Nrf2/ARE通路在炎症性肠病中的研究进展
2016-06-21罗和生
李 越,沈 磊,罗和生
武汉大学人民医院消化内科,湖北 武汉 430060
专题·炎症性肠病
Nrf2/ARE通路在炎症性肠病中的研究进展
李 越,沈 磊,罗和生
武汉大学人民医院消化内科,湖北 武汉 430060
Nrf2(nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2)能激活细胞抗氧化机制并抑制炎症反应,在机体抗氧化应激中起关键作用。Nrf2/ARE通路能够缓解包括炎症性肠病(inflammatory bowel disease,IBD)在内的多种炎症相关疾病。IBD是目前临床治疗的难点之一,其发病机制尚未阐明,多项研究表明氧化损伤在IBD的发生、发展过程中起重要作用。本文就Nrf2/ARE通路在IBD中的研究进展作一概述。
炎症性肠病;Nrf2/ARE通路;抗氧化
Nrf2属于CNC(cap’n’collar)转录因子家族成员,连接于Ⅱ相解毒/抗氧化酶和相关氧化应激反应蛋白启动区的抗氧化反应元件部位,调控抗氧化基因的表达,在机体对抗氧化应激反应中起关键作用[1]。研究[2]表明,Nrf2/ARE通路在抗炎症反应、抗肿瘤、神经保护等方面也发挥重要作用。炎症性肠病(inflammatory bowel disease,IBD)是指一组肠道慢性非特异性炎症性疾病,包括溃疡性结肠炎(ulcerative colitis,UC)和克罗恩病(Crohn’s disease,CD)。IBD不仅严重影响患者的身体健康及生活质量,还有增加罹患结直肠癌风险的趋势。目前IBD的发病机制尚不明确,一般认为是遗传易感性、免疫功能失调、肠道菌群失衡、环境因素共同作用的结果[3]。近年来,氧化损伤在IBD的发生、发展中的作用日益突显,Nrf2/ARE通路能够缓解炎症相关的多种疾病,包括IBD[4],本文就Nrf2/ARE通路在IBD中的研究进展作一概述。
1 Nrf2的概述
Nrf2是具有亮氨酸拉链结构的CNC转录因子家族成员之一[5],Moi等[6]首次发现它能与β-珠蛋白基因启动子上的NF-E2/AP-1重复序列结合,是CNC转录因子家族成员中活力最强的转录调节因子。Nrf2含有多个稳定的结构域,包括N端疏水结构域、与胞浆Kelch样ECH结合蛋白1(Kelch-like ECH associating protein 1,Keap1)相结合的结构域、转录活性结构域、CNC结构域、基础结构域及亮氨酸拉链结构域[7]。Nrf2通过亮氨酸拉链结构域与sMaf蛋白或Jun蛋白形成异二聚体,再与抗氧化反应原件(antioxidant response element,ARE)相结合,从而启动目标基因转录[8]。生理状况下,Nrf2位于细胞质中,并与细胞质的Keap1蛋白相结合而处于非活性状态,且通过泛素蛋白酶体途径不断被降解;当受到氧化应激信号刺激后,Nrf2立即与变构的Keap1解偶联,并转位入核与sMaf蛋白形成异二聚体,再与基因中ARE上的相应位点结合,以启动ARE调控的Ⅱ相解毒酶及抗氧化蛋白基因的转录及翻译[9]。
2 Nrf2/ARE通路的作用
Nrf2/ARE通路与肿瘤、IBD、神经系统疾病、自身免疫性疾病等多种疾病的发生、发展密切相关,是治疗多种疾病的潜在靶点[10]。研究[11]表明,褪黑素通过激活Nrf2/ARE通路抑制肌间神经元的损伤而缓解IBD。组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂也可通过激活Nrf2/ARE通路改善外伤导致的神经元损伤[12]。Nrf2基因敲除小鼠对胡椒基丁醚诱导的肝癌有更高的易感性[13]。此外,Nrf2诱导剂萝卜硫素、姜黄素等对减轻脑水肿、神经功能障碍有一定作用[14]。Nrf2诱导剂二甲基富马酸口服制剂能通过储存髓磷脂、轴突、神经元而有效缓解自身免疫性脑脊髓炎[15]。
3 Nrf2/ARE通路与IBD的发病
炎症反应是机体对抗感染和组织损伤的一种生理性的保护机制,但炎症反应紊乱又会产生多种炎症相关疾病,如IBD等。Nrf2/ARE通路能负性调控炎症调节因子和酶类,如炎性细胞因子、炎症趋化因子、细胞黏附分子、金属蛋白酶、诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)、环氧合酶2(COX-2)等,抑制氧化应激及促炎因子过表达的恶性循环是机体抵抗炎症、组织损伤的必要条件[10]。在脑脊髓炎的小鼠模型中,与野生型小鼠相比,Nrf2缺陷的小鼠脊椎提取物中促炎细胞因子(IFN-γ、IL1-β、TNF-α和IL-12)、与炎症相关的酶(iNOS等)、趋化因子(BLC和MIG)的基因表达水平明显升高,提示Nrf2/ARE通路可调控自身免疫性神经炎症反应[16]。杜鹃素可通过激活Nrf2/ARE通路调控的血红素氧合酶1(HO-1)表达减轻炎症反应[17]。此外,Nrf2/ARE通路还可通过影响其他炎症信号通路如核因子κB(nuclear factor-κB,NF-κB)来抑制机体的炎症反应[18]。
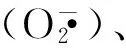
4 Nrf2/ARE通路与IBD的治疗
在醋酸诱导的IBD大鼠模型中,Nrf2、HO-1的表达量明显下降,而低分子肝素的治疗不仅阻止了Nrf2、HO-1表达水平的下降,还显著提高了其表达,提示低分子肝素可能通过Nrf2/ARE通路来缓解IBD的氧化损伤[29]。与野生型小鼠相比,抗增殖蛋白转基因的IBD小鼠表现出Nrf2 mRNA表达水平上调,核蛋白的转位和DNA键合增加,肠道损伤情况减轻,表明抗增殖蛋白在机体应对氧化应激损伤时可调控Nrf2/ARE通路,并通过不断促进Nrf2的表达来减轻炎症相关的氧化损伤,从而有效治疗IBD[30]。异硫氰酸酯萝卜硫素-Nrf2的诱导物降低了IBD小鼠的DAI、缓解IBD小鼠结肠的缩短,说明异硫氰酸酯萝卜硫素有潜力成为IBD的治疗药物[31]。在DSS诱导的IBD小鼠模型中,五倍子酸通过激活Nrf2/ARE通路增加抗氧化酶GR、GPx、NQO1等的表达,增强酶促防御系统,减少氧自由基,阻断DSS诱导结肠炎的发生[32]。可可粉被认为是Nrf2及其下游基因的强效诱导剂,对结肠炎诱导的结肠癌有一定的防护作用[33]。这些研究表明靶向调控Nrf2/ARE通路对IBD治疗有一定的作用。
IBD严重影响了患者的身体健康及生活质量,并与结肠炎诱导的结直肠癌密切相关[34]。目前IBD的治疗药物主要是美沙拉嗪、糖皮质激素、免疫抑制剂和以TNF-α单抗为代表的生物制剂,然而,这些药物在治疗过程中存在一定的毒副反应,出现药物抵抗或不能耐受的现象。Nrf2/ARE通路与IBD的发生、发展密切相关,进一步研究两者联系的具体分子机制对于临床研发治疗IBD安全有效的药物具有重要意义。
[1]Harder B, Jiang T, Wu T, et al. Molecular mechanisms of Nrf2 regulation and how these influence chemical modulation for disease intervention [J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2015, 43(4): 680-686.
[2]Cui W, Bai Y, Miao X, et al. Prevention of diabetic nephropathy by sulforaphane: possible role of Nrf2 upregulation and activation [J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2012, 2012: 821936.
[3]Kaistha A, Levine J. Inflammatory bowel disease: the classic gastrointestinal autoimmune disease [J]. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care, 2014, 44(11): 328-334.
[4]Pall ML, Levine S. Nrf2, a master regulator of detoxification and also antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and other cytoprotective mechanisms, is raised by health promoting factors [J]. Sheng Li Xue Bao, 2015, 67(1): 1-18.
[5]Bryan HK, Olayanju A, Goldring CE, et al. The Nrf2 cell defence pathway: Keap1-dependent and -independent mechanisms of regulation [J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2013, 85(6): 705-717.
[6]Moi P, Chan K, Asunis I, et al. Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1994, 91(21): 9926-9930.
[7]Niture SK, Khatri R, Jaiswal AK. Regulation of Nrf2-an update [J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2014, 66: 36-44.
[8]Hirotsu Y, Katsuoka F, Funayama R, et al. Nrf2-MafG heterodimers contribute globally to antioxidant and metabolic networks [J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2012, 40(20): 10228-10239.
[9]Uruno A, Motohashi H. The Keap1-Nrf2 system as an in vivo sensor for electrophiles [J]. Nitric Oxide, 2011, 25(2): 153-160.
[10]Kim J, Cha YN, Surh YJ. A protective role of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) in inflammatory disorders [J]. Mutat Res, 2010, 690(1-2): 12-23.
[11]Shang B, Shi H, Wang X, et al. Protective effect of melatonin on myenteric neuron damage in experimental colitis in rats [J]. Fundam Clin Pharmacol, 2016, 30(2): 117-127.
[12]Wang B, Zhu X, Kim Y, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibition activates transcription factor Nrf2 and protects against cerebral ischemic damage [J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2012, 52(5): 928-936.
[13]Tasaki M, Kuroiwa Y, Inoue T, et al. Lack of nrf2 results in progression of proliferative lesions to neoplasms induced by long-term exposure to non-genotoxic hepatocarcinogens involving oxidative stress [J]. Exp Toxicol Pathol, 2014, 66(1): 19-26.
[14]Zhang M, An C, Gao Y, et al. Emerging roles of Nrf2 and phase Ⅱ antioxidant enzymes in neuroprotection [J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2013, 100: 30-47.
[15]Linker RA, Lee DH, Ryan S, et al. Fumaric acid esters exert neuroprotective effects in neuroinflammation via activation of the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway [J]. Brain, 2011, 134(Pt 3): 678-692.
[16]Johnson DA, Amirahmadi S, Ward C, et al. The absence of the pro-antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 exacerbates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis [J]. Toxicol Sci, 2010, 114(2): 237-246.
[17]Ci X, Lv H, Wang L, et al. The antioxidative potential of farrerol occurs via the activation of Nrf2 mediated HO-1 signaling in RAW 264.7 cells [J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2015, 239: 192-199.
[18]Checker R, Patwardhan RS, Sharma D, et al. Schisandrin B exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through modulation of the redox-sensitive transcription factors Nrf2 and NF-κB [J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2012, 53(7): 1421-1430.
[19]Zhu H, Li YR. Oxidative stress and redox signaling mechanisms of inflammatory bowel disease: updated experimental and clinical evidence [J]. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 2012, 237(5): 474-480.
[20]Trivedi PP, Jena GB. Role of α-lipoic acid in dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice: studies on inflammation, oxidative stress, DNA damage and fibrosis [J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2013, 59: 339-355.
[21]Khor TO, Huang MT, Kwon KH, et al. Nrf2-deficient mice have an increased susceptibility to dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis [J]. Cancer Res, 2006, 66(24): 11580-11584.
[22]Osburn WO, Karim B, Dolan PM, et al. Increased colonic inflammatory injury and formation of aberrant crypt foci in Nrf2-deficient mice upon dextran sulfate treatment [J]. Int J Cancer, 2007, 121(9): 1883-1891.
[23]Wang Y, Wang H, Qian C, et al. 3-(2-Oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinolin-4(11bH)-one (compound 1), a novel potent Nrf2/ARE inducer, protects against DSS-induced colitis via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome [J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2016, 101: 71-86.
[24]Naito Y, Takagi T, Yoshikawa T. Heme oxygenase-1: a new therapeutic target for inflammatory bowel disease [J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2004, 20 Suppl 1: 177-184.
[25]Naito Y, Takagi T, Uchiyama K, et al. Heme oxygenase-1: a novel therapeutic target for gastrointestinal diseases [J]. J Clin Biochem Nutr, 2011, 48(2): 126-133.
[26]Sheikh SZ, Hegazi RA, Kobayashi T, et al. An anti-inflammatory role for carbon monoxide and heme oxygenase-1 in chronic Th2-mediated murine colitis [J]. J Immunol, 2011, 186(9): 5506-5513.
[27]Yao J, Zhao L, Zhao Q, et al. NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways contribute to wogonin-mediated inhibition of inflammation-associated colorectal carcinogenesis [J]. Cell Death Dis, 2014, 5: e1283.
[28]Buelna-Chontal M, Zazueta C. Redox activation of Nrf2 & NF-κB: a double end sword? [J]. Cell Signal, 2013, 25(12): 2548-2557.
[29]Yalniz M, Demirel U, Orhan C, et al. Nadroparin sodium activates Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in acetic acid-induced colitis in rats [J]. Inflammation, 2012, 35(3): 1213-1221.
[30]Theiss AL, Vijay-Kumar M, Obertone TS, et al. Prohibitin is a novel regulator of antioxidant response that attenuates colonic inflammation in mice [J]. Gastroenterology, 2009, 137(1): 199-208, 208.e1-e6.
[31]Wagner AE, Will O, Sturm C, et al. DSS-induced acute colitis in C57BL/6 mice is mitigated by sulforaphane pre-treatment [J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2013, 24(12): 2085-2091.
[32]Pandurangan AK, Mohebali N, Norhaizan ME, et al. Gallic acid attenuates dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in BALB/c mice [J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2015, 9: 3923-3934.
[33]Pandurangan AK, Saadatdoust Z, Esa NM, et al. Dietary cocoa protects against colitis-associated cancer by activating the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway [J]. Biofactors, 2015, 41(1): 1-14.
[34]Pandurangan AK, Esa NM. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-a promising target in colitis-associated cancer [J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2014, 15(2): 551-560.
(责任编辑:马 军)
Research progress of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in inflammatory bowel disease
LI Yue, SHEN Lei, LUO Hesheng
Department of Gastroenterology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, China
Nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) can activate cellular protection against oxidative stresses and inhibit inflammatory response. Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway can attenuate several inflammatory diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). IBD is one of the most difficult points in clinical treatment, its pathogenesis remains unclear. Numerous studies have indicated that oxidative damage is a key role of IBD. In this paper, the research progress of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in IBD was reviewed.
Inflammatory bowel disease; Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway; Antioxidant
李越,硕士,研究方向:木犀草素对实验性小鼠结肠炎的治疗作用。E-mail:yzejy@126.com
沈磊,副教授,主任医师,硕士生导师,研究方向:消化内镜的诊断与治疗。E-mail:leishenwuhan@126.com
10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2016.07.001
R574.62
A
1006-5709(2016)07-0721-03
2016-01-12
