病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全可追溯系统的构建与应用
2016-07-18谢菊芳胡肄农贾伟亚
高 绪,谢菊芳,樊 磊,胡肄农,贾伟亚,李 雪
(1西南大学工程技术学院,重庆 400716;2江苏省农业科学院,南京 210014;3江苏涟水县林业局,江苏淮安 223400)
病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全可追溯系统的构建与应用
高绪1,谢菊芳1,樊磊2,胡肄农2,贾伟亚3,李雪1
(1西南大学工程技术学院,重庆 400716;2江苏省农业科学院,南京 210014;3江苏涟水县林业局,江苏淮安 223400)
摘要:【目的】实现病死猪无害化处理运输车辆在无害化处理厂和收集点之间流通的安全追溯。【方法】以病死猪无害化处理运输车辆作为研究对象,系统总体构架由三层结构设计:数据服务层、数据处理层和数据采集层;数据采集层采用北斗/GPS双模用户机、温度传感器、无线射频阅读器、有源电子标签和GPRS无线传输模块组成,实现对病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全可追溯系统(traceability safety system of the transport vehicle for dead pig harmless handling,TSDPHH)运输车辆地理位置信息、车厢温度信息、消毒点车载有源电子标签信息的采集与传输。其中,运输车辆地理位置信息主要使用采集到的北斗导航定位系统数据,当北斗导航定位系统数据出现较大偏差时,将GPS导航定位的WGS-84坐标系数据转换到北斗导航系统的BJ-45坐标系,利用GPS导航定位系统对数据进行修正,实现互补定位,提高运输车辆地理位置信息采集精度;在数据处理层实现对采集到的数据进行提取、修改、储存等操作;数据服务层主要是给工作人员、监控部门提供信息服务。本系统以Visual Studio 2010为集成开发环境,采用C#语言进行系统开发,在数据库SQL server 2008中利用SQL语言实现对数据的存储、修改。【结果】TSDPHH的功能包括线路安全管理、消毒安全管理、温度监控管理、卫生防疫管理和安全预警管理;利用蚁群算法对病死猪无害化处理运输车辆的路径规划进行仿真,合理规避大型养殖厂、人群密集地等规避区域,仿真结果切合实际,为病死猪无害化处理运输车辆在指定运输区域进行合理路径规划提供参考。TSDPHH为无害化处理厂的工作人员提供了实现运输车辆行走线路监测、运输车辆智能调配、车厢温度监控、车辆信息查询等管理功能,系统在江苏省涟水县病死猪无害化处理厂试点基地进行实地测试,测试表明系统硬件模块工作稳定,网络丢包率为0.26%,车载有源电子标签识别误差率为0.97%;通过运输车辆行走线路ArcGIS监控管理功能模块,对运输车辆进行连续2 h行走路线实时监控,并且对温度监控管理、消毒安全管理等功能模块进行测试,系统各个模块工作正常,能够满足TSDPHH运行要求;同时,通过监控客户端实现以电话、网络、短信的方式为动物卫生防疫的监控管理部门提供服务,将TSDPHH监测数据(车辆行走线路、车厢温度等信息)实时推送给监管部门,实现对病死猪无害化处理运输车辆进行全方位监督管理,保证动物卫生安全。【结论】为病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全管理提供了有效手段,实现对病死猪无害化处理运输车辆实行全方位监督管理,合理规避动物卫生安全事件的发生,并给其他病死猪无害化处理综合管理系统的开发提供了参考与借鉴。
关键词:病死猪;无害化处理;车辆监控;可追溯系统;无线识别技术;北斗/GPS卫星导航
联系方式:高绪,Tel:15723278639;E-mail:401701638@qq.com。通信作者谢菊芳,E-mail:xjufang0311@qq.com
0 引言
【研究意义】病死猪无害化处理是畜禽养殖清洁生产关键环节之一。农业部《关于进一步加强病死动物无害化处理监管工作的通知》中提出,各地畜牧兽医部门要扎实做好病死动物无害化处理监控管理工作[1-2]。目前,病死猪无害化处理是防止动物疫病扩散、有效控制和扑灭动物疫情、防止病原体扩散的重要举措和最有效方法[3-4]。截至 2014年 6月,中国生猪的存栏量为42 895万头,每年因病死的生猪数量为2 144.75万头,如果这类病死猪产品利用不正规渠道流入市场,不仅给消费者身心健康带来极大的影响,而且对畜牧市场会造成很大冲击[5]。因此,实现病死猪无害化处理车辆安全追溯体系具有重要意义:一是保证运输安全,规避动物卫生安全事件的发生;二是强化病死猪无害化处理厂的企业责任,保障卫生安全;三是加强政府监管,当出现问题时能够迅速追其根源。【前人研究进展】追溯系统在国外的发展相对来讲比较完善。起因是1985年英国发现疯牛病(BSE)以来,短短十来年时间,疯牛病相继在法国、德国、爱尔兰、西班牙、意大利、瑞士、荷兰和丹麦等 20多个国家发生,成为让全球恐慌的重要动物疫病[6]。因此,20世纪90年代,欧盟率先通过管理与动物标识的实施,在肉类企业和加工业生产中,采用结合危害分析和关键控制点HACCP(Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point)、良好操作规范GMP(Good Manufacturing Practice)与国际标准化组织制定的质量保证系列标准 ISO 9000 (International Organization For Standardization)规范的前提下,促进食品信息可追溯系统的建立,来提高食品安全性[7]。可追溯系统的定义按照国际食品法典委员会的一个特别委员会的阐述为“食品生产、加工、贸易各个阶段的信息流的连续性保障体系”[8]。2002年,美国与加拿大也分别对食品安全的跟踪与溯源提出了“生物反恐法案”与“品牌加拿大战略”[9-10]。2003年7月,欧盟国家正式发布了食品安全的白皮书,对肉制品和家禽实施追溯体系的建立[11],针对水产品制定了追溯计划[12]。澳大利亚通过牲畜标识计划(NLIS),将家畜从出生到屠宰的信息全部保存在数据库中,以实现家畜产品的全程追溯[13]。韩国国会于2007年12月公布了牛与牛肉可追溯性法案,对每一头牛都要求能够识别有全程追溯的 ID号,实现牛与牛肉产品的全程追溯[14]。中国与国外相比,在产品追溯上还存在着很大的差距,但是针对肉制品、水产品、蔬菜、粮油等农产品的追溯体系的建立也取得了不少进展。2008年北京奥运会举办期间,对奥运食品安全实施全程监控和追溯体系建立[15]。2015年9月河北省对包装熟肉制品、保健食品、婴幼儿产品以及酒类商品进行电子追溯,建立了河北省食品安全追溯电子平台[16]。近年来,陆昌华等[17]利用SQL Server 2000和VB.NET应用在猪肉安全生产追溯系统中,实现了工厂化猪肉的信息可追溯系统。任守纲等[18]利用RFID与GIS物联网技术,实现肉制品的跟踪追溯系统的搭建。杨信廷[19]、钱建平[20]等对水产品与蔬菜、水果等农产品进行了追溯溯源管理系统的建立与应用。【本研究切入点】运输车辆作为病死猪无害化处理中最为重要的部分。针对病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全的追溯与管理可以有效规避动物卫生安全事件的发生,特别是对畜牧业大国来说,具有无法替代的作用,但国内尚未见病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全追溯方面的研究报道。【拟解决的关键问题】以病死猪无害化处理运输车辆的运输为主线,通过研究分析整个过程中车辆安全关键因素,开展跟踪与追溯关键技术的研究,构建病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全可追溯系统(traceability system for the vehicle safety of dead pig harmless handling,TSDPHH)框架,实现病死猪无害化处理运输车辆的全程信息追溯。
1 系统总体框架设计
1.1 系统目标
构建TSDPHH的框架,从病死猪无害化处理运输车辆监控管理的实际情况出发,设计运输车辆全程跟踪与溯源框架。终端采集系统采用北斗/GPS双模用户机、温度传感器和GPRS无线传输模块实现。利用蚁群算法对病死猪无害化处理运输车辆行走路径进行规划,合理规避大型养殖基地,避免所在地区有动物疫情的可能。
1.2 系统构架
TSDPHH针对规模化的病死猪无害化处理厂,在运输环节中对车辆的线路、消毒、环境参数等各个环节业务流程的分析,采用HACCP与故障模型效应和关键分析(failure mode effect and criticality analysis,FMECA)方法[21-22],提出病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全的关键要素,设计终端采集系统,获取运输车辆全过程的信息采集、传输与保存,构建包含线路安全、消毒安全、温度监控、防疫管理和预警管理等功能的TSDPHH平台,除了满足病死猪无害化处理厂运输车辆内部管理与追溯要求外,开发了基于短信、电话、邮件的安全监控管理接口,当病死猪无害化处理运输车辆在实际的运输过程出现行驶线路偏离、不按照指定消毒通道进行消毒、车厢温度较高等违反病死猪无害化处理运输车辆工作章程的时候,通过TSDPHH向政府卫生防疫部门发送邮件、短信等提醒,为卫生防疫部门对本地区病死猪无害处理运输车辆安全运输的实时监控、监督管理提供有效手段。
同时,该系统采用数据服务层、数据处理层和数据采集层3个层次进行设计。数据采集层主要由病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全关键因素指标的选取,为实现 TSDPHH提供数据支持;数据处理层由信息采集、无线传输、信息交换以及相关硬件的开发,为TSDPHH提供硬件支撑;数据服务层由短信、网络、邮件等多种方式为监管部门提供病死猪无害化处理运输车辆的安全信息进行监管与督查服务。图1表示系统总体框架。
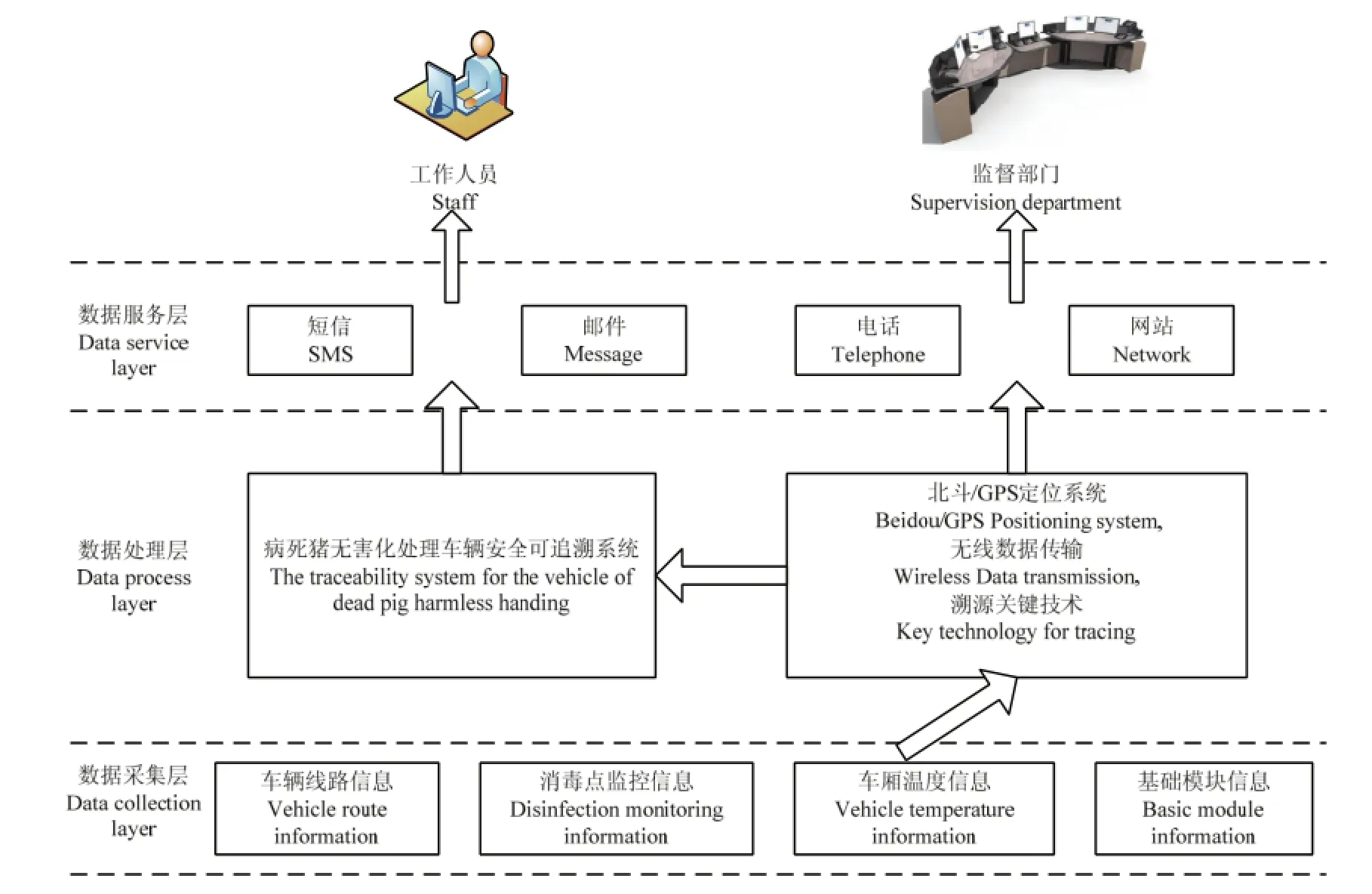
图1 病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全可追溯总体框架Fig. 1 System architecture diagram for the vehicle of dead pig harmless hand tracing
1.3 系统功能设计
TSDPHH由线路安全管理、消毒安全管理、温度监控管理、卫生防疫管理和安全预警管理5个子系统组成。线路安全管理系统主要是对运输车辆的行走路线进行实时监控,并可实时查询追溯历史数据;消毒安全管理系统是病死猪无害化处理运输车辆在消毒点进行消毒监控管理数据的查询追溯;温度监控管理系统主要是对运输车辆车厢内环境温度进行实时监控、查询;卫生防疫管理系统主要是针对运输车辆及其工作人员按照病死动物无害化处理技术规范中的要求,对运输车辆、操作工具和工作人员进行检疫管理,实时记录检疫记录,方便以后追溯和查询;安全预警管理是针对运输车辆在运输过程出现线路偏差、轿厢温度较高情况下进行安全预警。
2 系统构建的关键技术
2.1 卫星导航技术
卫星导航系统是建立TSDPHH的前端,它是溯源过程信息采集与处理的基础。
北斗/GPS双模用户机主要是完成运输车辆线路信息的采集,采集运输车辆的位置信息:经度、纬度、高度。系统采用UM220-III北斗/GPS双系统导航授时模块,模块可以提供两种导航信息。一种是GPS导航定位信息,另一种是北斗导航定位信息,但是两种导航定位采用的坐标系并不相同。北斗导航定位采用是BJ-45坐标系,而GPS导航定位采用的WGS-84坐标系,将WGS-84坐标系转化成直角坐标系后,再转化成BJ-45坐标,实现两种定位算法坐标系的相互转化,大地坐标系转化成直角坐标系如公式(1)所示[23-26]。
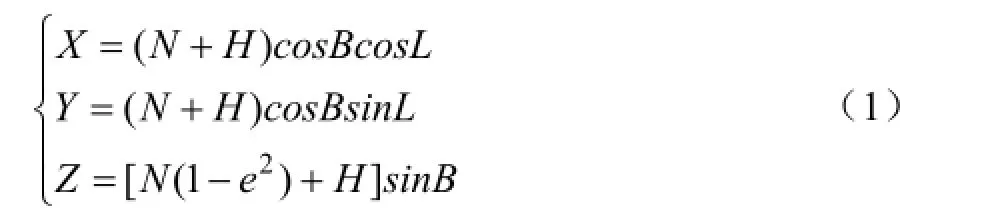
式中L代表位置所在的经度(°);B代表位置所在的纬度(°);H代表位置高程(m);N代表该处的卯酉圈曲率半径(m),N=α/(1-e2sin2B)1/2;α表示该大地坐标系中对应椭球的长半轴(m);e为第一偏心率。系统采用北斗导航定位系统作为主要导航算法,当北斗导航系统出现偏差时,利用GPS导航定位算法进行修正,实现互补定位。
2.2 路径规划技术
病死猪无害化处理运输车辆在运输的过程中,根据当前的收集任务合理规划路径,寻求一条距离近、安全性高的线路进行运输,能够合理的规避运输车辆的生物安全问题,避免给周围环境带来二次污染。
2.2.1 蚁群算法 路径规划是指在有障碍物的环境中,按照一定的评价标准,寻找一条从起始状态到目标状态无碰撞的路径。蚁群算法是由意大利学者Dorigo等观察到蚂蚁在觅食的过程中食物与蚁穴之间的行走线路既不是曲线也不是其他形式,而是几乎近似的直线,利用这一现象发现蚁群拥有较好的路径寻优能力[27-29]。TSDPHH需要运输车辆合理的规避运输区域内大型的养殖基地,又要选择最短的运输路径,适合蚁群算法的基本原理。
2.2.2 路径规划算法分析 病死猪无害化处理运输车辆的路径规划属于二维路径规划问题,利用MAKLINK图论建立路径规划的二维空间[30-31],初始化路径规划采用 Dijkstra算法规划出一条从起点到终点的初始路径,图上依次通过路径节点的一条次优路径。通过Dijkstra算法得到路径经过自由连接线时,只要通过一组不同的划分节点就可以得到一条新的路线,采用蚁群算法需要将工作空间进行离散化,由于初始化选择的自由连接线不同,因此,采用固定距离划分法,设定划分长度,对每条线路进行划分。蚁群寻优寻找路径参数集合,使得在空间中得到最短的路径,假设有m只蚂蚁从起点S出发到终点T,循环路径可以表示为:S→n1j→n2j……ndj→T,其中,ndj代表d条连接线上的第j个等分点上,在移动的过程中,当蚂蚁选择下一个连接点j的方法如式(2)所示:

式中,i为连接线上所有的点的集合,q为 [0,1] 区间内的随机数,q0为[0,1]区间内的可调参数;ηi,j为启发值,τi,k为信息素。j的计算方式:首先一次计算当前连接线节点i到下条连接线节点j的选择概率Pij,然后选择概率Pij,采用轮盘赌法找出下一个节点 j,其中Pij的计算公式如式(3)所示。

通过对实时信息素和路径信息素更新实现路径寻优的依次迭代,实时信息素更新是指每一只蚂蚁在选择一个节点后必须对该节点的信息素进行更新,更新公式如(4)所示。

其中,τ0为信息素的初始值;ρ为[0,1]区间内可调参数。当所有蚂蚁走完从初始点到终点完成依次迭代后,选择所有蚂蚁经过最短的一条更新该条路径上的每一个点的信息素。按照公式(5)进行更新。
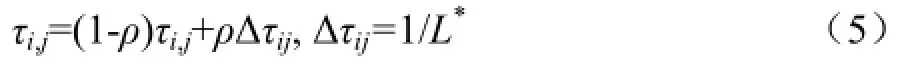
其中,L*为最短路径的长度,ρ为[0,1]区间内可调参数。
2.2.3 路径规划算法仿真 首先使用Dijkstra算法生成初始次优路径,其次将运输车辆所走区域内大型养殖场进行坐标设置在图中用红色填充图来表示,利用蚁群算法求解全局最优路径,每条链路均离散化为10小路段,种群个体数为10,个体长度为6,算法迭代次数为500次,图2为规划的初始路径图,图3表示蚁群算法适应度曲线。

图2 规划初始路径Fig. 2 The initial path planning
由图3可知经过500次迭代后,输出最优距离值为173.8157 km,具有较好的鲁棒性,收敛性较好。
2.3 可追溯系统软件开发技术
TSDPHH采用 5层软件管理信息系统的开发模式,主要可以分成:数据采集层,数据库层,业务逻辑层、网络传输层与操作层组成[13,32-34],其软件结构框架如图4所示。
2.3.1 服务端的开发环境 运行平台:Windows 7/Windows XP + SQL server 2008 + IIS7.0组成,采用NET Framework 4.0框架。数据库:Microsoft SQLServer 2008。开发语言:C#。
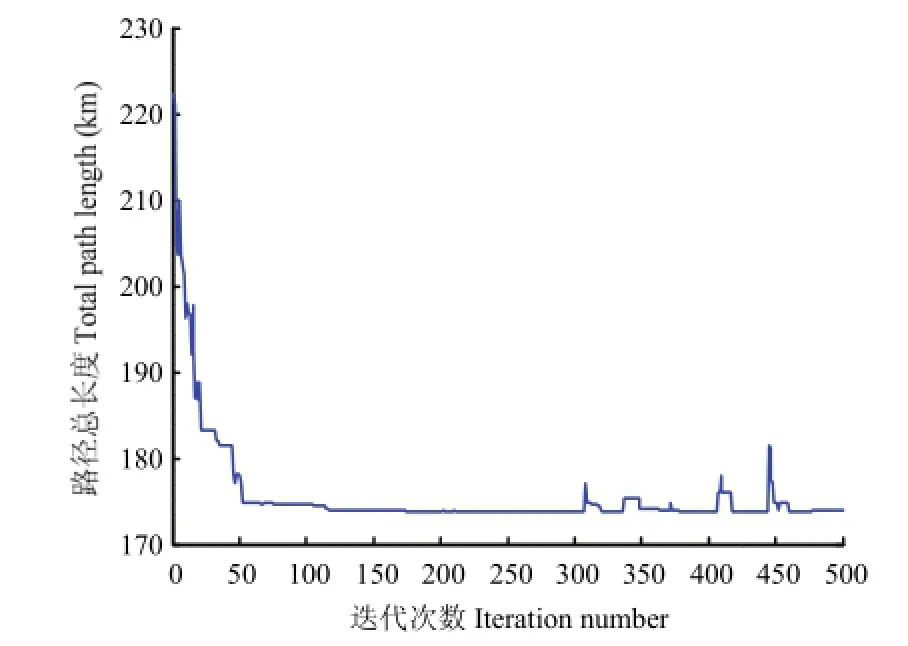
图3 蚁群算法适应度曲线Fig. 3 Ant colony algorithm fitness curves
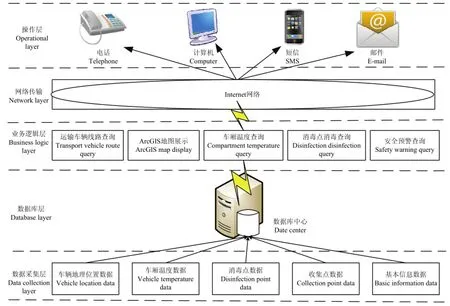
图4 TSDPHH软件框架Fig.4 The software framework for the vehicle of dead pig harmless hand tracing
2.3.2 客户端开发环境 系统开发平台:Visual studio 2010,NET Framework 4.0框架。开发语言:C#。
2.3.3 ArcGIS线路显示 系统利用ArcGIS对车辆线路的安全追溯进行开发,通过SQL Server 2008进行车辆地理位置数据进行管理,ArcSDE将地图数据存放在 SQL Server 2008数据库中,通过 Personal Geodatabase管理,将地图数据通过Shapefile格式存放在文件夹中。地图的浏览、空间查询、监控管理等GIS功能模块的实现主要是通过ActiveX DLL工程中实现,模块中的小功能点通过类来实现,可以为各个功能设置自己的图标、命名、有效性等,然后将多个命令集合成接口[35-37]。
3 系统实现
3.1 数据采集软件实现
TSDPHH的数据采集软件是visual Studio 2010系统开发环境下采用C#语言建立Windows窗体应用程序,实现对运输车辆地理位置信息、车厢温度、消毒点消毒信息的读取、存储,通过GPRS无线数据传输终端实现采集数据的远程传输,消毒点消毒数据的采集主要是通过在消毒点的消毒通道上安装射频无线阅读器对车载射频卡进行读取。GPRS无线传输模块采用济南有人物联网有限公司生产的 GPRS DTU无线数传终端,通过GPRS网络,将数据传送至网络之中拥有公网固定 IP地址的服务器[38-41],并且可以通过该模块实现车辆安全预警的通知,通过对该模块进行AT指令的配置,实现运输车辆脱离安全轨道、车厢温度较高等情况时,自动拨号、发送短信通知工作人员和监管人员。数据采集软件的界面图如图 5所示。
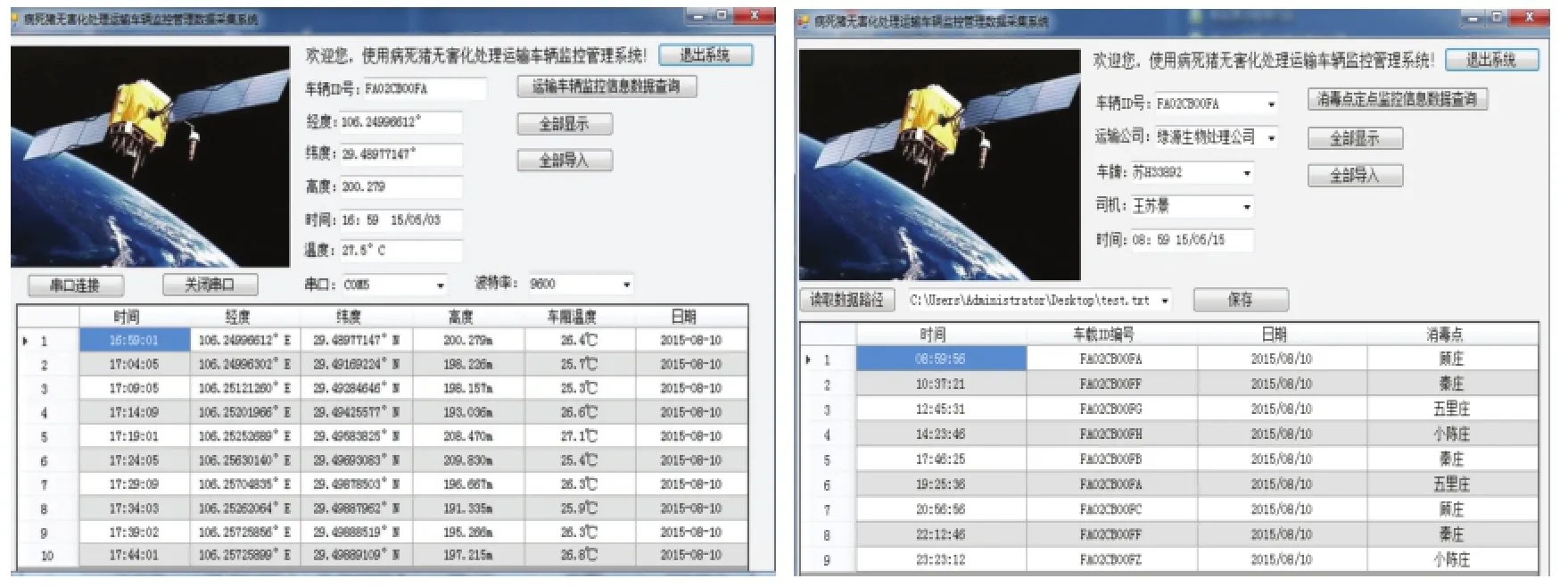
图5 数据采集软件界面Fig. 5 The interface of data acquisition
3.2 ArcGIS实现
2015年8月15日,在江苏省淮安市涟水县病死猪无害化处理厂试点基地进行实地测试,病死猪无害化处理在各个不同的收集点间流通时还需要在指定的消毒站进行定点消毒(每15 km处设定一个消毒点),确保运输车辆的安全,合理规避污染源。车载终端采集系统与北斗卫星建立通信后,运输车辆以30 km·h-1的速度匀速行前进,运行线路全程约为65 km,需要经过4个消毒点。系统试验时设定采集系统每隔1 min传输一次数据,连续监测2 h,测试的结果如表1所示,由表1可知终端采集系统网络丢包率为0.26%。

表1 网络丢包率统计Table 1 PLR values of Beidou

表2 车辆识别率测试统计Table 2 test of vehicle identification
从2015年8月15日至2015年8月19日进行了连续5 d的不间断采集,对消毒点的车载电子标签的有效识别率进行统计,试验结果如表2所示,车辆电子标签的识别误差率为 0.97%,系统识别率高,稳定可靠。
试验表明,终端数据采集系统在连续2 h的线路监测中未出现硬件故障,系统运行稳定可靠,能够满足TSDPHH的线路采集的要求;消毒点对运输车辆可进行有效识别,车辆识别误差率低,且系统通信稳定可靠。通过 ArcGIS实现对运输车辆行驶线路的实时追溯与预警,方便监管人员对运输车辆的行驶路线进行安全追溯与查询,车辆运行线路如图6所示。

图6 车辆运输线路可追溯系统界面Fig. 6 The Vehicle transportation line traceability system
4 讨论
4.1 卫星导航定位的实现途径
卫星导航技术与无线传输技术是 TSDPHH建立的基础。本研究主要在淮安市涟水县病死猪无害化处理厂,针对病死猪无害化处理厂运输车辆在向各个区县以下各个收集点之间流通过程进行安全追溯。本系统采用北斗/GPS双模用户机作为导航定位的数据采集装置,对运输车辆在流通过程中导航定位数据的采集。系统运行的结果与单一的GPS定位导航方法相比[24,42-43],具有明显的优势。针对涟水县城乡公路导航数据采集上准确度较高,线路偏离误差小。本系统在导航定位数据远程传输上采用北斗一代卫星特有的短报文通信功能,将导航定位装置采集到的数据传输至远程监控管理中心,通过系统测试,网络丢包率仅为 0.26%,系统整体运行稳定可靠。此外,笔者对前人文献[12-26]中采用GSM、GPRS无线传输方式进行了对比分析,发现采用北斗短报文通信功能进行数据的远程传输,不受传统基站的影响,且全天候24 h运行,通信稳定、可靠。由此可见采用北斗/GPS作为病死猪无害化处理运输车辆的地理位置信息数据采集与传输装置能满足病死猪无害化处理运输车辆监控的需求,并且系统运行安全可靠,也为未来国产化软件深度开发及数据共享服务提供可能。
4.2 消毒点识别的实现途径
TSDPHH中车辆的生物安全消毒是至关重要的一个部分,本系统研究测试是以涟水县病死猪无害化处理厂运输车辆到涟水县内最大的商品猪生产厂家康源慕德猪场作为测试线路,沿途需要经过 4个定点消毒站,对病死猪无害化处理运输车辆安全可追溯系统中,采用运输车辆指定消毒站定点消毒监控与追溯是保证生物安全的重要关口。本系统在消毒站的消毒通道上安装无线射频阅读器,在运输车辆上放置有源电子标签,对消毒点运输车辆流通进行定点监控与数据采集。系统运行结果与国内采用车牌识别研究比较[44-45]:前者车牌识别率为 97%,后者车牌识别率为 98%,本系统采用的消毒点运输车辆识别误差率仅为0.97%。由此可见,利用无线射频识别技术对运输车辆在消毒站进行定点监控,系统运行的可靠性较高。
5 结论
作为病死猪无害化处理中的核心组成部分,病死猪无害化处理运输车辆的安全问题直接影响到整个无害化处理工作开展的成效。以病死猪无害化处理运输车辆作为研究对象,采用卫星导航技术、路径规划技术、可追溯系统软件开发技术,建立了全方位、多层次的TSDPHH。本系统可以通过网络、短信、电话、邮件等多种方式向工作人员、政府卫生防疫监管部门提供服务。该系统还利用蚁群算法对运输区域内合理选择运输线路与规避大型养殖基地的情况进行仿真,并且可以通过邮件、电话、短信多种手段实现运输车辆的预警管理,规范了病死猪无害化处理的过程,提高了政府监管的监督能力,优化了管理效率。
References
[1] 农业部关于进一步加强病死动物无害化处理监管工作的通知. http://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/201204/t20120410_2599643.htm Notice of the further strengthens and supervision of the handling of the dead animals of ministry of agriculture department of China. http://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/201204/t20120410_2599643.htm
[2] 沈立君, 赵立欣, 孟海波. 我国病畜禽无害化处理现状与对策. 中国农业科技导报, 2013, 15(6): 167-173. SHEN L J, ZHAO L X, MENG H B. Present statue of harmless disposal of dead livestock and poultry in China and counter-measure. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013, 15(6): 167-173. (in Chinese)
[3] 宋建德, 黄保续, 袁丽萍, 姜雯, 王媛媛, 孙淑芳, 魏荣. 有关国家常用病死动物无害化处理方法应用情况研究. 中国动物检疫, 2013,30(9): 11-15. SONG J D, HUANG B X, YUAN L P, JIANG W, WANG Y Y, SUN S F, WEI R. Common method for carcass disposal in some countries. China Animal Health Inspection, 2013, 30(9): 11-15. (in Chinese)
[4] 刘思华, 王琦, 郑文成, 张思圆. 湖南省病死动物无害处理工作调研. 中国动物检疫, 2014, 31(12): 13-15. LIU S H, WANG Q, ZHEN W C, ZHANG S Y. Investigation on biosafety disposal of animals died of disease in Human province. China Animal Health Inspection, 2014, 31(12): 13-15. (in Chinese)
[5] 陈翠, 孙德林, 贾海燕, 崔蓉. 全国养猪形势月报. 猪业月报, 2014,2(7): 11-18. CHEN C, SUN D L, JIA H Y, CUI R. The national pig situation monthly report. Pig Industry Monthly Report, 2014, 2(7): 11-18. (in Chinese)
[6] 林荣泉. 关于英国疯牛病风波的来龙去脉. 肉类工业, 2001, 244(9):35-38. LIN R Q. The history of the Britain's BES. Meat Industry, 2001,244(9): 35-38. (in Chinese)
[7] 王立方, 陆昌华, 谢菊芳, 胡肄农. 家畜和畜产品可追溯系统研究进展. 农业工程学报, 2005, 21(7): 168-174. WANG L F, LU C H, XIE J F, HU S N. Review of traceability system for domestic animals and livestock products. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2005, 21(7): 168-174. (in Chinese)
[8] 殷俊峰, 陶运来, 刘铁兵, 陈书梅, 俉玉菡, 董军, 田素润, 柯立良.食品可追溯系统建设之处探. 安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(27):11985-11987. YIN J F, TAO Y L, LIU T B, CHEN S M, WU Y H, DONG J, TIAN S R, KE L L. Study on food traceability system construction. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science. 2008, 36(27): 11985-11987. (in Chinese)
[9] 陆昌华, 王长江, 胡肄农. 动物及动物产品标识技术与可追溯管理.北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2007: 35-37. LU C H, WANG C J, HU S N. Identification and Traceability System for Animals and Animal Products. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Science and Technology Press, 2007: 35-37. (in Chinese)
[10] 程浩. 畜产品安全控制与溯源技术研究的探讨. 现代农业科技,2007(13): 169-170. CHENG H. Animal product safety control and traceability technologies. Modern Agriculture Science and Technology, 2007(13):169-170. (in Chinese)
[11] 陆昌华, 王长江, 何孔旺. 动物卫生及其产品风险分析. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2011: 6-7. LU C H, WANG C J, HE K W. Animal Health and Risk Analysis. Beijing: Chinese Agriculture Science and Technology Press, 2011: 6-7. (in Chinese)
[12] 颜波, 石平, 黄广文. 基于RFID和EPC物联网的水产品供应链可追溯平台开发. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(15): 172-183. YAN B, SHING P, HUANG G W. Development of traceability system of aquatic foods supply chain based on RFID and EPC internet of things. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(15): 172-183. (in Chinese)
[13] 郑火国, 刘世洪, 孟泓, 胡海燕, 苏晓路. 粮油产品质量安全可追溯系统构建. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(9): 3243-3249. ZHENG H G, LIU S H, MENG H, HU H Y, SU X L. Construction of Traceability system for quality safety of cereal and oil products. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2009, 42(9): 3243-3249. (in Chinese)
[14] 丰城金桥商贸网. 韩国牛与牛肉可追溯性法案. http://www.fcjqsm. gov.cn/fengcheng/viewNews.do?id=5948662. Trade web of FengCheng JinQiao. The bill of traceability of Korea's cattle and beef. http://www.fcjqsm.gov.cn/fengcheng/viewNews.do?id= 5948662. (in Chinese)
[15] 闫燕. 盘点2008中国食品安全重要经历. 食品安全导刊, 2009(1):21-29. YAN Y. Inventory of 2008 Chinese food safety important experience. Food Safety Guide, 2009(1): 21-29. (in Chinese)
[16] 林果质量监督检验网. http://www.lgzj.gov.cn/fcms/. Fruit quality supervision and inspection network. http://www.lgzj.gov. cn/fcms/.(in Chinese)
[17] 陆昌华, 谢菊芳, 王立方, 胡肄农, 白云峰, 时勇, 薛启奎, 李保生. 工厂化猪肉安全生产溯源数字系统的实现. 江苏农业学报,2006, 22(1): 51-54. LU C H, XIE J F, WANG L F, HU Y N, BAI Y F, SHI Y, XUE Q G, LI B S. Completion of digital tracing system for safety of factory pork Production. Jiangsu Journal of Agriculture Sciences, 2006, 22(1):51-54. (in Chinese)
[18] 任守纲, 徐焕良, 黎安, 周光宏. 基于 RFID/GIS物联网的肉品跟踪及追溯系统的设计与实现. 农业工程学报, 2010, 26(10):229-235.REN S G, XU H L, LI A, ZHOU G H. Meat-productions tracking and traceability system based on internet of things with RFID and GIS. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(10): 229-235. (in Chinese)
[19] 杨信廷, 钱建平, 孙传恒, 吉曾涛. 农产品及食品质量安全追溯系统关键技术研究进展. 农业机械学报, 2014, 45(11): 213-222. YANG X T, QIAN J P, SUN C H, JI Z T. Key technologies for establishment agricultural products and food quality safety traceability systems. Translations of the Chinese Society for Agriculture Machinery,2014, 45(11): 213-222. (in Chinese)
[20] 钱建平, 杨信廷, 张保岩, 吴晓明, 薛彬. 基于RFID的蔬菜产地追溯精确度提高方案及应用. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(15): 234 -239. QIAN J P, YANG X T, ZHANG B Y, WU X M. RFID-based solution for improving vegetable producing area traceability precision and its application. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(15): 234-239. (in Chinese)
[21] MASSIMO B, MAURIZIO B, ROBERTO M. FMECA approach to product traceability in food industry. Food Control, 2004, 17(9):137-145.
[22] 康锐. FMECA技术及其应用. 北京: 国防大学出版社, 2006. KANG R. FMECA Approch and Its Application. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[23] STEPHANE H, MOHAMMED Q, NADINE R S, ANDREW D. Developing advanced route choice models for heavy goods vehicle using GPS data. Transportation Research Part E, 2015, 77: 29-44.
[24] 刘爽, 贾传荧, 贾银山, 马文耀. 基于 GPS/GSM 和电子地图的车辆定位系统设计与实现. 辽宁石油化工大学学报, 2005, 25(1):82-85. LIU S, JIA C Y, JIA Y S, MA W Y. Design and implementation of vehicle monitoring system based on GPS/GSM and electronic map. Journal of LiaoNing University of Petroleum & Chemical Technology,2002, 25(1): 82-85. (in Chinese)
[25] QU X H, ZHUANG D F, QIU D S. Studies on GIS based tracing and traceability of safe crop product in China. Agricultural Science in China (English), 2007, 6(6): 724-731.
[26] 刘碧贞, 黄华, 祝诗平, 向必万. 基于北斗/GPS的谷物收割机作业综合管理系统. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(10): 204-210. LIU B Z, HUANG H, ZHU S P, XIANG B W. Integrated management system of grain combine harvester based on Beidou & GPS. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(10): 204-210. (in Chinese )
[27] 段海滨, 王道波, 朱家强, 黄向华. 蚁群算法理论及应用研究的进展. 控制与决策, 2004, 19(12): 1321-1326. DUAN H B, WANG D B, ZHU J Q, HUANG X H. Development on ant colony algorithm theory and its application. Control and Decision. 2004, 19(12): 1321-1326. (in Chinese)
[28] 刘志硕, 申金升, 柴跃廷. 基于自适应蚁群算法的车辆路径问题研究. 控制与决策, 2005, 20(5): 562-566. LIU Z S, SHEN J S, CHAI Y T. Vehicle routing problem based on an adaptive ant colony algorithm. Control and Decision, 2005, 20(5):562-566. (in Chinese)
[29] MOHAMED M A, YUVRAJ G, TAREK Y E. Hybridized ant colony algorithm for the multi compartment vehicle routing problem. Applied Soft Computing, 2015(37): 196-203.
[30] 赵冬玲, 杨艳, 潘正运. 一种车辆路径规划的新型蚁群算法研究.电子器件, 2014, 37(3): 519-523. ZHAO D L, YAN Y, PAN Z Y. The research of an newly ant colony algorithm of vehicle of vehicle route planning. Chinese Journal Electron Devices, 2014, 37(3): 519-523. (in Chinese)
[31] 王飞, 王红勇. 基于 Malink图和遗传算法的改航路径规划方法研究. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2014, 14(5): 154-160. WANG F, WANG H Y. A Re-routing path planning method based on Maklink graph and GA algorithm. Journal of Transportation System Engineering and Information Technology, 2014, 14(5): 154-160. (in Chinese)
[32] 许世卫, 王东杰, 李哲敏. 大数据推动农业现代化应用研究. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(17): 3429-3438. XU S W, WANG D J, LI Z M. Application research on big data promote agricultural modernization. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015,48(17): 3429-3438. (in Chinese)
[33] 谢菊芳, 胡肄农, 胡东, 陆昌华. 动物卫生风险评估数据库系统的构建与应用. 江苏农业学报, 2014, 30(5): 1095-1101. XIE J F, HU S N, HU D, LU C H. Establishment and application of animal health risk assessment database system. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 30(5): 1905-1101. (in Chinese)
[34] 戴建国, 王克如, 李少昆, 赖军臣, 肖春华, 李栓明, 王琼. 基于REST架构和 XML的农情数据共享研究. 中国农业科学, 2012,45(20): 4156-4165. DAI J G, WANG K R, LI S K, LAI J C, XIAO C H, LI S M, WANG Q. Research on agricultural data sharing based on REST and XML. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(20): 4156-4165. (in Chinese)
[35] ZHANG S L, HUANG X B. Development of virtual campus system based on ArcGIS. Physics Procedia, 2012, 33: 1133-1139.
[36] 康玲, 傅俊峰, 王怀清, 蔡劲松. 基于ArcGIS Server 的WebGIS应用系统的开发. 水电能源科学, 2007, 25(1): 26-29.KANG L, FU J F, WANG H Q, CAI J S. Development of WebGIS based on ArcGIS server. Water Resource and Power, 2007, 25(1):26-29. (in Chinese)
[37] 吴彤, 倪绍祥, 张春晖, 吴小铭. 基于ArcGIS Server的气象设备监控系统的设计与实现. 地理信息科学学报, 2011, 13(1): 80-87. WU T, NI S X, ZHANG C H, WU X M. Design and implementation of the system for atmospheric equipment monitoring based on ArcGIS Server technique. Journal of GEO-Information Science, 2011, 13(1):80-87. (in Chinese)
[38] 肖新清, 齐林, 傅泽田, 张小栓. 基于压缩感知的鲜食葡萄冷链物流监测方法. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(22): 259-266. XIAO X Q, QI L, FU Z T, ZHANG X S. Monitoring method for cold chain logistics of table grape based on compressive sensing. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(22): 259-266. (in Chinese)
[39] RAUL L, LAURA P, GABRIEL V, SEPTIMIU M, OTILIA B S. Implementation of a GPRS based remote water quality analysis instrumentation. Measurement, 2015(65): 81-93.
[40] 韩文霆, 吴普特, 郁晓庆, 张增林, 李鼎. 农业环境信息无线传感器网络监测技术研究进展. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(S12): 326-330. HAN W T, WU P T, YU X Q, ZHANG Z L, LI D. Research progress in wireless sensor network for agriculture environment monitoring. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(S12): 326-330. (in Chinese)
[41] 罗红品, 李光林, 杨芳. 柑橘根系不同深度温度和湿度远程实时监控系统研究. 西南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 35(12): 131-138. LUO H P, LI G L, YANG F. Research on remote real-time monitoring system for the Rhizosphere temperature and humidity of in a citrus garden. Journal of Southwest University: Natural Science Edition,2013, 35(12): 131-138. (in Chinese)
[42] 苏洁, 周东方, 岳春生. GPS车辆导航中国的实时地图匹配算法.测绘学报, 2001, 35(3): 252-256. SU J, ZHOU D F, YUE C S. Real-time map-matching algorithm in GPS navigation system for vehicles. Act Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2001, 35(3): 252-256. (in Chinese)
[43] 徐和平, 徐德军, 钟美. 基于电子地图的 GPS车辆导航系统研究.地理空间信息, 2005, 3(4): 39-40, 66. XU H P, XU D J, ZHONG M. GPS Vehicular navigation system in electronic map. Geospatial Information, 2005, 3(4): 39-40, 66. (in Chinese)
[44] 胡爱明, 周孝宽. 基于先验知识的红外图像汽车牌照定位方法. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2003, 29(2): 128-131. HU A M, ZHOU X K. Infrared image car license plate location method based on apriori knowledge. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2003, 29(2): 128-131. (in Chinese)
[45] 骆雪超, 刘桂雄, 冯云庆, 申柏华. 一种基于车牌特征信息的车牌识别方法. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 31(4): 70-73. LUO X C, LIU G X, FENG Y Q, SHEN B H. A Vehicle license plate Recognition method based on the characteristic on vehicle license plate. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2003, 31(4): 70-73. (in Chinese)
(责任编辑 赵伶俐)
Construction and Application of a Traceability System for the Vehicle Safety of Harmless Handling of Pigs Die of Diseases
GAO Xu1, XIE Ju-fang1, FAN Lei2,HU Yi-nong2, JIA Wei-ya3, LI Xue1
(1School of Engineering and Technology, Southwest University, Chongqing 400716;2Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Nanjing 210014;3Lianshui County Forestry Bureau, Huai'an 223400, Jiangsu)
Abstract:【Objective】 The purpose of the study was to trace vehicles for the transport and harmless handling of pigs die ofdiseases from the harmless treatment plant to the circulation of safety traceability between collection points. 【Method】The system takes the transport vehicle for the harmless treatment of dead pigs as the research object. The system frame is designed with a three layer structure: a data service layer, a data processing layer, and a data collection layer. The data collection layer is composed of Beidou/GPS dual mode receiver, a temperature sensor, a wireless radio frequency reader, an active electronic label, and a GPRS wireless transmission module. The study sought to collect the transport vehicle location information, compartment temperature information, and disinfection point vehicle active electronic tag information of the traceability safety system of the transport vehicle for harmless handling of dead pigs, and then transfer this data. The location information of the transport vehicle is mainly gathered by use of the collected data of the Beidou navigation and positioning system. The GPS navigation and positioning data from the WGS-84 coordinate system was converted to the BJ-45 coordinate system of the Beidou navigation and positioning system, and the GPS navigation and positioning system was used to modify the data when the Beidou navigation positioning system data appeared to show a larger deviation, to achieve the purpose of improving the acquisition accuracy of the transport vehicle location information. The data processing layer was implemented to extract, modify, and store the collected data. The data service layer mainly provided information services for the staff and monitoring department. This system was developed by using C# language in a Studio Visual 2010 integration environment and using SQL language to store and modify the data in the database server SQL 2008. 【Result】 The function of the system includes route safety management, disinfection safety management, temperature monitoring, control management, health and epidemic prevention management, and safety pre-warning management. An ant colony algorithm was used to carry out the simulation of transport vehicle path planning for the harmless handling of dead pigs away from large farms, living groups, and other areas in the driving region. The simulation result was realistic, and it provides a reference for transport vehicles for the harmless handling of dead pigs to plan a reasonable path in the designated transport area. The traceability safety system of the transport vehicle for the harmless handling of dead pigs provides management staffs of harmless treatment plants with monitoring of transport vehicles, intelligent allocation of transport vehicles, compartment temperature monitoring, and vehicle information query functions. The system carried out on-site testing in a harmless handling of dead pigs pilot plant in Lianshui County, Jiangsu Province. The result showed that the hardware module of the system runs stably, the network packet loss rate was 0.26%, and the vehicle identification error rate was 0.97%. Through the ArcGIS monitoring and management function module, continuous monitoring of the transport vehicles running routes was done for 2 hours. Testing of the temperature monitoring management function, and the disinfection safety management function showed that each module of the system was working properly, and met the requirements of the traceability safety system of the transport vehicle for the harmless handling of dead pigs. Meanwhile, it can provide services for a monitoring and management department of animal health and epidemic prevention through the monitoring client by means of telephone, network, and short messages. It can also send the monitoring data such as vehicle running route, compartment temperature,and other information to the supervision department in real time to realize the implementation of the comprehensive supervision and management of a transport vehicle for the harmless treatment of dead pigs and ensure animal health and safety. 【Conclusion】This study has provided an effective method off safety management for a transport vehicle for the harmless treatment of dead pigs,accomplished the comprehensive supervision and management of transport vehicle for the harmless treatment of dead pigs, and reasonably avoided the occurrence of animal health and safety incidents. As it provides a reference for other harmless treatment of dead pigs die of diseases integrated management systems, it has practical value.
Key words:dead pig; harmless treatment; vehicle monitoring; traceability system; RFID; Beidou/GPS satellite navigation
收稿日期:2015-10-29;接受日期:2016-03-28
基金项目:国家公益性行业(农业)科研专项(200903055)、中央高校基本科研费(XDJK2013C107)
