Classification of Phase Portraits of Z2-Equivariant Planar Hamiltonian Vector Fields of Degree 7(Ⅵ)*
2015-09-13LiYanmei
Li Yanmei
(School of Mathematics and Statistics,Chuxiong Normal University,Yunnan Chuxiong,675000,China)
The Hilbert’s 16th problem has been studied for more than one hundred years,but it is still a mathematics problem for twenty - one century[1].In recent decades,some progresses have been made,but there are still many works to be done.In order to use the method of disturbance to get the limit cycles,the phase portraits of undisturbed system must be obtained first.The work here is to study the phase portraits of the following Z2-equivariant planar Hamiltonian vector fields of degree 7 and get 25 new phase portraits which are different from those appeared in the papers[2-6],where k is a parameter with k > 0 and m=k+0.1,n=k+0.2.
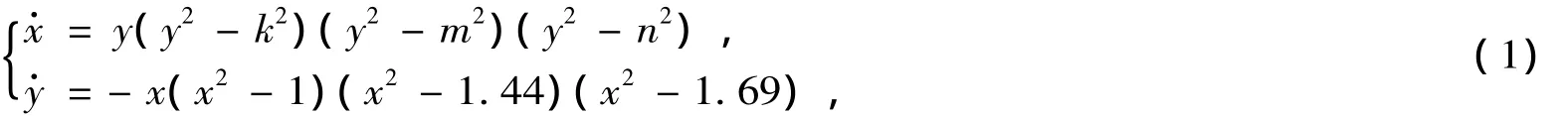
1 Qualitative analysis of system(1)
Obviously,the system has 49 singular points:(0,0),(±1,0),(±1.2,0),(±1.3,0),(0,±k),(0,± m),(0,± n),(±1,± k),(±1.2,± k),(±1.3,± k),(±1,± m),(±1.2,± m),(±1.3,± m),(± 1,± n),(± 1.2,± n)and(± 1.3,± n).Because the system(1)is of Z2- equivariant property,we only discuss the singular points in the first and second quadrants.
The Jacobian of the system(1)is

Investigating the Jacobians of these singular points,we have no difficulty in obtaining the following results:
Theorem 1 The singular points(0,0),(±1.2,0),(0,m),(±1.2,m),(±1,k),(±1.3,k),(±1,n)and(± 1.3,n)are center,and the others are saddle points.
2 The Global Phase Portraits of the System(1)
The Hamiltonian of the system(1)is

Investigating the Hamiltonians of the singular points,we get the following results.
Theorem 2 The system(1)has 25 different phase portraits,each of them corresponding to the value of k in the following ranges:(1)0 < k < 0.121978,(2)k=0.121978,(3)0.121978 < k < 0.437713,(4)k=0.437713,(5)0.437713 < k < 0.438442,(6)k=0.438442,(7)0.438442 < k < 0.545598,(8)k=0.545598,(9)0.545598 < k < 0.545936,(10)k=0.545936,(11)0.545936 < k < 1.05729,(12)k=1.05729,(13)1.05729 < k < 1.05825,(14)k=1.05825,(15)1.05825 < k < 1.05828,(16)k=1.05828,(17)1.05828 < k < 1.25187,(18)k=1.25187,(19)1.25187 < k < 1.31853,(20)k=1.31853,(21)1.31853 < k < 1.88784,(22)k=1.88784,(23)1.88784 < k < 1.9545,(24)k=1.9545,(25)k > 1.9545.
Proof We separately denote H(0,0),H(±1,0),H(±1.2,0),H(± 1.3,0),H(0,k),H(0,m),H(0,n),H(± 1,k),H(± 1,m),H(± 1,n),H(± 1.2,k),H(± 1.2,m),H(± 1.2,n),H(± 1.3,k),H(1.3,m),H(± 1.3,n)and H(x,y)by h00,ha0,hb0,hc0,h0k,h0m,h0n,hak,ham,han,hbk,hbm,hbn,hck,hcm,hcnand hxy.Obviously,hxy=hx0+h0y,ha0< hc0< hb0< 0,h0n< h0k< h0m.Since the difference of the phase portraits depends on the relations of the Hamiltonians of the singular points of the system,we only need to study the relations between the value of k and the Hamiltonians of the singular points.For the case of brevity,merely the cases(1)~(5),(11)~(15),(21)~(25)are proven here.
(1)When 0 < k < 0.121978,the values of hxysatisfy the relations
han<hak<ha0<ham<hcn<hck<hc0<hcm<hbn<hbk<hb0<hbm<h0n<h0k<h00<h0m,and the phase portraits of system(1)is displayed by Fig.1(1).
(2)When k=0.121978,h0m=0,and the values of hxysatisfy the relations
han<hak<ha0=ham<hcn<hck<hc0=hcm<hbn<hbk<hb0=hbm<h0n<h0k<h00=h0m,hence,the phase portraits of system(1)is displayed by Fig.1(2).
(3)When 0.121978 < k < 0.437713,the values of hxysatisfy the relations
han<hak<ham<ha0<hcn<hck<hcm<hc0<hbn<hbk<hbm<hb0<h0n<h0k<h0m<h00,and the phase portraits of system(1)is displayed by Fig.1(3).
(4)When k=0.437713,hc0=hbn,and the values of hxysatisfy the relations
han<hak<ham<ha0<hcn<hck<hcm<hc0=hbn<hbk<hbm<hb0<h0n<h0k<h0m<h00,hence,the phase portraits of system(1)is displayed by Fig.1(4).
(5)When 0.437713 < k < 0.438442,the values of hxysatisfy the relations
han<hak<ham<ha0<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hc0<hbk<hbm<hb0<h0n<h0k<h0m<h00,and the phase portraits of system(1)is displayed by Fig.1(5).
(11)When 0.545936 < k < 1.05729,the values of hxysatisfy one of the following relations
han<hak<ham<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hbk<hbm<ha0<hc0<hb0≤h0n<h0k<h0m<h00,
han<hak<ham<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hbk<hbm<ha0<hc0<h0n<hb0≤h0k<h0m<h00,
han<hak<ham<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hbk<hbm<ha0<hc0<h0n<h0k<hb0≤h0m<h00,
han<hak<ham<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hbk<hbm<ha0<hc0<h0n<h0k<h0m<hb0<h00,where hb0=h0nas k=1.05702,hb0=h0kas k=1.05705,bb0=h0mas k=1.05717,so the phase portrait is displayed by Fig.1(11).
(12)When k=1.05729,we have hc0=h0n,the values of hxysatisfy the relations
han<hak<ham<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hbk<hbm<ha0<hc0=h0n<h0k<h0m<hb0<h00,and the phase portrait is displayed by Fig.1(12).
(13)When1.05729 < k < 1.05825,the Hamiltonians of the singular points satisfy one of the following relations
han<hak<ham<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hbk<hbm<ha0<h0n<hc0≤h0k<h0m<hb0<h00,
han<hak<ham<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hbk<hbm<ha0<h0n<h0k<hc0≤h0m<hb0<h00,
han<hak<ham<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hbk<hbm<ha0<h0n<h0k<h0m<hc0<hb0<h00,where h0k=hc0as k=1.05732,h0m=hc0as k=1.05744,and the phase portrait is displayed by Fig.1(13).
(14)When k=1.05825,we get ha0=h0n,and the Hamiltonians of the singular points satisfy the relations
han<hak<ham<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hbk<hbm<ha0=h0n<h0k<h0m<hc0<hb0<h00,so the phase portrait is displayed by Fig.1(14).
(15)When 1.05825 < k < 1.05828,the Hamiltonians of the singular points satisfy the relations
han<hak<ham<hcn<hck<hcm<hbn<hbk<hbm<h0n<ha0<h0k<h0m<hc0<hb0<h00,and the phase portrait is displayed by Fig.1(15).
(21)When1.31853 < k < 1.88784,the Hamiltonians of the singular points satisfy one of the following relations
han<hak<ham≤hcn<hck<hbn<hbk<hcm<hbm<h0n<h0k<h0m<ha0<hc0<hb0<h00,
han<hak<hcn<ham≤hck<hbn<hbk<hcm<hbm<h0n<h0k<h0m<ha0<hc0<hb0<h00,
han<hak<hcn<hck<ham<hbn<hbk<hcm<hbm<h0n<h0k<h0m<ha0<hc0<hb0<h00,where ham=hcnas k=1.76678,ham=hckas k=1.83353,and the phase portrait is displayed by Fig.1(21).
(22)When k=1.88784,the Hamiltonians of the singular points satisfy the relations
han<hak<hcn<hck<ham=hbn<hbk<hcm<hbm<h0n<h0k<h0m<ha0<hc0<hb0<h00,and the phase portrait is displayed by Fig.1(22).
(23)When 1.88784 < k < 1.9545,the Hamiltonians of the singular points satisfy the relations
han<hak<hcn<hck<hbn<ham<hbk<hcm<hbm<h0n<h0k<h0m<ha0<hc0<hb0<h00,and the phase portrait is displayed by Fig.1(23).
(24)When k=1.9545,the Hamiltonians of the singular points satisfy the relations
han<hak<hcn<hck<hbn<ham=hbk<hcm<hbm<h0n<h0k<h0m<ha0<hc0<hb0<h00,and the phase portrait is displayed by Fig.1(24).
(25)When k > 1.9545,the Hamiltonians of the singular points satisfy the relations
han<hak<hcn<hck<hbn<hbk<ham<hcm<hbm<h0n<h0k<h0m<ha0<hc0<hb0<h00,and the phase portrait is displayed by Fig.1(25).


Fig.1(1)~(25)The phase portraits of Sy.(1)
Obviously,none of the phase portraits is alike those appeared in the papers[2-7],although the second equation of system(1)is the same as that in the paper[7].
[1]Steve Smale.Mathematical problems for the next century.Math.Intell.Vol.20,no.2,7—15,1998.
[2]Li Yanmei,Hu Zhao.Classification of Phase Portraits of Z2- Equivariant Planar Hamiltonian-Vector Field of Degree 7(Ⅰ)[J].Journal of Chuxiong Normal University,2012,27(6):1—5.
[3]Li Yanmei.Classification of Phase Portraits of Z2-Equivariant Planar Hamiltonian Vector Field of Degree 7(Ⅱ)[J].Journal of Chuxiong Normal University,2012,27(9):1—5.
[4]Li Yanmei.Classification of Phase Portraits of Z2-Equivariant Planar Hamiltonian Vector Field of Degree 7(Ⅲ)[J].Journal of Chuxiong Normal University,2013,28(9):1—4.
[5]Li Yanmei.Global Phase Portraits and Classification of Z2-Equivariant Planar Hamiltonian Vector Fields of Degree 7 with infinite singular points(Ⅰ)[J].Journal of Chuxiong Normal University,2014,29(3):1—4.
[6]Li Yanmei.Classification of Phase Portraits of Z2-Equivariant Planar Hamiltonian Vector Field of Degree 7(Ⅳ)[J].Journal of Chuxiong Normal University,2014,29(9):1—5.
[7]Li Yanmei.Classification of Phase Portraits of Z2-Equivariant Planar Hamiltonian Vector Field of Degree 7(Ⅴ)[J].Journal of Chuxiong Normal University,2015,30(6):1—6.
