An lnnovative Strategy for Reciprocal Distant Hybridization between Spartina alterniflora and Rice
2015-11-08QikangCHENBoCHENHuilanLUHuiZHOUZhipingMEl
Qikang CHEN,Bo CHEN,Huilan LU,Hui ZHOU,Zhiping MEl
1.Nantong Kangbole Agricultural Science and Technology Co.,Ltd.,Nantong 226001,China;
2.Nanjing Haipeite Agricultural Science and Technology Co.,Ltd.,Nanjing 210007,China
An lnnovative Strategy for Reciprocal Distant Hybridization between Spartina alterniflora and Rice
Qikang CHEN1,2*,Bo CHEN1,2,Huilan LU1,Hui ZHOU2,Zhiping MEl1
1.Nantong Kangbole Agricultural Science and Technology Co.,Ltd.,Nantong 226001,China;
2.Nanjing Haipeite Agricultural Science and Technology Co.,Ltd.,Nanjing 210007,China
[Objective]This study aimed to explore germplasm resources of salt tolerant Spartina alterniflora and high yield rice,and develop an innovative strategy for distant hybridization between S.alterniflora and rice.[Method]Crossing(rice♀):hot water emasculation and glume-cutting pollination method,heat emasculation and pollen-suction pollination method;reciprocal crossing(S.alterniflora♀):glume-cutting emasculation and pollination method,continuous emasculation-pollination method,hot wateremasculation and continuous emasculation-pollination method. [Result]In crossing groups(rice♀ ×S.alterniflora♂),compared with hot water emasculation and glume-cutting pollination treatment,the number of seed-bearing combinations,seed number per spike and seedling emergence rate in heat emasculation and pollen-suction pollination treatment were improved by 34.09%,121.21%and 60.07%,respectively;hybridization efficiency was improved by 6-7 times.In reciprocal crossing groups (S.alterniflora♀ ×rice♂),compared with glume-cutting emasculation and pollination treatment,the number of seed-bearing combinations and seed number per spike in continuous emasculation-pollination treatment were improved by 3.14and 4.21 times,respectively;seedling emergence rate wasimproved by 68.47%;hybridization efficiency was improved by 7-8 times.[Conclusion]Heat emasculation and pollen-suction pollination method is suitable for hybridization between rice♀ ×S.alterniflora♂;continuous emasculation-pollination method is suitable for hybridization between S.alterniflora♀ ×rice♂.
Spartina alterniflora/rice;Distant hybridization method;New technology;Germplasm innovation
A t present,the distribution area of Spartina alterniflora Loisel. ranks first among various Spartina species in coastal areas of China.S.alterniflora,a perennial C4herbaceous plant in the genus Spartina Schreb.of family Poaceae,was introduced from the United States by Nanjing University in 1979.S.alterniflora has strong salt tolerance,which is suitable for cultivation in middle tidal zone of the coast areas.S.alterniflora stems are 1-3 m in height and 1 cm in diameter with high yield,which are suitable for grazing and feeding cattle,sheep and other plant-eating animals[1].S.alterniflora panicles are 20-45 cm in length and florets are approximately 1 cm in length;two white feather-like stigmas of pistil are very long and exposed when flowering;matured anther of stamen cracks longitudinally and releases yellow pollens. S.alterniflora blooms successively in June-November.The seeds are usually matured in August-December and lose their germination ability after dehydration.S.alterniflora has bisexual flowers,whose female flowers mature before the male ones.The stigmaselongate before pollen sac rupture to accept pollens from precocious flowers,thereby contributing to allogamy[2].
Under the guidance of Professor Zhong Congxin from Nanjing University,we have introduced S.alterniflora since 1980 and established the first Spartina farm in China.We undertake the national science research project "SeasidePastureExperiment"and rear more than 3 200 cattle and sheep with S.alterniflora as feed.The established seaside pasture was identified as the domestic origination[3].In 2005,it was found that S.alterniflora has excellent properties such as salt tolerance,but it exhibits small seed size and low seed setting rate,which is difficult to be used as feed for meeting the nutritional needs of cattle and sheep,suggesting the importance of excavating salt-tolerance gene and other gene resources in S.alterniflora.
Rice is a common crop belonging to the genus Oryza of family Poaceae,which exhibits abundant variety resources,good seed plumpness and high yield.Rice straws can be used as feed of sheep and cattle.Rice grains contain 8% crude protein with the highest NFE (nitrogen free extract)content and the highest effective energy value among various grain crops as a high-quality energy feed[4].Rice provides excellent germplasm resources for the improvement of S.alterniflora. Beneficial genes of male parent plants can be introduced via distanthybridization to create new germplasms,improve diversity and expand the genetic basis of rice[5].
Distant hybridization between S.alterniflora and rice was performed during 2006-2010.However,the hybridization is difficult to be carried out due to the small florets,protogyny and exserted pistils of S. alterniflora. Therefore,S.alterniflora♀ ×rice♂(reciprocal crossing)test had not been conducted,while only rice♀×S.alterniflora♂ (crossing)test was performed and the materials were pollinated once with S.alterniflora male parent,with the hybrid grain seed setting rate of 5.4%-9.37%,which indicated a lack of in-depth research on hybridization methods[6-8].In hybridization between rice♀×S.alterniflora♂,rice female parent should be emasculated. The existing emasculation methods of rice[9-14]have various advantages and disadvantages: the heavy workloads ofglume-cutting emasculation method greatly damage florets and reduce seed setting rate;hot water emasculation method leads to high seed setting rate with high technical requirements,which can kill all stamens without causing damage to pistils;CO2gas vacuum pump method exhibits high emasculation efficiency,but it requires a set of supporting equipments with high cost;bagging emasculation method is convenient,but the bagging time is not easy to master[15].As an effective breeding measure,distant hybridization can introduce beneficial genes from different genera and families,which provides an important way for the improvement of existing varieties[16].The innovation of hybridization methods is the key to improving seed setting rate and emergence rate in distant hybridization between S.alterniflora and rice.Accelerating the creation of new germplasms of salt tolerant crops for saline-alkali land management has important practical significance and broad application prospects.In this study,distant hybridization between S.alterniflora and rice was investigated to develop an innovative strategy for crossing(rice♀× S.alterniflora♂)and reciprocal crossing(S.alterniflora♀ ×rice♂)between S.alterniflora and rice.
Materials and Methods
Experimental time and sites
Experimental time:April 2014-May 2015.
Experimental sites: (1)experimental field of the Institute of AgriculturalScience in CoastalArea of Jiangsu Province,where experimental operations were performed in the field and laboratory;(2)saline-alkali experimental field of the New District in Tongzhou Bay of Jiangsu Province,where pollen suction and pollination were performed in the saline-alkali field.
Experimental materials
Spartina alterniflora S.alterniflora seedlings were obtained from Xingken Huanghai Coastal Spartina Farm in Qidong City ofJiangsu Province,transplanted to the experimental field of the Institute of Agricultural Science in Coastal Area of Jiangsu Province,and incubated in ceramic cylinders.In addition,S.alterniflora seedlings were planted in the saline-alkali experimental field of the New District in Tongzhou Bay of Jiangsu Province.
Screening and incubation of S.alterniflora:at three months before hybridization (early May),S.alterniflora seedlings with vigorous growth and multiple thick stems in middle tidal zone of the coast were collected with sea soil,transplanted into prepared ceramic cylinders(26 cm in internal diameter,30 cm in height),placed in the experimental field,irrigated thoroughly with 1%salt water,and watered with 1%salt water every 15 d to breed S. alterniflora materials for hybridization. The number of S.alterniflora seedlings planted was determined based on the numberofcrosscombinations.At growth stage,S.alterniflora in each ceramic cylinder bore 20-30 panicles,and 4-6 panicles were required for each cross combination.
Rice cultivars ① Dahuaxiangnuo;②Jindao 1007;③Wuxiangnuo 8333;④ Yanjing No.9;⑤ Yinxiang 18;⑥Yanjing No.10;⑦Wuyunjing No.7;⑧Wujing 15;⑨Chengnuo 218;⑩Wujing No.7;11○ Ningjing No.1;12○Tongyujing No.14;13○ Nanjing 45;14○Nanjing 46;15○Nanjing 47;16○Shangshi 400;17○Nipponbare;18○7K339;19○Wujing13;20○ YandaoNo.9;21○Wuyunjing No.8;22○Youfujing.
Different rice varieties were planted in the experimental field of the Institute of Agricultural Science in Coastal Area of Jiangsu Province and the experimental field of the New Districtin Tongzhou Bay ofJiangsu Province.S.alterniflora flowers successively in late June and reaches blossom stage in August-October.For flower synchronization and timely hybridization,since April 20,2014,22 rice varieties were sown every 15 d for four batches.
lnstruments and equipments (1)Self-made elevating hot water emasculation iron stand,12 kg plastic buckets (commerciallyavailable),selfmade elevating heat emasculation iron stand,2 kg wild-mouth bottles and transparent thick plastic insulation bags (commercially available),ther-mometer,clock.Pencils,pens,rulers,record forms,paper clips,bagging paper and scissors should be clean and dry,and stored in the box before use.
(2)Pollen suction equipments:①Vacuum suction deviceMc-DL200(commercially available),weighing 1.3 kg,supply voltage 220 V,rated power 400 W;②portable multi-function suction device GD-03 (commercially available),weighing 0.5 kg,supply voltage 220 V,rated power 150 W.
Methods
Observation of flowering habits of male and female parents The flowering habits of S.alterniflora and rice were observed after spike emergence to determine hybridization method,emasculation and pollination methods and time.
Crossing groupⅠ(rice♀):hot water emasculation and glume-cutting pollination Emasculation:In the afternoon of the day before hybridization,seedlings of rice female parent at initial blossom stage with 2/3-3/4 leaf sheath exposed were transplanted into plastic basins with soil,brought back into the laboratory and watered. At 7:00-7:30 a.m.on the next day,after the removal of blooming florets and tender spikelets on the lower part of spikes, suitable spikes on rice seedlings were retained for hybridization.The roots of rice seedlings for emasculation were covered with plastic bags and hanged upside down on the self-made elevating hot water emasculation iron stand.A plastic bucket filled with warm water was placed under rice seedlings,and the water temperature was controlled at 42℃.Rice spikes were soaked into the warm water for 10 min.Subsequently,rice seedlings were placed into plastic basins.After about 20 min,florets bloomed successively for approximately 20 min.Unbloomed florets and bloomed anthers should be removed;approximately 1/3 of the upper part of glume was removed to improve stigma exposure rate and seed setting rate.After emasculation and glume cutting,rice seedlings were bagged.At 8:30-11:30 a.m.,spikes of S.alterniflora male parent were dry and flowering.
Pollination:floweringspikesofS.alterniflora with pollen exposure were cut off and shaken on the top of spikes of emasculated and bagged seedlings of rice female parent.Each cross combination was pollinated once in the afternoon of the day and the next day,respectively.The bags were sealed and marked with No.of cross combination and hybridization date.
Treatment of hybrid seedlings:after pollination,seedlings of rice female parent were transplanted into the experimental field.After 20-25 d,mature hybrid seeds were harvested in time to prevent mildew.
Crossing groupⅡ (rice♀):heat emasculation and pollen-suction pollination method Emasculation: In the afternoon of the day before hybridization,seedlings of rice female parent at initial blossom stage with 2/3-3/4 leaf sheath exposed were transplanted into plastic basins with soil,brought back into the laboratory and watered.At 7:00-7:30 a.m.on the next day,after the removal of blooming florets and tender spikelets on the lower part of spikes,suitable spikes on rice seedlings were retained for hybridization.
Five wild-mouth bottles could be hanged with mesh bags on the selfmade elevating heat emasculation iron stand to emasculate five basins of rice female parent simultaneously.Each wild-mouth bottle could be filled with 2 kg of hot water,and the bottles were placed in transparent thick plastic insulation bags.Firstly,wild-mouth bottles were filled with 60℃warm water. In emasculation,the warm water was poured out(a thermometer was inserted into the mouth of transparent plastic insulation bag,and the internal temperature of the wild-mouth bottle was around 45℃,which could be maintained for 7-9 min).The emasculated rice spikes were covered with empty wild-mouth bottles hanged upside down with the elevating iron stand. The mouth of transparent plastic insulation bag was sealed along with rice stems,thermometer and the mouth of wild-mouth bottle.After 5 min,empty wild-mouth bottles were removed.After about 20 min,rice spikes bloomed successively for approximately 30 min. Subsequently,pollens in all the bloomed anthers were immediately collected with the suction device.After the removal of unbloomed florets,rice seedlings were bagged before pollination.
Pollination:The pollination operations of crossing groupⅡwere consistent with that of crossing groupⅠ.
Treatment ofhybrid seedlings: Hybrid seedlings of crossing groupⅡwere treated with the similar method to crossing groupⅠ.
Selection and treatment of S.alterniflora as female parent for reciprocal crossing Based on the growth characteristics of S.alterniflora,corresponding measures were taken as follows.(1)Spike selection:In the afternoon of the first day,S.alterniflora seedlings with vigorous growth and multiple thick stems were collected.In the top of S.alterniflora spikes(spike tips were about 3-5 cm in length),a small amount of ivory-white stigmas of female flowers were exposed.Single spikes of S.alterniflora were selected,on which upper spikelets were bloomed and middle spikelets would bloom within 1-2 d.(2)Spike processing:All of the upper bloomed spikelets,lower branches and tender grains in leaf sheaths were cut off with scissors.Unbloomed spikelets in the middle part were retained for cross pollination.(3)Bagging:The pruned spikes were immediately bagged and marked with bagging time.
Reciprocal crossing groupⅠ(S.alterniflora♀):glume-cutting emasculation and pollination method
Emasculation:After spike processing,single flowers of S.alterniflora were emasculated artificially with tweezers. About 1/4 of the upper part of glume was cut off,and anthers were removed with tweezers.Emasculated spikes were bagged with paper bags and marked with emasculation date.
Pollination:On the 2ndand 3rdd,ivory-white stigmas of female flowers were exposed and pollinated with pollens from rice male parent for two continuous days.After hybridization,the bags were sealed and marked with No.of cross combination and hybridization date.
Reciprocal crossing groupⅡ(S.alterniflora♀):continuous emasculation-pollination method After bagging,at 7:00-8:30 a.m.of the first day, the bagged S. alterniflora seedlings were checked to remove sta-mens in time.Once the stigmas of pistils appeared,S.alterniflora seedlings were pollinated immediately and marked with the variety of rice male parent and the first hybridization date. Subsequently,the hybridization and pollination operations were repeated every day with pollens of rice variety in the first cross combination until the stigmas of pistils in bags withered and stamens no longer appeared.After hybridization of the cross combination,the bags were sealed and marked with the last hybridization date.During the hybridization process,after each bag checking,emasculation should be performed before pollination.
In this study,the original emasculation and pollination operations of S.alterniflora were performed in the experimental field and laboratory instead of the coastal area;the original hybridization method (pollination without emasculation)was changed with continuous emasculation and pollination.
Reciprocal crossing groupⅢ(S.alterniflora♀):hot water emasculation and continuous emasculationpollination method After spike processing,spikes of S.alterniflora were directly soaked into 38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47 and 48℃water for 10 min,respectively.The emasculated spikes of S.alterniflora were immediately bagged.The bags were sealed and marked with emasculation date and emasculation temperature.Subsequently,the effects of 38-48℃hot water emasculation on S.alterniflora were observed and compared.
After hotwateremasculation,continuous emasculation and pollination operations of reciprocal crossing groupⅢwere consistent with that of reciprocal crossing groupⅡ.
Seedling emergence test with hybrid seeds of S.alterniflora×rice Crossing (rice♀×S.alterniflora♂): Hybrid seeds were stored at room temperature.Reciprocalcrossing(S.alterniflora♀ ×rice♂):Hybrid seeds were stored in two ways:(1)storage at room temperature;(2)hybrid seeds were soaked in 1.5%saline and stored at 0-5℃ in a refrigerator.Hybrid seeds of reciprocal crossing groupⅢwere also stored in two ways due to multiple seeds at 38℃-42℃.S.alterniflora seeds in control group were collected in the coastal area of the New Districtin Tongzhou Bayof Jiangsu Province in late November 2014.Hybrid seeds were sown in the saline-alkali experimental field of the New Districtin Tongzhou Bayof Jiangsu Province on May 10-11,2015,where soil salinity reached 7-10‰.
Results and Analysis
Observation of flowering habits of male and female parents
Observation of flowering habits of S.alterniflora The stigmas were exposed at 3-7 d after spike emergence,and the stigmas of non-pollinated S.alterniflora seedlings could grow for 5-6 d.White feather-like styles of female flowers stretched out early and were exposed during the flowering stage.Stamens appeared at 4-5 d after stigma emergence,and the withered stigmas were pushed aside. The flowering rate of stamens reached the highest at 8:30-11:30 a.m.Anthers were stretched out and cracked. Mature anthers cracked longitudinally,and yellow pollen grains scattered within 2 h.Filaments were elongated rapidly and withered after 2 h.
Observation of flowering habits of rice After spike emergence,spikelets began to blossom within 1-2 d.Filaments were elongated simultaneously;anthers cracked and yellow pollen grains scattered.Mostrice seedlings bloomed at 8:30-11:30 a.m. on a sunny day.
Differences and similarities between flowering habits of S.alterniflora and rice Differences between flowering habits of S.alterniflora and rice:Compared with rice,stigmas of female flowers of S. alterniflora stretched out earlier and were exposed during the flowering stage.Stamens appeared at 4-5 after stigma emergence.
Similarities between flowering habits of S.alterniflora and rice:Without pollination,stigmas of S.alterniflora could grow for 5-6 d.Stigmas of pistils of rice could be pollinated and fertilized within 3-5 d;most stamens of rice bloomed at 8:30-11:30 a.m.
It could be concluded that S.alterniflora as a female parent could be pollinated with pollens from rice stamens within 4-5 d;rice as a female parent could be pollinated with pollens from S.alterniflora stamens within 2-3 d;the emasculation should be performed before 8:00 a.m.,and the pollination should be performed at 8:30-11:30 a.m.
Crossing:rice♀×S.alterniflora♂Crossing groupⅠ(rice♀):hot water emasculation and glume-cutting pollination In 2006,six seedlings of rice female parent were treated by hot water emasculation and glume-cutting,and pollinated once with pollens of S.alterniflora;among 39 spikes hybridized,32 spikes generated seeds,and 115 hybrid seeds were obtained,with an average number of 3.59 seeds per spike[6].In 2009,seedlings of rice female parent were treated by hot water emasculation and glume-cutting,and pollinated once with pollens of S. alterniflora;35 spikes were hybridized in total,and 328 hybrid seeds were obtained,with an average number of 9.37 seeds per spike[7-8].
With hot water emasculation and glume-cutting pollination method,seedlings of rice female parent were pollinated twice with pollens of S.alterniflora.Among 50 spikes hybridized,34 spikes generated seeds,and totally 431 hybrid seeds were obtained,with an average number of 12.68 seeds per spike, which was improved by 253.20%and 35.33%compared with that in 2006 and 2009,respectively. The hybrid seed setting in distant hybridization between rice♀ ×S.alterniflora♂was shown in Table 1.
Existing problems in hot water emasculation and glume-cutting pollination hybridization method:due to high requirements of hot water emasculation technique,appropriate emasculation temperature and spike soaking time should be controlled strictly to kill all stamens without causing damage to pistils.A slight negligence might either fail in emasculation or destroy the entire spike.Glume cutting exhibited heavy workloads and cost plenty of time,which remarkably affected hybridization efficiency and combination number.
Crossing groupⅡ (rice♀):heat emasculation and pollen-suction pollination method In crossinggroupⅡ,2 723 hybrid seeds were obtained.At harvest stage,114 false hybrid seeds with significantly similar morphological characteristics to rice female parent,pure yellow husks and those remarkably differed from hybrid seeds were preliminarily removed,which accounted for 4.19%,and the actual seed number was 2 609.Crossing groupⅡwas also pollinated twice with pollens of S.alterniflora,and 102 spikes were hybridized,which were improved by 1-fold compared with crossing groupⅠ (50 spikes);the number of seed-bearing spikes was improved by 34.09%;seed number per spike was 28.05,which was improved by 121.21%compared with crossing group Ⅰ (12.68).Hybrid seeds in crossing groupⅡ were not moldy,but the percentage of moldy seeds in crossing groupⅠwas 8.35%. The hybrid seed setting in distant hybridization between rice♀ ×S.alterniflora♂was shown in Table 1.
Heat emasculation and pollensuction pollination method was simple and convenient,which could not only damage pollens,but also promote flowering.The materials bloomed fully within 30 min.Thus,unbloomed florets could be distinguished and removed,avoiding confusion between selfing and hybridization.In addition,pollens in all the bloomed anthers were immediately collected with the suction device to prevent incomplete emasculation and selfing.
According to the comparison results between two suction devices,portable multi-function suction device GD-03 was more convenient,flexible and suitable for pollen suction due to low weight(0.5 kg),low power(150 W),low cost and gentle operations without causing damage to rice leaves and florets.

Table 1 Seed setting in distant hybridization between rice♀×S.alterniflora♂
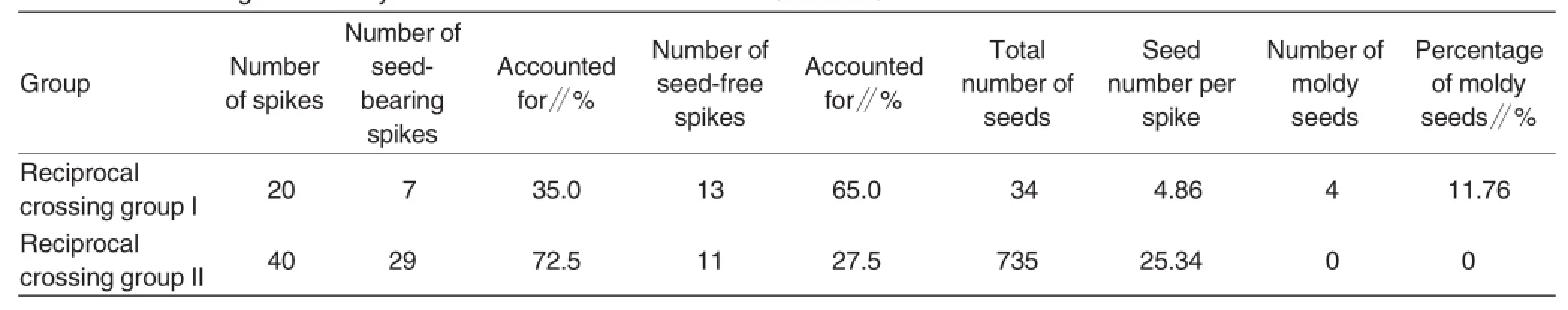
Table 2 Seed setting in distant hybridization between S.alterniflora♀×rice♂
Reciprocal crossing:S.alterniflora♀×rice♂
Reciprocal crossing groupⅠ(S.alterniflora♀):glume-cutting emasculation and pollination method
After emasculation by glume cutting,S.alterniflora was pollinated twice with pollens of rice.Due to small floral organs of S.alterniflora,artificial glumecutting emasculation was difficult and labor costing.Although stigmas of female flowers were not stretched out,a slight negligence might cause damage to floral organs and reduce seed setting rate.In reciprocal crossing groupⅠ,seed-bearing spikes accounted for 35%,but seed number per spike was only 4.86.Moreover,the percentage of moldy seeds was 11.76%.Therefore,glume-cutting emasculation and pollination method was not suitable for distant hybridization between S.alterniflora and rice.Seed setting in distant hybridization between S.alterniflora♀×rice♂was showninTable2.
Reciprocal crossing groupⅡ(S.alterniflora♀):continuous emasculation-pollination method In reciprocal crossing groupⅡ,S.alterniflora was emasculated and pollinated continuously for 4-5 d,and 40 spikes were hybridized,which were improved by 1-fold compared with reciprocal crossing groupⅠ(20 spikes).In addition,the numberofseed-bearing spikes was improved by 3.14 times;total seed number was improved by 20.62 times;seed number per spike was improved by 4.21 times.Hybrid seeds in reciprocal crossing groupⅡwere not moldy.
After bagging,the emergence of stamens,pistil styles was checked at 7:00-8:00 a.m.every day.The results indicated that:(1)At 1-5 d after bagging,stamens,pistil styles generated new spikes every day;(2)at 4-5 d after bagging,pistil styles in the bags withered and stamens no longer appeared,suggesting the termination of pollination and checking.The entire process of continuous emasculation and pollination of S.alterniflora lasted 4-5 d.Seed setting in distant hybridization between S.alterniflora♀× rice♂was shown in Table 2.
Reciprocal crossing groupⅢ(S.alterniflora♀):hot water emasculation and continuous emasculationpollination method On the basis of continuous emasculation-pollination method in reciprocal crossing groupⅡ,the materials were treated at different temperature.Specifically,at 38-42℃,seed-bearing spikes accounted for 44.44-60.00%,and seed number per spike was 17.13-19.78,which reached the highest at 42℃;at 43-48℃,the percentage ofseed-bearing spikes and seed number per spike were both reduced gradually;at 46-48℃,after hot water emasculation,most spikes withered within 1-2 d.Seed setting in distant hybridization between S.alterniflora♀ ×rice♂ after hot water emasculation at different temperature was shown in Table 3.
According to the experimental results,in distant hybridization between S.alterniflora♀ ×rice♂,hot water emasculation at 42℃ achieved that best effect.Seed-bearing spikes ac-counted for 60.00%,and seed number per spike was 19.78,which were both reduced compared with reciprocal crossing groupⅡ (72.5%,25.34).At 38-42℃,new stamens,pistil styles generated new spikes every day within 1-5 d after hot water emasculation,which required continuous artificial emasculation and pollination,indicating that hot water emasculation on the first day did not work but slightly damaged floral organs and influenced seed setting rate;at 43-48℃,the percentage of seed-bearing spikes and seed number perspike were both reduced gradually,which indicated that extremely high temperature would cause serious damage to floral organs and even the entire spikes.Hot water emasculation at different temperature increased workloads and exhibited poorer effect than reciprocal crossing groupⅡ.Therefore,hot water emasculation and continuous emasculationpollination method was not suitable for distant hybridization between S.alterniflora♀×rice♂.

Table 3 Seed setting in distant hybridization between S.alterniflora♀×rice♂after hot water emasculation at different temperature

Table 4 Seedling emergence test with hybrid seeds of S.alterniflora×rice after storage with different methods
Seedling emergence test with hybrid seeds of S.alterniflora×rice
Seedling emergence test with hybrid seeds of rice♀×S.alterniflora♂ after storage at room temperature As shown in Table 4,compared with crossing groupⅠ,the number of cross combinations(spike number)in crossing groupⅡ was improved by 1-fold;the number of seeds sown and numberofseedlings emerged in crossing groupⅡwere improved by5.6 and 9.57 times,respectively;seedling emergence rate was improved by 60.07%.
Seedling emergence test with hybrid seeds of S.alterniflora♀×rice♂ after storage at room temperature In reciprocal crossing groups,seeds stored at room temperature were sown for seven batches,and 375 seeds were sown in total.In control groups,100 seeds were sown.During three months from May 1 to July 30,no bud germination or seedling emergence was observed,and the seeds decayed,which indicated that the hybrid seeds might have inherited the characteristics of S.alterniflora that seeds lose the germination ability after dehydration[2].
Seedling emergence test with hybrid seeds of S.alterniflora♀×rice♂after storage at low temperature with saline Compared with reciprocal crossing groupⅠ,the number of cross combinations(spike number)in reciprocal crossing groupⅡwas improved by 1-fold,and the number of seeds sown was improved by 23.5 times.After storage at room temperature,no seedling emergence was observed in these two reciprocal crossing groups.After storage at low temperature with saline,seedling emergence rate was 56.15%in reciprocal crossing groupⅡ,which was improved by 68.47%and 33.69%compared with reciprocal crossing groupⅠand control group(42%),respectively.
In reciprocal crossing groupⅢ,after storage at low temperature with saline,seedling emergence rate was 39.33%-45.76%in 38-42℃groups;seedling emergence rate reached the highest(45.76%)in 42℃group,which was improved by 8.95%compared with control group but was reduced by 22.71% compared with reciprocal crossing groupⅡ(56.15%).
Conclusion and Discussion
Determination of distant hybridization method,emasculation and pollination frequency and time based on observation of flowering habits of S.alterniflora and rice
Female flowers of S.alterniflora matured before the male ones;the stigmas stretched out before pollen sac ruptures to accept pollens from precocious flowers,thereby contributing to allogamy.The stigmas of nonpollinated S. alterniflora seedlings could grow for 5-6 d.Stigmas of pistils of rice could be pollinated and fertilized within 3-5 d.Thus,both parents could be pollinated continuously for 2-3 times.
Innovation point:The flowering habits of S.alterniflora were conducive to allogamy with pollens from rice male parent,indicating that S.alterniflora and rice could be hybridized.Both S.alterniflora and rice bloomed at 8: 30-11:30 a.m.,indicating that the materials should be emasculated before 8:00 a.m.and pollinated at 8:30-11:30 a.m.
Heat emasculation and pollen-suction pollination method is suitable for hybridization between rice♀ × S.alterniflora♂(crossing)
Compared with hot water emasculation and glume-cutting pollination treatment(crossing groupⅠ),in heat emasculation and pollen-suction pollination treatment(crossing groupⅡ),there were 102 cross combinations,which were improved by 1-fold.The number of seed-bearing combinations was improved by 34.09%compared with crossing groupⅠ;seed number per spike was 28.05,which was improved by 121.21%compared with crossing group Ⅰ (12.68);hybrid seeds in crossing groupⅡ were not moldy,while the percentage of moldy seeds in crossing group Ⅰ was 8.35%;the number of seeds sown and number of seedlings emerged were improved by 5.6 and 9.57 times,respectively;seedling emergence rate was improved by 60.07%;hybridization efficiency was improved by 6-7 times.Thus,heat emasculation and pollen-suction pollination method greatly eased the labor shortage in the process of cross breeding.
Innovation point:The original pollination operations of rice female parent were performed in the experimental field and laboratory.The materials were pollinated twice continuously. Heat emasculation and pollen suction with a portable multi-function suction device were combined to omit hot water emasculation and glume cutting processes,which increased the technical content of rice emasculation without the demand for supporting equipments,reduced the operation difficulty and cost,and improved hybridization efficiency.After hybridization,the obtained seeds exhibited good plumpness,thereby significantly improved seed setting rate and seedling emergence rate.
Continuous emasculation-pollination method is suitable for hybridization between S.alterniflora♀×rice♂(reciprocal crossing)
Compared with glume-cutting emasculation and pollination treatment(reciprocal crossing groupⅠ),in continuous emasculation-pollination treatment(reciprocal crossing groupⅡ),there were 40 cross combinations,which were improved by 1-fold.The number of seed-bearing combinations,total seed number and seed number per spike were improved by 3.14,20.62 and 4.21 times,respectively;hybrid seeds in reciprocal crossing groupⅡwere not moldy;the number of seeds sown was improved by 23.5 times.After storage at low temperature with saline,seedling emergence rate in reciprocal crossing group Ⅱreached 56.15%,which was improved by 68.47%and 33.69%compared with reciprocal crossing groupⅠand control group,respectively;hybridization efficiency was improved by 7-8 times.
Innovation point:The original pollination operations of S.alterniflora female parent were performed in the experimental field and laboratory.According to the flowering habits of S.alterniflora,the female parent materials were emasculated and pollinated continuously to omit hot water emasculation and glume cutting processes,which increased the technical content ofemasculation and pollination of S.alterniflora without the demand for supporting equipments and reduced the operation difficulty,thereby significantly improved seed setting rate,seedling emergence rate and hybridization efficiency.
Further research projects Field screening and molecular detection The created new hybrid germplasms were planted in the saline-alkali land for field observation,screening of hybrid seeds,identification of true and false hybrids,record and analysis of saline-alkali toleranceand other agronomic traits,and comprehensive screening of hybrid germplasms.The screened hybrids were detected and verified in the laboratory.
Expanding the application of distant hybridization methods Selection of hybridization mode and parents: In distant hybridization,crossing and reciprocal crossing easily leads to different combination rates and different hybridization results.Therefore,both crossing and reciprocal crossing should be carried out[17];in hybridization between cultivars and wild species,cultivars should be used as the female parent;in distanthybridization of materials with different chromosome number,those with more chromosomes should be used as the female parent[18].In subsequent research,the application of innovative methods for crossing (rice♀×S.alterniflora♂)and reciprocal crossing(S.alterniflora♀×rice♂)should be further expanded to accelerate the creation ofnew germplasmsand breeding of salt tolerant dual-purpose crops.
Distant hybridization is an important method for biological evolution and variation creation and an important way to form new varieties and new germplasms.This study provided an innovative distant hybridization strategy for exploring germplasm resources of salt tolerant S.alterniflora and high yield rice,which accelerated the creation of new germplasms of salt tolerant dual-purpose crops for saline-alkali land managementand fine/coarse fodder production,exhibiting important scientific significance and economic value for resource utilization,agricultural efficiency improvement,food security and cultivated land strategy with broad application prospects.
[1]QIN P(钦佩),JING MD(经美德),ZHANG ZR(张正仁),et al.Seed germination and salt tolerance of three ecotypes of Spartina alterniflora under(美国互花米草Spartina alterniflora三个生态型的种子耐盐萌发试验)[J].Journal of Nanjing University(南京大学学报),1985,5:237-244.
[2]GUAN DM(关道明).Spartina Salt-Marsh Ecosystem and Management in the Coastal Wetland of China(中国滨海湿地米草盐沼生态系统与管理)[M].Beijing:China Ocean Press(北京:海洋出版社),2009,12:1-15.
[3]ZHONG CX(仲崇信),CHEN QK(陈启康).The First Spartina Pasture in China·Island Environment and Coastal Development(中国第一个大米草羊场·海岛环境与海岸开发)[M].Nanjing:Nanjing University Press(南京:南京大学出版社),1993,1:359-366.
[4]ZHANG ZY(张子仪).Feed Science in China(中国饲料学)[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Press(北京:中国农业出版社),2000,10:350-351,607.
[5]CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES(中国农业科学院). Rice Science in China(中国稻作学)[M]. Beijing:China Agricultural Press(北京:中国农业出版社),1986,8:317,327-328.
[6]CHEN QK(陈启康),SHA WF(沙文锋),HU YJ(顾拥建),et al.A preliminary study on distant hybridization between Spartina alterniflora and rice(互花米草与水稻远缘杂交试验初报)[J].Livestock and Poultry Industry(畜禽业),2007,2: 24-25.
[7]CHEN QK,TIAN ZY,SHA WF,et al. Exploration and innovation of distant hybridization germplasm of Oryza sativa and Spartina alterniflora[J].Agricultural Science&Technology,2012,13(1):131-133,172.
[8]CHEN QK(陈启康),TIAN CY(田曾元),SHA WF(沙文锋),et al.Exploration and innovation of distant hybridization germplasm of Oryza sativa×Spartina alterniflora in tideland(海涂互花米草与水稻远缘杂交种质资源发掘与创新Ⅳ)[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences(安徽农业科学),2011,39(36): 22251-22253.
[9]ZHANG JW (张集文).Improvement of rice hybridization method by hot water emasculation(水稻温水杀雄杂交方法的改进)[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences(湖北农业科学),1978,(6):3.
[10]HUANG ZP(黄治平).Improvements of rice hybridization methods(水稻杂交方法的一些改进)[J].Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology(农业科技通讯),1979,(5):4.
[11]ZHOU GY(周根友),CHEN QK(陈启康),XIA H(夏华),et al.Study and application of rice hybridization methods and techniques(水稻杂交方法及其新技术研究应用)[J].Sichuan Agricultural Science And Technology(四川农业科技),2005,(12):10.
[12]WANG Z(王忠).A method for rice hybridization(水稻杂交方法一靠交法)[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology(农业科技通讯),1993,(1): 4-5.
[13]XU GS(徐国生),TAN WB(谭文兵). Study on ofrice hybridization by glume-cutting and hot water emasculation(水稻杂交剪颖温汤去雄方法的研究)[J].Hunan Agricultural Sciences(湖南农业科学),1983,(3):1 7-l8.
[14]ZHANG FM(张凤鸣),HU W(胡伟).Introduction of methods for rice hybridization(有关水稻杂交方法的介绍)[J].Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology(农业科技通讯),1956,(7): 434-435.
[15]YU FY(余飞宇),WANG DL(王冬兰),LI FF(李飞飞),et al.Study on a new method for rice hybridization:Glumecutting water-spraying emasculation method(水稻杂交新方法一剪颖喷水去雄法的研究)[J].Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology(上海农业科技),2010-6:32.
[16]NORTHWEST A&F UNIVERSITY(西北农学院).Crop Breeding(作物育种学 )[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Press(北京:中国农业出版社),1981,1: 125.
[17]XIE GH(谢庚华),TANG XH(唐锡华),et al.Rice Science(稻作科学)[M].Beijing: China Agricultural Press(北京:中国农业出版社),1985,12:180.
[18]YUN JF(云锦凤),MI FG(米福贵),YANG C(杨川),et al.Forage Breeding Technology(牧草育种技术)[M].Beijing:Chemical Industry Press(北京:化学工业出版社),2004,2:111.
Responsible editor:Xiaohui FAN
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
海涂互花米草与水稻正反远缘杂交创新方法研究
陈启康1,2*,陈 博1,2,陆惠兰1,周 慧2,梅治平1
(1.南通市康博乐农业科技有限公司,江苏南通 226001;2.南京海培特农业科技有限公司,江苏南京 210007)
[目的]发掘海涂互花米草耐盐、水稻高产种质资源,创新互花米草与水稻正反远缘杂交适用方法。[方法]正交:水稻♀温汤杀雄剪颖授粉法、热气杀雄吸花授粉法;反交:互花米草♀剪颖去雄授粉法、连续去雄授粉法、温汤杀雄连续去雄授粉法。[结果]水稻♀热气去雄吸花授粉法比温汤杀雄剪颖授粉法结籽组合数提高34.09%,穗均结籽提高121.21%,出苗率提高60.07%,提高工效6-7倍;互花米草♀连续去雄授粉法比剪颖去雄授粉法结籽组合数增加3.14倍,穗均结籽增加4.21倍,出苗率提高68.47%,提高工效7-8倍。[结论]水稻♀热气去雄吸花授粉杂交法适用于水稻♀×互花米草♂;互花米草♀连续去雄授粉杂交法适用于互花米草♀×水稻♂。
互花米草/水稻;远缘杂交方法;新技术;新种质创制
2014年江苏省南通市科技创新及产业化项目:沿海耐盐碱米草稻新品种(品系)培育 (编号:HL2014020);2014年江苏省南京领军型科技创业人才计划项目 (编号616035)。
陈启康(1952-),男,江苏启东人,研究员,主要从事动植物遗传育种、畜禽营养与饲料、海涂湿地开发研究,E-mail:chqk58@126.com。*通讯作者。
2015-09-17
Supported by 2014 ProjectforScientific and TechnologicalInnovation and Industrialization of Nantong City,Jiangsu Province"Breeding of New Varieties(Lines)of Saline-alkali Tolerant Spartina alterniflora and Rice in Coastal Areas"(HL2014020);2014 Program for Leading Talents of Scientific and Technological Innovation of Nanjing City,Jiangsu Province(616035).
*Corresponding author.E-mail:chqk58@126.com
Received:September 17,2015 Accepted:November 20,2015
修回日期 2015-11-20
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Study on Engineering Characteristics and Application of Sticky Rice
- Periodical Development Trend of Vertical Greening
- Advances in Microbial Remediation on the Application of Heavy Metal Pollution in Agricultural Water Resources
- Analysis on Status quo and Future Development of Fruit and Vegetable Protreatment
- Effect of Three Treatment Measures on Harmless Seedling Raising of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Litv.
- Discussions and Recommendations for Supervision of Vegetable Quality and Safety in Miyun County
