Correlation between Carotenoids Content and Several Quality Traits of Wheat Varieties
2015-12-14DeqiangRENYuanyuanWUJianZHOUYanJIANGWenyinZHENGWenmingZHANGWenshanGUODanianYAO
Deqiang REN, Yuanyuan WU, Jian ZHOU, Yan JIANG, Wenyin ZHENG, Wenming ZHANG,Wenshan GUO, Danian YAO*
1. College of Agronomy, Anhui Agricultural University, Key Laboratory of Wheat Biology and Genetic Breeding in Huang-huai Southern Areas of the Ministry of Agriculture, P.R. China, Collaborative Innovation Center on Crops of Anhui Province, Hefei 230036, China;
2. Collaborative Innovation Center on Crops of Jiangsu Province, Yangzhou 225000, China
Carotenoid is an important nutritional quality trait of wheat[1].Carotenoids improvement of wheat has become the research hotspot of wheat genetics and breeding in foreign countries in recent years[2]. However, wheat quality improvement in China is mainly focused on its protein content and the improvement of quality-related traits[3].And breeding improvement of wheat carotenoids is still at its preliminary stage.Carotenoids usually refer to the summation of hydrocarbon of C40(carotene) and their dioxide derivatives (lutein)[4].Carotenoid is a kind of isoprene compound,containing a lot of conjugated double bonds. It usually has C40basic structural framework with relatively great molecular weight.Carotenoid generally does not dissolve in water, but is soluble in most organic solvents.Due to the existence of conjugated double bonds, carotenoid has strong absorption performance and unique absorption zone.Spectrophotometer method can be used to detect a large amount of samples at early generation, which is economic,simple,rapid and accurate[5].
Carotenoid has anti-oxidation effect and relatively high nutritional value,which is helpful to human health.Due to the antitumor activity,carotenoid prevents cardiovascular diseases, protects the black region of retina, reduces the incidence of cataract, prevents the age pigments and so on. Carotenoid is the precursors of vitamin A (VA)[6], and has the source activity of VA. Therefore, it is used to prevent vitamin A deficiency(VAD) and to reduce the blindness in children caused by VAD. Besides, the antioxidation of carotenoid delays the lipoxidase (LOX) damage to en-dosperm nutritional quality, and prolongs the storage period of seeds.
In this research, a total of 31 wheat varieties (lines) were used as experimental materials, aiming at analyzing the genotypic differences in carotenoid content of wheat wholemeal, lipoxygenase activity (LOX), total pentosan (TP) content, water-soluble pentosan(WSP)content,water-insoluble pentosan (WIP) content,chromatic meter parameter, RVA parameter, near infrared spectrometer and farinograph parameter. Relationships between carotenoid content and several quality traits were researched,aiming at providing references for the quality improvement and variety resources screening.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Field test was carried out in experimental farm of Anhui Agricultural University from 2011 to 2012. Randomized block design was adopted with in all three repetitions. There were five rows in each block with 2 m row length and 0.25 m row spacing. Field management was the same as field production level. During mature stage,wheat was harvested, dried under the sun and stored in room for two months.
Preparation of wheat wholemeal
Wheat was wet for 24 h so that the moisture content reached about 14%. Then, wheat was grinded into powder by SCINO CT-410 pulverizer,passed through a 0.5 mm sieve, and sealed by kraft paper sacks in a refrigerated counter. Thus, the wheat wholemeal could be used to analyze the quality-related traits.
Quality-related traits included carotinoid content, LOX activity, pentosan content,colorimeter parameters,rapid viscosity analyzer(RVA)parameters, and near infrared instrument(NIR) parameters. Parameters of colorimeter included brightness, redness,yellowness and whiteness. Parameters of rapid viscosity analyzer included peak viscosity(PV),through viscosity, final viscosity, break down, set back,peak time and pasting temperature. Parameters of near infrared instrument included protein content, unit weight,wet gluten,formation time,stability time, zeleny, hardness and extraction rate.
Detection of carotinoid content
The detection method for carotinoid: according to 14 -50 of AACC method,carotinoid was detected.
A total of 2 g wheat wholemeal was transferred into a 40 ml centrifuge tube.After adding 10 ml water saturated n-butanol, vibrating extraction was carried out for 1 h. After placed for 15 min,the solution was centrifuged at 10 000 r/min for 10 min. Supernatant was collected. Absorbance was detected at 440 nm by Alpha-1860 spectrophotometer (Shanghai Lab-Spectrum Instruments Co.,Ltd.).
Carotinoid content (mg/kg)=C×V/m
Detection of other quality traits
LOX activity of wheat was detected according to the improved spectrophotometer method of Larisa Catod[7].
Pentosan content was detected according to the orcinol-hydrochloric acid method[8].Contents of water-soluble pentosan and total pentosan were detected, so as to calculate the content of water-insoluble pentosan(Content of water-insoluble pentosan=Total pentosan content-Content of water-soluble pentosan).
Whiteness was calculated according to the equation of (Wht=100 -[(100-L)2+a2+b2]1/2). In the equation, L,a and b values were detected by CR410 color difference meter (Konica Minolta).
Detection of rapid viscosity analyzer parameters: peak viscosity, pasting temperature, breakdown and other RVA parameters were detected by rapid viscosity tester (RVA-super3,Newport Scientific).
Seed moisture content, protein content, wet gluten content, sedimentation value, hardness and other parameters were detected by DA7200 near infrared spectrometer(Perten).
Statistical analysis
The research was carried out in the experimental farm and Seed Science and Engineering Laboratory of Anhui Agricultural University. Data were analyzed by Data Processing System and other statistical softwares.Variance analysis, correlation analysis, Duncan’s multiple comparison and clustering analysis were carried out. The map was established by Excel.
Results and Analyses
Variance analysis of carotinoid content and other quality traits
Table 1 reported that the carotinoid contents in wheat wholemeal of different varieties reached extremely significant differences. Activity of lipoxygenase showed significant differences. Total pentosan, water-insoluble pentosan, water-insoluble pentosan, colorimeter parameter, RVA parameter and near-infrared parameter showed extremely significant differences among varieties. These indicated that carotinoid content, lipoxygenase and other quality traits had significant or extremely significant differences among different varieties.
Multiple comparison of carotenoid and other quality traits
Table 2 reported that in the tested wheat varieties (lines), the range of carotenoid content in wheat wholemeal was 0.79-3.08 mg/kg, with the average content being 1.72 mg/kg.Among them, Huaimai22 had the maximum content of carotenoid (3.08 mg/kg); while Zhenmai168 and Wanmai 48 had the minimum content(both 0.79 mg/kg). Carotenoid content was relatively high in Jimai22 (2.90 mg/kg)and Meng0318 (2.30 mg/kg),but was relatively low in Yangmai13 (0.99 mg/kg) and Yangfumai2 (1.00 mg/kg).The great variation of carotenoid content indicated that it was of practical significance to carry out wheat variety screening and quality improvement according to the carotenoid content.
The variation amplitude of lipoxygenase activity was 92-191.47 AU/(min·g), with the average activity being 145.06 AU/(min ·g). Among them,Zhouyou102 (191.47 AU/(min·g))and Luo9908 (189.07 AU/(min·g))had the maximum lipoxygenase activity;while Zhoumai13 (92 AU/(min·g))was the minimum. The variation amplitude of total pentosan content was 5.88%-11.71%,with the average content being 9.26% . Among them,Huaimai22 (11.71% ) and Jimai22(11.64%) had the maximum content;while Zhengnong88(5.88%)and Tianhe0519 (5.95% ) had the minimumcontent.The content change of watersoluble pentosans was 0.54%-1.15%,with the average content being 0.86%.Among them, Jimai22 and Xumai270(1.07% ) had the maximum content(1.15%); while Yannong5158 had the minimum content (0.54%).The variation amplitude of waterinsoluble pentosans was 5.08%-10.73%, with the average content being 8.39%. Among them, Huaimai22 (10.73%) had the maximum content; while Tianhe0518(5.08%)had the minimum content.
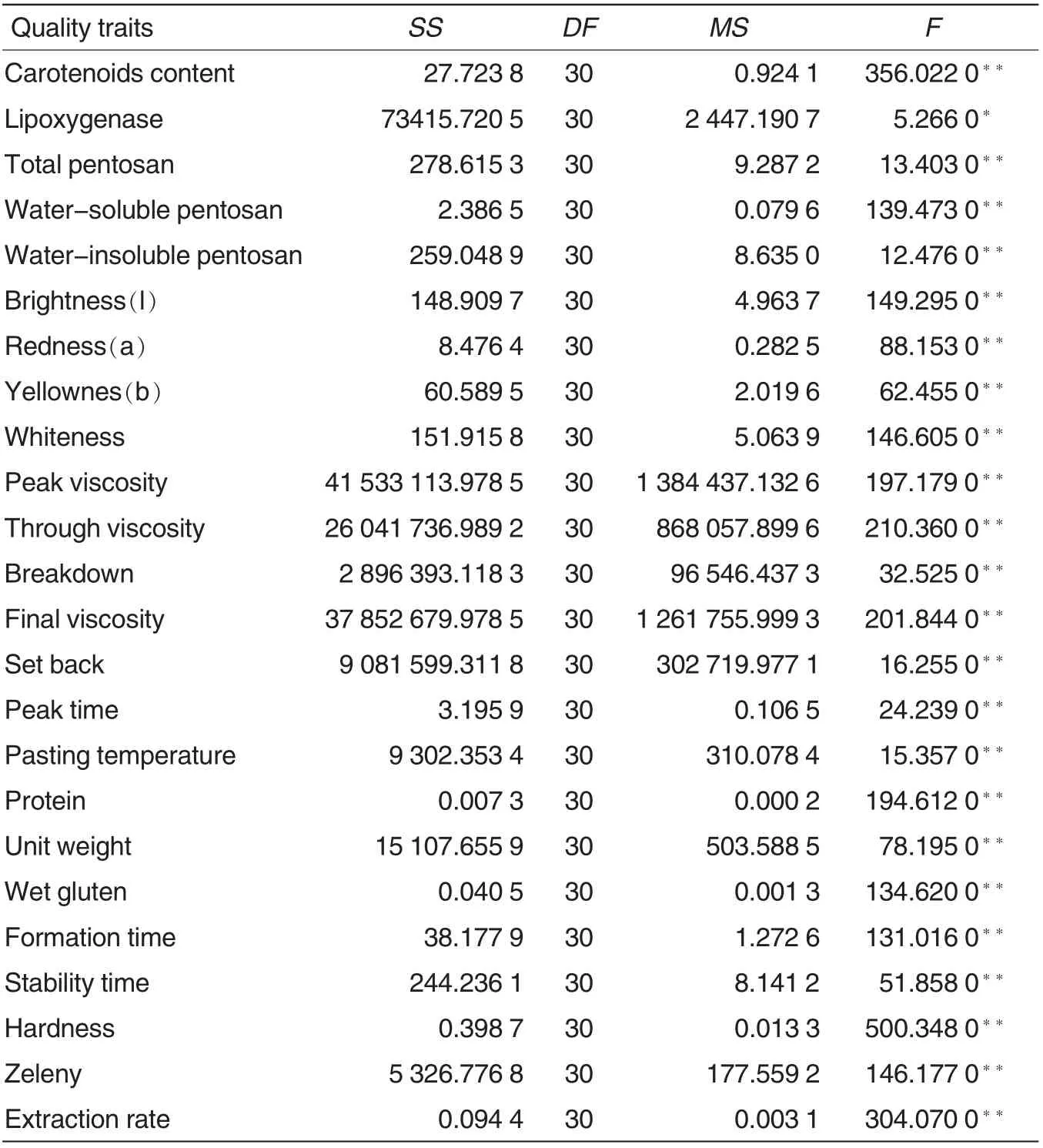
Table 1 Variance analysis of 24 quality traits
The variation amplitude of brightness in colorimeter was from -32.6 to-26.98, with the average value being-29.24. Among them, Yanzhan4110 had the maximum brightness(-26.98);while Jimai22 was the minimum(-32.6). The variation amplitude of redness was from 0.05 to 1.21, with the average value being 0.57. Among then, Zhenmai168 had the maximum value (1.21); while Meng0318 was the minimum (0.05).The variation amplitude of yellowness was 5.88 -8.74,with the average value being 7.48. Among them, yellowness of Meng-0318 was the maximum (8.73), and that of Wanmai48 was the minimum (5.88).The variation amplitude of whiteness was from -27.14 to -32.88, with the average value being -29.46. Among them, Yanzhan4110 (-27.14) and Zhengnong21 (-27.24) were the maximum; while Jimai22 (-32.88) and Kaimai18(-31.4)were the minimum.
In RVA parameters,range of peak viscosity was 1612.33-4495.33, with the average value being 3246.75.Among them, Zhenmai168 had the maximum peak viscosity (4495.33);while Jimai22 had the minimum value(1612.33). The range of through viscosity was 703-3008.67, with the average value being 1 928.01. Among them, Zhenmai168 had the maximum through viscosity (3008.67); while Jimai22 had the minimum value (703).The variation amplitude of breakdown was 912.67-1 646.67, with the mean value being 1 321.13. Among them,the maximum value of breakdown was 1 646.67; while the minimum value was 912.67(Jimai22).The range of final viscosity was 2 193-4 730,with the average value being 3 622.75. Among them, Zhenmai168 had the maximum final viscosity (4730); while Ningmai11 had the minimum content (2193).The variation amplitude of set back was 974.67-2 337.67,with the mean value being 1 684.09. Among them, Kaimai-18 had the maximum value (2337.67);while Luo9908 was the minimum(974.67). The range of peak time was 5.62-6.51 min, with the mean value being 6.21 min. Among them, Zhenmai168 had the maximum peak time(6.51 min);while Jimai22 had the minimum value (5.62 min). The range of pasting temperature was 50.37-86.65℃, with the mean value being 71.26℃. Among them, Luomai23 had the maximum pasting temperature (86.65℃); while Jimai22 was the minimum(50.37 ℃).
In near infrared parameters, the range of protein content was 11.48%-15.78%, with the mean value being 13.31% . Among them, Zhenmai168 had the maximum protein content(15.78%);while Luo9908 had the minimum content (11.48%).The range of unit weight was 752.67-806.33 g,with the average value being 783.34 g.Among them, Zhenmai168 had the maximum unit weight(806.33 g);while Jimai22 had the minimum value(752.67 g). The variation amplitude of wet gluten was 33.2%-23.76%, with the mean value being 27.63%.Among them, Zhenmai168 had the maximum wet gluten (33.2%); while Luo9908 had the minimum value(23.76%).The variation amplitude of stability time was 1-8.4 min, with the mean value being 5.04 min. Among them, Zhenmai168 had the maximum stability time (8.4 min);while Luo9908 had the minimum value (1 min). The range of formation time was 1.13-3.87 min with the mean value being 2.28 min. Among them, Zhenmai168 had the maximum formation time (3.87 min); while Huaimai22 had the minimum value(1.13).The range of hardness was 51.33%-79%,with the mean value being 63.42% . Among them,Luo9908 had the maximum hardness(79%);while Yangfumai2 had the min-
imum value (51.33%). The range of zeleny was 19.73=60.3 ml, with the mean value being 30.38 ml. Among them, zeleny was the maximum in Luo9908 (60.3 ml) and the minimum in Luomai23(19.73 ml).
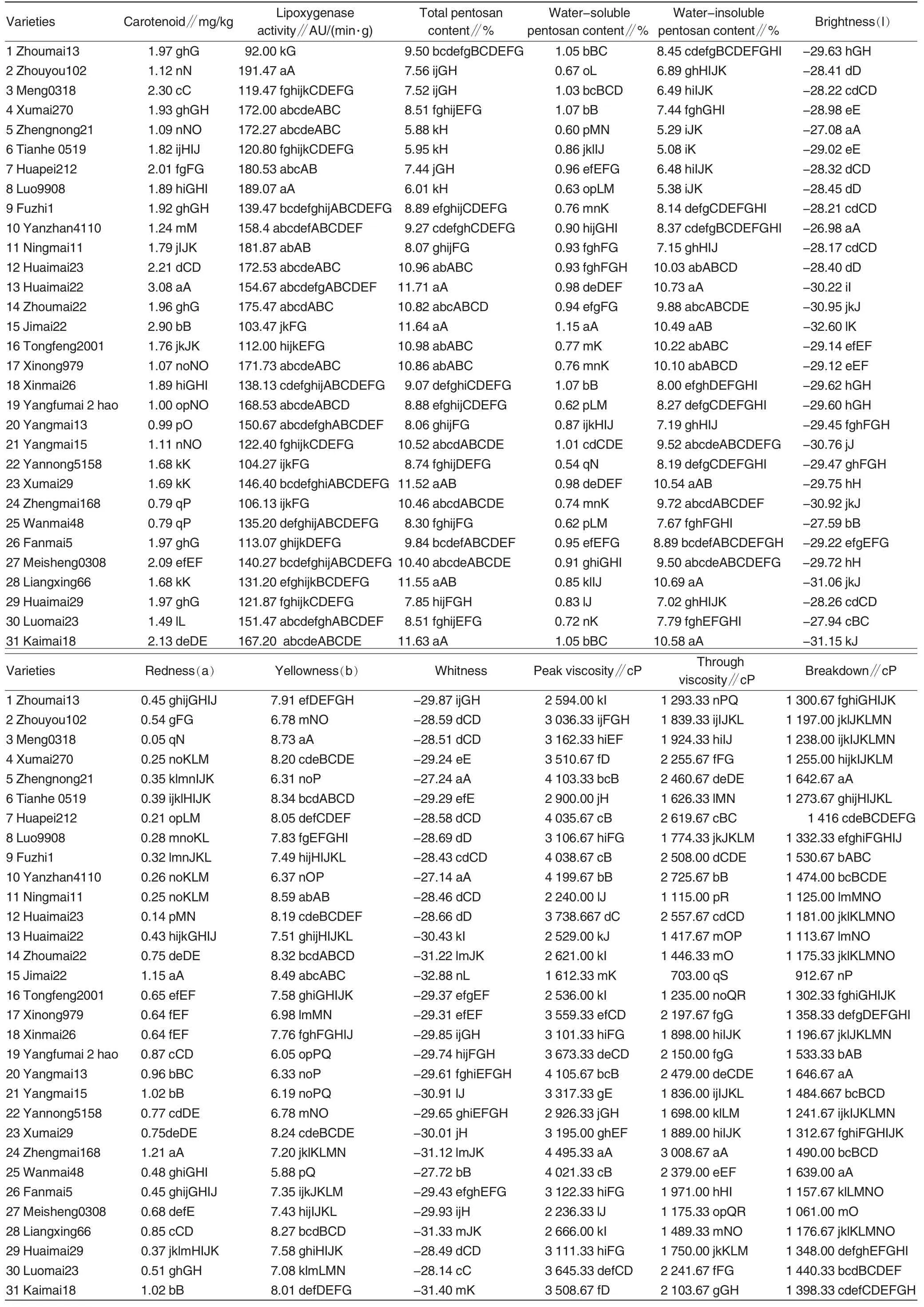
Table 2 Multiple comparison of 24 quality traits from 31 varieties(lines)
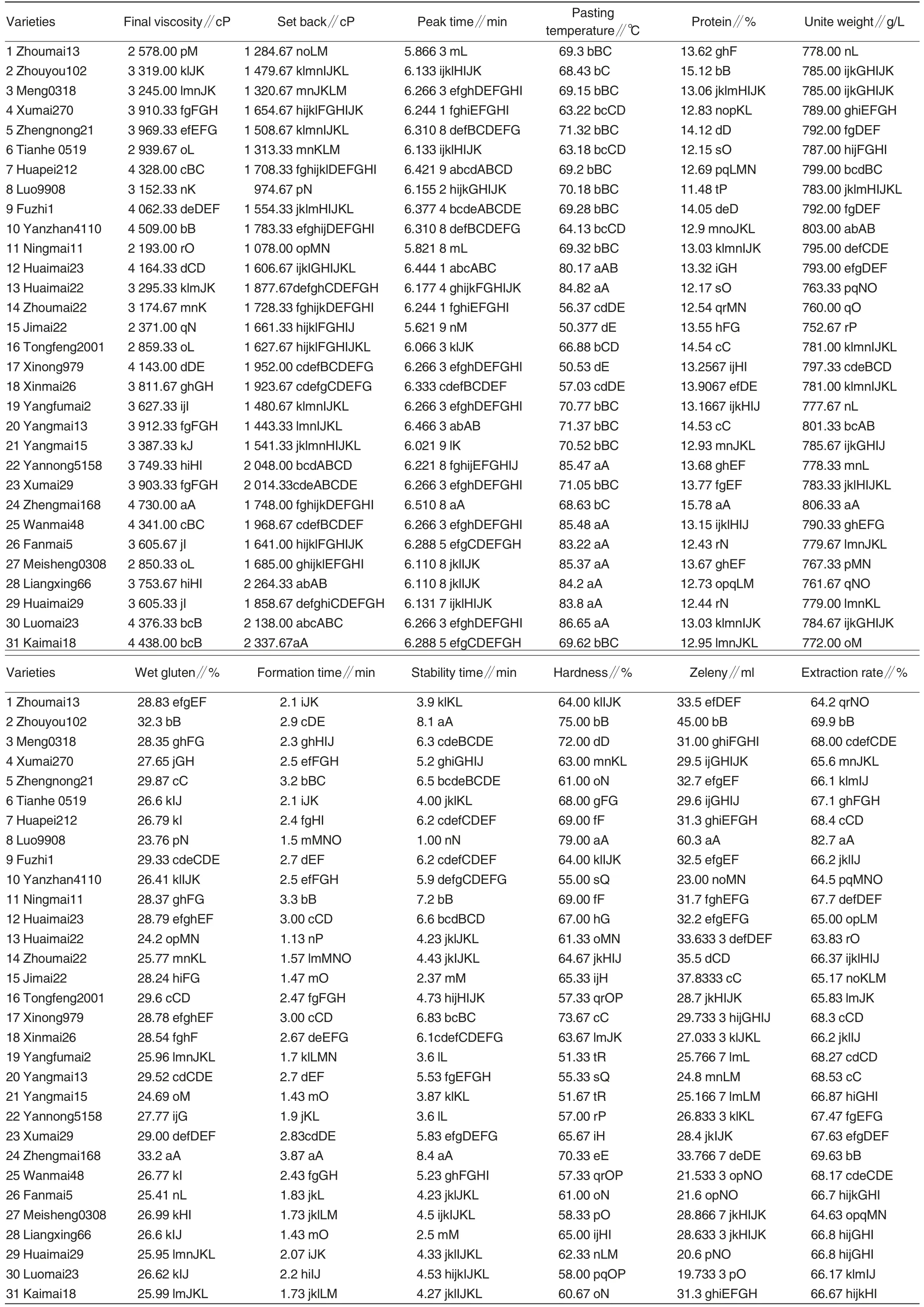
Continued(Table 2)
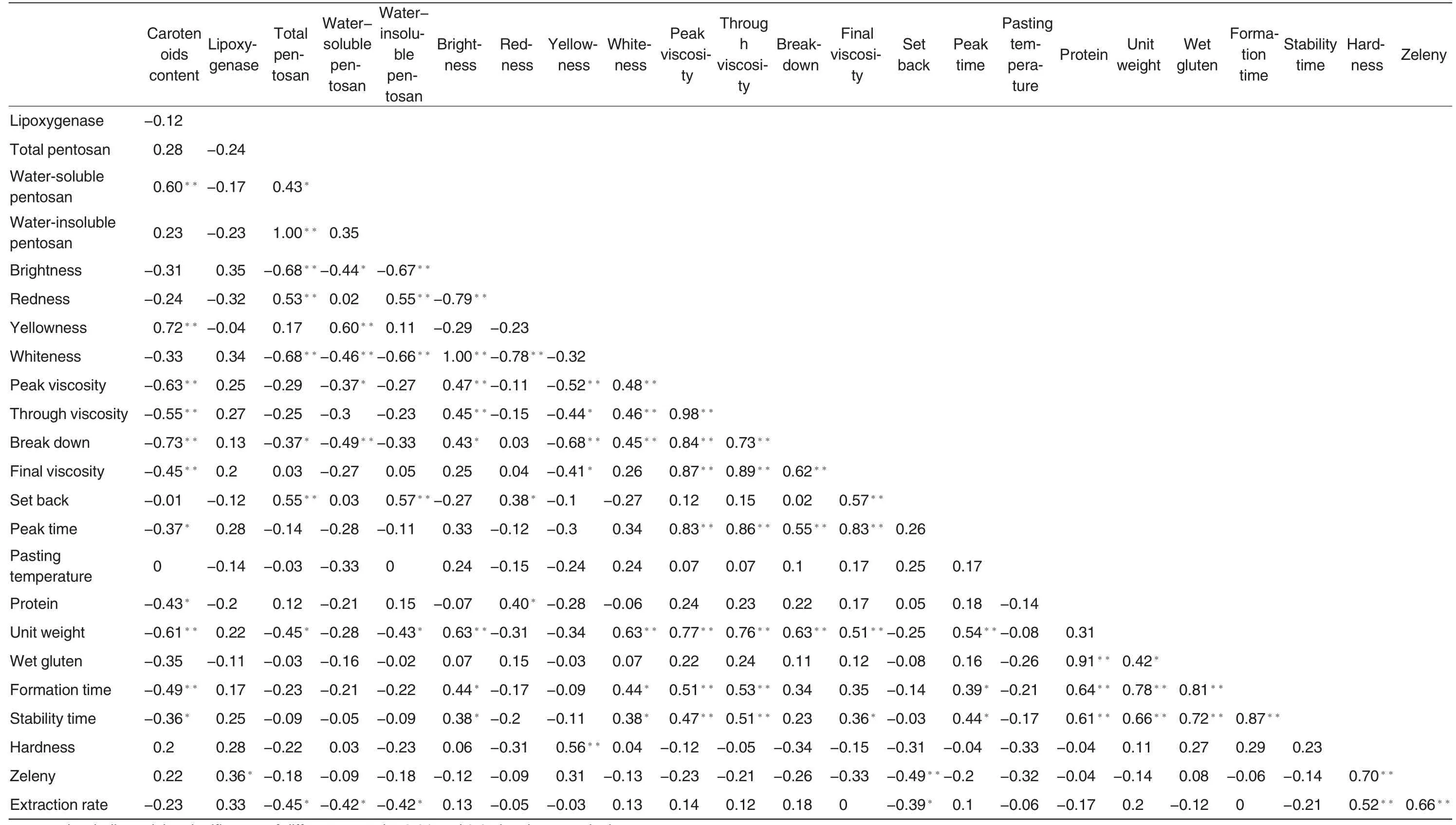
Correlation analysis of 24 quality traitsTable 3
Correlation analysis of carotinoid contents in wheat wholemeal of 31 varieties (lines) and other quality traits
Table 3 showed that carotinoid content had extremely significant positive correlation with water-soluble pentosan, and had extremely significant negative correlation with peak viscosity, through viscosity, breakdown,final viscosity, unit weight, formation time.At the same time,carotinoid content showed significant negative correlation with peak time,protein content and stability time.
Lipoxygenase activity had significant negative correlation with zeleny;total pentosan content showed extremely significant positive correlation with water-insoluble pentosan, redness and set back,had extremely significant negative correlation with whiteness, had extremely significant positive correlation with water-soluble pentosan, and showed extremely significant negative correlation with zeleny,unit weight and extraction rate.Water-soluble pentosan content had extremely significant positive correlation with yellowness, had extremely significant negative correlation with whiteness and zeleny, had significant negative correlation with brightness,peak value and extraction rate. Waterinsoluble pentosan content had extremely significant positive correlation with redness and set back, had extremely significant negative correlation with brightness and whiteness, and had significant negative correlation with unit weight and extraction rate.
Brightness had extremely significant positive correlation with white ness, peak viscosity, through viscosity and unit weight, showed extremely significant negative correlation with redness, had significant positive correlation with zeleny, stability time and formation time.Redness had extremely significant negative correlation with whiteness, had significant positive correlation with set back and protein.Yellowness had extremely significant positive correlation with hardness, had extremely significant negative correlation with peak viscosity and zeleny,and had significant negative correlation with through viscosity and final viscosity. Whiteness had extremely significant positive correlation with peak viscosity,zeleny and unit weight,and showed significant positive correlation with stability time and formation time.
Peak viscosity showed extremely significant positive correlation with through viscosity,zeleny,set back,unit weight, stability time and formation time. Through viscosity had extremely significant positive correlation with zeleny, final viscosity, peak time, unit weight, stability time and formation time. Zeleny had extremely significant positive correlation with final viscosity,peak time and unit weight. Final viscosity had extremely significant positive correlation with set back, peak time and unit weight, but had significant positive correlation with stability time. Set back had extremely significant negative correlation with zeleny,and showed significant negative correlation with extraction rate. Peak time had extremely significant positive correlation with unit weight, and showed significant positive correlation with formation time and stability time.
Protein content had extremely significant positive correlation with wet gluten, stability time and formation time.Unit weight had extremely significant positive correlation with stability time and formation time, and showed significant negative correlation with wet gluten. Wet gluten showed extremely significant positive correlation with stability time and formation. Stability time had extremely significant positive correlation with formation time. Harness had extremely positive correlation with zeleny and extraction rate. And zeleny showed extremely significant positive correlation with extraction rate.
Cluster analysis of carotinoid content
Cluster analysis of carotinoid contents from 31 wheat verities(lines)was carried out by Euclidean distance method (Fig.1). Results showed that they could be divided into three categories.
Category Ⅰ included 19 wheat verities (lines) with middle carotinoid content. The range of carotinoid content was 1.68-2.30 mg/kg, with the mean value being 1.93 mg/kg. They were Meng0318, Huaimai23,Kaimai18, Meisheng0308, Huapei212,Zhoumai13, Fanmai 5, Huaimai29,Zhoumai22, Xumai270, Fuzhi1, Luo9908, Xinmai26, Tianhe0519, Ningmai11, Tongfeng2011, Xumai29,Liangxing66 and Yannong5158.
Category Ⅱ included 10 wheat verities (lines) with relatively low carotinoid content. The range of carotinoid content was 0.79-1.49 mg/kg, with the mean value being 1.07 mg/kg. They were Luomai23,Yanzhan4110, Zhouyou102, Yangmai15, Zhengnong21, Xinong979,Yangfumai2, Yangmai13, Wanmai48,and Zhenmai168.
Category Ⅲincluded 2 wheat verities (lines) with relatively high carotinoid content. The range of carotinoid content was 2.90-3.08 mg/kg,with the mean value being 2.99 mg/kg. They were Huaimai 22 and Jimai22.
Discussions
Carotinoid content in wheat wholemeal
Sun Dao-jie[9](2006) and Wang Fan[10](2012) argued that carotinoid content in wheat showed significantdifferences among different verities;and carotinoid content in wheat wholemeal was significantly positive correlated with yellowness. Analysis results of this research were basically the same. The correlation coefficient between carotinoid content and yellowness was 0.72, showing extremely significant positive correlation.However,carotinoid content in wheat wholemeal showed no significant correlation with redness and brightness.
Hu Ruibo[11](2004) pointed out that carotinoid content was significantly negative correlated with flour whiteness, which was the main reason for the decrease of flour whiteness.Wang Fan[9](2012) argued that carotinoid content had significant correlation with lipoxygenase. However, in this research, carotinoid content showed no significant correlation with whiteness and lipoxygenase, which was different from the research results of Wang Fan[10](2012). This might be because that the tested varieties were different and wheat wholemeal was adopted in this research.
Cluster analysis of carotinoid contents from 31 wheat verities(lines)was carried out by Euclidean distance method. Results showed that they could be divided into three categories.And the variety resources with different carotinoid contents could be screened according to different breeding target.
Lipoxygenase and other quality traits
In this research,lipoxygenase had no significant correlation with pentosan; brightness was significantly negative correlated with total pentosan,water-soluble pentosan and water-insoluble pentosan; and whiteness also had significant negative correlation with total pentosan, water-soluble pentosan and water-insoluble pentosan, which were basically consistent with the research results of Wang Hui(2011)[12].
Peak viscosity had extremely significant positive correlation with through viscosity, breakdown, final viscosity and peak time. Through viscosity was extremely significantly positive correlated with breakdown, final viscosity and peak time. Breakdown had extremely significant positive correlation with final viscosity and peak time.Final viscosity showed extremely significant positive correlation with set back and peak time.All these research results were basically the same as the results by Xue Xiang[13](2007)and Yan Jun[14](2001).
Xu Yao-fei[15](1999)argued that protein participated in the formation of gluten network structure, which improved the properties of dough;stability time reflected the toughness of dough; and formation time reflected the quality and quantity of dough. In this research, correlation coefficients between protein and wet gluten,stability time and formation time were 0.91,0.61 and 0.64,showing extremely significant positive correlation. Thus, the research results mentioned above were verified.
In general, variance analysis and cluster analysis of wheat carotinoids and other quality traits were carried out; the relationship between the variety differences of carotinoid content and the quality traits were researched,which was of certain significance to the variety screening of wheat.
[1]ZHANG B Q(张伯桥),ZHENG Y(郑义),ZHANG P P (张平平), et al. Quality Analysis of Wheat Varieties in the Yangtze River Area( 长江流域小麦品种(系) 的品质状况分析)[J].Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences(江苏农业学报),2009,25(3):478-483.
[2]SHI W X (施万喜).Status of Wheat Quality Traits and Strategy of Improvement in China (我国小麦品质现状与改良对策).Seed(种子),2006(10).
[3]HU C L(胡承霖),MA C X(马传喜),LI J C(李金才),CAO C F(曹承富),et al.Anhui Wheat Planting. Anhui (安徽麦作学):Anhui Science&Technology Publishing House (安徽: 安徽科学技术出版社),2009.
[4]MENG E, LOYNS A, PENA RJ. Wheat quality in the developing word :trends and opportunities, In"Wheat facts and futures"(Eds J Dison etal;CIMMYT:Mexico,D F),2009,pp:26-41.
[5]VON LINTIG J, WYSS A. Molecular analysis of vitamin A formation:cloning and haracterization of β-caroteone 15,15'-dioxygenase.Archives of Biochemistry andBiophysics.2001,385:47-52.
[6]LV J L (吕俊丽).Antioxidant component analysis and functional evaluation and functional of different genotype wheat in Maryland (美国马里兰不同品种小麦抗氧化成分分析与功能性评价).2013.
[7]BORRELLI G M, TROCCOLI A, DI FONZO N, FARES C. Durum wheatlipoxygenase activity and other quality parameters that affect pastacolor.Cereal Chemistry,1999,76(3):335-3440.
[8]HU R B(胡瑞波),TIAN J C(田纪春),LV J H (吕建华).Stability Analysis of Carotenoid Content and Its Coefficient Correlation with Yellow Alkaline Noodle Color Characteristics in Common Wheat(Triticum aestivum L.)( 小麦类胡萝卜素含量的稳定性及其与黄碱面条色泽性状的相关性分析).Acta Agronomica Sinica(作物学报),2004,30(6):597-600.
[9]SONG H D(宋华东),FAN Q Q(樊庆琦),LIU A F (刘爱峰), et al.Screening of wheat germplasm with high flour whiteness and analysis of its quality (面粉高白度小麦种质资源筛选及其品质分析).Journal of Triticeae Crops (麦类作物学报),2012,32(1):54-59.
[10]HE Z H (何中虎),ZHUANG Q S.Chinese wheat improvement and pedigree analysis (中国小麦品种改良及系谱分析)[A].Peking:China Agriculture Press,2003,519-542.
[11]ZHENG W Y(郑文寅),WANG F(汪帆),SI H Q (司红起), et al. Variations of LOX and PPO activities and carotenoid content as well as their influence on whole flour color in common wheat (普通小麦籽粒LOX?PPO活性和类胡萝卜素含量变异及对全麦粉色泽的影响). Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 2013, 46(6):1087-1094.
[12]AACC. Approved Methods of the American Association of CerealChemists(9thed).MN,St.Paul,USA,1995.
[13]CATO L, HALMOS A L, SMALL D M..Measurement of lipoxygenase in Australian white wheat flour: the effect of lipoxygenase on the quality properties of white salted noodles [J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2006,86:1670-1678.
[14]LI C X (李春喜), QIU Z B (邱宗波),JIANG L N (姜丽娜), et al.Analysis of Pentosan Content and Stability in Wheat (小麦籽粒戊聚糖含量及其稳定性分析)[J].Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences (河南农业科学), 2003(4):7-9.
[15]SUN D J (孙道杰),HE Z H (何中虎),WANG H (王辉).Gene Related With Yellow Pigment in Wheat Flour(小麦面粉黄色素相关基因研究)[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica(西北植物报),2006,26(4):0655-0660.
[16]WANG F(汪帆),ZHENG W Y(郑文寅),HUANG J H (黄建华),et al.Lipoxygenase Activity, Carotenoids Content and Wholemill Flour Colors in Grains of Twenty Wheat Varieties (20 个小麦品种(系)籽粒LOX 活性和类胡萝卜素含量及全麦粉色泽的研究).Journal ofTriticeae Crops (麦类作物学报),2012,32(1):68-73.
[17]WANG H (王慧).Lipoxygenase Activity and Its Genotype and Environment Interactions for Kernels of Different Wheat Varieties (不同小麦品种籽粒中LOX 活性及基因型和环境互作分析).2011.
[18]XUE X (薛香), YANG Z Q (杨忠强),YUE H F (岳海风), et al.Analysis of Genetic Effects of Wheat Starch Pasting Characteristics(小麦糊化特性参数的遗传效应分析).Liaoning Agricultural Sciences(辽宁农业科学),2007(5):1-4.
[19]YAN J(阎俊),ZHANG Y(张勇),HE Z H(何中虎).Investigation on paste Property of Chinese Wheat (小麦品种糊化特性研究). Scientia Agricultura Sinica(中国农业科学),2001,34(1):1-4.
[20]XU Z F(徐兆飞),ZHANG H Y(张惠叶),ZHANG D Y (张定一). Quality Traits and Improvement of Wheat (小麦品质及其改良)[M].Peking:China Meteorological Press(北京:中国气象出版社),2000.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effect of Tree Species and Dosage of Rhizomorph Wood on Asexual Propagation of Wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi
- Effects of Different Application Times of Tillering Fertilizer on Grain Yield and Population Development of Double-cropping Rice Transplanted by Machine
- Biological Characteristics and Pathogenicities of Shewanella algae and Shewanella abalone from Babylonia
- Research on Physiological Characteristics of Tall Fescue under Nitrogen Stress
- Cloning and Characterization of Phytochrome A Gene FaPHYA from Tall Fescue
- Changes in Physiological Indexes of SPDS Transgenic Potato Plants under Low Temperature Stress
