive估计方法,假设样本容量n=50.其结果列于表2中.当测量误差方差σ=0.2时,对于非参数g(·)的估计展示于图1中.
由表1,发现模拟-推断估计方法比Naive法减少了估计偏差,且偏差随着样本容量的增加而减少;但是模拟-推断估计的标准差比Naive法的略大些.由表2还可以发现偏差随着测量误差方差的增大而增大.

表2 在不同测量误差下参数β的SIMEX及Naive估计及其标准差SD

图1 非参数g(·)的估计曲线图. 实线表示真实曲线. 虚线表示模拟-推断估计曲线. 点虚线表示Naïve估计曲线. 从上至下从左至右依次表示样本容量n=50,100,150的情形


表3 参数β的HL及SIMEX估计的偏差

表4 非参数的HL及SIMEX估计的均方误差
4 结 论
本文提出非参数部分带有测量误差的部分线性模型的模拟-推断估计.在适当的条件下得到了参数估计量的渐近偏差及方差.在模拟实验中与忽略测量误差的Naive估计进行比较,得以验证本文提出的模拟-推断估计的有效性与优越性;此外本文还与Liang(2000)提出的估计方法进行比较,结果表明本文提出的方法处理测量误差问题的合理性.值得一提的是,本文的方法无需对无法观测的协变量Xi提出分布假设.
本文所提的方法还可以推广至更为一般的模型;如部分线性单指标测量误差模型、变系数部分线性测量误差模型等,进一步我们还可以考虑相应变量缺失的测量误差模型,这些均已超出本文的研究范围,在此不作详细介绍.
附 录
定理1的证明.首先给出定理满足的条件




其中

类似于模拟-推断的算法,我们的证明也分模拟、估计、推断三部分进行,假设B是一固定的正整数.
(i)模拟
对每个b,由标准渐近理论有

(1)

(2)
其中



(3)
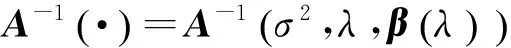

(4)
(ii)估计

定义
及


(5)

(6)
(iii)推断

及




(7)


其中

定理2的证明.类似于定理1的证明.此处略去.
[1]柴根象, 徐克军. 半参数回归的线性小波光滑[J]. 应用概率统计, 1995, 15(1): 97-105.
[2]任哲, 陈明华.L-统计量的Bootstrap逼近[J]. 工科数学, 1995, 4(11): 78-81.
[3]周恒忠,陈明华. 关于Vou-Mises统计量的非一致性收敛速度[J]. 工科数学, 1995, 4(11): 103-106.
[4]Carroll R J, Lombard F, Kuchenhoff H and Stefanski L A. Asymptotics for the SIMEX estimation in structural measurement error models[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1996, 91: 242-250.
[5]Drum M, McCullagh P. Regression models for discrete longitudinal responses[J]: Comment. Statistical Science, 1993, 8(3): 300-301.
[6]Engle R F, Granger C W J, Rice J, et al. Semiparametric estimates of the relation between weather and electricity scales[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1986, 81: 310-320.
[7]Huang Z S. Empirical likelihood for the parametric part in partially linear errors-in-function models[J]. Statistics and Probability Letters, 2012, 82: 63-66.
[8]Liang H. Generalized partially linear mixed-effects models incorporating mismeasured covariants[J]. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 2009, 61(1): 27-46.
[9]Liang H. Asymptotic normality of parametric part in partially linear models with measurement error in the nonparametric part[J]. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 2000, 86: 51-62.
[10]Liang H Y, Jing B Y. Asymptotic normality in partial linear models based on dependent errors[J]. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 2009, 139(4): 1357-1371.
[11]Robinson P M. Root-n-consistent semiparametric regression[J]. Economerika, 1988, 56: 931-954.
[12]Schimek M G. Estimation and inference in partially linear models with smoothing splines[J]. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 2000, 91(2): 525-540.
[13]Shen C W, Tsou T S, Balakrishnan N. Robust likelihood inference for regression parameters in partially linear models[J]. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2011, 55(4):1696-1714.
[14]Wang Q H. Consistent estimators in random censorship semiparametric regression models[J]. Science in China, Series A, 1996, 39: 163-176.
[15]Wang Q H, Jing B Y. Empirical likelihood for partial linear models[J]. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 2003, 55(3): 585-595.
[16]Xue L G, Liu Q. Bootstrap approximation of wavelet estimates in a semiparametric regression model[J]. Acta Mathematic a Sinica-English Series, 2010, 26(4): 763-778.
[17]Xue L G, Zhu L X. L_1-norm estimation and random weighting method in a semiparametric model[J]. Acta Mathematicae Applicatae Sinica, 2005, 21(2): 295-302.
[18]Zeger S L, Diggle P J. Semiparametric models for longitudinal data with application to CD4 cell numbers in HIV seroconverters[J]. Biometrics, 1994, 50: 689-699.
[19]Zhu L X, Xue L G. Empirical likelihood confidence regions in a partially linear single-index model[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B, 2006, 68(3): 549-570.
Simulation-Extrapolation Estimation in Partially Linear Errors-in-Function Models
ZHAO Xin
(Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China)
We consider partially linear model with measurement errors. The covariate in nonparametric part is not observable, but its surrogate variable is available. We propose estimators of parameter and nonparametric function by using local linear regression and the Simulation-extrapolation (SIMEX) technique. The asymptotic biases and variances of proposed estimators are obtained in some conditions. Some simulations are conducted to illustrate the proposed method. We compare our method with the estimators proposed by Liang (2000) and the results indicate that SIMEX technique is valid to deal with the measurement errors. Furthermore, it is worth pointing out that our method need not assume the distribution of the covariates in the nonparametric part.
measurement errors; partially linear model; surrogate variable; SIMEX technique
2016-04-01;[修改日期]2016-04-22
国家自然科学基金(10871072; 11501292);国家统计科学研究重点项目(2013LZ45);中央高校基本科研基金(30920130111015);江苏省自然科学基金面上项目(BK20131345)资助.
赵昕(1992-),女,硕士,研究生在读. 从事非参数统计分析研究. Email: 2690167203@qq.com
O212.7
A
1672-1454(2016)04-0012-08
