Effect of Tree Species and Dosage of Rhizomorph Wood on Asexual Propagation of Wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi
2015-12-14XueqiangXIE
Xueqiang XIE
Department of Environment and Life Science, Sichuan University for Nationalities, Kangding 626001, China
Gastrodia elata is not only a traditional precious Chinese medicine but also a health care ingredient favored by current people. It mainly cures hypertension,dizziness, headache, facial paralysis etc.and also plays an important role in the regulation and improvement of human body’s function. Because of the good shape,high drying rate,excellent quality,wild place,low number and little artificial cultivation, the price of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow is 3-4 times higher than that of Gastrodia elata.BI.f elata and Gastrodia elata BL.f.flavida S. Chow[1]. Due to the large demand in China and abroad for the no-polluted wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi, it is over exploited and the resource is drying up. In order to protect the resource of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi and meet people’s needs, the domestication of Gastrodia elata is essential. Mycelia colonized woodlogs is needed for Gastrodia elata cultivation and the mycelia colonized woodlogs is Armillariella mellea(Vahl exFr.) Karst rhizomorph wood[2].Tree species and dosage of Armillariella mellea rhizomoph wood had big effects on the yield of Gastrodia elata[3]. There are a plenty of tree specieses of Armillariella mellea rhizomorph wood in Ganzi for Gastrodia elata cultivation. Under natural condition, Gastrodia elata grows hardly because the ecology in Ganzi is weak.How to efficiently, continuously and environmentally friendly develop the effect of the tree species of Armillariella mellea rhizomorph wood on the domestication of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow is urgent to be studied.The influences of tree species and dosages of Armillariella mellea rhizomorph wood on wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow were studied in this study in order to provide a reference for the domestication of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow.
Materials and Methods
Test materials
Seed stem of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow (1) The first generation G1 produced by sexual propagation from wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Kangding: the wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow grows in Kangding forestry at the altitude of 2 800 m.The mature tuber type is flat oval and its weight is 40-275 g.The wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow has long inflorescence internodes and few flowers. It was hand-pollinated in greenhouse in April, 2012 and then the seeds were sowed. The smallest immature tuber and the small white immature tuber of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow harvested in March next year were used as seed stem.
Tree species of Armillariella mellea rhizomorph wood and fabrication of short-cut wood Two kinds of trees were selected as the tree species of Armillariella mellea rhizomorph wood.One was white birch S1with a coarse grained wood, which was easily to be rotted. The other was Quercus spinosa with a close grained wood,which was not easily to be rotted.Branches with a diameter of 5 cm ofthe two trees were selected.Both ends were cut obliquely into a 40 cm long short-cut wood and bevel connections were cut with an interval of 10 cm,and the cuts reached xylem.
Culture of Armillariella mellea rhizomorph wood (1)Culture of mother strain AmG of Armillariella mellea:AmG was obtained by tissue isolation from the tuber of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Kangding adhered with Armillariella mellea rhizomorph.
(2) Fungal stick cultivation of Armillariella mellea: shoot sections of nanking cherry (Prunus tomentosa Thunb.) (diameters were about 1 cm and length were 1-2 cm)were put into a 600 ml brown volumetric flask. 20 g corn flour, 20 g white sugar and 8 g agar were added to 1 000 ml water.The solution was kept boiling until dissolved and added to the brown volumetric flask(shoot sections were submerged). Autoclaved sterilization was performed at 121 ℃for 1 h.AmG was inoculated after the medium was cooled. The process was conducted from late January to late February.
(3) Culture of Armillariella mellea rhizomorph wood: AmG fungal stick of nanking cherry was used as strain and inoculated in different soil pits. Armillariella mellea rhizomorph wood was cultured on S1and S2short-cut woods.The method was shown as follows: 80 cm long, 40 cm wide and 30 cm deep soil pits were excavated,and a layer of 1 cm thick leaves of white birch was paved in the bottom of each pit.A layer of short-cut wood was parallelly paved on the leaves.A fugal stick was put on both ends of the short-cut wood and each bevel connection. The apertures of short-cut woods were filled with basic compost [three triplicate of saw powder of white birch + a share of clean coarse river sand (mass ratio,followings were the same)]and a layer of 0.5 cm thick compost was covered on the short-cut woods. Three times were repeated as above. Finally, 5 cm thick basic compost and a layer of white birch leaves were used for cover.The process was started in late February and completed in late March.
Test method
Plastic greenhouse was constructed on mountain land of forestry edge at an altitude of 2 800 m.The soil type was cinnamon soil and the fertility was uniform.
G1and G2were the two seed stems. S1(white birch), S2(Quercus spinosa) and S3(1/2 S1+1/2 S2) were involved as tree species of Armillariella mellea rhizomoph wood. Dosage of Armillariella mellea rhizomoph wood were set as A1-the interval between two Armillariella mellea rhizomoph woods was 5 cm, A2-the interval between two Armillariella mellea rhizomoph woods was 10 cm and A3-the interval between two Armillariella mellea rhizomoph woods was 15 cm. A total of 18 treatments were set. Randomized block design was adopted in the test with four replicates. The plot area was 1.00 m2and the aisle was 30 cm.
Sowing: the sowing method was referred to Xie[4]. The seed stem and Armillariella mellea rhizomoph wood were sowed after seed and strain selection. The grades of the two seed stems were the same and a kilogram contained 170 seed stems. A layer of seed stem was uniformly sowed in each plot and the weight of seed stems was 1.2 kg, and the sowing depth was 20 cm. The seed stems were in close proximity to the growing point of rhizomorph. The basic compost of 5 cm thick and a layer of fallen leaves of white birch were used for coverage after sowing and they were drenched with water.
Management and harvest: the temperature in the greenhouse was kept at 18-25 ℃and the humidity was kept at 65%-70%. The seed stems were sowed in early April, 2013 and harvested in late March,2014.
由于本系统采用两路信号同时滤波,且为达到尽可能理想的滤波器及处理性能与FPGA逻辑资源之间的平衡。本系统利用FIR滤波系统在具备线性相位时的对称特点,采用对称结构对此滤波器进行实现,以减少对乘法器资源的使用以及尽量增大滤波器的阶数,使其更接近于理想滤波器[12-14]。
Investigation and measuring items
Yield: sediments and impurities were wiped out during harvest and the total fresh weight of different levels of Gastrodia elata in each plot area was recorded as a plot yield.
Drying rate of mature tuber of Gastrodia: the fresh weight of mature tuber of Gastrodia was weighed after it was cleaned and the dry weight were obtained after mature tuber of Gastrodia was steamed for 30 min and dried at 80 ℃in drying oven.The proportion of dry weight and fresh weight of mature tuber of Gastrodia in each plot was defined as the drying rate.
Results and Analysis
Yield
The results of variance analysis indicated that the yields of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow were different among the different combinations of the three factors: type of seed stem, tree species and dosage of Armillariella mellea rhizomoph wood,and different levels of each single factor. There was no interaction effect among the factors.
Combination effect of the factors
Variances of the asexual reproduction yields of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in different combinations of the three factors were shown in Table 1. Among the 18 combinations, the average yield of G2-S2-A2was the highest and the yield was 9.200 kg/m2.The yield of G2-S3-A2was 9.025 kg/m2, which was the second highest. The difference of the average yields between the two combinations was not significant. The average yield of G1-S1-A3was the lowest and the yield was 3.100 kg/m2. The average yield of G1-S1-A1was 3.800 kg/m2,which was a slightly higher than that of G1-S1-A3. There was a significant difference between the average yields of the two combinations.
Effect of a single factor The average asexual reproduction yields of seed stems of different wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow had a significant difference. The average yield of the first generation G2of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Yusaping was 7.753 kg/m2and the average yield of the first generation G1of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Kangding was 4.819 kg/m2.A mong the different tree species of Armillariella mellea rhizomorph wood,the average asexual reproduction yields of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow with Quercus spinosa S2,half of Quercus spinosa and half of white birch S3and white birch S1as rhizomorph wood were 6.775, 6.629 and 5.454 kg/m2, respectively. The difference between S2and S3was not significant while the difference between S2and S1was significant.Among the different dosages of Armillariella mellea rhizomorph wood,the average asexual reproduction yields of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow with 10, 5 and 15 cm as the intervals were 7.254,6.192 and 5.413 kg/m2, respectively. The differences among the three treatments were significant(Table 2).
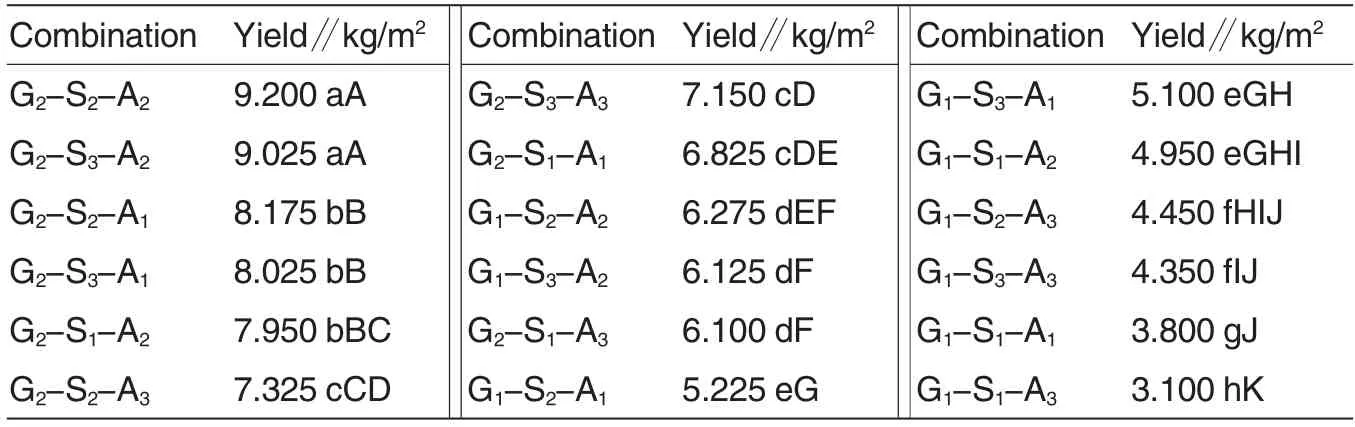
Table 1 Effect on the yield of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow by asexual reproduction of the combinations of seed stem types,tree species of rhizomorph wood and dosage of rhizomorph wood
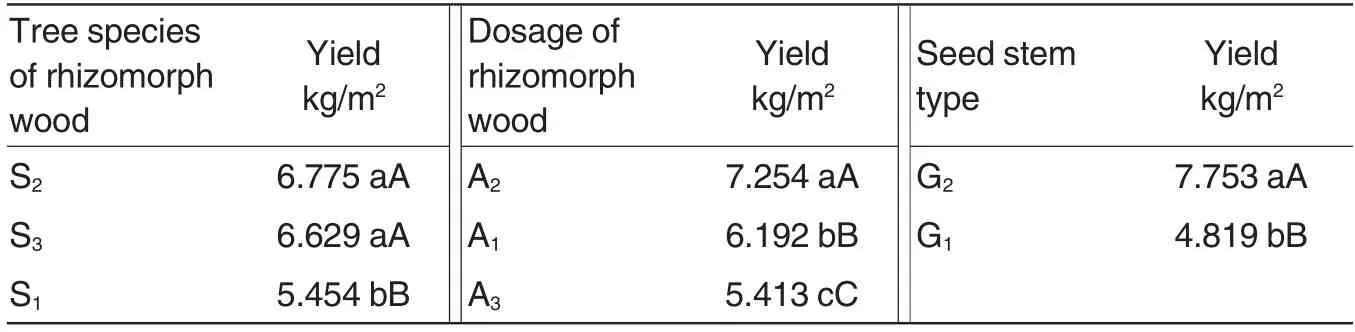
Table 2 Effect on the yield of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow by asexual reproduction of seed stem types, tree species of rhizomorph wood and dosage of rhizomorph wood
Drying rate
Variance analysis indicated that the drying rate of mature tuber of Gastrodia had significant differences between different combinations of the three factors and the different levels of a single factor including seed stem types and tree species of rhizomorph wood. There was no interaction effect among the factors.
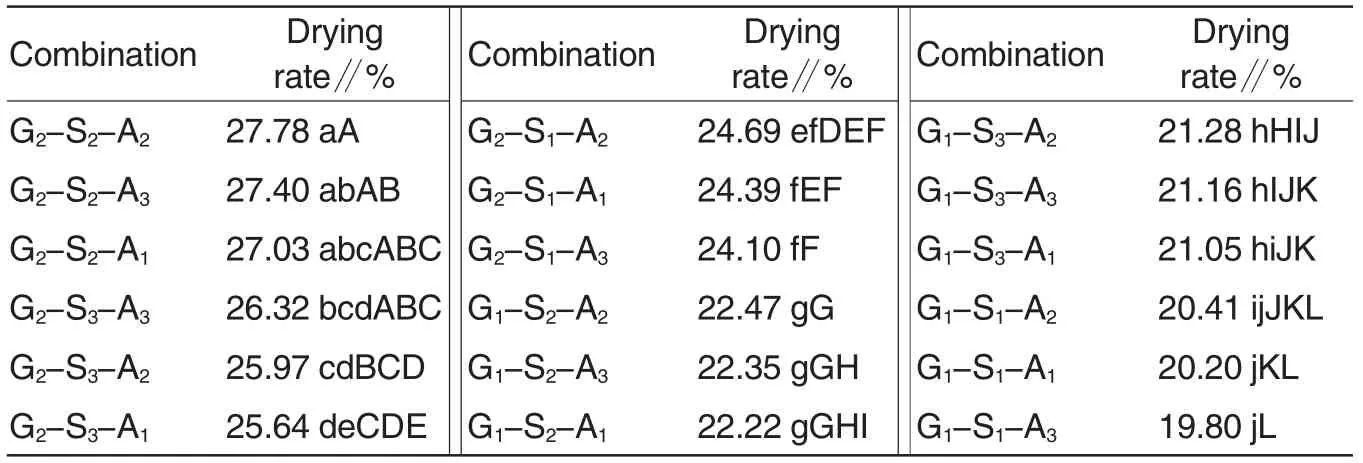
Table 3 Effect on the drying rate of mature tuber generated from wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow by asexual reproduction of the combinations of seed stem types,tree species of rhizomorph wood and dosage of rhizomorph wood
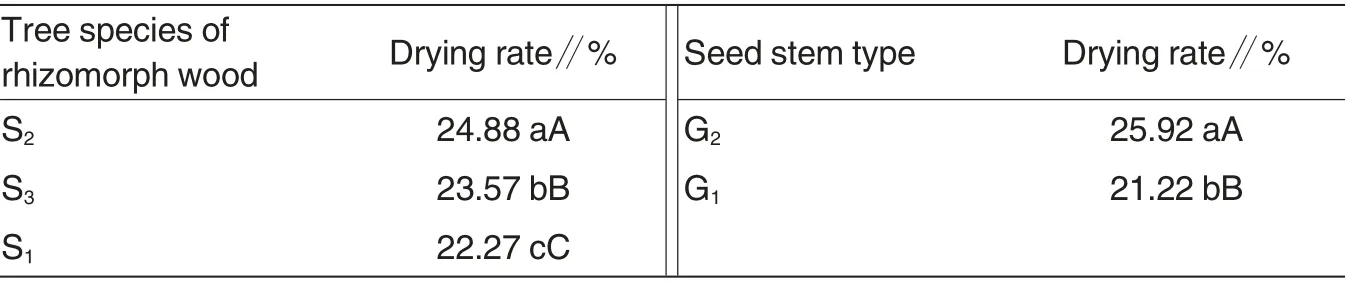
Table 4 Effect on the drying rate of mature tuber generated from wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow by asexual reproduction of seed stem types and tree species of rhizomorph wood
Combination effect of the factors
The drying rates of mature tuber generated by asexual reproduction of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi were extremely significant different between different combinations of the factors (Table 3).Among the 18 combinations, the average drying rate of G2-S2-A2was 27.78%, which was the highest.The average drying rate of G2-S2-A3was 27.40%, which was the second highest.The drying rate of G2-S2-A1was ranked third and the value was 27.03%.The differences between the three combinations were not significant. G1-S1-A3had the lowest drying rate and the average value was 19.80%. The average drying rates of G1-S1-A1and G1-S1-A2were 20.20%and 20.41%, respectively. The differences between the later three combinations were not significant as well.
Effect of a single factor The drying rates of mature tuber generated by asexual reproduction from seed stems of different wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow were extremely significant different (Table 4). The average drying rate of mature tuber generated from the first generation G2of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Yusaping was 25.92% and the average drying rate of mature tuber generated from the first generation G1of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Kangding was 21.11%. The drying rates of mature tuber generated by asexual reproduction of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow with Quercus spinosa S2, half of Quercus spinosa and half of white birch S3, and white birch S1as rhizomorph wood were 24.88%, 23.57% and 22.27%,respectively. The differences between the treatments were extremely significant. The drying rates between different levels of rhizomorph wood dosage were not significantly different.
Conclusions and Discussions
Wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi contains different ecotypes
The asexual reproduction yield and drying rate of mature tuber of the Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Yusaping were higher than that in Kangding, which illustrated that the wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi contained different ecotypes. Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Yusaping belongs to the low altitude ecotype while the Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Kangding belongs to the high altitude ecotype. The Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow of low altitude ecotype originated from warm and humid environment and timbers in the environment rotted quickly, thus the geneticcharacteristics of high yield and drying rate were formed. However, the Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow of high altitude ecotype originated from cool and dry environment and timbers in the environment rotted slowly,thus the genetic characteristics of low yield and drying rate were formed.
Extremely significant effects of tree species of rhizomorph wood on yield of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow and drying rate of mature tuber of Gastrodia
The yield and drying rate of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Yusaping and Kangding with Quercus spinosa as rhizomorph wood were significantly higher than that with white birch, which illustrated that the tree species of rhizomorph wood had extremely significant effect on the asexual reproduction of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi. Quercus spinosa of Fagaceae belongs to the tree species with close grained wood which is not easily rotted while white birch of Betulaceae belongs to the tree species with coarse grained wood which is easily rotted. Under the condition of an appropriate and stable temperature in the greenhouse all the year, the growth and development time of Armillariella mellea and Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow was longer. Compared with white birch,Quercus spinosa could provide nutrition for Armillariella mellea longer,thus the supply time of nutrient for Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow was prolonged. Therefore, more dry matters accumulated in Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow that the yield and drying rate were higher. Rong et al.[3]reported that under the similar environment of wild cultivation condition, the highest yield of different types of Gastrodia elata were obtained when Betula luminifera H. Winkl. of Betulaceae was used but not Quercus fabri Hance of Fagaceae and tree species of rhizomorph wood did not has significant effect on the drying rate of mature tuber of Gastrodia.Under the similar environment of wild cultivation condition,loosened and easily rotted timbers can quickly provide more nutrients for Armillariella mellea and Gastrodia elata during a short time in summer. In winter, the environment temperature and humidity decreased, and the growth and development of Armillariella mellea and Gastrodia elata slow down until stop.Though the remaining nutrient of close grained wood is more than that of coarse grained wood,it do not has enough effect on the growth and development of Armillariella mellea and Gastrodia elata.Therefore,under the similar environment of wild cultivation condition, the existing time of appropriate temperature and humidity is short that the yield of Gastrodia elata together sowed with Armillariella mellea rhizomoph wood cultured with coarse grained wood is higher than that with close grained wood while the drying rates are similar. However, under the controllable temperature and humidity in greenhouse, the yield of Gastrodia elata together sowed with Armillariella mellea rhizomoph wood cultured with close grained wood is higher than that with coarse grained wood because of the prolonging of the appropriate temperature and humidity and the drying rate was higher as well.
Dosage of rhizomorph wood only affects the yield of Gastrodia elata but not the drying rate of mature tuber of G.elata
Dosage of rhizomorph wood had a significant effect on the asexual reproduction yield of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi. In the test, the average yield of Gastrodia elata was the highest and reached 7.254 kg/m2when rhizomorph woods of 5 cm in diameter were placed with 10 cm as the interval. The average yields of Gastrodia elata were significantly decreased when the intervals were 5 cm and 15 cm. When the dosage of rhizomorph wood was increased,there was more abnormal tuber of Gastrodia elata because the growth and development space was decreased, and Gastrodia elata was restricted by rhizomorph wood. When the dosage of rhizomorph wood was decreased,the tuber numbers of Gastrodia elata was few because the coalesce chance between Gastrodia elata and Armillariella mellea was small.Therefore, the yield of Gastrodia elata could reach an ideal level only when the dosage of rhizomorph wood was appropriate. Too much or too few rhizomorph woods were disadvantage to the growth and development of Gastrodia elata, and the yield of Gastrodia elata could be significantly influenced.
Under the appropriate temperature and humidity in the greenhouse all the year, the drying rate of mature tuber of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow was not affected by the dosage of rhizomorph wood because the drying rate was decided by the accumulation of dry matter while the accumulation of dry matter was decided by the combination of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow type, tree species of rhizomorph wood and Armillariella mellea strain, which was accorded with the study result of Rong et al.[3].During the process of imitation of wild cultivation, all the nutrients contained in rhizomorph wood cultured by trees with coarse grained wood were supplied for Gastrodia elata while a plenty of nutrients contained in rhizomorph wood cultured by tree with close grained wood were remained. Therefore,the yield of the former was higher than that of the latter while the drying rates of sword Gastrodia’s mature tuber had no significant difference.
Main technical measures of cultivation for asexual reproduction of wild Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi
Firstly, seed stem should be selected based on the different objectives. In order to protect the wild resources of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow, various ecotypes of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow should be used as seed stems for cultivation. In order to obtain high yield and benefits,Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Yusaping should be used as seed stem for cultivation. Secondly, tree species should be used protectively and tree species of rhizomorph wood should be selected reasonably. The tree resources in Ganzi are abundant and there are many tree species appropriate to cultivate together with Gastrodia elata. The tree species included 21 species of Fagaceae, 19 species of Betulaceae, seven species of Juglandaceae, 49 species of Salicaceae, 153 species of Rosaceae,seven species of Elaeagnaceae, etc[5].Arbor,shrub,wild tree species and cultivated fruit tree were involved.Branches and trunks of the trees ob-tained after clip or selective cutting can be used for rhizomorph wood culture.The tree resources can be efficiently protected and sustainably used, and vegetation in Ganzi can be efficiently protected without destruction of ecological environment during the production of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow. In addition, tree species of rhizomorph wood should be selected according to the cultivation environment of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow.Tree species of Betulaceae, Juglandaceae, Salicaceae, Rosaceae, etc.can be selected when wild or field cultivations were imitated. Fagaceae can be selected when cultivated in greenhouse with an appropriate and stable temperature and humidity. Thirdly,dosage of rhizomorph wood should be confirmed scientifically to improve the Gastrodia elata yield per unit rhizomorph wood and productivity effect of Gastrodia elata.
[1]WANG SB (王绍柏). Cultivation Technology of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow (乌天麻栽培技术)[J]. Peasant Consultant(农家顾问),2005(9):37.
[2]XU JT (徐锦堂). Cultivation Science of Chinese Gastrodia elata(中国天麻栽培学)[M].The first edition(第一版).Beijing(北京): Unionsverlag of Beijing Medical University and China Xie-he Medical University(北京医科大学中国协和医科大学联合出版社),1993.
[3]RONG LH(容丽华),CAI CT(蔡传涛).Effect on Gastrodia elata yield of different rhizomorph wood(不同菌材对天麻产量的影响)[J].Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research (武汉植物学研究) ,2010, 28(6):761-766.
[4]XIE XQ (谢学强). Effect of Armillariella mellea on asexual reproduction of Gastrodia elata.Bl.f.glauca S.Chow in Ganzi prefecture (蜜环菌对甘孜州野生乌天麻无性繁殖的影响)[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences(广东农业科学),2011,38(12):29-31.
[5]HE JR (贺家仁).Trees in Ganzi prefecture(甘孜州树木)[M]. Chengdu (成都):Sichuan Science and Technology Press(四川科学技术出版社),1993.
[6]XIE XQ (谢学强). Effect of nutriment from different sources on the growth of Armillariella mellea in bottle stick cultivation(不同营养源对培养蜜环菌瓶装菌枝的影响)[J]. Serves of Agricultural Technology(农技服务),2009,26(10):84-85.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Evaluation on Suitability of Camellia sinensis Planting Based on GIS
- Light Quality-controlled Phytochemicals Biosynthesis in Vegetables and Fruits
- Cloning and Characterization of Phytochrome A Gene FaPHYA from Tall Fescue
- Genetic Analysis of Embryo Production Frequency in Wheat×Maize Cross
- The Application Effects of Truly Biodegradable Mulch in Potato Farmlands
- The Analysis and Prospect of Development of Fresh Cut Flower Industry Based on the Patent Analysis
