抗生素利福平对Q 烟粉虱防御基因表达水平的影响
2015-12-09刘凌云方艺伟张友军
刘凌云,苏 奇,方艺伟,张友军,褚 栋*
(1.青岛农业大学农学与植物保护学院,山东省植物病虫害综合防控重点实验室,山东青岛 266109;2.中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所,北京 100081)
烟粉虱Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius)属半翅目Hemiptera 粉虱科Aleyrodidae,是一个由至少31 个隐种组成的物种复合体(Dinsdale et al.,2010;Xu et al.,2010;De Barro et al.,2011;Wang et al.,2013)。烟粉虱寄主十分广泛,它可通过直接取食韧皮部汁液,或分泌蜜露诱发煤污病及传播许多植物病毒来危害作物(Brown et al.,1995,2002;Inbar and Gerling,2008)。尤其是B 烟粉虱(即MEAM1 隐种)与Q 烟粉虱(即MED 隐种)在过去的近30年间传入世界各地,给各国农业生产造成了严重的损失 (Brown et al.,1995;Liu et al.,2007;Chu et al.,2006,2010)。烟粉虱的入侵机制成为了世界各国昆虫学和害虫防治领域研究的重要科学问题,而共生菌对烟粉虱物种形成、生物学的影响引起了世界各国昆虫学者的广泛关注(Chiel et al.,2009;Himler et al.,2011)。
利用抗生素去除烟粉虱共生菌是研究共生菌的功能的重要途径(周淑香等,2009;童蕾蕾等,2012;Zhong and Li,2013)。研究发现许多抗生素(如青霉素、卡那霉素、四环素和利福平)能降低烟粉虱共生菌的含量,进而导致烟粉虱宿主种群适合度下降 (Costa et al.,1997;Ruan et al.,2012;Su et al.,2013;Zhong and Li,2013)。其中,利福平是一种常用于去除昆虫共生菌的抗生素。例如,Ruan 等(2012)研究发现利福平能延迟B 烟粉虱和ZHJ-1 生物型烟粉虱的发育历期,并且能减少ZHJ-1 后代的存活率,但不影响B 烟粉虱后代存活率。一般认为,抗生素对节肢动物没有直接影响 (Dedeine et al.,2000;Jeanne et al.,2012)。
利福平能够抑制细菌的RNA 聚合酶与DNA 结合,也可抑制一些动物病毒的生长以及致癌病毒的DNA 聚合酶与RNA 结合(Wehrli et al.,1968;Subak-Sharpe et al.,1969;Gallo et al.,1970;Scolnick et al.,1971)。然而,一些研究发现抗生素如利福平能够诱导各种基因的表达 (Chang et al.,1997;Bowen et al.,2000;Rodrigues-Antona et al.,2000;LeCluyse et al.,2000;Meunier et al.,2000;Runge et al.,2000)。例如,应用荧光定量PCR (qRT-PCR)技术研究发现高浓度的利福平能改变人类LS180 细胞系(Weiss et al.,2012)和HepG2 细胞内内参基因的表达(Weiss et al.,2012),选择性地诱导人类肝细胞内若干基因(如CYP2C8、FMO4 和MAO-B 等)或诱导人类细胞内CYP2C8 和CYP2C9 表达(Gerbal-Chaloin et al.,2001;Rae et al.,2001)。抗生素(例如利福平)是否影响昆虫(如烟粉虱)功能基因的表达,还不得而知。
烟粉虱体内具有许多与防御相关的基因,如乙醇脱氢酶adhIII、抗菌肽knottin、丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂serpin、四次跨膜蛋白tetraspanin-3、TCP1-delta (Mahadav et al.,2008)。为了揭示抗生素对烟粉虱功能基因的影响,本研究利用qRT-PCR 方法比较了取食不同浓度利福平处理的棉花叶片的Q烟粉虱与对照种群体内上述5 个防御基因的表达量,探讨了抗生素对Q 烟粉虱体内防御基因的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试昆虫
本实验所用的Q 烟粉虱饲养在温度为27℃±1℃、RH 60%±5%,光周期L∶D=16 h∶8 h 的养虫室中,种群每代随机抽取20 头采用限制性内切酶Vsp I 酶切扩增多态序列的方法来鉴定(Khasdan et al.,2005)。
1.2 抗生素处理棉花叶片饲喂烟粉虱
所用抗生素为利福平(北京博奥拓达科技有限公司,中国)。将25 g 蔗糖用0.005 mol/L 磷酸缓冲液(PB,PH=7.0)定容于100 mL,得到含25.0% 蔗糖的0.005 mol/L 的PB。分别溶解5.0 mg和10.0 mg 抗生素于PB 缓冲液中,得到50.0 μg/mL 和100.0 μg/mL 的抗生素,即为实验组,而25.0%的PB 缓冲液为对照种群。将棉花叶片浸泡在对照种群和实验组的液体中12 h 后,将棉花叶片晾干,放在底部含1%琼脂的玻璃瓶中,分别让烟粉虱取食棉花叶片。20 头烟粉虱作为一个重复,每一个处理3 个重复。
1.3 烟粉虱取食抗生素处理叶片后防御基因的表达量变化
烟粉虱取食不同浓度的抗生素处理和未处理的棉花叶片后,使用Trizol 试剂(Invitrogen 公司,美国)提取烟粉虱RNA,后用PrimeScriptTMRT regent 试剂盒(Takala 公司,中国)合成cDNA,cDNA 被用来定量防御基因 (adhIII、knottin、serpin、tetraspanin-3 与 TCP1-delta) (Mahadav et al.,2008)的表达量。反应体系为5 μL 2×SYBR Premix Ex Taq (TaKaRa Biotechnology),1 μL DNA,3.6 μL ddH2O,0.2 μL 引物。基因的引物如表1。反应程序为:95℃ 15 min;95℃10 s,60℃20 s,72℃25 s,共45 个循环。基因的表达量用2-ΔΔCt方法计算。

表1 本研究中烟粉虱体内基因的引物序列Table 1 Primer sequences of genes in Bemisia tabaci used in this study
1.4 数据分析和处理
使用SPSS 软件对烟粉虱饲喂抗生素处理叶片与未处理叶片的防御基因adhIII、knottin、serpin、tetraspanin-3 与TCP1-delta 分别利用T-test 方法进行显著性分析,在0.05 显著性水平进行比较。
2 结果与分析
2.1 取食50.0 μg/mL 利福平处理棉花叶片烟粉虱防御基因变化
用50.0 μg/mL 抗生素处理过的烟粉虱的adh-classIII、knottin、tetraspanin-3 的基因表达量显著高于未处理的烟粉虱对照组(P<0.05),其中adh-classIII 的基因表达量是对照种群的1.76 倍[图1 (A)],knottin 的基因表达量是对照种群的1.70 倍[图2 (A)],tetraspanin-3 的基因表达量是对照种群的1.68 倍[图4 (A)],而serpin 和TCP1-delta 的基因表达量没有显著差异 (P >0.05)[图3 (A)和图5 (A)]。
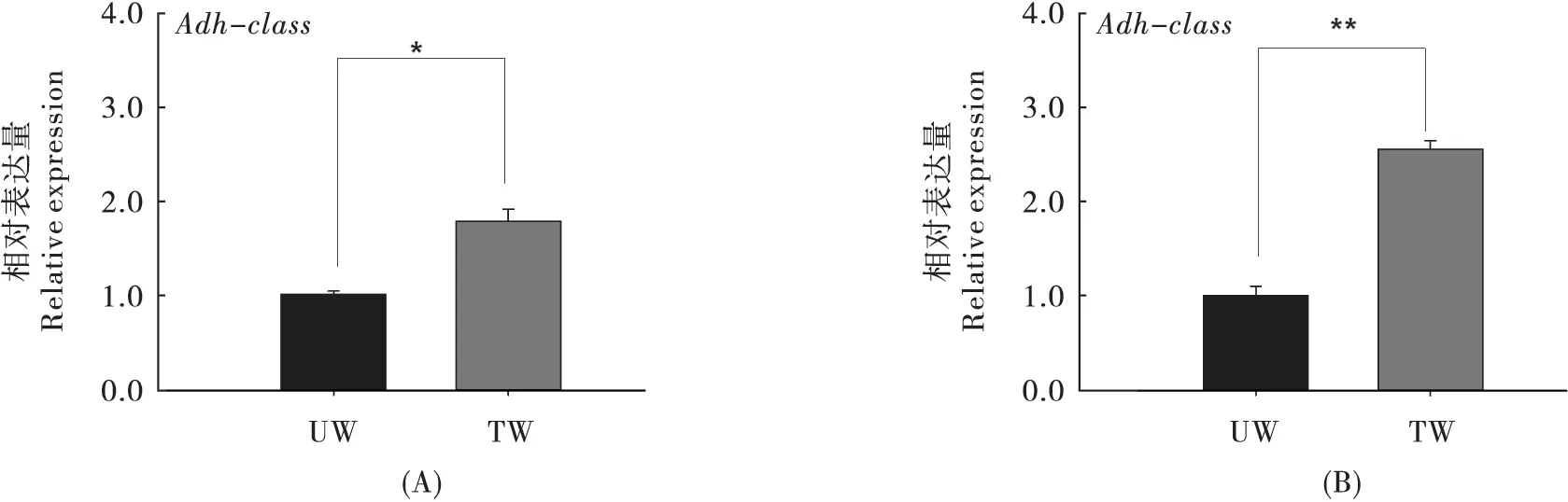
图1 不同浓度利福平处理后adh-classIII 基因的表达量Fig.1 The expression of adh-classIII gene under different concentration of rifampicin

图2 不同浓度利福平处理后knottin 基因的表达量Fig.2 The expression of knottin gene under different concentration of rifampicin
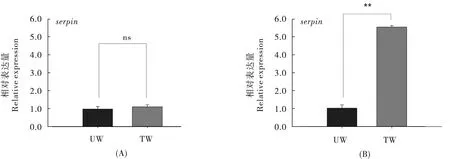
图3 不同浓度利福平处理后serpin 基因的表达量Fig.3 The expression of serpin gene under different concentration of rifampicin
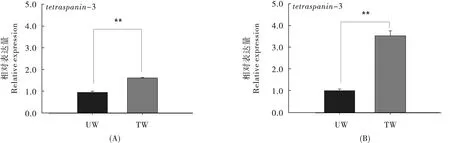
图4 不同浓度利福平处理后tetraspanin-3 基因的表达量Fig.4 The expression of tetraspanin-3 gene under different concentration of rifampicin
2.2 取食100.0 μg/mL 利福平处理棉花叶片烟粉虱防御基因变化
用100.0 μg/mL 抗生素处理过的烟粉虱其5 个基因表达量显著高于未处理的烟粉虱(对照种群)的基因表达量(P<0.05),其中adh-classIII 的基因表达量是对照种群的2.54 倍[图1 (B)],knottin 的基因表达量是对照种群的3.38 倍[图2(B)],serpin 的基因表达量是对照种群的5.37 倍[图3 (B)],tetraspanin-3 的基因表达量是对照种群的3.48 倍[图4 (B)],TCP1-delta 的基因表达量是对照种群的2.90 倍[图5 (B)]。
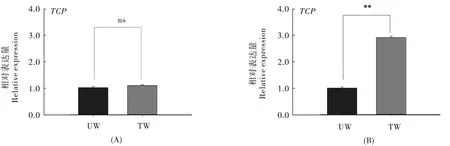
图5 不同浓度利福平处理后TCP1-delta 基因的表达量Fig.5 The expression of TCP1-delta gene under different concentration of rifampicin
3 结论与讨论
前人研究发现,抗生素处理往往会对昆虫适合度具有一定的负面影响。例如,昆虫通过不同途径取食四环素、青霉素或卡那霉素后,其生殖受到阻碍、死亡率增加(Mittler,1971;Griffiths and Beck,1974;Nogge and Gerresheim,1982)。用四环素处理的丽蚜小蜂Encarsia formosa 寿命缩短,产卵量降低,进而种群适合度下降(Stouthamer et al.,1994,2002;周淑香等,2009;童蕾蕾,2012)。一般认为,抗生素对昆虫适合度的影响与其能减少共生菌密度或去除共生菌密切相关。如四环素能去除松毛虫赤眼蜂体Trichogramma dendrolimi 内的Wolbachia,并改变其生殖方式(张海燕等,2009)。四环素处理烟粉虱B 隐种,Wolbachia 含量降低,导致烟粉虱后代发育迟缓(Zhong and Li,2013)。用利福平处理共生麦二叉蚜Schizaphis graminum,胞内共生菌含量降低,种群适合度下降(胡祖庆等,2012)。
用利福平处理B 烟粉虱、ZHJ-1 型烟粉虱和Q烟粉虱,烟粉虱生长和发育受到影响,后代发育缓慢等(Costa et al.,1997;Ruan et al.,2006;Su et al.,2013)。同样地,用利福平处理能降低Q 烟粉虱寄生能力(Xue et al.,2012)。这与某些共生菌被抗生素抑制或去除密切相关 (Stouthamer et al.,1994,2002;张海燕等,2009;周淑香等,2009;童蕾蕾,2012;Zhong and Li,2013)。本研究结果表明,烟粉虱体内防御基因在抗生素利福平的影响下,其表达量上升。这些防御基因在昆虫生殖发育等过程中起着重要作用 (Ligoxygakis et al.,2002;Tarrant et al.,2003;Chiche et al.,2004;Abraham et al.,2005;Levy and Shoham,2005;Zou and Jiang,2005;Ferrandon et al.,2007;Colinet et al.,2009)。如:adh-classIII 属于氧化还原酶类,在昆虫代谢、蜕皮及变态发育中起着重要的作用,并能对外界压力产生抗性(Oudman et al.,1992;Mahadav et al.,2008);TCP1-delta 存在于昆虫的血淋巴中,能引起红血球凝聚,并与血淋巴溶菌酶协同作用,参与昆虫防御反应 (Limura et al.,1998;Halwani et al.,1999;Blitvich et al.,2001)。昆虫防御能力与其存活率及繁殖能力平衡 (Sheldon and Verhulst,1996;Rolff and Siva,2003)。烟粉虱防御基因的上升是否会导致其适合度的降低(如存活率等)有待于进一步的研究。
当前,利福平对烟粉虱防御基因表达量的影响机理尚不清楚。利福平是通过和依赖于DNA 的RNA 多聚酶的β 亚基结合,抑制细菌RNA 的合成,防止RNA 多聚酶与DNA 连接,从而阻断RNA 的转录过程,使DNA 和蛋白质的合成停止(Campbell et al.,2001)。高浓度利福平也可影响真核生物的RNA 聚合酶,例如能抑制人类淋巴细胞RNA 聚合酶II (Pogo,1972),或结合线粒体真核RNA 聚合酶,或抑制蛋白质合成(Buss et al.,1978;Hartmann et al.,1985)。利福平能够诱导人类肝细胞CYP1A1、CYP2B6、CYP3A4、CYP3A5、CYP2C8、CYP2C9、EROD、T6H 等基因的表达,并能促进环磷酰胺、异环磷酰胺、GST 和UGT 的表达 (Chang et al.,1997;Bowen et al.,2000;Rodriguez-Antona et al.,2000;Rung et al.,2000、Rae et al.,2001)。高浓度利福平能够抑制人类LS180 细胞和HepG2 细胞的生长,并且能影响内参基因的表达,如增加G6PDH 的表达,减少RPL13、GU、villin、hPRT 等基因的表达等(Rae et al.,2001;Weiss et al.,2012)。利福平对烟粉虱防御基因表达量的影响可能与其直接阻断RNA的转录相关;这种影响是否与烟粉虱体内共生菌的间接影响相关,目前不得而知。利福平对昆虫功能基因的影响机理尚需进一步的研究。
References)
Abraham EG,Pinto SB,Ghosh A,et al.An immune-responsive serpin,SRPN6,mediates mosquito defense against malaria parasites[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2005,102 (45):16327-16332.
Blitvich BJ,Rayms-Keller A,Blair CD,et al.Complete cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of the chaperonin containing T-complex polypeptide 1 (CCT)delta subunit from Aedes triseriatus mosquitoes[J].DNA Sequence,2001,12:203-208.
Bowen WP,Carey JE,Miah A,et al.Measurement of cytochrome P450 gene induction in human hepatocytes using quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction [J].Drug Metabolism and Disposition,2000,28:781-788.
Brown JK,Frohlich DR,Rosell RC.The sweetpotato or silverleaf whiteflies:Biotypes of Bemisia tabaci or a species complex[J].Annual Review of Entomology,1995,40:551-534.
Brown JK,Czosnek H.Whitefly transmission of plant viruses [J].Advances in Botanical Research,2002,36:65-100.
Buss WC,Morgan R,Guttmann J,et al.Rifampicin inhibition of protein synthesis in mammalian cells[J].Science,1978,200:432-434.
Campbell EA,Korzheva N,Mustaev A,et al.Structural mechanism for rifampicin inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase [J].Cell,2001,104:901-912.
Chang TK,Yu L,Maurel P,et al.Enhanced cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide activation in primary human hepatocyte cultures:Response to cytochrome P-450 inducers and autoinduction by oxazaphosphorines [J].Cancer Research,1997,57:1946-1954.
Chiche L,Heitz A,Gelly JC,et al.Squash inhibitors:From structural motifs to macrocyclic knottins[J].Current Protein and Peptide Science,2004,5:341-349.
Chiel E,Zchori-Fein E,Inbar M,et al.Almost there:Transmission routes of bacterial symbionts between trophic levels [J].PLoS ONE,2009,4:e4767.
Chu D,Wan FH,Zhang YJ,et al.Change in the biotype composition of Bemisia tabaci in Shandong Province of China from 2005 to 2008[J].Environmental Entomology,2010,39:1028-1036.
Chu D,Zhang YJ,Brown JK,et al.The introduction of exotic Q biotype of Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius)from the Mediterranean region into China on ornamental crops[J].Florida Entomologist,2006,89:168-174.
Colinet D,Dubuffet A,Cazes D,et al.A serpin from the parasitoid wasp Leptopilina boulardi targets the Drosophila phenoloxidase cascade[J].Developmental and Comparative Immunology,2009,33 (5):681-689.
Costa HS,Henneberry TJ,Toscano NC.Effects of antibacterial materials on Bemisia argentifolii (Homoptera:Aleyrodidae)oviposition,growth,survival,and sex ratio [J].Journal of Economic Entomology,1997,90:333-339.
De Barro PJ,Liu SS,Boykin LM,et al.Bemisia tabaci:A statement of species status[J].Annual Review of Entomology,2011,56:1-19.
Dedeine F,Vavre F,Fleury F,et al.Removing symbiotic Wolbachia bacteria specifically inhibits oogenesis in a parasitic wasp[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2001,11 (98):6247-6252.
Dinsdale A,Cook L,Riginos C,et al.Refined global analysis of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera:Sternorrhyncha:Aleyrodoidea:Aleyrodidae) mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase 1 to identify species level genetic boundaries[J].Annals of the Entomological Society of America,2010,103:196-208.
Ferrandon D,Imler JL,Hetru C,et al.The Drosophila systemic immune response:Sensing and signalling during bacterial and fungal infections [J].Nature Reviews Immunology,2007,7:862-874.
Gallo RC,Yang SS,Ting RC.RNA dependent DNA polymerase of human acute leukaemic cells[J].Nature,1970,5275 (228):927-929.
Gerbal-Chaloin S,Pascussi JM,Pichard-Garcia L,et al.Induction of CYP2C genes in human hepatocytes in primary culture[J].Drug Metabolism and Disposition,2001,29:242-251.
Griffiths G,Beck S.Effects of antibiotics on intracellular symbiotes in the pea aphid,Acrythosiphon pisum[J].Tissue Research,1974,148:287-300.
Gurgo C,Ray RK,Thiry L,et al.Inhibitors of the RNA and DNA dependent polymerase activities of RNA tumour viruses [J].Nature,1971,4 (229):111-114.
Halwani AE,Dunphy GB.Apolipophorin-III in Galleria mellonella potentiates hemolymph lytic activity [J].Developmental and Comparative Immunology,1999,23 (7):563-570.
Hartmann GR,Heinrich P,Kollenda MC,et al.Molecular mechanism of action of the antibiotic rifampicin [J].Angewandte Chemie Internation Edition in English,1985,24:1009-1014.
Himler AG,Adachi-Hagimori T,Bergen JE,et al.Rapid spread of a bacterial symbiont in an invasive whitefly is driven by fitness benefits and female bias[J].Science,2011,332:254-256.
Hu ZQ,Kang JX,Hu XS,et al.Effects of bacterial symbionts on growth,development and fecundity of Schizaphis graminum[J].Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University,2012,27 (1):23-28.[胡祖庆,亢菊侠,胡想顺,等.胞内共生菌对麦二叉蚜生长发育和繁殖的影响[J].云南农业大学学报,2012,27(1):23-28]
Inbar M,Gerling D.Plant-mediated interactions between whiteflies,herbivores,and natural enemies [J].Annual Review of Entomology,2008,53:431-448.
Jeanne AZ,Melvin MB,Angelica JA,et al.From father to son:Transgenerational effect of tetracycline on sperm viability [J].Scientific Reports,2012,2:375.
Khasdan V,Levin I,Rosner A,et al.DNA marker for identifying biotypes B and Q of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera:Aleyrodidae)and studying population dynamics[J].Bulletin of Entomological Research,2005,95:597-603.
LeCluyse E,Madan A,Hamilton G,et al.Expression and regulation of cytochrome P450 enzymes in primary cultures of human hepatocytes [J].Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology,2000,14:177-188.
Levy S,Shoham T.The tetraspanin web modulates immune-signalling complexes [J].Nature Reviews Immunology,2005,5:136-148.
Ligoxygakis P,Pelte N,Ji CY,et al.A serpin mutant links Toll activation to melanization in the host defense of Drosophia[J].The EMBO Journal,2002,21 (23):6330-6337.
Limura Y,Ishikawa H,Yamamoto K,et al.Hemagglutinating properties of apolipophorin III from the hemolymph of Galleria mellonella larvae[J].Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology,1998,38 (3):119-125.
Mahadav A,Gerling D,Gottlieb Y,et al.Parasitization by the wasp Eretmocerus mundus induces transcription of genes related to immune response and symbiotic bacteria proliferation in the whitefly Bemisia tabaci[J].BMC Genomics,2008,9:342.
Meunier V,Bourrie M,Julian B,et al.Expression and induction of CYP1A1/1A2,CYP2A6 and CYP3A4 in primary cultures of human hepatocytes:A 10-year follow-up[J].Xenobiotica,2000,30:589-607.
Mittler TE.Some effects on the aphid Myzus persicae of ingesting antibiotics incorporated into artificial diets[J].Journal of Insect Physiology,1971,17:1333-1347.
Nauen R,Denholm I.Resistance of insect pest to neonicotinoid insecticides:Current status and future prospects[J].Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology,2005,58 (4):200-215.
Nauen R,Stumpf N,Elbert A.Toxicological and mechanistic studies on neonicotinoid cross resistance in Q-type Bemisia tabaci(Hemiptera:Aleyrodidae)[J].Pest Management Science,2002,58 (9):868-875.
Nogge G,Gerresheim A.Experiments on the elimination of symbionts from tsetse fly,Glossina morsitans morsitans (Diptera:Glossinidae),by antibiotics and lysozyme [J].Journal of Invertebrate Pathology,1982,40:166-179.
Oudan L,van Delden W,Kamping A,et al.Interaction between the Adh and alpha Gpdh loci in Drosophila melanogaster:Adult survival at high temperature [J].Heredity,1992,68:289-297.
Pogo BG.Specific inhibition by rifampicin of transcription in human lymphocytes stimulated by phytohemagglutinin [J].Journal of Cell Biology,1972,55:515-519.
Rae JM,Johnson MD,Lippman ME,et al.Rifampicin is a selective,pleiotropic inducer of drug metabolism genes in human hepatocytes:Study with cDNA and oligonucleotide expression arrays [J].The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics,2001,299 (3):849-857.
Roditakis E,Grispou M,Morou E,et al.Current status if insecticide resistance in Q biotype Bemisia tabaci populations from Crete[J].Pest Management Science,2009,65 (3):313-322.
Rodriguez-Antona C,Jover R,Gomez-Lechon MJ,et al.Quantitative RT-PCR measurement of human cytochrome P-450s:Application to drug induction studies [J].Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,2000,376:109-116.
Rolff J,Siva-Jothy MT.Invertebrate ecological immunology [J].Science,2003,301:472-475.
Ruan YM,Xu J,Liu SS.Effects of antibiotics on fitness of the B biotype and a non-B biotype of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci [J].Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata,2006,121:159-166.
Runge D,Kohler C,Kostrubsky VE,et al.Induction of cytochrome P450 (CYP)1A1,CYP1A2,and CYP3A4 but not of CYP2C9,CYP2C19,multidrug resistance (MDR-1) and multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP-1)by prototypical inducers in human hepatocytes [J].Biochemical and Biophysicals Research Communications,2000,273:333-341.
Scolnick EM,Aaronson SA,Todaro GJ,et al.RNA dependent DNA polymerase activity in mammalian cells [J].Nature,1971,5283 (229):318-321.
Sheldon BC,Verhulst S.Ecological immunology:Costly parasite defenses and trade offs in evolutionary ecology [J].Trends in Ecology and Evolution,1996,11:317-321.
Stouthamer R,Lukoe S,Mark F.Influence of parthenogenesis Wolbachia on host fitness[J].Norwegian Journal of Agricultural Science,1994,16:117-122.
Stouthamer R,Mark F.Influence of antibiotics on the offspring production of the Wolbachia-infected parthenogenetic parasitoid Encarsia formosa[J].Journal of Invertebrate Pathology,2002,80 (1):41-45.
Su Q,Pan HP,Liu BM,et al.Insect symbiont facilitates vector acquisition,retention,and transmission of plant virus [J].Scientific Reports,2013a,3:1367.
Su Q,Oliver KM,Pan HP,et al.Facultative symbiont Hamiltonella confers benefits to Bemisia tabaci,an invasive agricultural pest worldwide[J].Environmental Entomology,2013b,42 (6):1265-1271.
Subak-Sharpe JH,Timbury MC,Williams JF.Rifampicin inhibits the growth of some mammalian virus[J].Nature,1969,5191 (222):341-345.
Tarrant JM,Robb L,van Spriel AB,et al.Tetraspanins:Molecular organisers of the leukocyte surface[J].Trends in Immunology,2003,24:610-617.
Tong LL,Qi LD,Zhang F,et al.Effects of antibiotic treatment on reproduction of Encarsia formosa (Hymenoptera:Aphelinidae)infected with Wolbachia[J].Acta Entomologica Sinica,2012,55 (8):933-940.[童蕾蕾,亓兰达,张帆,等.抗生素处理对感染Wolbachia 的丽蚜小蜂生殖的影响[J].昆虫学报,2012,55 (8):933-940]
Wang ZY,Yan HF,Yang YH,et al.Biotype and insecticide resistance status of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci from China [J].Pest Management Science,2010,66 (12):1360-1366.
Wang HL,Yang J,Boykin LM,et al.The characteristics and expression profiles of the mitochondrial genome for the Mediterranean species of the Bemisia tabaci complex [J].BMC Genomics,2013,14:401.
Weiss J,Theile D,Haefeli WE.Rifampicin alters the expression of reference genes used to normalize real-time quantitative RT-PCR data[J].Naunyn-schmiedebergs Archives of Pharmacology,2012,385:1025-1034.
Wehrli W,Nuesch J,Knusel F,et al.Action of rifamycins on RNA polymerase[J].Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,1968,1:215-217.
Xue X,Li SJ,Ahmed MZ,et al.Inactivation of Wolbachia reveals its biological roles in whitefly host [J].PLoS ONE,2012,7:e48148.
Xu J,De Barro PJ,Liu SS.Reproductive incompatibility among geneticgroups of Bemisia tabaci supports the proposition that the whitefly is a cryptic species complex [J].Bulletin of Entomological Research,2010,100:359-366.
Zhang HY,Zhang Y,Cong B,et al.Effects of environmental factors on stability of thelytoky of Trichogramma dendrolimi infected with Wolbachia[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2009,42 (7):2366-2372.[张海燕,张莹,丛斌,等.外界生态因子对感染Wolbachia 的松毛虫赤眼蜂生殖稳定性影响[J].中国农业科学,2009,42 (7):2366-2372]
Zhong Y,Li ZX.Influences of tetracycline on the reproduction of the B biotype of Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera:Aleyrodidae)[J].Applied Entomology and Zoology,2013,48:241-246.
Zhou SX,Li Y,Zhang F.Influence of Wolbachia on reproduction and the fitness of the parasitoid wasp Encarsia formosa [J].Acta Phytophylacica Sinica,2009,36 (1):7-10.[周淑香,李玉,张帆.Wolbachia 共生对丽蚜小蜂生殖和适合度的影响[J].植物保护学报,2009,36 (1):7-10]
Zou Z,Jiang HB.Manduca sexta serpin-6 regulates immune serine proteinases PAP-3 and HP8:cDNA cloning,protein expression,inhibition kinetics,and function elucidation [J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2005,280 (14):14341-14348.
