Distribution and Accumulation of Nutrient Elements in Organic Tissue of Eucalyptus grandis Saplings
2015-11-08AnminMlNYuWANGHongxiaLlNanFElFengmingLl
Anmin MlN,Yu WANG,Hongxia Ll,Nan FEl,Fengming Ll
1.Sichuan Academy of Forestry Science,Chengdu 610066,China;
2.Forestry Bureau of Xinjin in Chengdu City,Xinjin 611430,China
Distribution and Accumulation of Nutrient Elements in Organic Tissue of Eucalyptus grandis Saplings
Anmin MlN1,Yu WANG1,Hongxia Ll1,Nan FEl1,Fengming Ll2
1.Sichuan Academy of Forestry Science,Chengdu 610066,China;
2.Forestry Bureau of Xinjin in Chengdu City,Xinjin 611430,China
The biomass,macroelements (N,P,K,Ca,Mg)and microelements(Fe,Zn)contents were detected in organs of 1a-3a Eucalyptus grandis saplings,as well as their accumulated amount.Results showed that contents of nutrient elements varied greatly in different organs.Total contents of macroelements N,P,K,Ca and Mg in 1a-3a E.grandis were distributed in the order of stem phloem,leaves>branches,roots>stem xylem.Accumulated amount of macroelements in 1a-3a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>branches>stem phloem >roots or stem xylem >stem xylem or roots.Accumulated amount law of nutrient elements was not affected by the plant age.Microelements Fe and Zn were mainly concentrated in the leaves and roots.The accumulation of macroelements was in the order of Ca>N>K>Mg> P;and the microelements was in the order of Fe> Zn.Accumulated amounts of microelements in 1a-3a E.grandis were 12.45 136.19 and 420.23 g per plants,respectively.Among the annual net accumulated amount of nutrient elements per plant in 1a-3a E.grandis,Ca element was the maximum,N and K elements took the second and third places.Mg element was relatively small and P element was the minimum.
Eucalyptus grandis;Organ;Nutrient element;Accumulated amount
T he growth speed of Eucalyptus grandis is extremely rapid.As the industrial raw material forest,E.grandis has short rotation period,and has become one of the strategic tree species of fast-growing and high-yield plantation in Southern China.At present,rotation period of E.grandis plantation in southern provinces of China is mainly between 5a and 7a.Since the supply is not adequate to the demand,investors use the management mode of short cycle and small diameter timber;the rotation period shortened to less than 5 a. Since this period is the fast growth stage of E.grandis,necessary nutrient elements should be supplied in order to ensure the normal growth of plant and to obtain higher yields.Therefore,it is necessary to research the nutrient elements distribution,accumulation and demands of E.grandis organs. Literatures have reported the nutrient elements distribution and accumulation of E.grandis of a certain forest age.However,no reports are found on the nutrient elements distribution,accumulation and demands of E.grandis of a certain forest age.Based on these,biomass and nutrient elements detection of organs in 1a-3a E.grandis were detected in this research,aiming at providing scientific references for the fertilization management of E.grandis young forest,to enhance the yield and shorten the rotation period of E.grandis,to obtain high economic benefit,to prevent soil fertility declination[1],and to realize the sustainable use of forest land.
Materials and Methods
Test materials
Young forest of 1a-3a E.grandis was used as the test materials.
Methods
Selection of investigation sites
Young forest of 1a-3a E.grandis was selectedinShuangliuCountyand Xinjin County in Chengdu City,which had relatively uniform site conditions(soil type,thickness,gradient,slope direction,altitude and so on)and operation management (especially the fertilization management).The plantation density was 1 665 plants/hm2;and planting spacing was 2 m×3 m.
lnvestigation method In the selected young forest of 1a-3a E.grandis,three sample sites(20 m×20 m)were designed according to the plant age. The average diameter at breast height and average plant height were calculated.Nine plants were selected as the sample trees from the investigation young forests[2],the diameter at breast height and plant height of which were between 95%and 105%.After cutting down,the fresh weights of underground roots and aboveground organs(leaves,stems and branches)were detected.The mean value of biomass fresh weight of the same forest age and organ was calculated.
Sample collection Based on the biomass investigation of E.grandis saplings,the leaves,branch xylem,branch phloem,stem xylem,stem phloem,root phloem and other organs were analyzed.Samples of the same age and organs were well mixed,in order to detect the biomass moisture content and nutrient elements of organs.The samples collected were immediately sent back to the laboratory for treatment and detection.
Sample detection item and method(1)Detection items of sample:moisture content,N,P,K,Ca,Fe,Zn,crude ash. (2)Sample detection method: moisture content-baking method;N-Kjeldahl method;PH2SO4-HClO4digestion,Mo-Sb colorimetric method;K,Ca,Mg-H2SO4-HClO4digestion,Fe,Zn-HNO3-HClO4 digestion,atomic absorption spectroscopy;crude ash-dry ashing,gravimetric method[3].There were 2 parallel samples in detection.
Results and Conclusions
Canopy characteristics of E.grandis young forest
Table 1 reported the canopy characteristics of E.grandis young forest(la-3a).
Investigation results showed that in the E.grandis young forest,small forest age had great differences under different site conditions.
Organ nutrient content and distribution of E.grandis
With 2a E.grandis as the example,Table 2 reported the nutrient element content of organ tissues.N,P,K and Mg contents in E.grandis leaf tissues were the maximum,those in stem or leaf xylem were the minimum. N,P,K and Mg contents in other organs were in the middle.Ca content in branch phloem was the maximum,and in root xylem was the minimum.Ca contents in other organs were in the middle.Microelement Fe content was in the order of root phloem>leaves>branch phloem >root xylem>stem xylem>branch xylem>stem phloem. Microelement Zn content was in the order of branch phloem >leaves>root phloem >root xylem >stem phloem>stem xylem>branch xylem. Crude ash content was the maximum in stem phloem and the minimum in stem xylem.The total trend was that macronutrient,middle element nutrient and microelement were relatively high in leaves and phloems,and were relatively low in xylem.Total ash element in phloem was higher than that in xylem.
The total content of macroelements and medium elements N,P,K, Ca and Mg was in the order of stem phloem >leaves>branch phloem>root phloem >root xylem >branch xylem > stem xylem.Amongthe macroelements and medium elements,Ca content was the maximum,N and K contents were relatively high,Mg content was relatively low,and P content was the minimum.Fe content in different organs were higher than Zn content,indicating that contents of different nutrition elements varied in different organs[4].The nutrition was mainly concentrated in leaves and phloems.During the growth process,demands for Ca,N and K were relatively more[5-6].

Table 1 Canopy characteristics of E.grandis young forest
Nutrient element content and distribution of different ages of E.grandis
As for the young forest of la-3a E.grandis,Table 3 reported the detection results of elements in different organs of E.grandis.
Nutrient contents of E.grandis organs Total contents of macroelements N,P,K,Ca and Mg in different organs of 1a E.grandis were in the order ofleaves > stem phloem >branches>roots>stem xylem.Total contents of macroelements in different organs of 2a-3a E.grandis were in the order of stem phloem > leaves>branches>roots>stem xylem,indicating that as the forest age increased,a large amount of nutrient elements were concentrated in phloem.Microelements Fe and Zn in organs of 1a forest were in the order of leaves>roots>branches>stem phloem >stem xylem;microelements Fe and Zn in organs of 2a forest were in the orderof leaves>roots>stem xylem>stem phloem>branches.Among them,total Fe and Zn contents in leaves and roots organs were much more higher than the contents in branches,stem xylem and stem phloem,indicating that microelements Fe and Zn were mainly concentrated in leaves and roots.

Table 2 Nutrient element contents in 2-year-old saplings of E.grandis
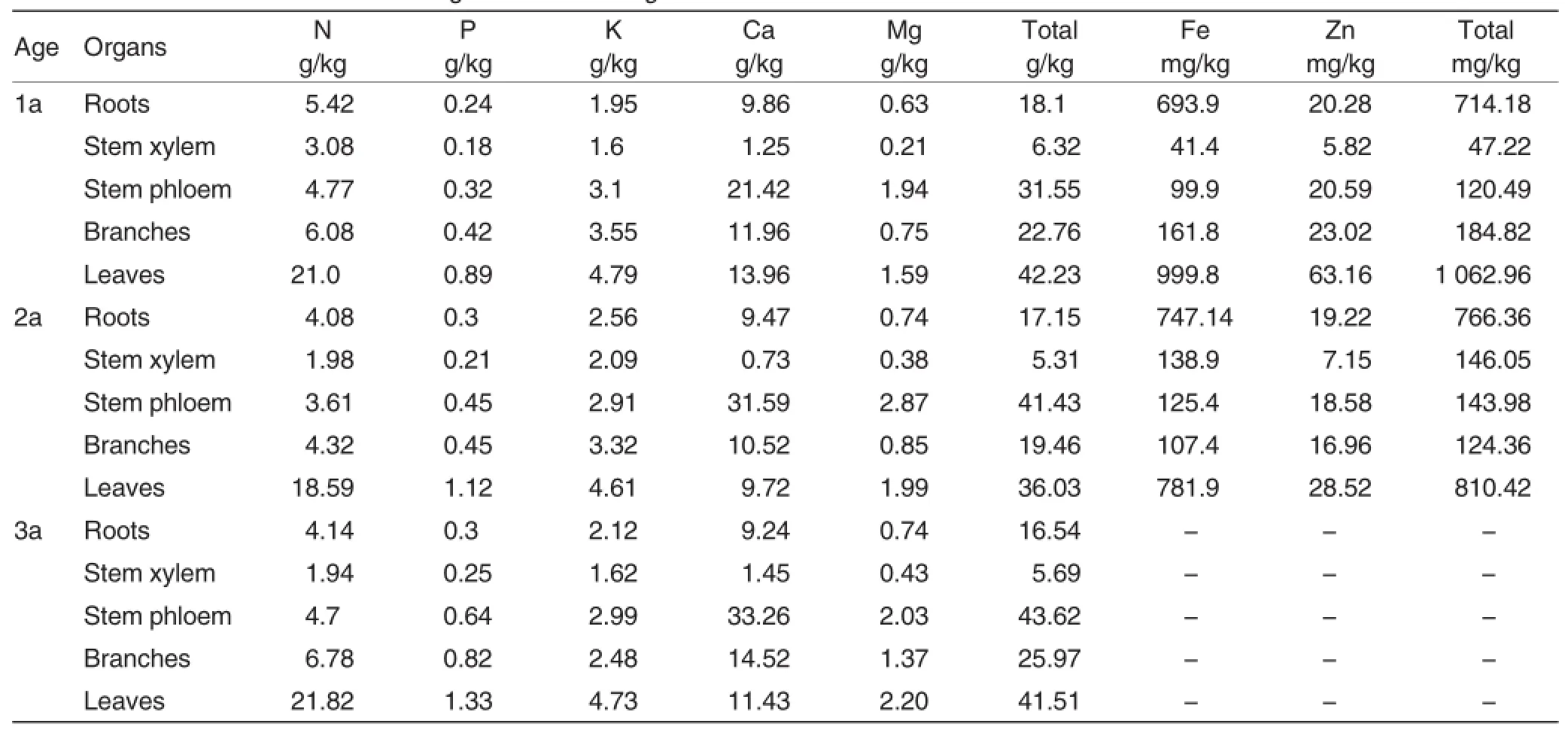
Table 3 Nutrient element contents in organs of 1a-3a E.grandis
Content and distribution of nutrient elements N element:N contents in 1a-3a E.grandis organs were in the order of leaves>branches>roots>stem phloem>stem xylem.With the increase of plant age,N contents declined in roots,stem xylem,branches and leaves,but enhanced slightly in stem phloem,indicating that N element gradually were concentrated in the stem phloem.
P element:P contents in 1a-3a E. grandis organs were in the order of leaves>branches>roots>stem phloem >stem xylem.With the increase ofplantage,P contents changed slightly in different organs, and increased slowly in phloem,branches,leaves and stem xylem.
K element:K contents in organs of 1a-2a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>branches>stem phloem>roots>stem xylem.K contents in organs of 3a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>stem phloem>branches>roots>stem xylem.With the increase of plant age,N contents in roots and branches showed a slow downward trend,but slightly enhanced in leaves and stem phloem,and changed only a little in stem xylem,indicating that K element were concentrated in leaves and stem phloem as plant age increased.
Ca element:Ca contents in organs of 1a E.grandis were in the order of stem phloem>leaves>branches>roots>stem xylem.Ca contents in organs of 2a-3a E.grandis were in the order of stem phloem >branches>leaves>roots>stem xylem.With the increase of plant age,Ca contents decreased slowly in roots and leaves,but enhanced in stem phloem and branches,indicating that Ca element were concentratedin stem phloem and branches as plant age increased.
Mg element:Mg contents in organs of 1a-2a E.grandis were in the order of stem phloem > leaves>branches>roots>stem xylem;Mg contents in organs of 3 a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>stem phloem >branches>roots>stem xylem.With the increase of plant age,Mg contents enhanced in roots,leaves,branches,stem phloem and stem xylem.
Fe elements:Fe contents in organs of 1a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>roots>branches>stem phloem>stem xylem.Fe contents in organs of 2a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>roots>stem xylem>stem phloem>branches.
Zn elements:Zn contents in organs of 1a E.grandis were in the orderof leaves>branches>stem phloem>roots>stem xylem.Zn contents in organs of 2a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>roots>stem phloem >branches>stem xylem.

Table 4 ANutrient accumulation and distribution per plant in E.grandis of different ages
Nutrient accumulation and distribution per plant in E.grandis of different ages
Table 4 reported the nutrient accumulation per plant in E.grandis of different ages.
Nutrient accumulation and distribution per plant Nutrient accumulation per plant in 1a-3a E.grandis multiplied as the plant age increased,indicating that the nutrient demand enhanced with the increase of plant age.E.grandis in differentages needed high Ca and N,and relatively high K.Accumulated amounts of macroelements N,P,K,Ca and Mg in organs of 1a-2a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>branches>stem phloem>roots>stem xylem.Accumulated amounts of macroelements in 3a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>branches>stem phloem >stem xylem>roots,indicating that the nutrient accumulated amount was the maximum in leaves,and had no correlation with forest age.Accumulated amounts of microelement Fe in organs of 1a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>roots>branches>stem phloem >stem xylem;accumulated amounts of microelement Zn were in the order of leaves> branches>roots>stem phloem >stem xylem. Accumulated amounts of microelement Fe in organs of 2a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>roots>stem xylem > branches > stem phloem;accumulated amounts of microelement Zn were in the order of leaves>branches>roots>stem xylem >stem phloem.Accumulated amounts of microelements in leaf tissues were the maximum,which had no correlation with forest age.
Accumulated amount of microelements in plants was not affected by the forest age.The accumulated amounts of macroelements and medium elements were in the order of Ca>N>K>Mg>P.Microelements Fe and Zn were not affected by forest age;and the accumulated amounts were in the order of Fe>Zn.
Accumulated amounts ofmicroelements in 1a-3a E.grandis were 12.45,136.19 and 420.23 g per plants. Accumulated amounts of nutrient elements in 2a and 3a E.grandis were 11 and 33 times of 1a E.grandis,respectively.Accumulated amounts of microelements Fe and Zn in 1a and 2a E.grandis were 254.0 and 2 569.2 mg per plant,respectively.Thus,accumulated amount of 2a E.grandis was 10 times of that of 1a E.grandis.
When the stand density was 1 665 plants/hm2(2 m×3 m planting spacing),the element accumulated amounts of 1a-3a E.grandis were 20.73,226.76 and 699.68 kg/hm2,showing that the forest biomass enhanced and the stand density absorbed more nutrients from forest land as the forest age increased.Therefore,during practical production, necessary fertilization should be applied to the forest land in order to ensure the normal growth of plant and to prevent soil fertility declination.The application amount of fertilization should be determined according to the nutrient demand of E.grandis and the supply situation of soil fertilization.
Nutrient accumulation per plant in E.grandis Accumulated amount of N element:accumulated amounts of N element per plant in 1a-3a E.grandis were 4.92,42.01 and 152.44 g per plant,accounting for 39.5%,30.8% and 36.3%of the total accumulated amounts of macroelement,respectively.This indicated that the growth demand of E.grandis for N element was great,which occupied more than 1/3 of the total nutrients.
Accumulated amount of P element:accumulated amounts of P element per plant in 1a-3a E.grandis were 0.25,3.30 and 12.49 g per plants,accounting for 2.0%,2.4%and3.0%of the total accumulated amounts of macroelement,respectively.This indicated that E.grandis had very small demand for P element,which occupied less than 3.0%of the total nutrients.
Accumulated amount of K element:accumulated amounts of K element per plant in 1a-3a E.grandis were 1.54,2l.67 and 49.10 g per plant,accounting for 12.4% ,15.9%and 11.7% of the totalaccumulated amounts of macroelement,respectively.This indicated that E.grandis needed more K nutrient as the plant age increased.Accumulated amount of K element per plant accounted for 10%-16%of the total nutrients.
Accumulated amount of Ca element:accumulated amounts of Ca element in 1a-3a E.grandis were 5.26,61.72 and 183.80 g per plant,accounting for 42.2%,45.3%and 43.7%of the total accumulated amounts of macroelement,respectively.This indicated that E.grandis had the maximum demand for Ca element,which accounted for more than 40%of the total nutrients.
Accumulated amount of Mg element:accumulated amounts of Mg element in 1a-3a E.grandis were 0.49,7.53 and 22.39 g per plant,accounting for 3.9%,5.5%and 5.3%of the total accumulated amounts of macroelement,respectively.This indicated that demand for Mg element increased slightly as the plant age enhanced. However,the Mg element occupied only very slight percentage of the total nutrients,which was 6.0%.
Accumulated amount of Fe element:accumulated amounts of Fe element in 1a-2a E.grandis were 238.6 and 2453.2 mg per plant,accounting for 93.9%and 95.5%of the total accumulated amounts of Fe and Zn,respectively.
Accumulated amount of Zn element:accumulated amounts of Zn element in 1a-2a E.grandis were 15.4 and 116.0 mg per plant,accounting for 6.1%and 4.5%of the total accumulated amounts of Fe and Zn,respectively.
Annual net accumulated amount of nutrients in E.grandis
Table 4 reported that annual net accumulated amount of nutrients in E.grandis enhanced as the plant age increased.The annual net accumulated amountofmacroelement and medium element in 1a E.grandis was 12.45 g per plant(20.73 kg/hm2,accounted based on 1 665 plants/hm2,the same as follows).Among them,the annual net accumulated amounts of N,P,K,Ca,Mg,Fe and Zn were 4.92,0.25,1.54,5.26,0.49,238.6 and 15.4 mg per plant,respectively.
The annualnetaccumulated amount of macroelement and medium element in 2a E.grandis was 123.74 g per plant(206.03 g/hm2).The annual net accumulated amount of nutrient was 90.8%of its accumulated amount. Among them,the annual net accumulated amount of N,P,K,Ca and Mg elements were 37.09,3.05,20.13,56.46 and 7.04 g per plant,respectively.They were 88.3% ,92.4% ,92.9%,91.5%and 93.5%of their accumulated amounts.The annual net accumulated amountofmicroelements Fe and Zn were 2214.6 and 100.6 mg per plant,which accounted for 90.3%and 86.7%pf their accumulated amounts.
The annualnetaccumulated amount of macroelement and medium element in 3a E.grandis was 284.04 g per plant(472.92 g/hm2).The annual net accumulated amount of nutrient was 67.6%of its accumulated amount. Among them,the annual net accumulated amount of N,P,K,Ca and Mg elements were 110.43,9.19,27.43,122.08 and 14.86 g per plant.They were 72.4%,73.6%,55.9%,66.4% and 66.4% oftheir accumulated amounts.
Among the annual net accumulated amount of nutrient elements per plant in 1a-3a E.grandis,Ca element was the maximum,N and K elements took the second and third places.Mg element was relatively small and P element was the minimum,which were consistent with the accumulation laws of nutrient elements.Therefore,1a-3a E.grandis needed relatively great Ca,N and K elements;2a E.grandis had the greatest increase in demand.During practical production,fertilization of N and K should be paid more attention based on the situation of soil nutrient supply.And Ca element could be replaced by P fertilizer,which usually contained abundant Ca.
Conclusions
Contents ofnutrientelements varied greatly in different organs.Total contents of macroelements N,P,K,Ca and Mg were distributed in the order of stem phloem>leaves>branch phloem>root phloem>root xylem>branch xylem>stem xylem.Contents of microelements Fe and Zn were relatively high in leaves,root phloem and branch phloem.MicroelementFe content was higher than Zn content in different organs.
Total contents of macroelements N,P,K,Ca and Mg in 1a-3a E.grandis were distributed in the order of stem phloem,leaves > branches,roots>stem xylem.As the plant age increased,nutrient elements were concentrated in phloem;and microelements Fe and Zn were mainly concentrated in the leaves and roots.
Accumulated amount of N,P,K,Ca and Mg in 1a-3a E.grandis were in the order of leaves>branches>stem phloem>roots or stem xylem>stem xylem or roots.Accumulated amount law of nutrient elements was not affected by the plant age.The accumulation of macroelements was in the order of Ca>N>K>Mg>P;and the microelements was in the order of Fe>Zn.
Accumulated amounts ofmicroelements in 1a-3a E.grandis were 12.45,136.19 and 420.23 g per plants,respectively.Among them,Accumulated amount of N and P elements occupied more than 1/3 and less than 3.0%of the total accumulated nutrients,respectively.The accumulated amount of K element accounted for 10%-16%of the total accumulated nutrients,that of Ca element exceeded more than 40%;accumulated amount of Mg element accounted for less than 6.0%of the total accumulated nutrients.
Accumulated amounts ofmicroelements Fe and Zn in 1a and 2a E.grandis were 254.0 and 2 569.2 mg per plant,respectively.Among them,accumulated amounts of Fe and Zn accounted for about 95%and 5%of the total accumulated nutrients,respectively.Among the annual net accumulated amount of nutrient elements per plant in 1a-3a E.grandis,Ca element was the maximum,N and K elements took the second and third places.Mg elementwasrelatively small and P element was the minimum.Therefore,1a-3a E.grandis needed relatively great Ca,N and K elements.
[1]NIE DP(聂道平).Biological cycle of nutrient elements in forest ecosystem (森林生态系统营养元素的生物循环)[J]. Forest Research(林业科学研究),1991,4(4):435-440.
[2]DONG ZY(董志勇).Technical manual for forest engineer(林业工程师实验技术手册)[M].Beijing:China Forestry Publishing(中国林业出版社),1995.
[3]ZHANG WR(张万儒),YANG GY(杨光滢),TU XN(涂星南),et al.Detection of total N,P,K,Na,Ca,Mg,Fe,Zn,Mg,Cu,S in forest plants and litter layer(森林植物与枯枝落叶层全氮、磷、钾、钠、钙、镁、铁、锌、锰、铜、硫等的测定)[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press(中国标准出版社),2000:270-272,279-297.
[4]XIE XJ(谢贤健),ZHANG J(张健),FENG MS(冯茂松).Accumulation and distribution of main nutrient elements of Eucalyptus grandis(巨桉主要养分元素积累与分布研究)[J].Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology(四川林业科技),2005,26(2):1-6.
[5]ZHU WZ(朱万泽),XUE JH(薛建辉),WANG JX(王金锡),et al.Accumulation of biomass and nutrient elements of Alnus formosana(台湾桤木林分生物量与营养元素的分布)〔J〕.Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(南京林业大学学报),2002,26(2):15-20.
[6]GUO TF(郭天峰),FENG HH(冯汉华),XU QH(徐期瑚).Nutrient accumulation and distribution of plantation ecosystem of Alnus cremastogyne Burkill(四川桤木人工林生态系统养分的积累与分布)[J].Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology(四川林业科技),2009,30(4):89-91.
Responsible editor:Na CHENG
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
巨桉幼树器官组织中养分元素的分布与积累特点
闵安民1*,王宇1,李红霞1,费楠1,李凤鸣2
(1.四川省林业科学研究院,四川成都610081;2.成都市新津县林业局,四川新津611430)
通过对林龄1a-3a巨桉幼树的器官生物量调查、器官组织中大量元素N、P、K、Ca、Mg和微量元素Fe、Zn的含量测定及其积累量的分析结果表明:大量元素总合量在各器官中的分布为干韧皮部、叶>枝、根>干木质部,微量元素主要富集于叶和根器官中;单株木器官中大量元素的累积量排序为叶>枝>干韧皮部>根或干木质部>干木质部或根,各养分元素积累量的规律不受林龄的影响,大量营养元素依次为Ca>N>K>Mg>P;微量元素累积量Fe>Zn;林龄1a-3a巨桉平均单株木大量元素累积总量分别是12.45、136.19和420.23 g/株;各养分元素的年净积累量以Ca为最大,N、K养分元素次之,Mg元素较少,P元素最小。
巨按;器官组织;养分元素;积累量
四川森林生态与资源环境研究重点实验室资助项目“四川省巨桉配方施肥技术研究”。
闵安民(1963-),男,四川资中人,研究员,主要从事土壤肥力、植物营养与施肥研究,E-mail:minanmin@126.com。*通讯作者。
2015-10-02
Supported by the Key Laboratory of Forest Ecology and Resource Environment of Sichuan Province.
*Corresponding author.E-mail:minanmin@126.com
Received:October 2,2015 Accepted:November 20,2015
修回日期 2015-11-20
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- An lnnovative Strategy for Reciprocal Distant Hybridization between Spartina alterniflora and Rice
- Study on Absorptive Capacity to Formaldehyde and Physiological and Biochemical Changes of Scindapsus aureus Based on the Regulation of LaCl3
- Dynamic Variation in Sugar,Acid,and ASA Contents of‘Ganmi 6’Kiwifruit(Actinidia eriantha Benth)Fruits
- Construction and Development of GMS Agricultural lnformation Network Based on Stakeholder Analysis
- Effects of Different Decolorants on Retention Rate of Total Triterpenes in Fruit and Rattan Stems of Schisandra chinensis(Turcz.)Baill
- Determination of Heavy Metals inDendrobium candidiumWall.ex Lindl.by lCP-MS
