Study on Evaluation Indicators of Agricultural Science and Technology Project Based on the Perspective of Innovation
——Case in Basic Research Project
2016-01-12,
,
1. Business School, Beijing Wuzi University, Beijing 101149, China; 2. College of Economics & Management, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100084, China
1 Introduction
National science and technology plan project in agricultural field is one of basic organization forms of China’s government implementing science and technology research in whole country, and is an important manner of realizing rational allocation of agricultural science and technology resources. It is worthy to follow how to promote larger breakthrough of agricultural science and technology innovation by depending on science and technology plan projects. Although science and technology projects at various grades and classes subsidized by government all emphasize innovation degree, namely innovation value, there are fewer researches about evaluation theory and method of innovation degree of the project, and an index system not only containing basic project approval requirements but also considering the evaluation of innovation degree is not formed. Therefore, in project approval evaluation process, it is especially necessary to improve science and justice of project approval by establishing objective, scientific, feasible and innovative evaluation indexes based on peer review system. In this paper, basic research project is taken as the case. This kind of project reveals general rule of nature development, and its value guide mainly shows at scientific value aspect, and original innovative result is generally taken as evaluation standard of the project, such as new finding, new concept, new theory and new method.
2 Initial establishment of evaluation index on innovation of agricultural science and technology project
Research steps are as below. At the first stage, the factors which have been demonstrated in the related literatures and affect the innovation of science and technology project are summarized, thereby forming many initial influencing factors. At the second stage, 3 cases are studied to verify the science and rationality of indexes in basic scale table, and it also checks if there exists missing variables. Case research results show that major factors in typical project innovation process have been covered in initial indexes. At the third stage, focus group interview is conducted. On the one hand, the opinions of review expert and project leader for the supposed scale table are consulted. On the other hand, influencing factors of innovation are consulted according to the projects involved by review experts. At the fourth stage, test questionnaires are issued to review experts and project leaders which are interviewed in prior period, and initial test of scale table reliability is conducted. In this paper, the related theories about agricultural science and technology innovation and project approval evaluation are combed and summarized. By combining application and finish books of science and technology support plan project in agricultural field of Ministry of Science and Technology with stronger innovation, case analysis and expert interview are conducted, and evaluation indexes of agricultural science and technology project based on innovation are proposed initially. Case analysis process is designed as below: research design, preparation of data collection, data collection and data analysis, and 50 initial indexes are obtained[1-7]. After that, via focus group discussion, qualitative research is conducted to further adjust innovative evaluation index factors, and 50 initial indexes are deleted to 41 (Table 1).
Table1Indexesofinnovationdegreeofagriculturalscienceandtechnologyproject(initialselection)
(to be continued)
(continued)
3 Screening of innovative indexes of agricultural science and technology project based on questionnaire investigation
In this paper, the used scoring manner of expert scoring scale table is seven-grade Likert scale, which uses 7 grades to score from index’s importance by the experts, and they are not necessary, very not important, little important, generally important, important, very important and most important (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 scores). The interviewed expert and questionnaire object cover rural center management personnel of Ministry of Science and Technology, rural center review expert of Ministry of Science and Technology, theory and practice experts in domestic agricultural field, senior project manager and leader of the enterprise involving agriculture. Firstly, investigation unit is determined, and then the contacting personnel of investigation unit are determined, and then questionnaire is issued in the form of electronic edition. Investigation units mainly include university involving agriculture, enterprise of scientific research institute, and promotion department directly under the government. There are 207 questionnaires in total, and 193 questionnaires are recovered, with recovery rate of 93.2%. In effective questionnaire, there are 88 persons from university, accounting for 45.5%; 48 persons from scientific research institution, accounting for 24.9%; 41 persons from enterprise (state owned business, private business and joint venture), accounting for 21.2%; 16 persons from promotion department directly under the government, accounting for 8.3%. The distribution basically corresponds with that of project review expert’s unit property. Seen from age structure, there are 5 persons between 35-40 years old, accounting for 2.6%; 30 persons between 41-45 years old, accounting for 15.2%; 104 persons between 46-50 years old, accounting for 53.9%; 33 persons between 51-55 years old, accounting for 17.1%; 18 persons between 56-60 years old, accounting for 9.3%; 4 persons above 60 years old, accounting for 2.1%, and the distribution is rational. The situation of each evaluation index of basic research project in the questionnaire is shown as Table 2.
4 Index classification and screening based on structural equation model
On the basis of theory carding, case research and expert interview, evaluation indexes on innovation of agricultural science and technology project are proposed initially, which are verified via questionnaire. Verification factor analysis overcomes the drawbacks of exploration factor analysis that hypothesis condition constraint is strong, and result may not correspond with theory and practice[8]. In this paper, multi-adjustment of initial models of three kinds of projects is conducted, which aims to obtain ideal fitting index and rational index relationship. Model modification method could be tested by fitting degree of the improved model output by AMOS software, including fitting index χ2, fitting goodness (GFI), comparative fitting (CFI) and estimated root mean square error (RMSEA). Under general condition, it needs referring to these fitting indexes to test if a model is rational. The values of GFI and CFI should be between 0-1, if the value is more than 0.85, it is thought that the model fitting is better. In addition, RMSEA is the most important reference index of verification factor analysis in structural equation model, and is approximate root mean square error. When RMSEA is lower than 0.1, it shows that the model fitting is better. When RMSEA is lower than 0.05, it shows that the model fitting is very good[9]. The verification factor analysis of collected effective questionnaires is conducted, and model construction and adjustment situations are as below.
Table2Descriptivestatisticsofindeximportancequestionnaire
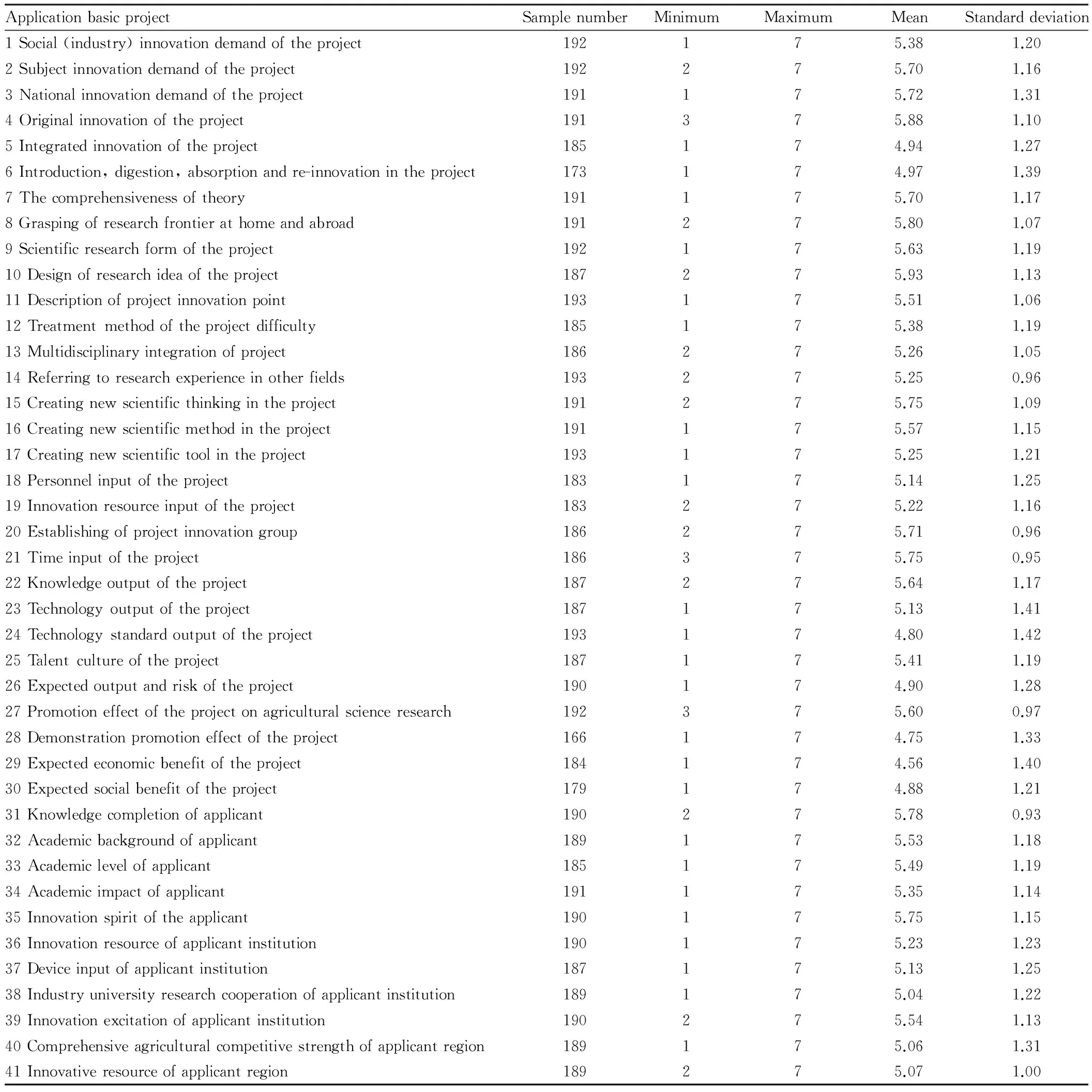
ApplicationbasicprojectSamplenumberMinimumMaximumMeanStandarddeviation1Social(industry)innovationdemandoftheproject192175.381.202Subjectinnovationdemandoftheproject192275.701.163Nationalinnovationdemandoftheproject191175.721.314Originalinnovationoftheproject191375.881.105Integratedinnovationoftheproject185174.941.276Introduction,digestion,absorptionandre-innovationintheproject173174.971.397Thecomprehensivenessoftheory191175.701.178Graspingofresearchfrontierathomeandabroad191275.801.079Scientificresearchformoftheproject192175.631.1910Designofresearchideaoftheproject187275.931.1311Descriptionofprojectinnovationpoint193175.511.0612Treatmentmethodoftheprojectdifficulty185175.381.1913Multidisciplinaryintegrationofproject186275.261.0514Referringtoresearchexperienceinotherfields193275.250.9615Creatingnewscientificthinkingintheproject191275.751.0916Creatingnewscientificmethodintheproject191175.571.1517Creatingnewscientifictoolintheproject193175.251.2118Personnelinputoftheproject183175.141.2519Innovationresourceinputoftheproject183275.221.1620Establishingofprojectinnovationgroup186275.710.9621Timeinputoftheproject186375.750.9522Knowledgeoutputoftheproject187275.641.1723Technologyoutputoftheproject187175.131.4124Technologystandardoutputoftheproject193174.801.4225Talentcultureoftheproject187175.411.1926Expectedoutputandriskoftheproject190174.901.2827Promotioneffectoftheprojectonagriculturalscienceresearch192375.600.9728Demonstrationpromotioneffectoftheproject166174.751.3329Expectedeconomicbenefitoftheproject184174.561.4030Expectedsocialbenefitoftheproject179174.881.2131Knowledgecompletionofapplicant190275.780.9332Academicbackgroundofapplicant189175.531.1833Academiclevelofapplicant185175.491.1934Academicimpactofapplicant191175.351.1435Innovationspiritoftheapplicant190175.751.1536Innovationresourceofapplicantinstitution190175.231.2337Deviceinputofapplicantinstitution187175.131.2538Industryuniversityresearchcooperationofapplicantinstitution189175.041.2239Innovationexcitationofapplicantinstitution190275.541.1340Comprehensiveagriculturalcompetitivestrengthofapplicantregion189175.061.3141Innovativeresourceofapplicantregion189275.071.00
4.1Innovationdemand,innovationmode,researchthinkingdesignandinnovationfeaturesofagriculturalfieldFig.1 is original model of innovation demand, innovation mode, research thinking design and agricultural feature.
It is unobvious to list agricultural features singly, in which treatment method of project difficulty is merged into thinking design. Multidisciplinary integration of project is related to referring to research experience of other fields and innovation mode, and agricultural feature index is deleted (Fig.2).
Combining the features of application basic project, integrated innovation and introduction, digestion, absorption and re-innovation are merged. For the project, it should actively encourage original innovation, and consider integrated innovation or introduction, absorption, digestion and re-innovation. Seen from Fig.3, via merging integration innovation and digestion, absorption and re-innovation, correlation relationship in factor structure is improved obviously.

Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=87.773,df=44,GFI=0.916,TLI=0.891,CFI=0.927,RMSEA=0.083.
Fig.1Originalmodelofinnovationdemand,innovationmode,researchthinkingdesignandagriculturalfeature

Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=54.922,df=28,GFI=0.935,TLI=0.915,CFI=0.947,RMSEA=0.081.
Fig.2Themodeldeletingagriculturalinnovationfeatureandmergingtreatmentmethodofprojectdifficultyintothinkingdesign
4.2Researchbasis,graspofinnovationmethodandprojectinputInitial model of research basis, innovation method’s grasping and project input is shown as Fig.4. Whether factor structure or correlation relationship, the index is better. Seen from Fig.4, "research basis-grasping of research frontier at home and abroad" in application book has residual correlation with"project input-time input". It could be understood that project group which grasps well research frontier at home and abroad may spend more time and experience in project application, and may spend more time in project after project approval. Correlation between two items will be embodied in application development project.

Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=74.356,df=36,GFI=0.923,TLI=0.890,CFI=0.928,RMSEA=0.085.
Fig.3Themodelofmergingintegrationinnovationanddigestion,absorptionandre-innovation
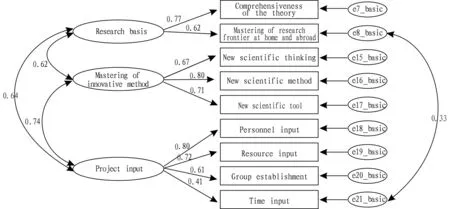
Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=42.102,df=23,GFI=0.938,TLI=0.927,CFI=0.954,RMSEA=0.075.
Fig.4Initialmodelofresearchbasis,innovationmethod’sgraspingandprojectinput
4.3PredictedoutputandpredictedbenefitSeen from Fig.5, when RMSEA is more than 0.1, model fitting is not good, especially that correlation coefficients between knowledge output, talent culture and predicted output are respectively 0.24 and 0.39. Seen from statistics, when it is weak correlation, it could consider deleting the two factors in the model, but scoring means of the two indexes are respectively 5.64 and 5.13, illustrating that the two indexes are important. That is to say, the two indexes need re-classification. In addition, there exists correlation of multiple factors in the model, which needs adjustment of the model.
Seen from Fig.6, knowledge output and talent culture are isolated to be a class, which is named as "thesis and talent culture". It is found that although model fitting index is improved somewhat, correlation relationship among factors still exists. Considering that "predicted benefit-promotion of the project on science research" is related to other items, and its correlation coefficient with expected benefit is only 0.18, the index is deleted. Meanwhile, "expected output and risk" is also adjusted, which is merged into "thinking design" (Fig.7).
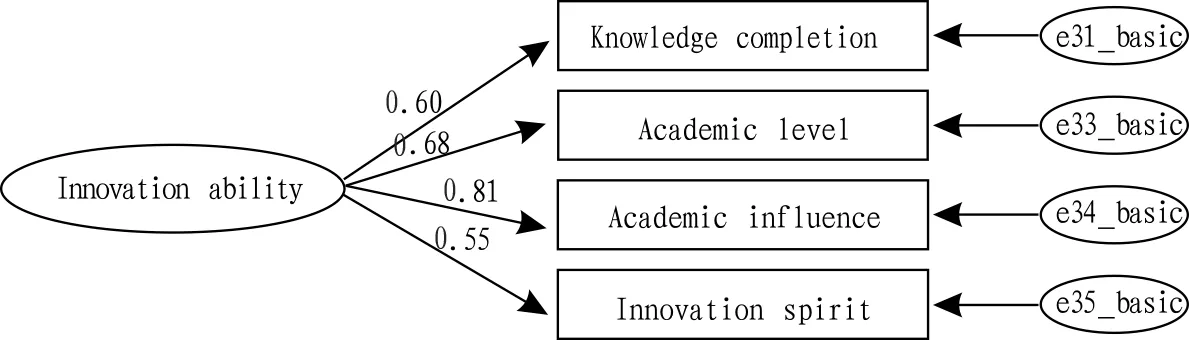
4.4InnovationabilityofapplicantThe original model of innovation ability is shown as Fig.8.
"Academic background" is highly related to "academic influence". By comparing correlation coefficients between the two indexes and upper index of "innovation ability", academic background is deleted, and structure adjustment of innovation ability model is conducted (Fig.9). It is clear that the model has very good fitting effect via adjustment, and there does not have residual correlation among indexes.

Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=45.715,df=16,GFI=0.931,TLI=0.912,CFI=0.950,RMSEA=0.113.
Fig.5Initialmodelofpredictedoutputandpredictedbenefit

Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=45.382,df=19,GFI=0.937,TLI=0.927,CFI=0.961,RMSEA=0.098.
Fig.6Themodelofmergingknowledgeoutputandtalentculture
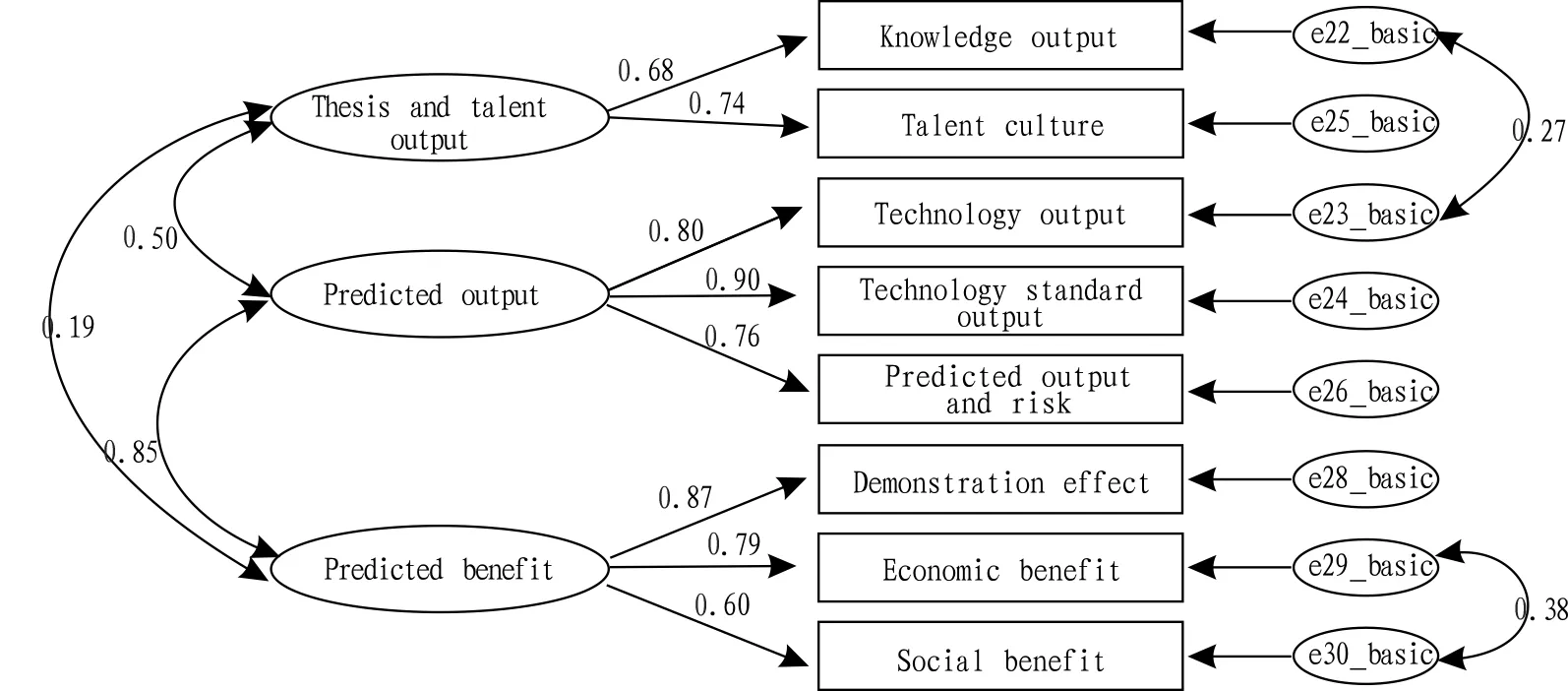
Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=36.548,df=15,GFI=0.943,TLI=0.932,CFI=0.963,RMSEA=0.099.
Fig.7Themodelofdeletingthepromotingeffectofprojectonscienceresearch
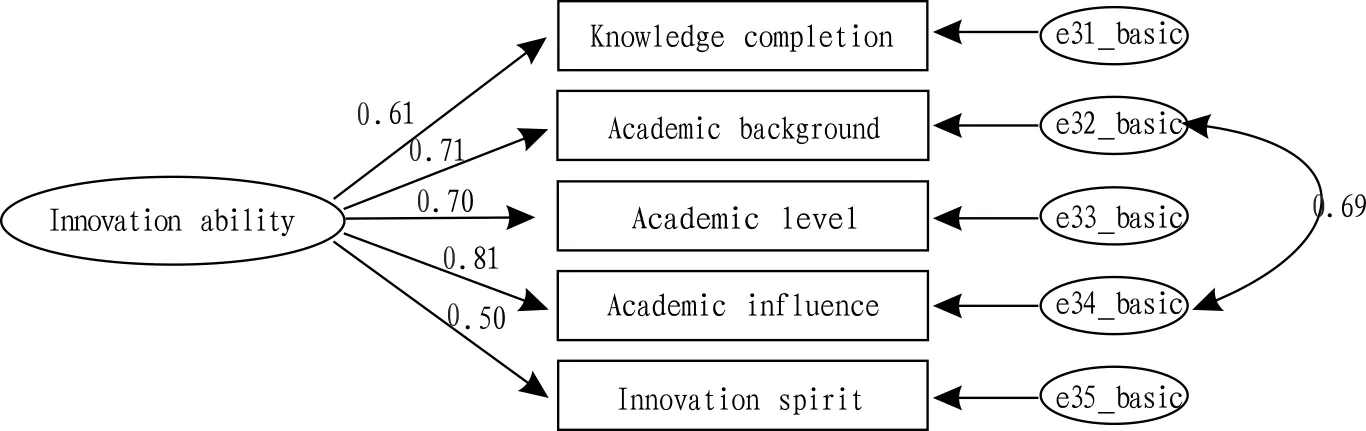
Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=4.047,df=4,GFI=0.947,TLI=0.999,CFI=1.0,RMSEA=0.009.
Fig.8Initialmodelofinnovationability
Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=0.846,df=2,GFI=0.997,TLI=1.026,CFI=1.0,RMSEA=0.000.
Fig.9Structurechartofinnovationabilityafterdeletingacademicbackground
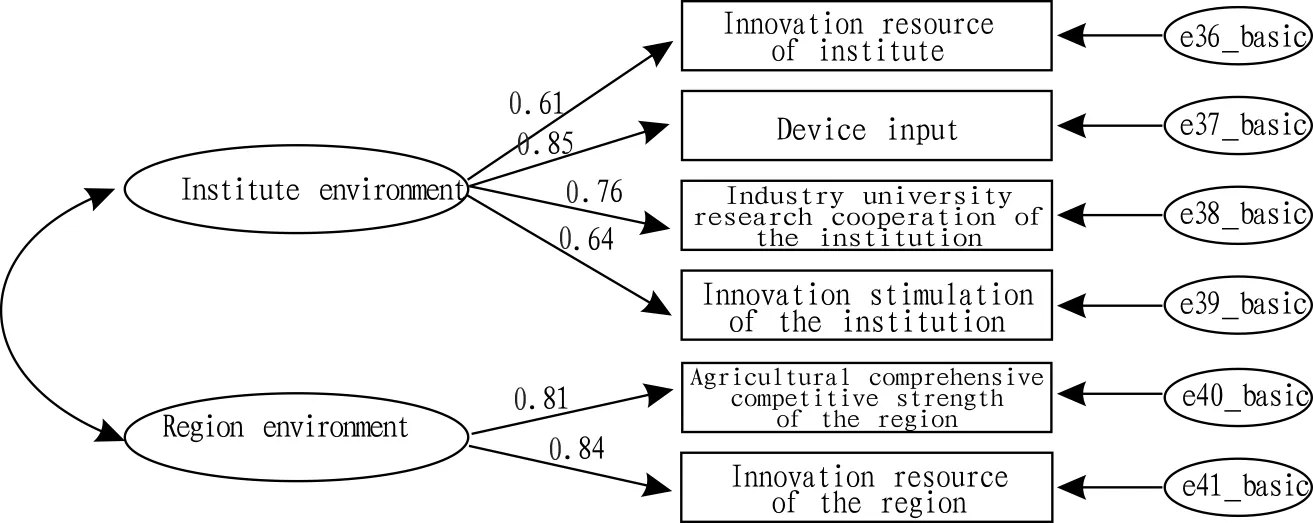
4.5InnovationenvironmentofinstitutionandinnovationenvironmentofregionInitial model of institution environment and region environment is shown as Fig.10.
Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=19.936,df=8,GFI=0.957,TLI=0.944,CFI=0.970,RMSEA=0.101.
Fig.10Initialmodelofinstitutionenvironmentandregionenvironment
Because that model fitting index RMSEA is more than 0.1, the two factors could be merged, and the model is shown as Fig.11. It is clear that institution environment and region environment are merged into "innovation environment", which is more rational.

Note: Statistical amounts:χ2=28.649,df=9,GFI=0.943,TLI=0.917,CFI=0.950,RMSEA=0.022.
Fig.11Themodelofmerginginstitutionenvironmentandregionenvironmentintoinnovationenvironmentfactor
Overall, by verification factor analysis of structural equation model on 5 Grade-one indexes, Grade-two indexes after revise are obtained (Table 3). In addition, it is worthy to specially note that in initial indexes, there is the index for the innovation feature of agricultural field, but its model list as Grade-one index is insignificant. It is because that the innovation of agricultural field corresponds with general rule of scientific development, which has been through to each index in whole research design. For example, the index "integrated innovation of the project/introduction, digestion, absorption and re-innovation in the project" indicates using agricultural science and technology information, agricultural science and technology management and agricultural innovation tool to select and integrate each innovation factor, or using various introduced agricultural technology resources to complete key innovation based on digestion and absorption. The index "science research form of the project" indicates corresponding with general rule, basic method and technical manner of agricultural related field research, especially science attempt of nature and biological rules. The index "treatment method of project difficulty" indicates treatment science and availability of control variables which may appear in agricultural field, such as climate, terrain, nature and life period. The index "expected social benefit of the project" indicates project application and promotion improving farmer’s production and living levels, increasing the quality of agricultural product, improving or protecting the environment, and its sustainability, which all bring distinctive agricultural characteristics.
Table3OriginalGrade-twoindexesandmodifiedGrade-twoindexes

Grade-oneindexOriginalGrade-twoindexGrade-twoindexaftermodelmodificationInnovationdemandoftheproject1Social(industry)innovationdemandoftheproject1Social(industry)innovationdemandoftheproject2Subjectinnovationdemandoftheproject2Subjectinnovationdemandoftheproject3Nationalinnovationdemandoftheproject3NationalinnovationdemandoftheprojectInnovationmodeoftheproject4Originalinnovationoftheproject4Originalinnovationoftheproject5Integratedinnovationoftheproject5Integratedinnovationoftheproject/introduction,digestion,ab-sorptionandre-innovation6Introduction,digestion,absorptionandre-innova-tionintheprojectMergenceWholequalityoftheproject7Thecomprehensivenessoftheory6Thecomprehensivenessoftheory8Masteringofresearchfrontierathomeandabroad7Masteringofresearchfrontierathomeandabroad9Scientificresearchformoftheproject8Scientificresearchformoftheproject10Designofresearchthoughtoftheproject9Designofresearchthoughtoftheproject11Descriptionofprojectinnovationpoint10Descriptionofprojectinnovationpoint11TreatmentmethodoftheprojectdifficultyInnovationfeatureinagriculturalfield12TreatmentmethodoftheprojectdifficultyAdjusting13MultidisciplinaryintegrationofprojectDeleting14ReferringtoresearchexperienceinotherfieldsDeletingMasteringofinnovationmethod15Creatingnewscientificthinkingintheproject12Creatingnewscientificthinkingintheproject16Creatingnewscientificmethodintheproject13Creatingnewscientificmethodintheproject17Creatingnewscientifictoolintheproject14CreatingnewscientifictoolintheprojectProjectinput18Personnelinputoftheproject15Personnelinputoftheproject19Innovationresourceinputoftheproject16Innovationresourceinputoftheproject20Establishingofprojectinnovationgroup17Establishingofprojectinnovationgroup21Timeinputoftheproject18TimeinputoftheprojectPredictedoutputoftheproject22Knowledgeoutputoftheproject19Knowledgeoutputoftheproject23Technologyoutputoftheproject22Talentcultivationoftheproject24Technologystandardoutputofproject20Technologyoutputoftheproject25Talentcultivationoftheproject21Technologystandardoutputoftheproject26ExpectedoutputandriskoftheprojectDeletingPredictedproductionefficiencyoftheproject27PromotioneffectoftheprojectonscienceresearchDeleting28Demonstrationeffectoftheproject23Demonstrationeffectoftheproject29Expectedeconomicbenefitoftheproject24Expectedeconomicbenefitoftheproject30Expectedsocialbenefitoftheproject25ExpectedsocialbenefitoftheprojectInnovationabilityofapplicant31Knowledgecompletionofapplicant26Knowledgecompletionofapplicant32AcademicbackgroundofapplicantDeleting33Academiclevelofapplicant27Academiclevelofapplicant34Academicimpactofapplicant28Academicimpactofapplicant35Innovationspiritoftheapplicant29Innovationspiritoftheapplicant
(to be continued)
(continued)

Grade-oneindexOriginalGrade-twoindexGrade-twoindexaftermodelmodificationInnovationenvironmentoftheap-plicantagency36Innovationresourceofapplicantinstitution30Innovationresourceofapplicantinstitution37Deviceinputofapplicantinstitution31Deviceinputofapplicantinstitution38Industryuniversityresearchcooperationofappli-cantinstitution32Industryuniversityresearchcooperationofapplicantinstitution39Innovationexcitationofapplicantinstitution33InnovationexcitationofapplicantinstitutionInnovationenvironmentofthere-gion40Comprehensiveagriculturalcompetitivestrengthofapplicantregion34Comprehensiveagriculturalcompetitivestrengthofapplicantre-gion
5 Conclusion
After attempting exploratory factor analysis, it is found that the result of factor analysis not only separates from the theory but also does not correspond with actual situation. On the basis of existing theory, confirmatory factor analysis in structural equation model is selected. Via the confirmatory factor analysis, it not only obtains index classification but also finds action mechanism among innovation demand, innovation mode, research thinking, treatment method of difficulty and expected risk. The research could straighten up thinking of review expert of basic research project in agricultural field, and provide the reference for applicant designing the project.
[1] LIU DC, PAN R. The example scientific research and innovative methods [M]. Beijing: Science and Technology of China Press,2012:25-26,46,58. (in Chinese).
[2] FU JJ. Technological innovation [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press,2000:19,35-37,82. (in Chinese).
[3] THOMAS K. The structure of scientific revolution [M]. JIN WL, HU XH(Translators), Beijing: Peking University Press,2012:9. (in Chinese).
[4] CHEN J, JING JS, TONG L. An empirical study on risk factors of CoPS innovation project [J]. R&D Management,2013, 17(6): 62-68. (in Chinese).
[5] WANG DP. Study on the key problems of science foundation and management [D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology,2015:23. (in Chinese).
[6] YANG JD. Study on the evaluation of the overall development and financial aid of agriculture——Based on the angle of farmers’ specialized cooperative [D]. Chengdu:Southwestern University of Finance and Economics,2014:21-30. (in Chinese).
[7] JAN F, DAVID M, RICHARD RN. The Oxford handbook of innovation [M]. LIU XL, ZHENG G, LIN L,etal. (Translators), Beijing: Intellectual Property Publishing House,2009:88-112. (in Chinese).
[8] QIU JP, WEN TX. Evaluation science:Theory method practice [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010:108. (in Chinese).
[9] YOU H. A sociological research on the relationship between emotion and trust [D]. Wuhan:Wuhan University,2009:88-92. (in Chinese).
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Feasibility Analysis of Agricultural Product Price Index Insurance Based on Pilot Cases
- Forecast on Price of Agricultural Futures in China Based on ARIMA Model
- Model Building for Community Participating in Rural Tourism and Game Analysis of Core Stakeholders
- Embedded Programmable Single Point Multiple Output Intelligent Data Acquisition and Transmission System
- A Study of the Factors that Affect Farmers’ Willingness to Transfer Land in the Central Regions Based on a Survey of 180 Farmers in Suizhou City
- Comparative Study of Cotton Plant Height Difference in the Arid Areas Based on LandSat8 OLI Data
