牛场肥水灌溉对冬小麦产量与氮利用效率及土壤硝态氮的影响
2016-08-24杜会英张克强郭海刚
杜会英, 冯 洁, 张克强, 王 风, 郭海刚
(农业部环境保护科研监测所,天津 300191)
牛场肥水灌溉对冬小麦产量与氮利用效率及土壤硝态氮的影响
杜会英, 冯 洁, 张克强*, 王 风, 郭海刚
(农业部环境保护科研监测所,天津 300191)

牛场肥水; 灌溉; 冬小麦; 产量; 氮利用效率; 土壤硝态氮积累
随着集约化饲养程度的不断提高,畜禽养殖产生大量粪污,根据“全国第一次污染源普查公报”数据,我国畜禽养殖业粪便年产量为2.43亿吨,尿液等废水产生量1.63亿吨[1]。然而养殖粪污处理和利用率极低,已成为影响我国环境质量的重要污染源之一,同时造成养分资源的极大浪费。作为一个农业大国,我国农业年用水量达到全年总用水量的60%以上[2],水资源贫乏及地域分布不均匀造成我国严重的农业用水危机,华北平原地区水资源短缺问题在农业生产中尤为突出,农灌区地下水严重超采,导致地下水位下降等诸多生态环境问题[3]。将处理后的养殖肥水作为水、氮资源进行农田灌溉,是减轻养殖肥水中氮污染水体的重要途径,也是缓解农业水资源短缺的重要措施之一。

1 材料与方法
1.1试验点概况

1.2试验设计
试验共设5个处理,每个处理3次重复,分别为: 不施肥、小麦各生育期进行清水灌溉(CK); 在冬小麦生育期内进行2次牛场肥水灌溉(越冬期和灌浆期,肥水灌溉带入氮量为160kg/hm2),其他生育期清水灌溉(T1); 在冬小麦生育期内进行3次牛场肥水灌溉(越冬期、拔节期、灌浆期,肥水灌溉带入氮量为240kg/hm2),其他生育期清水灌溉(T2); 在冬小麦生育期进行4次牛场肥水灌溉(越冬期、拔节期、抽穗期和灌浆期,肥水灌溉带入氮量为320kg/hm2),不进行清水灌溉(T3); 农民习惯施肥,冬小麦播种时,N、P2O5和K2O施入量分别为56kg/hm2、79kg/hm2和23kg/hm2、冬小麦拔节期追纯氮量为276kg/hm2,全生育期氮投入量为332kg/hm2,各生育期清水灌溉(CF)。各处理在小麦收获后进行取样分析。试验小区面积60m2(长15m×宽4m)。所有处理灌水定额均为830m3/hm2,灌溉方式为漫灌,灌水量利用超声波流量计计量,灌溉误差1%以内。冬小麦全生育期灌水4次。供试冬小麦品种为济麦22。

1.3样品采集与分析
冬小麦收获时每个小区采收2m2的小麦样品,风干后脱粒,分籽粒和秸秆两部分称量其干重,将采集的小麦籽粒、秸秆样品烘干、粉碎、混匀,然后用浓H2SO4-H2O2消解,采用流动注射分析仪(FIA-6000+)测定籽粒和秸秆的氮含量。

1.4计算方法
植株氮积累量(kg/hm2)=(籽粒干量×籽粒含氮量)+(秸秆干量×秸秆含氮量);
氮表观利用率(%)=(施氮区地上部氮积累量-不施氮区地上部氮积累量)/氮肥投入量×100;
氮农学效率(kg/kg)=(施氮肥区产量一不施氮肥区产量)/施氮量;
土壤硝态氮残留量(kg/hm2)= 土层厚度×土壤容重×硝态氮浓度;
1.5统计方法:
试验数据用SAS和Excel软件进行统计分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1牛场肥水灌溉的产量效应


表1 不同肥水N带入量下冬小麦的产量 (kg/hm2)
注(Note): 同列数据不同字母表示差异达5% 显著水平Valuesfollowedbydifferentlettersinthesamecolumnmeansignificantdifferenceat5%level.
2.2肥水灌溉对冬小麦氮吸收的影响


图1 20112013年不同肥水灌溉次数下冬小麦植株的氮积累Fig.1 Plant N accumulation of winter wheat under different effluent irrigation frequency in 2011-2013
吸收[16-18],随着肥水灌溉年限的增加,肥水促进植株氮吸收的效果增加,对比不同年限间植株氮吸收量,2012年冬小麦产量整体较2011和2013年低,植株氮吸收量也较低。在肥水灌溉的三个处理中,2011年和2012年肥水灌溉的三个处理之间差异不显著,2013年T2和T3处理植株氮吸收量显著高于T1处理。
2.3肥水灌溉对冬小麦氮利用的影响
由表2可以看出,冬小麦肥水氮表观利用率和农学效率均随肥水灌溉带入氮量的增加而降低,且随着肥水灌溉年限的增加而增加,三年氮表观利用率和氮农学利用率均以T1最高,三年平均分别为48.57%和37.15kg/kg,2011年和2013年T1处理显著高于T3和农民习惯施肥处理,2012年T1与T3和习惯施肥处理差异不显著。张福锁等[19]报道小麦平均施氮量169.0kg/hm2,氮表观利用率和农学效率分别为28.20%和8kg/kg,李瑞奇等[20]研究表明,小麦生产中施氮240kg/hm2可以获得较理想的氮素利用效率,本研究与此一致。
2.4牛场肥水灌溉对土壤硝态氮积累的影响
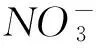
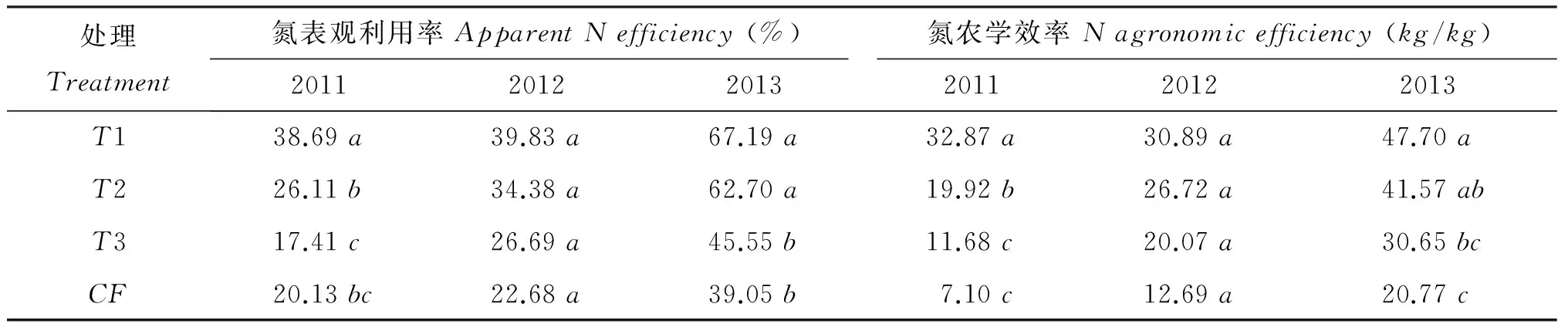
表2 灌溉肥水中氮的利用效率
注(Note): 同列数据后不同字母表示差异达5% 显著水平Valuesfollowedbydifferentlettersinthesamecolumnmeansignificantdifferenceat5%level.
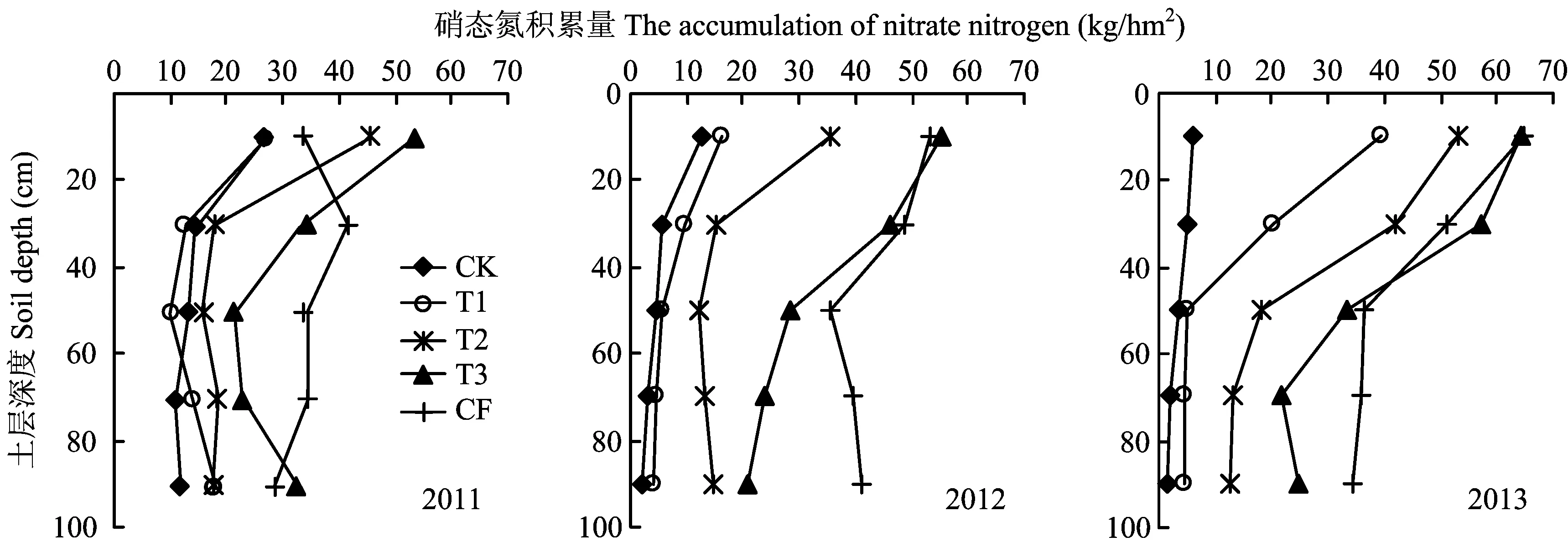
图2 牛场肥水灌溉对冬小麦收获后土壤硝态氮的影响Fig.2 Effects of dairy effluents irrigation on soil -N after the harvest time of winter wheat
3 结论

[1]中华人民共和国环境保护部. 第一次全国污染源普查公报[R]. 北京: 中华人民共和国国家统计局, 2010.
MinistryofEnvironmentalProtectionofthePeople’sRepublicofChina.Thebulletinofthefirstpollutionsourcecensus[R].Beijing.NationalBureauofStatisticsofthePeople’sRepublicofChina, 2010.
[2]中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴2013[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2013.
NationalBureauofStatisticsofChina.Chinastatisticalyearbook2013[M].Beijing:ChinaStatisticsPress, 2013.
[3]张光辉, 费宇红, 刘春华, 等. 华北平原灌溉用水强度与地下水承载力适应性状况[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(1): 1-10.
ZhangGH,FeiYH,LiuCH, et al.AdaptationbetweenirrigationintensityandgroundwatercarryingcapacityinNorthChinaPlain[J].TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyofAgriculturalEngineering, 2013, 29(1): 1-10.
[4]SaundersOE,FortunaAM,HarrisonJH, et al.ComparisonofrawdairymanureslurryandanaerobicallydigestedslurryasNsourcesforgrassforageproduction[J].InternationalJournalofAgronomy, 2012, 1-10.
[5]Valencia-GicaRB,YostRS,PorterG.Biomassproductionandnutrientremovalbytropicalgrassessubsurfacedrip-irrigatedwithdairyeffluent[J].GrassandForageScience, 2012, 67 (3): 337-349.
[6]AliciaMC,FuensantaGO,JorgeMS, et al.Short-termeffectsoftreatedwastewaterirrigationonMediterraneancalcareoussoil[J].SoilandTillageResearch, 2011, 112: 18-26.
[7]BelaidN,CatherineN,MonemK, et al.Longtermeffectsoftreatedwastewaterirrigationoncalcisolfertility:AcasestudyofSfax-Tunisia[J].AgriculturalSciences, 2012, 3(5): 702-713.
[8]黄红英, 曹金留, 常志州, 等. 猪粪沼液施用对稻、麦产量和氮磷吸收的影响[J]. 土壤, 2013, 45(3): 412-418.
HuangHY,CaoJL,ChangZZ, et al.Effectsofdigestedpigslurryapplicationonyields,nitrogenandphosphorousuptakesbyriceandwheat[J].Soils, 2013, 45(3): 412-418.
[9]乔冬梅, 齐学斌, 樊向阳, 等. 养猪废水灌溉对冬小麦作物-土壤系统影响研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2010, 29(1): 32-35.
QiaoDM,QiXB,FanXY, et al.Theinfluenceoflivestockwastewaterirrigationonwinterwheatcrop-soilsystem[J].JournalofIrrigationandDrainage, 2010, 29(1): 32-35.
[10]郭海刚, 杜会英, 王风, 等. 规模化牛场废水灌溉对土壤水分和冬小麦产量品质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2012, 21(8): 1498-1502.
GuoHG,DuHY,WangF, et al.Effectsofdairywastewaterirrigationonsoilmoistureandtheyieldandqualityofwinterwheat[J].EcologyandEnvironmentalSciences, 2012, 21(8): 1498-1502.
[11]林治安, 赵秉强, 袁亮, 等. 长期定位施肥对土壤养分与作物产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(8): 2809-2819.
LinZA,ZhaoBQ,YuanL, et al.Effectsoforganicmanureandfertilizerslong-termlocatedapplicationonsoilfertilityandcropyield[J].ScientiaAgricultureSinica, 2009, 42(8): 2809-2819.
[12]杜臻杰, 樊向阳, 李中阳, 等. 猪场沼液灌溉对冬小麦生长和品质的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(3): 547-554.
DuZJ,FanXY,LiZY, et al.Growthandgrainqualityofwinterwheatirrigatedwithbiogasliquidfromaswinefarm[J].JournalofAgro-EnvironmentScience, 2014, 33(3): 547-554.
[13]李克南, 杨晓光, 刘园, 等. 华北地区冬小麦产量潜力分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38(8): 1483-1493.
LiKN,YangXG,LiuY, et al.DistributioncharacteristicsofwinterwheatyieldanditsinfluencedfactorsinNorthChina[J].ActaAgronomicaSinica, 2012, 38(8): 1483-1493.
[14]Martínez-SullerL,ProvoloG,BrennanD, et al.Anoteontheestimationofnutrientvalueofcattleslurryusingeasilydeterminedphysicalandchemicalparameters[J].IrishJournalofAgriculturalandFoodResearch, 2010, 49: 93-97.
[15]AbubakerJ,CederlundH,ArthursonV, et al.Bacterialcommunitystructureandmicrobialactivityindifferentsoilsamendedwithbiogasresiduesandcattleslurry[J].AppliedSoilEcology, 2013, 72: 171-180.
[16]ChristophM,RonaldJL,PeterC, et al.Effectsofrepeatedfertilizerandcattleslurryapplicationsover38yearsonNdynamicsinatemperategrasslandsoil[J].SoilBiologyandBiochemistry, 2011, 43: 1362-1371.
[17]NannenDU,HerrmannA,LogesR, et al.RecoveryofmineralfertilizerNandslurryNincontinuoussilagemaizeusingthe15Nanddifferencemethods[J].NutrientCyclinginAgroecosystems, 2011, 89: 269-280.
[18]LalorSTJ,SchröderJJ,LantingaEA, et al.Nitrogenfertilizerreplacementvalueofcattleslurryingrasslandasaffectedbymethodandtimingofapplication[J].JournalofEnvironmentalQuality, 2011, 40: 362-373.
[19]张福锁, 王激清, 张卫峰, 等. 中国主要粮食作物肥料利用率现状与提高途径[J]. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(5): 916-924.
ZhangFS,WangJQ,ZhangWF, et al.NutrientuseefficienciesofmajorcerealcropsinChinaandmeasuresforimprovement[J].ActaPedologicaSnica, 2008, 45(5): 916-924.
[20]李瑞奇, 李雁鸣, 何建兴, 等. 施氮量对冬小麦氮素利用和产量的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2011, 31(2): 270-275.
LiRQ,LiYM,HeJX, et al.Effectofnitrogenapplicationrateonnitrogenutilizationandgrainyieldofwinterwheat[J].JournalofTriticeaeCrops, 2011, 31(2): 270-275.
[21]杨军, 张蕾, 张克强, 等. 猪场废水灌溉对潮土硝态氮含量变化的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2009, 25(5): 35-39.
YangJ,ZhangL,ZhangKQ, et al.Effectsofirrigationwithpiggerywastewateronnitratenitrogendynamicsinfluvio-aquaticsoil[J].TransactionsoftheChineseSocietyofAgriculturalEngineering, 2009, 25(5): 35-39.
[22]JuXT.Directpathwayofnitrateproducedfromsurplusnitrogeninputstothehydrosphere[J].ProceedingsoftheNationalAcademyofSciencesoftheUnitedStatesofAmerica, 2014, 111(4): 416-416.
Effectsofdairyeffluentsirrigationonyieldandnitrogenuseefficiencyofwinterwheatandsoilnitratenitrogen
DUHui-ying,FENGJie,ZHANGKe-qiang*,WANGFeng,GUOHai-gang
(Institute of Agro-environmental Protection, Ministry of Agriculture of China, Tianjin 300191, China)
【Objectives】Studyontheeffectsofdairyeffluentsongrainyield,nitrogenuseefficiencyandsoilnitratecontentswillprovidetheoreticalbasisfortheassessmentoflivestockeffluentsirrigationonfarmland,soastodecreasetheriskofnitrogenlosefromlivestockeffluents.【Methods】AfieldexperimentusingdairyeffluentsforirrigationinwinterwheatwasconductedsuccessivelyforthreeyearsintheplainofNorthChina.Thestudyincludedfivetreatmentswiththreereplications:Nofertilizerandirrigatedwithfreshwater(CK);twoirrigationwithdairyeffluentsinwinteringandfillingstages,twofreshwaterirrigation,thetotalnitrogenbroughtwitheffluentswas160kg/hm2(T1);threeirrigationwithdairyeffluentsinwintering,jointingandfillingstages,onefreshwaterirrigationinheadingstage,thetotalnitrogenbroughtwitheffluentswas240kg/hm2(T2);fourirrigationwithdairyeffluentsinwintering,jointing,headingandfillingstages,withtotalnitrogenbroughtwitheffluentsof320kg/hm2(T3);andfarmercustomizedfertilization,inorganiccompoundfertilizerwith375kg/hm2afterplanting,and600kg/hm2ureaapplicationatthewheatjointingstageandfreshwaterirrigationinwheatgrowingseason(CF).Thetotalirrigationquotawas830m3/hm2,andtheirrigationquantitywascontrolledbywaterUltrasonicflowmeters.Thesoilnitritenitrogencontentandwinterwheatyieldwereinvestigatedatharvest. 【Results】 1)Thedairyeffluentsirrigationsignificantlyincreasedtheyieldofwinterwheatwhichwasfluctuatedwiththeinputofnitrogenfromtheeffluents,thehighestyieldwasobtainedinthethreedairyeffluentsirrigationswiththeNinputof240kg/hm2. 2)ThenitrogenaccumulationinplantsandgrainsofwheatirrigatedwitheffluentswassignificantlyhigherthanthoseoftheCK.In2011and2012,therewerenosignificantdifferencesinthenitrogenaccumulationsinplantsamongthetreatments,in2013,however,thoseinT2andT3weresignificantlyhigherthaninT1andCF. 3)Withtheincreasingofnitrogenbroughtbydairyeffluents,thenitrogenrecoveryefficiencyandnitrogenagronomicefficiencyweredecreased,withtheaveragevaluesof48.57%and37.15kg/kginT1,respectively. 4)Aftertheharvestofwinterwheat,thesoilnitratenitrogenaccumulationin0-100cmlayerwasincreasedwiththeincreasingofnitrogenamountofdairyeffluents.The0-100cmlayerofsoilnitratenitrogenaccumulationintheT3wassignificantlyhigherthanthoseinT1andT2.【Conclusions】Dairyeffluentsirrigationsignificantlyincreasesthegrainyieldofwinterwheat.Withtheincreaseofnitrogenamountfromdairyeffluents,thenitrogenrecoveryefficiencyandnitrogenagronomicefficiencyofdairyeffluentsaredecreased.Thenitratenitrogenaccumulationin0-100cmsoillayerissignificantlyenhancedwith320kg/hm2ofnitrogenbroughtwiththefourirrigationofdairyeffluents.Thisresultindicatesthatmostofnitrogenisnotutilizedbywinterwheat,mightleachedintodeepsoil.Undertheexperimentconditions,consideringcomprehensively,thepropernitrogenamountbroughtwithdairyeffluentinwinterwheatwas160-240kg/hm2.
dairyeffluents;irrigation;winterwheat;grainyield;nitrogenuseefficiency;soilnitratenitrogen
2014-07-28接受日期: 2015-01-16网络出版日期: 2015-07-06
国家科技支撑计划(2012BAD15B02)资助。
杜会英(1977—),女,河北唐山人,副研究员,博士,从事养殖废弃物面源污染控制和农田安全利用方面研究。
E-mail:duhuiying2008@163.com。*通信作者E-mail:kqzhang68@126.com
S143.1
A
1008-505X(2016)02-0536-06
