不确定系统鲁棒协方差交叉融合稳态Kalman滤波器
2015-10-13王雪梅刘文强邓自立
王雪梅 刘文强 邓自立
不确定系统鲁棒协方差交叉融合稳态Kalman滤波器
王雪梅①②刘文强①邓自立*①
①(黑龙江大学电子工程学院 哈尔滨 150080)②(黑龙江工商学院计算机科学与技术系 哈尔滨 150025)
针对带不确定模型参数和噪声方差的线性离散多传感器系统,基于极大极小鲁棒估值原理,该文提出一种鲁棒协方差交叉(CI)融合稳态Kalman滤波器。首先,用引入虚拟噪声补偿不确定模型参数,把模型参数和噪声方差两者不确定的多传感器系统转化为仅噪声方差不确定的系统。其次,应用Lyapunov方程证明局部鲁棒Kalman滤波器的鲁棒性,进而保证CI融合Kalman滤波的鲁棒性,且证明了CI融合器的鲁棒精度高于每个局部滤波器的鲁棒精度。最后,给出一个仿真例子来说明如何搜索不确定参数的鲁棒域,并验证所提出的鲁棒Kalman滤波器的优良性能。
多传感器信息融合;不确定系统;鲁棒Kalman滤波器;虚拟噪声;协方差交叉融合
1 引言
信息融合的主要目的是得到系统状态的一个融合估值器,这个估值器是由多传感器系统中的局部观测数据或者局部状态估值融合而成,它的精度要高于每一个局部估值的精度[1]。随着信息科学技术的发展,为了改善系统状态的估计精度,多传感器信息融合Kalman滤波在国内外引起了广泛关注,也已经被广泛地应用到包括国防、导航、信号处理、无人机、GPS定位等多个领域。比较常用的两种Kalman滤波融合方法是集中式融合和分布式融合[5,6]。对于分布式融合方法,有按矩阵加权、按对角阵加权和按标量加权的3种最优加权状态融合方法。为了得到最优加权状态融合Kalman滤波器,要求计算局部Kalman滤波器误差方差和互协方差,而在实际应用中,存在互协方差未知不确定,或者互协方差计算复杂等问题[2]。为了克服这种局限性,Julier和Uhlmann在文献[2,7,8]中提出了带未知互协方差系统协方差交叉(Covariance Intersection, CI)融合算法,并被进一步发展,且广泛的应用于许多领域。
经典Kalman滤波器的设计前提是要求系统的模型参数和噪声方差都是精确已知的,否则Kalman滤波器性能就会降低甚至可能引起滤波发散[16]。这推动了鲁棒Kalman滤波器的研究,所谓鲁棒Kalman滤波器是指,对于所有容许的不确定性,Kalman滤波器的实际滤波误差方差有一个最小上界,这个特性为Kalman滤波器的鲁棒性[17]。
鲁棒Kalman滤波器通常采用的两种重要方法是Riccati方程方法[5,17,18]和线性矩阵不等式(Linear Matrix Inequation, LMI)方法[15,16,19]。两种方法主要针对噪声方差精确已知,模型参数不确定性的系统。
到目前为止,模型参数和噪声方差都不确定的鲁棒Kalman滤波器很少被研究,文献[20,22]对带噪声方差不确定的系统提出鲁棒CI融合Kalman滤波器,但模型参数是精确已知的。
对于模型参数和噪声方差都不确定的多传感器系统,本文用虚拟噪声补偿技术补偿模型参数不确定性,把参数和噪声方差两者不确定系统鲁棒滤波问题转化为仅带不确定噪声方差系统的鲁棒滤波问题。应用极大极小鲁棒估值原理[23],基于带噪声方差保守方差上界的最坏情形保守系统,提出了一种鲁棒CI融合稳态Kalman滤波器,用Lyapunov方程方法证明了其鲁棒性,并证明它的鲁棒精度高于每个局部滤波器的鲁棒精度。为了保证Kalman滤波器的鲁棒性,给出了不确定参数鲁棒域的搜索方法。
2 局部鲁棒稳态Kalman滤波器
考虑带不确定模型参数和噪声方差的多传感器系统:
假设2 多传感器系统式(1)~式(3)是完全可观和完全可控的,且为稳定矩阵。
问题是设计鲁棒CI融合稳态Kalman滤波器。
根据假设2,保守的局部稳态最优Kalman滤波器为
所以,相应的实际局部滤波误差方差和互协方差为
引理1[1]Lyapunov方程
定理1 对带不确定模型参数和噪声方差的多传感器系统式(1),式(2),在假设1和假设2下,实际局部稳态Kalman滤波器式(13)是鲁棒的,即存在一个鲁棒域,使得对于所有容许的不确定模型参数扰动,及满足(5)的不确定噪声方差和,相应的实际滤波误差方差阵有上界,即
且称实际局部Kalman滤波器为鲁棒局部Kalman滤波器,并称是第个局部鲁棒Kalman滤波器不确定参数的鲁棒域。
其中定义:
根据稳态Kalman滤波理论[24],由于,和式(7)知是非奇异阵,并且由于有
注2 对式(19)两侧同时做矩阵迹运算得
3 鲁棒稳态CI融合Kalman滤波器
根据CI融合原理[2]对式(1)~式(3),本文提出鲁棒稳态CI融合Kalman滤波器为
用式(31)减式(27)得到实际滤波误差:
由式(32)得到实际滤波误差方差为
文献[20]证明了由局部滤波器鲁棒性可以得出CI融合滤波器也是鲁棒的,即
由式(30)得出
对式(34)取矩阵迹运算,并由式(36)得到局部和CI融合鲁棒Kalman滤波器具有鲁棒精度关系:
这表明CI融合器的鲁棒精度高于每个局部滤波器的鲁棒精度,且CI融合器的实际精度高于它的鲁棒精度。
4 仿真分析
考虑带不确定模型参数和噪声方差的2传感器时变系统式(1)~式(3),其中在仿真中取,,,,,,,,,。其中是不确定的扰动参数,当,对取欧几里得范数得,所以的鲁棒域对应于的鲁棒域,即。
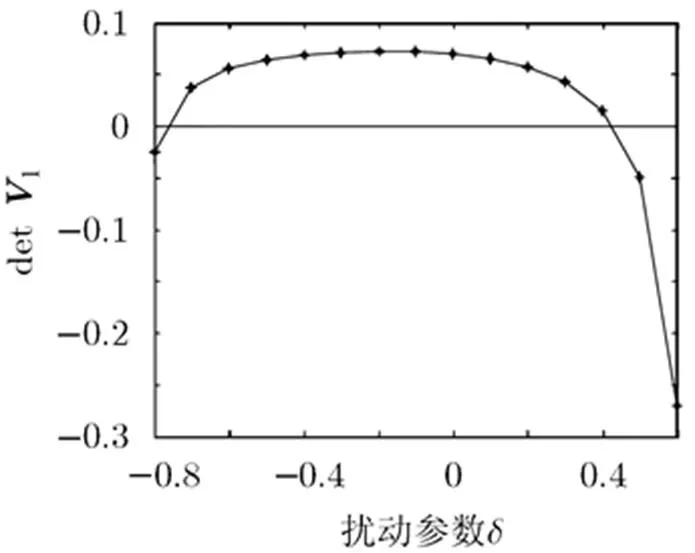
图1 局部鲁棒Kalman滤波器的鲁棒域
下面仿真结果均以第1个子系统为例。
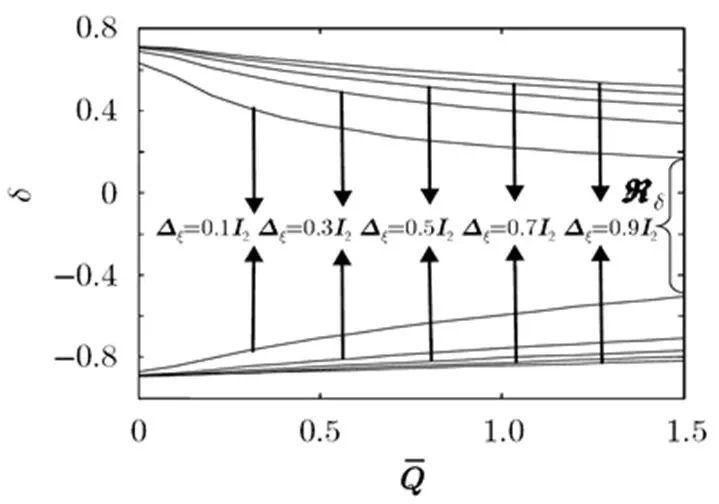
图2不确定模型参数的鲁棒域随和变化的曲线
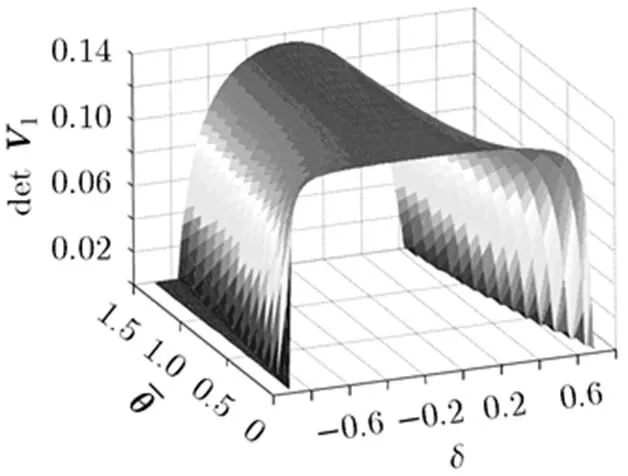
图3随着不确定性和的变化情况

图4局部鲁棒Kalman滤波器鲁棒域随着和的变化情况
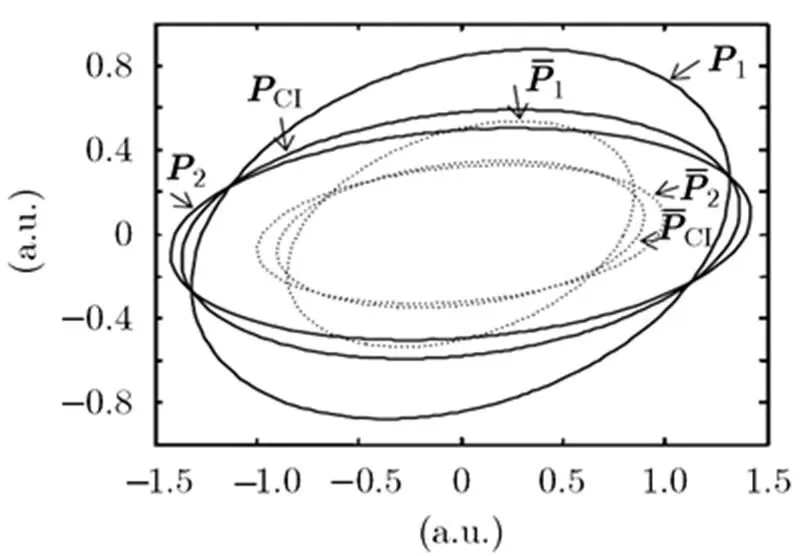
图5 基于协方差椭圆的局部和CI融合鲁棒Kalman滤波器的精度比较
为了验证理论精度关系,图6给出进行1000次Monte-Carlo仿真实验得到的局部和CI融合的均方误差(Mean Square Error, MSE)曲线,均方误差可看成是实际误差方差阵的采样方差的迹,直线代表相应的实际误差方差阵的迹,从图中可看到MSE曲线接近相应的直线,这验证了采样方差的一致性。

图6 局部和CI融合鲁棒Kalman滤波器的MSE曲线

表1鲁棒精度和实际精度的比较
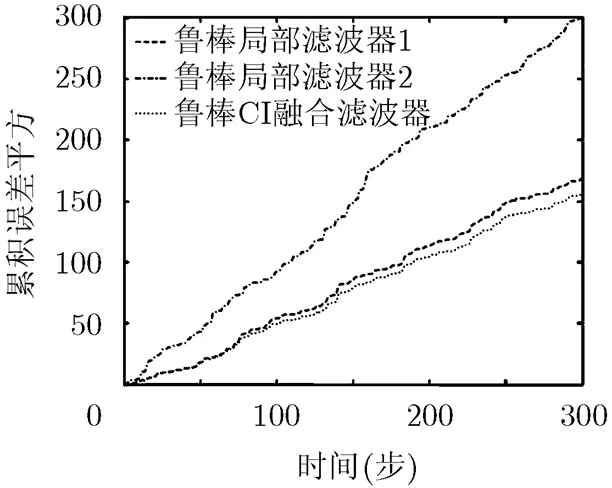
图7 累积滤波误差平方曲线比较
5 结束语
对于带不确定模型参数和噪声方差的多传感器系统,采用虚拟噪声补偿不确定模型参数,将系统模型转化为仅带噪声方差不确定的多传感器系统。用极大极小鲁棒估计原理,基于稳态Kalman滤波理论和带噪声方差保守上界的最坏情形保守多传感器系统,提出了局部和CI融合鲁棒稳态Kalman滤波器方法。采用Lyapunov方程方法,证明了所提出局部和CI融合稳态Kalman滤波器的鲁棒性,即实际Kalman滤波误差方差有一个较小的保守上界,这种证明方法不同于Riccati方程方法和LMI方法。仿真例子给出了局部和CI融合滤波器鲁棒域的搜索方法,并验证了鲁棒CI融合器精度高于鲁棒局部Kalman滤波精度,结果表明本文提出的CI融合滤波器具有良好的性能。
参考文献
[1] Hall D L and Llinas J. An introduction to multisensor data fusion[J]., 1997, 85(1): 6-23.
[2] Julier S J and Uhlmann J K. General Decentralized Data Fusion with Covariance Intersection. Handbook of Multisensor Data Fusion: Theory and Practice[M]. Second Edition, New York: CRC Press, 2008: 319-342.
[3] Hajiyev C G and Soken H E. Robust adaptive Kalman filter for estimation of UAV dynamics in the presence of sensor/ actuator faults[J]., 2013, 28(1): 376-383.
[4] Le M S, Shin H S, Markham K,.. Cooperative allocation and guidance for air defence application[J]., 2014, 32: 236-244.
[5] Feng J X, Wang Z D, and Zeng M. Distributed weighted robust Kalman filter fusion for uncertain systems with autocorrelated and cross-correlated noises[J]., 2013, 14(1): 78-86.
[6] Li X R, Zhu Y M, and Han C Z. Optimal linear estimation fusion-Part I: Unified fusion rules[C]., 2003, 49(9): 2192-2208.
[7] Julier S J and Uhlmann J K. Non-divergent estimation algorithm in the presence of unknown correlations[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE American Control Conference, Albuquerque, 1997: 2369-2373.
[8] Uhlmann J K. Covariance consistency methods for fault-tolerant distributed data fusion[J]., 2003, 4(3): 201-215.
[9] Julier S J and Uhlmann J K. Using covariance intersection for SLAM[J]., 2007, 55(1): 3-20.
[10] Sijs J and Lazar M. State fusion with unknown correlation: Ellipsoidal intersection[J]., 2012, 48: 1874-1878.
[11] Lazarus S B, Tsourdos A, Zbikowski R,.. Robust localisation using data fusion via integration of covariance intersection and interval analysis[C]. International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems COEX, Seoul, Korea, 2007: 199-206.
[12] Ferreira J and Waldmann J. Covariance intersection-based sensor fusion for sounding rocket tracking and impact area prediction[J]., 2007, 15(4): 389-409.
[13] Qi W J, Zhang P, and Deng Z L. Robust sequential covariance intersection fusion kalman filtering over multi-agent sensor networks with measurement delays and uncertain noise variances[J]., 2014, 40(11): 2632-2642.
[14] Gao Q, Chen S Y, Leung H R,.. Covariance intersection based image fusion technique with application to pansharpening in remote sensing[J]., 2010, 180(18): 3434-3443.
[15] Deng Z L, Zhang P, Qi W J,.. Sequential covariance intersection fusion Kalman filter[J]., 2012, 189: 293–309.
[16] Sriyananda H. A simple method for the control of divergence in Kalman filter algorithms[J]., 1972, 16(6): 1101-1106.
[17] Lewis F L, Xie L H, and Popa D. Optimal and Robust Estimation[M]. Second Edition, New York: CRC Press, 2007: 315-340.
[18] Qu X M and Zhou J. The optimal robust finite-horizon Kalman filtering for multiple sensors with different stochastic failure rates[J]., 2013, 26(1): 80-86.
[19] Deng Z L, Zhang P, Qi W J,.. The accuracy comparison of multisensor covariance intersection fuser and three weighting fusers[J]., 2013, 14(2): 177-185.
[20] Qi W J, Zhang P, and Deng Z L. Robust weighted fusion Kalman filters for multisensor time-varying systems with uncertain noise variances[J]., 2014(99): 185-200.
[21] Qi W J, Zhang P, Nie G H,.. Robust weighted fusion Kalman predictors with uncertain noise variances[J]., 2014(30): 37-54.
[22] Qi W J, Zhang P, and Deng Z L. Robust weighted fusion time-varying Kalman smoothers for multisensory system with uncertain noise variances[J]., 2014 (282): 15-37.
[23] Qu X M. A mini-max fusion strategy in distributedmulti- sensor system[C]. International Conference on System Science and Engineering, Xiamen, China, 2012: 330-333.
[24] Kailath T, Sayed A H, and Hassibi B. Linear Estimation[M]. New York: Prentice Hall, 2000, 766-772.
Robust Covariance Intersection Fusion Steady-state Kalman Filter for Uncertain Systems
Wang Xue-mei①②Liu Wen-qiang①Deng Zi-li①
①(,,150080,)②(,,150025,)
For the linear discrete time multisensor system with uncertain model parameters and noise variances, a Covariance Intersection (CI) fusion robust steady-state Kalman filter based on the minimax robust estimation principle is presented.Firstly, introducing the fictitious noise, the model parameter uncertainty can be compensated, so the multisensory system with both the model parameter and noise variance uncertainties is converted into that with only uncertain noise variances.Secondly, using the Lyapunov equation, the robustness of the local robust Kalman filter is proved, so the robustness of the CI fused Kalman filter is guaranteed and it is proved that the robust accuracy of the CI fuser is higher than that of each local filter. Finally, a simulation example shows that how to search the robust region of uncertain parameters and shows the good performance of the proposed robust Kalman filter.
Multisensor information fusion; Uuncertain system; Robust Kalman filter; Fictitious noise; Covariance Intersection (CI) fusion
TP391
A
1009-5896(2015)08-1900-06
10.11999/JEIT141515
邓自立 dzl@hlju.edu.cn
2014-11-27收到,2015-03-27改回,2015-06-08网络优先出版
国家自然科学基金(60874063, 60374026)资助课题
王雪梅: 女,1978年生,博士生,讲师,研究方向为信息融合、鲁棒Kalman滤波.
刘文强: 男,1980年生,博士生,讲师,研究方向为信息融合、鲁棒Kalman滤波.
邓自立: 男,1938年生,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为信息融合、鲁棒Kalman滤波.
