Study on the therapeutic mechanisms of pseudolaric acid in m ice with allergic contact dermatitis
2016-06-29YinHuShuFangDaiYangLiuBinWangeiQu
Yin-E Hu, Shu-Fang Dai, Yang Liu, Bin Wang, W ei Qu
Dermatology Department, Henan University Affiliated Huaihe Hospital, Kaifeng, Henan, 475000, China
Study on the therapeutic mechanisms of pseudolaric acid in m ice with allergic contact dermatitis
Yin-E Hu*#, Shu-Fang Dai*#, Yang Liu, Bin Wang, W ei Qu
Dermatology Department, Henan University Affiliated Huaihe Hospital, Kaifeng, Henan, 475000, China
ART ICLE IN FO
Article history:
Received 15 April 2016
Received in revised form 16 May 2016 Accepted 15 June 2016
Available online 20 July 2016
Keywords:
Pseudolaric acid
Allergic contact dermatitis Immune adjustment
ABSTRACT
Objective: To study the therapeutic mechanisms of pseudolaric acid on allergic contact dermatitis in m ice. Methods: A total of 50 BALB/C mice were selected and random ly divided into control group, model group, and treatment A, B, C groups with 10 rats in each group. ACD model was established in model group, and treatment A, B, C groups but not in control group. Model group received no treatment, but treatment A, B, C groups were treated with external application of the concentration of 0.1%, 0.2% and 0.4% of the pseudolaric acid for the lesions of ear skin. And the weight gain and the swelling degree of the m ice’ ear were recorded, weight of thymus and spleen were measured. Spleen suspension was prepared to test T lymphocyte and B lymphocyte levels of m ice in five groups. Changes in serum IFN-γ,IL-4 and IL-10 levels were tested through the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Results: The weight gain of m ice in model group were significant lower than those of mice in the control group and the treatment A, B, C groups (P<0.05). Weight gain of m ice in treatment A, B groups were significant lower than that of control group (P<0.05), but the difference in weight gain between treatment C group and control group showed no significant difference (P>0.05). The swelling degree and the weight of m ice ears in model group were significant higher than those of m ice in control group and treatment A, B, C groups (P<0.05). Swelling degree and the weight of m ice ears of treatment A, B, C groups were obviously higher than that of control group (P<0.05). The swelling degree and weight of m ice’ ears in treatment A,B, C groups were decreased with the increase of the drug dosage, but comparison between A, B and C group showed statistically differences (P<0.05). The thymus and spleen index of m ice in model group were significant higher than those of the other four groups (P<0.05),among the four groups, thymus and spleen index of treatment A and B group were higher than control group and treatment C group (P<0.05). The stimulation index of T and B cells of m ice in model group was significantly higher than the rest four groups (P<0.05). The serum IFN-γ level of m ice in control group and treatment A, B and C group was obviously lower than that of mice in model group (P<0.05). The serum IFN-γ level of mice in treatment A, B and C group were decreased with the increasing of the drug dosage, and the level of C group was obviously lower than that of A and B group (P<0.05). Conclusion: The pseudolaric acid has anti-inflammation and immune adjustment the effects show ing a remarkable therapeutic effects for the ACD m ice.
#These authors contribute equally to this paper.
Tel: 13938604120, 18637831680
E-mail: hldaishufang@sina.com
Foundation project: Supported by the Science and Technology Key Project of Education Department of Henan province (grant No.: 15A320046).
1. Introduction
A llergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is the skin inflammatory disease caused by skin exposure with allergic source of external environmental, which presents as the symptoms of erythema,papula, edema, blister and even necrosis with different degree of ache, pruritus or burning sensation [1-3]. The allergic contactdermatitis can be induced by many different sensitizers, but most of them are the chem icals of low molecular weight, which can form the antigenic substance of high molecular weight by combined with the epidermal protein [4]. A period of 4-14 days after the patients contact with the allergic source is called latent period, and the organism of patients is in the allergic state during this period, and the patients w ill suffer the ACD w ithin 48 hours if they get in touch with the allergic source again[5]. Studies have shown that[6] ACD is the allergic reaction mediated by T-cell, the immune cells and the cytokines,chemotactic factors and inflammatory mediators that secreted by immune cells have the key effect on the occurence of ACD. In the clinical treatment, the patients should be initially kept away from the allergic source, and treated with the antihistam ine drugs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the hormone drugs. However,sometimes it is impossible to avoid the allergic sources completely,and the antihistam ine drugs and the hormone drugs could not cure ACD, hence the ACD could severely influence patients’ life quality[7]. Pseudolaric acid is the new diterpenoid acid chem ical compounds extracted from dry bark of pseudolarix raempferi gordon, which can be used to treat the tinea, and has the effect of Insecticidal and anti-itch effects[8]. A researche has confirmed that[9]pseudolaric acid has the prominent effects on ACD. The BALB/C mice were selected to establish the ACD model in this study in order to observe the immune adjustment and the treatment effect of the pseudolaric acid on the ACD m ice, and the intervention treatment of pseudolaric acid was given to observe its treatment effects and mechanism of action on the ACD m ice, which aimed at providing the theoretical basis for the clinical application.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Experimental animal
A total of 50 SPF grade, BALB/C male m ice with ages of 12 weeks and body weight of 18-22 g were selected for the experiment and the m ice were provided by the Laboratory Animal Centre of our hospital. The mice were feed freely in the room temperature of (23±3) ℃. In the process of the experiment, the handling of animals was strictly abided by the Regulation of Experimental Animals, and approved Ethics Comm ittee of Henan University. This experiment was operated and finished at the Experiment Center of Henan University.
2.2. Medicines and instruments
The pseudolaric acid was purchased from Chengdu Biopurify Phytochem icals Ltd., w hich was made by emulsifiable paste to the ointment of the depthness of 0.1%, 0.2% and 0.4%. The dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) was purchased from Shanghai Shifeng Biological Technology Co., Ltd. The Compound Dexamethasone Acetate Cream was produced by Sanjiu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., the dexamethasone sodium phosphate injection was produced by Tianjin Jinyao Amino Acid Co., Ltd., and the ciclosporin was purchased by North China Pharmaceutical Group Corperation Veterinary Co.,Ltd. The TS100 type inverted microscope was purchased by Ni Kon Ltd., the biological spectrophotometric meter was purchased by Germany Eppendorf Ltd., the MCO-AC carbon dioxide cell incubator was manufactured by SANYO Electrical Co., Ltd., and the C-4040ZOOM optical m icroscope was manufactured by Shanghai Ailang Instrument Co. Ltd., the ELISA reader was manufactured by BIO-RAD Co., Ltd..
2.3. Model establishing method
The dinitrofluorobenzene was used to establish the ACD mice model. Method: the 8% of sodium sulfide was used to remove the fur of the fixed position of the rat’s abdomen1 day before establishing the model, which was (2×2) cm. And the 1% of 30 μL dinitrofluorobenzene was applied on the fur removal part on the first and the second day of establishing model. The fur of the m ice back was removed on the sixth day of establishing model, and 5% of 30 μL dinitrofluorobenzene was applied for stimulation, then 24 hours later the model was prepared successfully.
2.4. Grouping and treatment
A total of 50 BALB/C mice were random ly divided into control group, model group, treatment A, B and C group with 10 rats in each group. ACD model in the rest 4 groups was induced by the dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB), but model was not established in control group. Model group received no treatment, the treatment A, B and C group were treated with external application of the concentration of 0.1%, 0.2% and 0.4% of the pseudolaric acid for the lesions of ear skin for tw ice a day.
2.5. Obvervational index
The weight gain and the swelling degree of the m ice’ ear were recorded after the first stimulating, and then the mice were executed at the 8th day of establishing model to test the weight of mice’ ears,then the weight of thymus and spleen was measured and their data indexes were calculated. And the spleen suspension was prepared to test T lymphocyte and B lymphocyte levels of m ice in five groups. Then the ophthalm ic venous plexus blood of m ice in five groups was extracted, and the changes of the serum IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-10 levels were tested through the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
2.6. Statistical analysis
The SPSS 13.0 software was used for data processing, the experimental data was expressed as Mean ± SD, and the one-way analysis of variance was used for the comparison among groups,P<0.05 was statistically different.
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of weight gain, swelling degree of ear and weight of ear of mice among five groups
The weight gain of mice in model group was significant lower than that of mice in control group and treatment A, B and C group(P<0.05), and weight gain of m ice in treatment A and B group were significant lower than that in the control group (P<0.05). The comparison of weight gain of m ice in treatment C group and control group showed no significant differences (P>0.05). The swelling degree of ear and weight of ear of m ice in model group were significant higher than those of m ice in control group and treatment A, B and C group (P<0.05), and the swelling degree of ear and weight of ear of treatment A, B and C group were significant higher than that of the control group (P<0.05). The swelling degree of ear and weight of ear of m ice in treatment A, B and C group were decreased with the increasing of the drug dosage, show ing significant differences between A, B and C group (P<0.05), the results were shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Comparison of weight gain, swelling degree of ear and weight of ear of mice in five groups (n=10).
3.2. Comparison of thymus and spleen indexes of mice among five groups
The thymus and spleen index of m ice in model group were significant higher than those of the other four groups (P<0.05),and the thymus and spleen index of treatment A and B group were higher than control group and treatment C group (P<0.05). The thymus index of m ice in treatment C group and control group showed no significant differences (P>0.05), but the spleen index of m ice in treatment C group was higher than that in control group (P<0.05), the results were shown in Table 2.
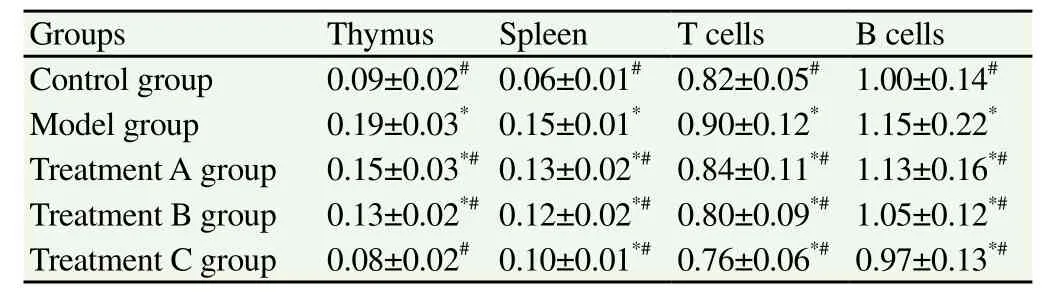
Table 2 Comparison of thymus and spleen indexes of m ice in five groups (n=10).
3.3. Comparison of splenic lymphocyte proliferation of rays in five groups
The stimulation index of T and B lymphocytes of m ice in model group was significant higher than that of the rest four groups (P<0.05). The stimulation index of T and B lymphocytes of m ice in treatment A, B and C group decreased with the increase of the drug dosage (P<0.05), and the decrease level of the stimulation index of T lymphocytes in treatment B and C group was higher than that of A group (P<0.05). The results were shownin Table 2.
3.4. Comparison of the serum IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-10 levels of mice among five groups
The serum IFN-γ level of m ice in control group and treatment A, B and C group was significant lower than that of m ice in model group (P<0.05). The serum IFN-γ level of mice in treatment A, B and C group decreased with the increasing of the drug dosage, and the level of C group was significant lower than that of A and B group (P<0.05); The comparison of serum IL-4 and IL-10 of m ice in model group and treatment A, B and C showed no statistical differences (P>0.05), and the results were shown in Table 3.

Table 3 Comparison of the serum IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-10levels of m ice amongfive groups (n=10).
4. Discussion
According to the epidemiologic investigation of the World Allergic Organization (WAO). 250 million out of the 1 200 million people have the allergic disease with different degrees [10]. Another report shows that [11] about 35 million in USA have suffered from hypersensitivity disease. And inhibiting the hypersensitivity disease has become one of the hottest issues in the world. The treatment of expenses of this disease in the world have surpassed 8 billion dollars[12]. Therefore,the prevention and cure of this disease becomes the burning issue to be solved.
ACD, the common disease in dermatology, is a delayed type hypersensitivity, which is the skin contact allergic reaction mediated by antigen-specific T cells [13]. The incidence of ACD is mainly on the contact sites, which can seriously cause the erythema and the swelling and then induce the erosion and scab of exudation [14]. In clinical treatment, the allergic source should be firstly found out and keep the patients away from it. If the allergic sources are confirmed,the patch test can be used for diagnosis. Drugs used to treat ACD mainly are the glucocorticoid and the H1 receptor antagonists. And the H1 receptor antagonists has stronger effects on type I allergic reation, but has deficient effects on type IV allergic reaction. Patients with a serious ACD can be treated with the glucocorticoid, which can effectively inhibit the type IV allergic reaction in a short period. However, it w ill induce the deficient effects, such as infection, peptic ulcer and rarefaction of bone that the patients can’t tolerant[15-18]. Pseudolaric acid is the new diterpenoid acid chemical compounds extracted from dry root bark of pseudolarix raempferi gordon, which can be used to treat tinea, and has insecticidal and anti-itch effects. Modern pharmacology confirms that pseudolaric acid can accelerate the proteasome to degrade the generation of the key factor HIF-1 innew vessels, reduce the accumulation of the key factor HIF-1, and has a remarkable anti-angiogenesis effects. And another research shows that [8] pseudolaric acid has effective role in ACD treatment,and it can adjust the organism immune of patients effectively. In this study, the weight gain of treatment A and B group were obviously lower than that of control group (P<0.05), but difference between treatment C group and control group was not significant (P>0.05)indicating that pseudolaric acid can influence the weight of m ice and improve the ill state of ACD. The swelling degree and the quality of m ice’ ears in treatment A, B, C groups were decreased with the increase of the drug dosage, and the comparison between A, B and C group showed statistically differences (P<0.05), indicating that pseudolaric acid can effectively treat the inflammatory lesions of the ear skin of ACD m ice.
T cells and B cells are the important lymphocytes in organism,w hich has the key effect on immune ad justment[19-23]. The stimulation index of T and B cells of m ice in model group was signifcant higher than the other four groups (P<0.05). The stimulation index of T and B cells of m ice in treatment A, B and C group were decreased with the increase of the drug dosage (P<0.05),and the decrease level of the stimulation index of T cells in treatment B and C group was significant higher than that of A group (P<0.05),indicating the concentration of 0.2%, 0.4% of pseudolaric acid has the selective role of inhibiting the proliferation of T cells, meanwhile the thymus and the spleen index of m ice in treatment A and B group were obviously higher than that of m ice in control group and treatment C group (P<0.05). The thymus index of mice in treatment C group and control group show ed no statistical differences (P>0.05), but the spleen index of m ice in treatment C group was higher than that in control group (P<0.05). The serum IFN-γ level of m ice in control group and treatment A, B and C group was significant lower than that of mice in model group (P<0.05). The serum IFN-γ level of m ice in control group and treatment A, B and C group was decreased with the increase of the drug dosage,and the level of C group was obviously lower than that of A and B group (P<0.05), indicating that pseudolaric acid has the remarkable immune adjustment function, which can inhibit the response of immune system to itself and the external antigen and is benefit to the ACD treatment.
The results of this study show that the pseudolaric acid has the effect of anti-inflammation and immune adjustment, which has the remarkable treatment effect for the ACD mice.
Declare of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Wang S, Yao X, Liu J. A case of lymphoma sample contact dermatitis caused by diam inobenzene allergic reation. Chin J Dermatol 2015;48(1):62.
[2] Zhao XQ. Clinical analysis of 37 cases of paraquat induced contact dermatitis. Chin J Dermatovenerol Integr Tradit & West Med 2015;14(1):48-49.
[3] Yu X, Liu HL, Wang Y, Wang XY, Tao Y, Bao KF, et al. Expression of IL-33 in different phases of allergic contact dermatitis mouse model. Chin Pharmacol Bulletin 2015; 33(9):1331-1332.
[4] Liu Y. The clinical curative effect of Kangfuxin Liquid on treatment of contact dermatitis. Chin J School Doctor 2015; 29(6):447, 450.
[5] Jiao XM. The intervention effect of health education on air source contact dermatitis. Chin J Aesthetic Med 2015; 5(1):160-161.
[6] Zhong S, Song ZQ. Update of the pathogenesis of contact dermatitis. China J Lepr & Skin Dis 2015; 31(1):29-31.
[7] Han R. Etiology and exacerbation factors in facial dermatitis. Med Aesthetic & Cosmetol 2015; 24(6):837.
[8] Sun Q, Li Y. Antitumor effect and molecular mechanism of Pseudolaric acid B. Chin J Integr Tradit & West Med Digestion 2014; 22(9):551-555.
[9] Yang Z, Zhang M, Wang YT, Zhang ML, Li T, Chen H. Discussion of inhibiting effect and mechanism of the ram ification HPB of new type of pseudolaric acid on T cells. Immunological J 2015; 31(7):591-594.
[10] Huang JY, Ding DD, Li Y, Rong FJ, Zhang CL. Ostomy care powder and is cured the contact clinical observation of dermatitis. Studies Trace Elements & Health 2015; 32(4):16-17.
[11] Yao HW, Sheng RJ, Yang DL, Yan ZY, Sun XM. Investigation and etiological analysis on an outbreak of occupational contact dermatitis. Practical Prev Med 2015; 22(8):955-958.
[12] Chen L. Observation of curative effect of daktarin powder combined 0.02% potassium on contact dermatitis. Strait Pharmaceutical J 2015;27(6):231-232.
[13] Qian JL, Xu HJ, Zhao Y, Xun QM, Ma XL, Huang HY, et al. Effect of benvitimod on allergic contact dermatitis in BALB/c m ice. Chin J Dermatol 2014; 47(9):654-658.
[14] Hu Y, Sun Y, Li T, Chen XM, Zhang HQ, Yu AH, et al. [Effects of stimulating food on allergic contact dermatitis in m ice model]. Chin J Dermatovenereol Integr Traditional & West Med 2014; 13(2):69-71.
[15] Bu P, Li YH, Zhu XF, Hu R. Effects of Yifu cream on allergic contact dermatitis of mouse model. China J Lepr & Skin Dis 2014; 30(11):679-681.
[16] Liu WG, Ding HM. Clinical observation of Xiaoyin granules on the treatment of allergic contact dermatitis. J Dermatol & Venereol 2014;36(1):34.
[17] Hu YM, Ai RD, Zhong ZD, Zhu XY. The effect of purslane extract on contact dermatitis in m ice skin silk poly protein and cysteine aspartic acid specific protease 14 protein expression. J Clin Dermatol 2014;43(2):80-82.
[18] Dong YQ, Wang XM, Liu YQ, Wang TT, Zhang YW. In vitro tests for allergic contact dermatitis. Int J Dermatol & Venereol 2014; 40(6):386-389.
[19] Wei N, Li T, Chen H, Mei X, Cao B, Zhang YY. The immunosuppressive activity of pseudolaric acid B on T lymphocytes in vitro. Phytother Res 2013; 27(7): 980-985.
[20] Li T, Chen H, Yang Z. Topical application of Pseudolaric acid B improve DNFB -induced contact hypersensitivity via regulating the balance of Th1/Th17/Treg cell subsets. Eur J Pharm Sci 2012; 45(5): 668-676.
[21] Li T, Wang H, Chen H, Liu X, Yang JN, Cao B, et al. The prelim inary study of pseudolaric acid B on specific imm une response. Chin Pharmacol Bull 2013; 29(2): 421-425.
[22] Tang Q, Zou P, Jin H, Fu J, Yang J, Shang L, et al. Grape-seed proanthocyanidins ameliorate contact hypersensitivity induced by 2,4 -dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) and inhibit T cell proliferation in vitro. Toxicol Lett 2012; 210(1): 1-8.
[23] Panda BB, Achary VM. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction and DNA repair network are involved in alum inum-induced DNA damage and adaptive response in root cells of Allium cepa L. Front Plant Sci 2014; 5(6):256.
doi:Document heading 10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.05.003
*Corresponding authors: Yin-E Hu, Dermatology Department, Henan University A ffiliated Huaihe Hospital, Kaifeng, Henan, 475000, China.
杂志排行
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- Predicted pattern of Zika virus infection distribution with reference to rainfall in Thailand
- Effect of partial splenic embolization on the immune function of cirrhosis patients with hypersplenism
- Perfusion of gastrodin in abdom inal aorta for alleviating spinal cord ischem ia reperfusion injury
- Study on the effect and mechanism of the dysfunction of CD4+T cells in the disease process of chronic cardiac failure
- Influence on radiosensitivity of lung glandular cancer cells when ERCC1 gene silenced by targeted siRNA
- Experimental study on the inhibition effect of m iR-106a inhibitor on tumor grow th of ovarian cancer xenografts m ice
