云计算数据中心服务器数量动态配置策略
2015-10-13张建军
卫 星 张建军 石 雷 翟 琰
云计算数据中心服务器数量动态配置策略
卫 星①②张建军*①②石 雷①翟 琰①
①(合肥工业大学计算机与信息学院 合肥 230009)②(安全关键工业测控技术教育部工程研究中心 合肥 230009)
云计算数据中心由通过高速网络连接的大量服务器构成,一种有效的节能措施是维持与系统负载成比例的活跃服务器数量同时切换剩余服务器到空闲模式,由此分别产生操作能耗和切换能耗。该文研究如何动态配置活跃服务器数量以最小化数据中心能耗(操作与切换能耗之和)的问题。首先,建立了问题的NP数学模型,并分析了无切换能耗情况下最优解的特性;其次,通过消除整数动态规划的递推过程,推导具有多项式复杂度的最优静态算法;最后,采用对未来负载的最坏预测结果作为约束制定了优化在线策略。仿真结果表明,所提出的静态最优和动态优化策略能够适应外界负载的剧烈变化趋势始终谨慎调整活跃服务器和休眠服务器的比例,以接近最优的能耗代价维持数据中心的平稳运行。
云计算;数据中心;活跃服务器;离线最优算法;动态规划;在线算法
1 引言
云计算通过整合存储和计算能力有限的大量终端服务器,使得系统用户只需通过网络“透明”的访问其中一台服务器就可获得近乎无限的计算能力以及语音、视频、信息搜索等服务,而资源由云计算数据中心统一调度、组织和管理。Amazon, Google, IBM, Microsoft等相继推出以集群计算为模型的云计算数据中心,采用层次结构实现且承载的主要是客户机/服务器模式应用,具有如下典型特征:(1)数据中心内部各服务器间具有高传输带宽。(2)数据中心能够实现服务器和虚拟机的便捷配置和迁移。(3)数据中心支持数十万甚至上百万台的服务器,并允许增量的部署和扩展,其服务能力远大于外部应用需求。
本文研究如何动态配置各时隙的活跃服务器数量从而最小化数据中心能耗的问题。首先,从数据中心工作模式出发,将任务分发策略简化为负载均衡方式并建立了问题数学模型;其次,分析了无切换能耗情况下最优解的特性,并给出了平周期与跟随周期递推法则;接下来通过消除整数动态规划的递推过程,给出了具有多项式复杂度的静态最优算法;最后以未来负载的最坏预测结果为约束制定了在线算法。
2 系统模型及问题
从而操作能耗函数为
其次推导切换能耗函数,由于活跃服务器切换到休眠模式需要负载迁移、机器折旧等损耗,而休眠模式到活跃模式的能耗极小可以忽略。切换能耗发生在相邻时隙和之间,表达为,其中切换系数为正常数。由于“负载均衡”调度策略被广泛接收是最优分配方式[6,12],则任意服务器被分配到的负载为,且有。综上所述,数据中心能耗最小化问题可表述为
问题1
3 最优解特性分析
3.1 无切换成本最优解
问题2
3.2 一般最优解特性

图1 最优解特性—跟随周期与平周期
4 离线最优算法
问题3

图2 递推用例

图3 计算时存在的两种情况
综合以上两种情况得

表1离线最优算法伪代码
5 在线优化算法

表2在线优化算法伪代码
6 仿真数值结果
由于条件所限,仿真实验在 matlab 2013a环境下,采用离散事件动态方法进行仿真。整体运行模式与流程类似于数据中心的模型设定:服务器数,服务容量,时隙总长;能耗参数分别设为,则操作能耗函数为。
6.1 离线仿真分析

图4 不同负载变化情况下活跃服务器数
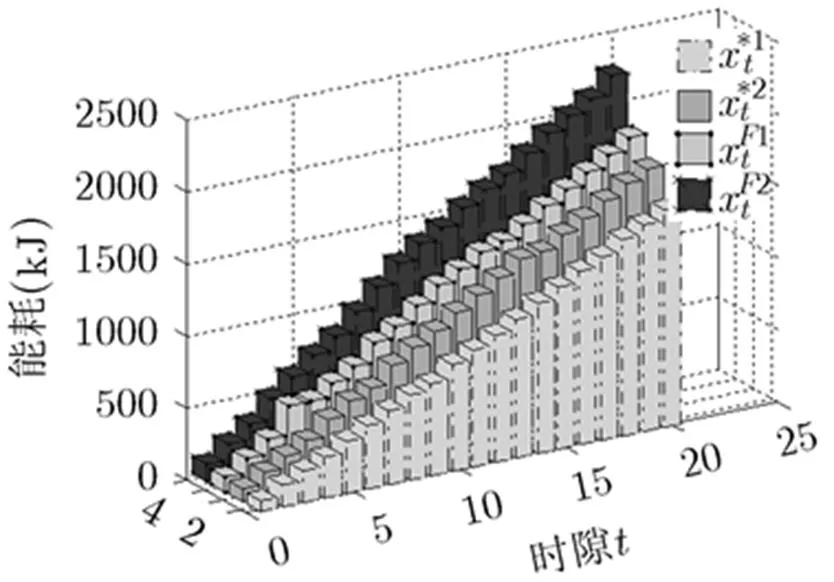
图5 不同负载变化情况下系统最小能耗
6.2 在线仿真分析

图6 在线算法与最优离线算法的比较
图7中online所示为100种场景下所得到的在线算法“性能比”曲线,可见其非常接近1。100种场景下的平均“性能比”为1.151,其中最大值和最小值分别为1.165和1.133。将作为一种在线算法进行比较,所得到的“性能比”并不接近1,因为其仅仅最小化了操作能耗。的“性能比”曲线其平均性能比为2.197,“性能比”最大值和最小值分别为2.297和2.111。而Lazy算法的“性能比”始终稳定在1.45,比本文的在线优化算法高出10%。由此可见,同时考虑操作能耗和切换能耗是十分必要的,两者必须同时达到均衡点才能使总体能耗最接近最优离线算法所得到的最优解。

图7 100组工作负载场景下“性能比”曲线
7 结束语
本文研究如何静态(离线)/动态(在线)配置连续运行时隙的活跃服务器数量,以最小化数据中心能耗的问题。数值结果表明,本文所提出的离线最优算法以较低的复杂度缩短了连续时隙运行时延,同时符合活跃服务器数量需为整数的要求,为在线算法提供最优参考依据。仿真分析表明,本文提出的在线优化算法,能够动态适应外界负载的剧烈变化趋势,始终较为谨慎地调整活跃服务器和休眠服务器的比例,始终以接近最优的能耗代价维持数据中心的平稳运行。进一步的工作可以分为两方面,一是以实际云计算数据中心的真实海量数据为来源,印证和提高算法的可行性与实用性,二是研究负载调度与活跃服务器配置联合的综合策略。
参考文献
[1] Chong F T, Heck M J R, Ranganathan P,Data center energy efficiency: improving energy efficiency in data centers beyond technology scaling[J].&, 2014, 31(1): 93-104.
[2] Li Jian, Shuang Kai, Su Sen,Reducing operational costs through consolidation with resource prediction in the cloud[C]. 12th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cloud and Grid Computing (CCGrid), Ottawa, Canada, 2012: 793-798.
[3] Wang Lin, Zhang Fa, Arjona Aroca J,GreenDCN: a general framework for achieving energy efficiency in data center networks[J]., 2014, 32(1): 4-15.
[4] Urgaonkar R, Kozat U C, Igarashi K,Dynamic resource allocation and power management in virtualized data centers[C]. IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium (NOMS), Osaka, Japan, 2010: 479-486.
[5] Guenter B, Jain N, and Williams C. Managing cost, performance, and reliability tradeoffs for energy-aware server provisioning[C]. 2011 Proceedings of IEEEInternational Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM), Shanghai, China, 2011: 1332-1340.
[6] Qureshi A, Weber R, Balakrishnan H,Cutting the electric bill for internet-scale systems[J]., 2009, 39(4): 123-134.
[7] Guo Yuan-xiong and Fang Yu-guang. Electricity cost saving strategy in data centers by using energy storage[J]., 2013, 24(6): 1149-1160.
[8] Rao Lei, Liu Xue, Xie Le,Minimizing electricity cost: Optimization of distributed internet data centers in a multi-electricity market environment[C]. 2010 Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM), San Diego, CA, USA, 2010: 1-9.
[9] Cao Jun-wei, Li Ke-qin and Stojmenovic I. Optimal power allocation and load distribution for multiple heterogeneous multi-core server processors across clouds and data centers[J]., 2014, 63(1): 45-58.
[10] Beloglazov A, Buyya R, Lee Y C,A taxonomy and survey of energy-efficient data centers and cloud computing systems[J]., 2011, 82(2): 47-111.
[11] Wang Kai, Lin Ming-hong, Ciucu F,Characterizing the impact of the workload on the value of dynamic resizing in data centers[C]. ACM SIGMETRICS/Performance, London, United Kingdom, 2012: 405-406.
[12] Rabbani M G, Zhani M F, and Boutaba R. On achieving high survivability in virtualized data centers[J]., 2014, E97B(1): 10-18.
[13] Liu Zhen-hua, Lin Ming-hong, Adam W,. Greening geographical load balancing[C]. Proceedings ACM SIGMETRICS, San Jose, CA, USA, 2011: 233-244.
[14] Mathew V, Sitaraman R K, and Shenoy P. Energy-aware load balancing in content delivery networks[C]. Proceedings of the ACM SIGMETRICS Joint International Conference on Measurement and Modeling of Computer Systems, Orlando, FL, USA, 2012: 954-962.
[15] Gandhi A, Gupta V, Harchol Balter M,Optimality analysis of energy-performance trade-off for server farm management[J]., 2010, 67(11): 1155-1171.
[16] Lin Ming-hong, Wierman A, Andrew L L H,. Dynamic right-sizing for power-proportional data centers[J]./, 2013, 21(5): 1378-1391.
[17] Michael R G and Johnson D S. Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-completeness[M]. San Francisco: WH Freeman & Co., 1979: 206-218.
Dynamic Active Servers Allocating Policy for Cloud Computing Data Centers
Wei Xing①②Zhang Jian-jun①②Shi Lei①Zhai Yan①
①(,,230009,)②(-,230009,)
Cloud computing data centers generally consist of a large number of servers connected via high speed network. One promising approach to saving energy is to maintain enough active severs in proportion to system load, while switch left servers to idle mode whenever possible. Then operating cost and switching cost is brought about respectively. The problem of right-sizing active severs to minimize energy consumption (total cost of operating and switching) in data centers is discussed. Firstly, the NP-hard model is established, and the characteristics of the optimal solution when omitting the switching cost are analyzed. Then by revising the solution procedure carefully, the recursive procedure is successfully eliminated. The optimal static algorithm with polynomial complexity is achieved. Finally, the online strategy is developed using the worst predicting load as the constraints. Simulation results show that the proposed offline and online algorithm can adapt the dramatic trend of external load and always carefully adjust the proportion of active servers, to guarantee minimum power consumption with a smooth computing process.
Cloud computing; Data center; Active servers; Offline optimal algorithm; Dynamic programming; Online algorithm
TP393
A
1009-5896(2015)08-2007-07
10.11999/JEIT141286
张建军 jianjun@hfut.edu.cn
2014-10-09收到,2015-04-16改回,2015-06-09网络优先出版
国家自然科学基金(61370088),国家国际科技合作专项项目(2014DFB10060)和中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金(2011HGBZ1321, 2012HGQC0012)资助课题
卫 星: 男,1980年生,博士后,主要研究方向为计算机网络、离散事件动态性能优化.
张建军: 男,1963年生,教授,主要研究方向为机电一体化、物联网工程、新能源汽车、汽车电子.
石 雷: 男,1980年生,讲师,主要研究方向为无线传感网.
翟 琰: 女,1977年生,讲师,主要研究方向为汽车电子、嵌入式系统.
