MAPKs阻滞剂U0126对创伤性脑损伤大鼠学习记忆功能的影响及机制探讨
2016-09-05刘兴宇甄艳凤崔建忠高俊玲
刘兴宇,甄艳凤,崔建忠,高俊玲
(1唐山市工人医院,河北唐山063000;2华北理工大学基础医学院)
MAPKs阻滞剂U0126对创伤性脑损伤大鼠学习记忆功能的影响及机制探讨
刘兴宇1,甄艳凤1,崔建忠1,高俊玲2
(1唐山市工人医院,河北唐山063000;2华北理工大学基础医学院)
目的观察丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPKs)阻滞剂U0126对创伤性脑损伤 (TBI)大鼠学习记忆功能的影响,并探讨其机制。方法将313只成年雄性SD大鼠随机分为假手术组52只、模型组87只、DMSO组87只、U0126组87只,除假手术组外其余各组制备大鼠弥漫性脑创伤模型。U0126组将0.1 mg/kg U0126以0.1 mmol/L的PBS稀释至300 μL,于造模前30 min尾静脉注射。DMSO组同时点尾静脉注射相同含量DMSO稀释溶液,假手术组和模型组同时点尾静脉注射生理盐水300 μL。造模30 min、3 h、12 h、24 h、48 h、72 h、7 d取各组大鼠各5只(假手术组3只),采用TUNEL法观察各组海马组织神经细胞凋亡情况。造模30 min、3 h、12 h、24 h、48 h、72 h、7 d取各组大鼠各6只(假手术组3只),采用Western blot法检测各组海马组织磷酸化细胞外信号调节激酶1/2(p-ERK1/2)蛋白表达。造模14、16、18、21 d取各组大鼠各10只,采用Morris水迷宫实验观察大鼠空间学习记忆能力。结果造模48、72 h时,U0126组海马组织神经细胞凋亡数少于DMSO组、模型组,P均<0.05;造模24、48、72 h时,U0126组、DMSO组、模型组海马组织神经细胞凋亡数均多于假手术组,P均<0.05;造模48、72 h时,U0126组海马组织p-ERK1/2蛋白相对表达量低于模型组、DMSO组,P均<0.05;造模12、24、48、72 h时,U0126组、DMSO组、模型组海马组织p-ERK1/2蛋白相对表达量均短于假手术组,P均<0.05;造模16、18、21 d时U0126组大鼠潜伏期均短于DMSO组、模型组,P均<0.05;造模14、16、18、21 d时U0126组、DMSO组、模型组大鼠潜伏期均长于假手术组,P均<0.05。相关性分析结果显示,海马区神经细胞凋亡数与p-ERK1/2表达呈正相关(r=0.468,P=0.002)。结论U0126可抑制TBI大鼠海马神经细胞凋亡,提高大鼠的学习记忆能力,可能与降低海马组织中p-ERK1/2表达有关。
创伤性脑损伤;学习记忆功能;丝裂原活化蛋白激酶阻滞剂;磷酸化细胞外信号调节激酶1/2
创伤性脑损伤 (TBI) 发生率高,后遗症多,是创伤医学、急救医学的重要研究课题[1,2]。其中学习记忆能力的损害是 TBI最持久和最严重的症状之一,目前尚无有效治疗方法。丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPKs)是细胞内的一类丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,是细胞应激和损伤反应的主要信号通路,可将胞外刺激信号传递至胞核[3]。细胞外信号调节激酶1/2(ERK1/2)是MAPKs的重要成员,磷酸化后可被激活。2014年1月~2015年11月,我们观察了MAPKs阻滞剂U0126对TBI大鼠学习记忆功能的影响,并探讨其可能的作用机制。现报告如下。
1 材料与方法
1.1模型制作及干预将313只健康成年清洁级雄性SD大鼠[体质量300~350 g,购自北京维通利华公司,许可证号:SCXK(京)2002-003]随机分为假手术组52只、模型组87只、DMSO组87只、U0126组87只,除假手术组外其余各组参照[1]制备大鼠弥漫性脑创伤模型:乙醚麻醉大鼠,用450 g、直径18 mm的铜锤自2 m高度垂直落下撞击置于大鼠冠状缝与矢状缝正中的不锈钢垫(直径10 mm厚3 mm),造成大鼠弥漫性脑创伤模型,假手术组仅麻醉大鼠,头皮切开、缝合。U0126组将0.1 mg/kg U0126(美国,Promega公司,药物批号:粤卫药准字第616021号)溶解于PBS中,并以0.1 mmol/L的PBS稀释为总量300 μL,于造模前 30 min自尾静脉注射。DMSO组同时点尾静脉注射相同含量DMSO稀释溶液,假手术组和模型组同时点尾静脉注射生理盐水300 μL。
1.2大鼠海马组织神经细胞凋亡情况观察采用TUNEL法。造模30 min、3 h、12 h、24 h、48 h、72 h、7 d取各组大鼠各5只(假手术组3只),以35 mg/kg戊巴比妥钠腹腔麻醉;仰卧位固定后开胸暴露心脏,左心室穿刺入升主动脉,用室温肝素生理盐水冲洗内脏血液10 min;4%多聚甲醛250 mL经心灌流,固定30~40 min;待大鼠全身僵硬后断头取脑组织,固定、石蜡包埋、切片,TUNEL染色后镜下观察,实验重复3次。均设阴性对照,以PBS代替一抗。所有操作严格按照德国BM公司说明书操作。TUNEL阳性细胞呈蓝紫色,细胞核着色。TUNEL阳性细胞阳性强弱用Image Proplus 6.0数码医学图像分析系统定量分析测定,以积分光密度(IOD)值来表示大鼠海马区神经细胞数。
1.3大鼠海马组织p-ERK1/2蛋白检测采用Western blot法。造模30 min、3 h、12 h、24 h、48 h、72 h、7 d取各组大鼠各6只(假手术组3只),处死大鼠后取海马组织;4 ℃PBS充分洗涤,加入3倍体积的4 ℃全细胞裂解液,冰浴中匀浆;4 ℃离心5 min,12 000 r/min,取上清。转膜、封闭后加入p-ERK1/2兔抗鼠单克隆抗体(美国Cell Signaling公司),DAB显色,实验重复3次。用图像分析仪测定各组p-ERK1/2蛋白条带的光密度,进行半定量分析。
1.4大鼠学习记忆能力检测采用Morris水迷宫实验。造模14、16、18、21 d,取10只各组大鼠进行Morris水迷宫实验。将安全岛随机置于水迷宫四个象限(N、S、E、W)中的任一象限,加水(奶粉冲呈乳白色)至高过安全岛10 mm,水温22~25 ℃,由摄象机及计算机自动跟踪、拍摄和统计大鼠分别由其他3个象限入水后寻找到安全岛的时间(潜伏期)。如在180 s内未找到安全岛,则潜伏期值记为180 s。水迷宫视频分析系统由中国医学科学院药物研究所提供。实验重复3次,取平均值。以搜索安全岛潜伏期表示其学习记忆能力。
2 结果
2.1各组海马组织神经细胞凋亡情况比较造模后不同时点各组海马组织神经细胞凋亡情况比较见表1。
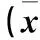
表1 造模后不同时点各组海马组织神经细胞凋亡情况比较±s)
注:与模型组和DMSO组比较,#P<0.05;与假手术组比较,*P<0.05。
2.2各组海马组织p-ERK1/2蛋白相对表达量比较造模后不同时点各组海马组织p-ERK1/2蛋白相对表达量比较见表2。
2.3各组大鼠学习记忆能力比较造模后不同时点各组大鼠学习记忆能力比较见表3。
2.4海马区神经细胞凋亡与p-ERK1/2表达的关系相关性分析结果显示,海马区神经细胞凋亡情况与p-ERK1/2相关性呈正相关(r=0.468,P=0.002)。
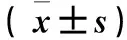
表2 造模后不同时点各组海马组织p-ERK1/2蛋白相对表达量
注:与模型组、DMSO组比较,#P<0.05;与假手术组比较,*P<0.05。
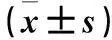
表3 造模14、16、18、21 d各组大鼠学习记忆能力比较
注:与DMSO组、模型组比较,﹟P<0.05; 与假手术组比较,*P<0.01。
3 讨论
MAPKs是细胞内的一类丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,是细胞应激和损伤反应的主要信号通路,可将胞外刺激信号传递至胞核。细胞外信号调节激酶ERK是MAPKs重要成员[3]。研究显示,脑缺血损伤后,激活的ERK1/2对神经元具有保护作用[4],但有更多文献报道与之相反。Mori等[5]研究显示,脑损伤后ERK1/2的激活与细胞凋亡密切相关,其特异性抑制剂可明显减少神经细胞死亡数目,减轻创伤后的脑损伤面积,并改善了损伤后的神经功能。Clausen等[6]在闭合性脑损伤的模型中,应用共聚焦显微镜观测到损伤中心及周边区活化的ERK1/2与TUNEL阳性细胞共同定位,为ERK通路活化可导致细胞凋亡提供最为直观的证据。本研究发现,海马区神经细胞凋亡与p-ERK1/2表达呈正相关。这一方面反应了创伤后ERK1/2的激活可加重脑损伤的病理过程,同时也提示ERK通路可能是脑损伤后治疗的新靶点。
U0126是高选择性和高效的MAPKs阻滞剂,可通过直接抑制MEK活性而阻滞其下游分子ERK1 /2的磷酸化[7]。本研究结果显示,与假手术组比较,模型组创伤后30 min海马区p-ERK1/2相对表达量升高,且随创伤时间增加其相对表达量逐渐升高,于创伤后24 h达到峰值,U0126组p-ERK1/2相对表达量低于模型组,可能原因为MAPKs通路被阻断。TUNEL检测结果显示,随着创伤时间延长,海马区神经细胞凋亡数增多;而U0126组较模型组海马区细胞凋亡数明显减少;说明脑损伤后, ERK的活化增加,导致了神经细胞凋亡的增多,加重了脑损伤,与以往文献报道一致。
海马作为学习记忆信息通路的必要结构,在空间学习记忆的巩固方面发挥着重要作用[8]。海马神经细胞凋亡可能是导致TBI后学习记忆功能障碍、特别是空间学习记忆能力下降的机制之一。p-ERK参与认知功能,如学习与记忆形成[9~12]。最新研究证实,Ras/ERK通路参与了人类的认知过程。Silva等[13]利用基因工程技术,在研究Ⅰ型神经纤维母细胞瘤与精神发育迟缓的关系中发现,学习功能的降低与海马Ras/ERK信号通路的缺损密切相关。目前临床普遍认为ERK通路参与了突触可塑性变化,进而影响了大脑信息存储及记忆巩固等过程。Mazzucchelli等[14]研究发现,ERK1基因敲除小鼠长时记忆功能显著增强,而短时记忆力保持。Zhang等[15]研究发现,经过气味休克训练1 h的正常幼鼠ERK1和ERK2磷酸化水平显著增强,从而激活ERK通路,而MAPK/ERK抑制剂PD98059可明显降低ERK磷酸化水平,进而影响大鼠的学习记忆功能。
本研究中,U0126可减少TBI大鼠海马神经细胞凋亡数,提高大鼠的学习记忆能力,可能与降低海马组织中p-ERK1/2表达有关。但ERK通路激活后,通过作用于哪些因子发挥脑保护作用还有待进一步研究。
[1] Marmarou A, Foda MA, Vanden BW, et al. A new model of diffuse brain injury in rats[J]. J Neuro Surg, 1994,80(2):301-313.
[2] 李金星,朱贤立,李玉,等.大鼠弥漫性脑损伤阻滞ERK通路下调脑组织MMP-9 mRNA的表达[J]. Chin J Neurosury, 2006,11(5):288-291.
[3] Abdul Rahman NZ, Greenwood SM, Brett RR. Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-2 deletion impairs synaptic plasticity and hippocampal-dependent Memory[J]. 2016,36(8):2348-2354.
[4] Yang Y, Zhang X, Cui H, et al. Apelin-13 protects the brain against ischemia/reperfusion injury through activating PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2014,7(68):44-49.
[5] Mori T, Wang XY, Jung JC, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition in traumatic brain injury: in vitro and in vivo effects[J].J Cere Blood Flow Metab, 2002,22(4):444-452.
[6] Clausen F, Lundqvist H, Ekmark S, et al. Oxygen free radical dependent activation of extracellular signal regulated kinase mediates apoptosis like cell death after traumatic brain injury[J]. J Neuro, 2004,21(9):1168-1182.
[7] Malemud CJ, Lewis AC, Wylie MA, et al. U0126, an inhibitor of MEK1/2, increases tumor necrosis factor-α-induced apoptosis, but not interleukin-6 induced apoptosis in C-28/I2 human chondrocytes[J].J Autoimmune Disord, 2015,1(1):4.
[8] Lazarov O, Hollands C. Hippocampal neurogenesis: Learning to remember[J]. Prog Neurobiol,2016,30(10):18-26.
[9] Kaneai N, Sumitani K, Fukui K, et al. Tocotrienol improves learning and memory deficit of aged rats[J]. J Clin Biochem Nutr,2016,58(2):114-121.
[10] Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhu G, et al. A calpain-2 selective inhibitor enhances learning & memory by prolonging ERK activation[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2016(105):471-477.
[11] Atkins CM, Yon M, Groome NP, et al. Regulation of myelin basic protein phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase during increased action potential firing in the hippocampus[J]. J Neurochem, 1999(73):1090-1097.
[12] Fija K, Nowak E, Lekiewicz M, et al. Working memory deficits and alterations of ERK and CREB phosphorylation following withdrawal from cocaine self-administration[J]. Pharmacol Rep, 2015,67(5):881-889.
[13] Silva AJ, Frankland PW, Marowitz Z, et al. A mouse model for the learning and memory deficits associated with neurofibromatosis type Ⅰ[J]. Nat Genet,1997,15(3):281-284.
[14] Mazzucchelli C, Vantaggiato C, Ciamei A, et al. Knockout of ERK /MAP kinase enhances synaptic plasticity in the striatum and facilitates striatal-mediated learning and memory[J]. Neuron, 2002,34(5):807-820.
[15] Zhang JJ, Okutani F, Inoue S, et al. Activation of the mitogen activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway leading to cyclic AMP response element binding protein phosphorylation is required for the longterm facilitation process of aversive olfactory learning in young rats[J]. Neuro Science, 2003(121):9-16.
Protective effects of MAPKs inhibitor U0126 on learning and memory function of rats with traumatic brain injury
LIUXingyu1,ZHENYanfeng,CUIJianzhong,GAOJunling
(1TangshanGongrenHospital,Tangshan063000,China)
ObjectiveTo observe the protection of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor U0126 on learning and memory function of rats with traumatic brain injury (TBI) and to investigate its mechanism. MethodsMale Sprague-Dawley rats (n=313) were randomly divided into four groups: the sham operation group (n=52), TBI group (n=87), DMSO group (n=87) and U0126 group (n=87). Except the TBI group, diffused brain injury rat models were established in the other groups. In the U0126 group, 0.l mg/kg U0126 was dissolved in PBS, and 0.1 mM PBS was diluted to the total amount of 300 μL, then, this solution was injected into the rats 30 min before modeling by caudal vein. Rats in the DMSO group were injected with the same amount of DMSO dilute solution, and rats in the sham operation group and TBI group were injected with 300 μL normal saline. The in situ apoptosis assay was used to observe the nerve apoptosis of hippocampus of each group at 30 min, 3 h, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 7 d after modeling (n=5 respectively, except for sham operation groupn=3). The phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 (p-ERK1/2) protein was detected in each group by Western blotting at 30 min, 3 h, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 7 d after modeling (n=6 respectively, except for sham operation groupn=3). The learning and memory function was evaluated by Morris water maze on the 14th, 16th, 18th and 21rd day after modeling in each group (eachn=10). ResultsThe number of nerve cell apoptosis of hippocampus in the U0126 group was lower than that of DMSO and TBI groups at 48 h and 72 h after modeling, allP<0.05; the number of nerve cell apoptosis of hippocampus in the U0126, DMSO and TBI groups was all higher than that of the sham operation group at 24 h, 48 h and 72 h, allP<0.05; the relative expression of p-ERK1/2 in hippocampus of the U0126 group was lower than that of the DMSOand TBL groups at 48 h and 72 h after modeling, allP<0.05; the relative expression of p-ERK1/2 in hippocampus of the U0126、DMSO and TBI groups was all higler than that of the sham group at 12 h, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h after modeling, allP<0.05; the incubation period in the U0126 group was shorter than that of the DMSO and TBI groups on the 16th, 18th and 21rd day, allP<0.05; the incubation period in the U0126, DMSO and TBI groups was longer than that of the sham operation group on the 16th, 18th and 21rd day, allP<0.05; correlation analysis showed that the number of nerve cell apoptosis in hippocampus was positively correlated with p-ERK1/2 expression (r=0.468,P=0.002). ConclusionU0126 can inhibit neuronal apoptosis in hippocampus and improve learning and memory in rats, which may be correlated with the decreased p-ERK1/2 expression.
traumatic brain injury; learning and memory function; mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor; phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2
河北省自然科学基金资助项目(H2012401071);河北省引进留学人员资助项目(2012-02)。
刘兴宇(1980-),男,硕士,主治医师,研究方向为脑创伤机制。E-mail: 15931588358@126.com
简介:高俊玲(1960-),女,博士,教授,研究方向为脑损伤与脑保护单位。E-mail: junlinggao@163.com
10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2016.18.007
R651.1
A
1002-266X(2016)18-0021-04
2015-11-08)
