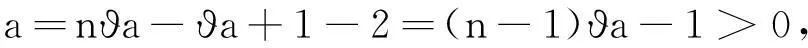一类带一般记忆核的Cahn-Hilliard方程解的能量衰减估计
2016-05-06涂馨予蒲志林
涂馨予, 蒲志林
(四川师范大学 数学与软件科学学院, 四川 成都 610066)
一类带一般记忆核的Cahn-Hilliard方程解的能量衰减估计
涂馨予,蒲志林*
(四川师范大学 数学与软件科学学院, 四川 成都 610066)
摘要:采用推广的带参数的Gronwall不等式,研究了一类带一般记忆核的Cahn-Hilliard方程解的能量衰减估计,证明方程的解是呈指数衰减的,衰减率可被精确地算出.
关键词:动态边界条件; 记忆核; 过去历史变量; 能量估计
Cahn-Hilliard方程是由J. W. Cahn和J. E. Hilliard[1]引入,用来描述二元合金在分解时的分离物随温度的变化情况,它在材料科学中有着重要意义.为了描述所谓的二元混合物的旋节分解(如金属合金的冷却),取Ω是R3中的有界集,并带有充分光滑的边界Γ,考虑粘性Cahn-Hilliard方程[1]
(1)
其中,u是混合物的相对浓度差,μ是带有粘性的化学势,α≥0,非线性项f(u)是一势函数的导数,常数α=0时,方程(1)是Cahn-Hilliard方程.对这类方程在标准边界条件下(Neumann边界条件、狄利克雷边界条件、周期边界条件)的柯西问题的讨论已经很充分[2-5].
为了描述特殊材料(如玻璃)的相分离现象,对方程(1)取μ满足Neumann边界条件,即
将通常u的Neumann边界条件换成非线性的动态边界条件,即u满足
其中,β是正常数,ΔΓ是边界上的Laplace-Beltrami算子,非线性项g(u)是一充分光滑的边界势函数的导数.许多作者对这类问题进行了讨论[6-13].
为了加速某些材料的旋节分离(如玻璃),考虑修改的Cahn-Hilliard方程
其中κ(s)是记忆核函数,它是呈指数衰减的,即满足条件κ′(s)+δκ(s)≤0,δ>0,这类Cahn-Hilliard方程已有大量研究[14-22].如在标准边界条件及光滑势条件下,3维空间上非恒温非粘弹条件下的弱解的存在[14]、解的适定性和正则性的结果[15]已得到.在2维空间上,取α=0已经证得了能量解在短的松弛时间的全局吸引子的存在[16].但这类问题在非线性动态边界条件下的研究还很少.
这里考虑一类在非线性动态边界条件下带记忆核的Cahn-Hilliard方程[23]:
其中,Ω⊂R3是具有光滑边界Γ的有界区域,α,β是正常数.未知量u=u(x,t):Ω×[0,∞)→R,u是混合物的相对浓度差,u|Γ=ψ(t),u满足非线性的动态边界条件,μ满足Neumann边界条件.ΔΓ是边界上的Laplace-Beltrami算子,η=ηt(x,s):Ω×R+×[0,∞)→R是过去历史变量,且对任意的s>0和t>0,有ηt(s)=∫0s-Δμ(t-y)dy,显然ηt(x,s)满足边界条件:ηt(x,0)=0,Ω×(0,∞).
对方程(3)给定初值条件如下:
(4)
ν(s)是方程的记忆核,它满足以下假设[23]:
(H1)ν(s)∈C1(R+)∩L1(R+),∀s∈R+;
(H2) ν(s)≥0,ν′(s)≤0,∀s∈R+;
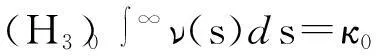
(H5) ν′(s)+ρ(s)ν(s)≤0,∀s∈R+;ρ(s)>0,ρ′(s)≤0,∀s∈R+;
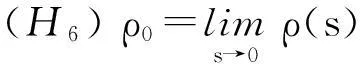
注满足假设(H1)~(H6)的记忆核ν(s)是存在的,如取ν(s)=e-λs,∀λ>ρ0.
非线性项f、g满足如下条件:
(K1) f,g∈C1(L2(Ω));
(K2) f,g∈C2(L2(Ω));
(K3) |f′(y)|≤cf(1+|y|2),|g′(y)|≤cg(1+|y|q),∀y∈L2(Ω);
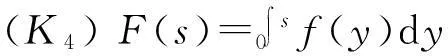

由(K5)可得[23]:
(5)
在文献[23]中,取非线性记忆核ν(s)满足ν′(s)+δν(s)≤0,δ>0是正常数,证得了变分解的存在;当α>0时,全局吸引子和指数吸引子的存在;以及α=0时,轨道吸引子的存在.受文献[4]的启发,本文考虑非线性动态边界条件下,满足更一般条件的非线性记忆核ν(s),它满足以下微分不等式[24]:
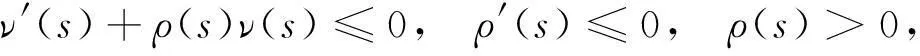
当取ρ(s)=δ时,即为文献[23]的情况,本文的记忆核更具一般性.再采用推广的带参数的Gronwall不等式,研究了带这类记忆核的Cahn-Hilliard方程解的能量衰减性,证明当t→∞时,方程的解的能量是指数衰减到0的,并精确地算出了衰减率.
本文在预备知识中介绍了一些定义、记号、不等式及定理;后面通过构建泛函L,对某个正常数C满足
1预备知识
Ω⊂R3是具有光滑边界Γ的有界区域,分别记(·,·),‖·‖;(·,·)Γ,‖·‖Γ为L2(Ω)和L2(Γ)的内积和范数,定义算子A:=-Δ,A是L2(Ω)上的非负自共轭的线性算子,取A的分数力Ar,则可定义一族插值空间如下:
当r=0时,V0=L2(Ω),在Vr上定义范数:
定义〈·〉为Ω上的空间平均,即
所以有
定义迹算子TrD为
引入空间
取Hilbert空间
M-1上的内积定义如下
定义T=-∂s是M-1上的线性算子
方程(3)的解满足以下质量守恒[23]:
(6)
最后,引入乘积Hilbert空间H=V1×M-1.下面介绍一些重要的不等式及引理:

2) Poincaré-Wirtinger不等式:‖u-〈u〉‖p≤C7‖u‖p.
3)W1,2(Ω)上的等价范数为:‖u‖W1,2(Ω)=‖u‖+‖u‖.

那么
注意:取ϑa∈(0,1),使得a=mϑa-ϑa+1-l=(m-1)ϑa+1-l>0,b=1-ϑa-γϑa>0,定义
则
2一致能量估计
关于方程(3)在t时刻的能量E(t)为
(7)
有如下的结果:
定理 2.1假设(H1)~(H5)和(K1)~(K5)成立,则存在正常数J,ω,2 即方程的解的能量是呈指数衰减的,且衰减率为ω,其中: 证明在方程(3)的第一项的两端同乘以μ,在Ω上积分,可以得到 利用方程(3)的第3项有 利用格林公式可得 由方程(3)的第2项可得 即 (8) 又由方程(3)的第4项及(6)式可得 将以上所求的项带入到方程(8)可以得到 由(H2)和(K4)可得 (9) 故 (10) 构建泛函: 利用方程(3)的第1项,在两端同时乘以A-1ut,再在区域Ω上积分可得 由(6)式可得〈ut〉=0,所以有 又由(H3)、(6)式以及Hölder不等式可得 即 所以 (11) 利用方程(3)的第4、3、2项以及格林公式得 由上式及(11)式有 所以 (12) 构建泛函 所以有 即 其中C0是与α相关的正常数. 由(9)、(12)式可得 又由Φ(t)的构造可得 所以 所以 有 其中Cf″、Cf‴、C2为正常数.又由(5)式可得 所以 故一定存在只依赖于C1、C2、α的常数C(C充分大)使得 (14) 在(14)式两端同时乘以e,再在s∈(0,t)上积分得: 所以有 由(13)式可得 由引理1.1,取m=n,l=2,q(s)=q=C,h=0,R=E(0)(1+C0n)可得 (15) 取ϑa∈(0,1),使得 由(13)及(15)式有 参考文献 [1] CAHN J W, Hilliard J E. Free energy of nonuniform system. I. interfacial energy[J]. J Chem Phys,1958,28:258-267. [2] NOVICK-COHEN A. The Cahn-Hilliard equation[C]//Handb Differ Equ IV: Evolutionary Equations. Amsterdam:Elsevier/North-Holland,2008:201-228. [3] TEMAM R. Infinite-Dimensional Dynamical Systems in Mechanics and Physics[M]. New York:Springer-Verlag,1997. [4] EFENDIEV M, MIRANVILLE A, ZELIK S. Exponential attractors for a singularly perturbed Cahn-Hilliard system[J]. Math Nachr,2004,272:11-31. [5] RYBKA P, HOFFMANN K H. Convergence of solutions to Cahn-Hilliard equation[J]. Commun PDE,1999,24:1055-1077. [7] GILARDI G, MIRANVILLE A, SCHIMPERNA G. On the Cahn-Hilliard equation with irregular potentials and dynamic boundary conditions[J]. Commun Pure Appl Anal,2009,8:881-912. [8] MIRANVILLE A, ZELIK S. Exponential attractors for the Cahn-Hilliard equation with dynamic boundary conditions[J]. Math Models Appl Sci,2005,28:709-735. [9] MIRANVILLE A, ZELIK S. The Cahn-Hilliard equation with singular potentials and dynamic boundary conditions[J]. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst,2010,28:275-310. [10] PRÜSS J, RACKE R, ZHENG S. Maximal regularity and asymptotic behavior of solutions for the Cahn-Hilliard equation with dynamic boundary conditions[J]. Ann Mat Pure Appl,2006,185(4):627-648. [11] RACKE R. The Cahn-Hilliard equation with dynamic boundary conditions[C]//Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations and Their Applications. GAKUTO Internat: Ser Math Sci Appl. Tokyo:Gakkotosho,2004,20:266-276. [12] RACKE R, ZHENG S. The Cahn-Hilliard equation with dynamic boundary conditions[J]. Adv Diff Eqns,2003,8:83-110. [13] WU H, ZHENG S. Convergence to equilibrium for the Cahn-Hilliard equation with dynamic boundary conditions[J]. J Diff Eqns,2004,204:511-531. [14] LORENZI A, ROCCA E. Weak solutions for the fully hyperbolic phase-field system of conserved type[J]. J Evol Eqns,2007,7:59-78. [15] CONTI M, COTI ZELATI M. Attractors for the non-viscous Cahn-Hilliard equation with memory in 2D[J]. Nonlinear Anal,2010,72:1668-1682. [16] VERGARA V. A conserved phase field system with memory and relaxed chemical potential[J]. J Math Anal Appl,2007,328:789-812. [17] GALENKO P, JOU D. Diffuse-interface model for rapid phase transformations in nonequilibrium systems[J]. Phys Rev,2005,E6125(71):1-13. [18] GALENKO P, JOU D. Kinetic contribution to the fast spinodal decomposition controlled by diffusion[J]. Physics,2009,A388:3113-3123. [19] GALENKO P, LEBEDEV V. Analysis of the dispersion relation in spinodal decomposition of a binary system[J]. Philos Mag Lett,2007,87:821-827. [20] GALENKO P, LEBEDEV V. Local nonequilibrium effect on spinodal decomposition in a binary system[J]. Int J Thermodyn,2008,11:21-28. [21] GALENKO P, LEBEDEV V. Nonequilibrium effects in spinodal decomposition of a binary system[J]. Phys Lett,2008,A372:985-989. [22] LECOQ N, ZAPOLSKY H, GALENKO P. Evolution of the structure factor in a hyperbolic model of spinodal decomposition[J]. Eur Phys J(Special Topics),2009,177:165-175. [23] CAVATERRA C, GAL C G, GRASSELLI M. Cahn-hilliard equations with memory and dynamic boundary conditions[J]. Asymptotic Analysis,2011,71:123-162. [24] SAID-HOUARI B, MESSAOUDI S A. General decay estimates for a cauchy viscoelastic wave problem[J]. Commun Pure Appl Anal,2014,13:1541-1551. [25] PATA V. Uniform estimates of Gronwall type[J]. J Math Anal Appl,2011,373:264-270. [26] GIORGI C, MUOZ RIVERA J E, PATA V. Global attractors for a semilinear hyperbolic equation in viscoelasticity[J]. J Math Anal Appl,2001,260:83-99. [27] GATTI S, PATA V, ZELIK S. A Gronwall-type lemma with parameter and dissipative estimates for PDEs[J]. Nonlinear Anal,2009,70:2337-2343. 2010 MSC:35B30; 35B99 (编辑周俊) The Energy Decay Estimates for Cahn-Hilliard Equation with General Memory Kernel TU Xinyu,PU Zhilin (CollegeofMathematicsandSoftwareScience,SichuanNormalUniversity,Chengdu610066,Sichuan) Abstract:In this paper the energy decay estimates for Cahn-Hilliard equation with general memory kernel are studied by a generalized Gronwall-type lemma with . It is proved that the solution of such an equation decays exponentially, and the decay rate can be explicitly calculated. Key words:dynamic boundary conditions; memory kernel; the past history variable; energy decay estimates doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-8395.2016.01.001 中图分类号:O213.2; O226 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1001-8395(2016)01-0001-07 *通信作者简介:蒲志林(1963—),男,教授,主要从事偏微分方程的研究,E-mail:puzhilin908@sina.com 基金项目:国家自然科学基金(11401409) 收稿日期:2015-03-11