母乳中有益微生物的益生作用
2015-07-22刘海燕张建伟河北联合大学公共卫生学院河北唐山063000唐山师范学院体育系河北唐山063000
刘海燕,张建伟(.河北联合大学公共卫生学院,河北唐山063000;.唐山师范学院体育系,河北唐山063000)
母乳中有益微生物的益生作用
刘海燕1,张建伟2
(1.河北联合大学公共卫生学院,河北唐山063000;2.唐山师范学院体育系,河北唐山063000)
摘要:母乳是新生儿的最佳食品。母乳提供的蛋白质、碳水化合物、脂质、矿物质和维生素的含量和比例最为适宜,能够确保婴幼儿的正确成长和发育。此外,母乳中还含有生物活性物质,具有多种益生作用,例如促进免疫系统成熟,防止感染。最近研究表明,人乳中已经成功分离出益生菌。综述了这些益生菌在动物模型和临床试验中的有益效果。促进免疫系统成熟、抗感染以及抗炎是这些益生细菌的主要健康作用。这些益生菌的成功分离,为婴儿配方奶粉中补充此类有益菌提供了科学参考,可以使婴幼儿配方奶粉更好的模拟母乳的营养和功能效果。
关键词:母乳;母乳微生物;益生菌;益生作用;婴幼儿营养
母乳是完全满足新生儿营养和免疫需要的具有复杂成分的物质。与配方奶喂养的婴儿相比,母乳喂养的婴儿各种传染病的发病率显著降低[1-2]。其抗感染作用是由于初乳和/或成熟乳中的多种生物活性物质,包括免疫球蛋白、免疫细胞、抗微生物的羧酸类物质、多胺类物质、低聚糖,溶菌酶,糖蛋白。这些生物活性物质通过单独或协同作用,来抑制病原微生物[3-4]。
最近的研究表明,母乳中存在微生物,并可以源源不断地提供共生细菌促进婴儿肠道健康[5-6]。这些细菌在降低母乳喂养婴儿传染病的发病率及严重程度方面都具有重要作用。以前就有研究表明,巴氏杀菌的奶会失去原有的抗菌活性,其也正说明了奶中存在微生物[7]。
母乳中发现的细菌,以葡萄球菌属、乳球菌属、肠球菌属和乳杆菌属的细菌最为常见[5-6](表1)。母乳中还有一些乳杆菌,如格氏乳杆菌、唾液乳杆菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌、植物乳杆菌和发酵乳杆菌。这些乳酸菌都具有潜在的益生作用(见表1),越来越引起人们的关注。
1 母乳喂养与疾病预防
在发展中国家,婴幼儿死亡的主要原因之一是感染性疾病,特别是消化道和呼吸道感染。非母乳喂养的新生儿因肺炎住院的人数是纯母乳喂养的17倍[8]。与母乳喂养的婴儿相比,不进行母乳喂养的婴儿腹泻的死亡率高出14.2倍[9]。母乳喂养还可以降低由流感嗜血杆菌引起的急性中耳炎[10],尿路感染[11]和脑膜炎的发病率[12]。
除了抗感染以外,母乳还可以调控新生儿的免疫系统[13]。虽然抗炎活性尚未得到体内实验的证实,但是许多流行病学研究表明,母乳喂养可以预防新生儿感染,并且不会产生由炎性反应所致的肠道或呼吸道粘膜的明显病变[14]。这可能是由于母乳生物活性成分能很好地调控抗炎系统的结果。
与配方奶粉喂养的婴儿相比,母乳喂养的婴儿可以在接种脊髓灰质炎、破伤风和白喉后产生更为有效的抗体产生反应[15],这也是源于母乳具有免疫调节作用。
与配方奶粉喂养的新生儿相比,母乳喂养的新生儿还具有更加有益健康的肠道菌群[16],这与母乳中存在乳酸杆菌,或其他双歧化合物,如低聚糖[17]有关。乳酸杆菌和双歧杆菌可以抑制病原微生物,如金黄色葡萄球菌、鼠伤寒沙门氏菌、小肠结肠炎耶尔森菌和产气荚膜梭菌的生长[18]。这些菌竞争性的定植于幼儿的肠道内,可以防止病原体的粘附。此外,据研究表明,有益菌和有害菌对营养素的竞争作用,是抑制致病微生物生长的另一个机制[19]。
分离于健康母乳的主要微生物见表1。

表1 分离于健康妇女母乳中的重要微生物Table 1 Bacterial species generally isolated from the breast milk of healthy women
共生菌的肠道定植在维持免疫系统动态平衡上也发挥了关键作用。这些细菌可以上调Th1免疫反应,并下调Th2反应。新生儿服用特定益生菌可以减少过敏性症状的发生[20]和由Th2反应引起的炎性过程,如坏死性小肠结肠炎[21]。
2 母乳中益生菌的分离
母乳中存在细菌的记载可以追溯到若干年前,但后来被认为是取样时的污染造成的[22]。在21世纪初,欧洲2个独立的研究团队都分别证实了乳酸菌在母乳中的存在和它们的益生潜能[5-6]。Heikkila等报告指出,这些母乳中的微生物可以保护母亲和新生儿免于葡萄球菌引起的感染。之后有一系列类似的报道,Martin等[6]描述了分离于母乳的乳酸菌,即格氏乳杆菌CECT571423[23],唾液乳杆菌CECT571324[24]和发酵乳杆菌CECT571623[23]。除了这些菌株,还有其他一些商业菌株与人乳相关。其中之一是罗伊氏乳杆菌ATCC55730,宣称是母乳来源,但它的起源一直未公布。鼠李糖乳杆菌LGG,虽然最初是肠源的[25],但是芬兰人的科研团队已在母乳中发现该菌。不过,其工作重点是研究格氏乳杆菌CECT5714、唾液乳杆菌CECT5713和发酵乳杆菌CECT5714的益生作用。分离于母乳的益生菌的益生作用见表2。
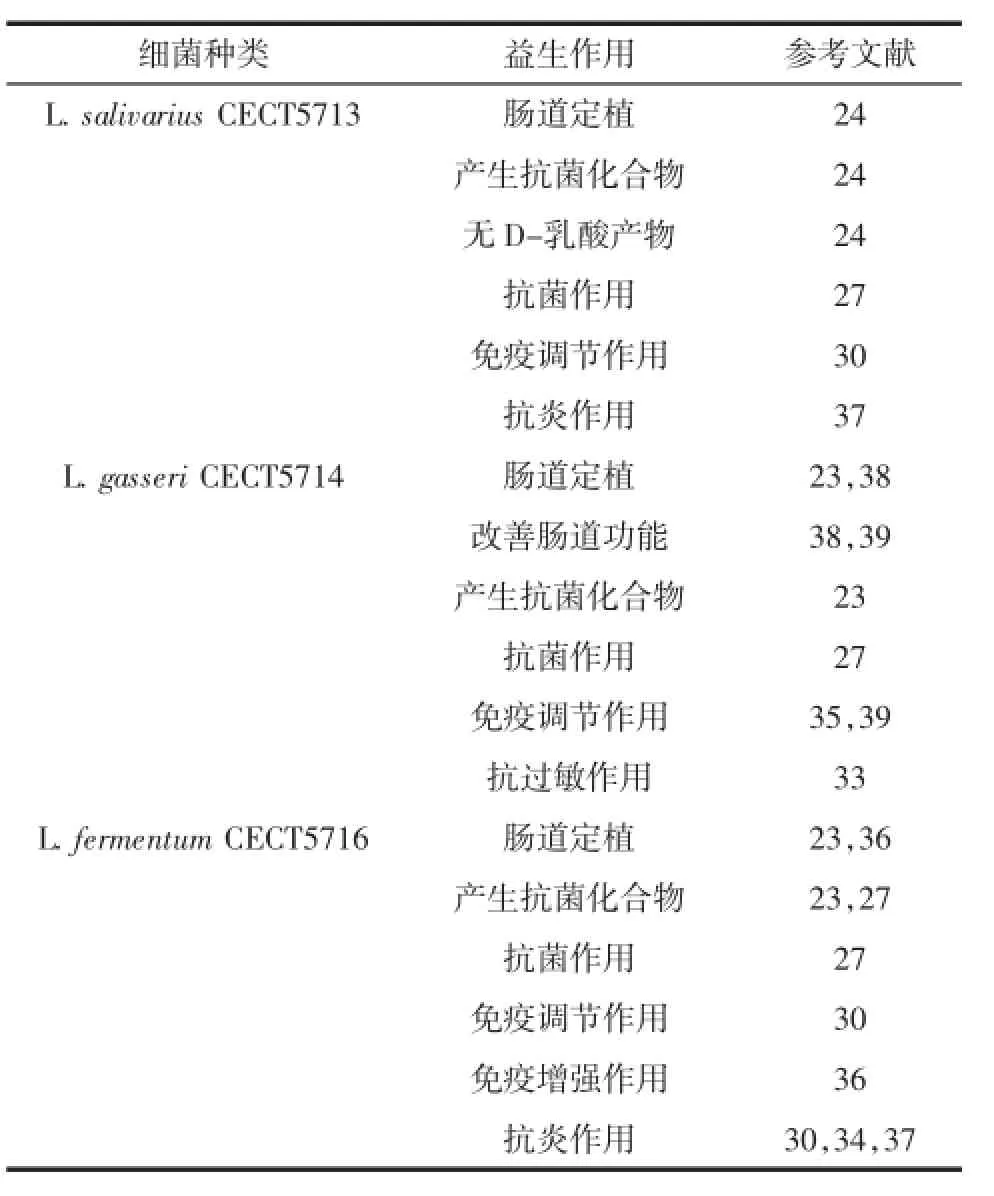
表2 分离于母乳的益生菌的益生作用Table 2 Beneficial effects of some breast milk-isolated probiotic strains
3 抗微生物作用
抗病毒或抗细菌感染是益生菌的最主要功能之一。现在有不同的机制来解释益生菌的抗微生物活性。体外研究表明,某些益生菌菌株可以产生抗微生物化合物,如有机酸、过氧化氢和/或细菌素[26]。这些抗微生物化合物可以抑制大肠杆菌、沙门氏菌和李斯特菌的生长[27]。已有研究表明有的乳酸菌可以产生过氧化氢,但是母乳中还没有发现产生细菌素的乳酸菌[23]。
此外,罗伊氏乳杆菌产生罗伊氏菌素,它是一种抗菌化合物[28]。存在于母乳中的某些细菌,可以通过增加黏蛋白的含量和减少肠道渗透性来改善肠屏障功能[27]。然而,与肠产毒细菌的营养物和上皮肠细胞的受体结合位点的竞争可能是益生菌[26-27]的的主要抗感染机制。
母乳中分离的益生菌格氏乳杆菌CECT5714,唾液乳杆菌CECT5713和发酵乳杆菌CECT5714可以抑制猪霍乱沙门氏菌粘附到粘蛋白上,并增加感染此病原菌小鼠的存活率[27]。唾液乳杆菌CECT5713的保护作用显著高于罗伊氏乳杆菌[29]。这可能是由于唾液乳杆菌CECT5713的免疫调节作用及竞争性活性共同作用的结果[30]。
多个临床试验都已表明,当不能进行母乳喂养时,婴幼儿配方奶粉中加入益生菌可以预防婴儿的传染性疾病。而大多数此类研究都涉及在婴幼儿配方奶粉中补充鼠李糖乳杆菌。因为研究表明鼠李糖乳杆菌可以降低轮状病毒感染的发病率,并可以缩短腹泻的持续时间[31]。自2000年以来,正在开展对母乳中其他细菌菌株的耐受性和有效性的评估研究,这类细菌包括罗伊氏乳杆菌ATCC55730和唾液乳CECT5713。
4 免疫调节特性
肠道定植通常是新生儿首次接触微生物的结果,这对新生儿的免疫系统的发展是至关重要的。据报道,肠道菌群的组成差异可以影响某些具有重要免疫特征的疾病的发病率,如过敏性或炎性过程[32]。益生菌的抗过敏作用,可以用Th1/Th2平衡理论进行解释,即益生菌诱导Th1反应,进而下调负责过敏反应的Th2细胞因子的数量。
与此相反,益生菌的抗炎作用目前很难解释。一些体外研究表明,益生菌的免疫调节作用依赖于细胞环境。因此,在没有额外刺激的情况下,母乳益生菌唾液乳杆菌CECT5713和发酵乳杆菌CECT5716可以促进TH1细胞因子如IL-2、IL-12及炎症介质TNF-a的产生。然而,当脂多糖及益生菌同时存在时,所培养的Th1细胞因子会减少[30]。这个调控机制可能是基于产生免疫抑制的细胞因子IL-10。有报道表明,这些益生菌可以提高该细胞因子含量[30]。
益生菌的免疫调节作用在涉及免疫系统疾病的病理学动物模型研究中也有报道。从母乳中分离的不同益生菌菌株可以提高小鼠的免疫防御,增加天然和获得性免疫[30]。这种免疫刺激活性可以参与抗感染作用。另外,母乳益生菌格氏乳杆菌CECT5714与棒状乳杆菌CECT5711联合作用,可以降低对牛奶蛋白过敏的动物模型过敏性反应的发生率和严重性[33]。最近的研究表明,发酵乳杆菌CECT5716对肠道炎症的动物模型表现出有益的作用,可以减轻炎症反应和肠道损伤[34]。
有报道表明,益生菌可以调控人的免疫应答反应。健康成人每日服用分离于母乳的益生菌,3个月后自然杀伤细胞的数量、吞噬活性和血浆IgA的浓度都增加[35]。最近有研究表明,发酵乳杆菌CECT5716可以提高26岁~40岁健康受试者对流感疫苗的敏感性,并减少流感样疾病的发病率[36]。
此外,很多报道都表明了益生菌在过敏性过程中发挥着积极作用。从这个意义上说,存在于人乳中的益生菌,尤其是鼠李糖乳杆菌LGG,可以降低儿童过敏性皮炎的发病率和严重程度[20]。也有研究数据表明格氏乳杆菌CECT5714对成人呼吸系统过敏症具有积极作用[33]。
5 对胃肠道的保护作用
越来越多的人关注通过调控肠道微生物来达到改善胃肠功能和营养吸收的目的。许多报道都显示,人乳益生菌可以定植于肠道,增加粪便中乳酸杆菌的数量,从而调整啮齿类动物[37]及人类的肠道菌群[38]。此外,通过分子生物学手段研究显示,这些细菌在人类肠道中具有代谢活性,可以增加功能性代谢物,如丁酸盐[38]的含量。丁酸盐是主要的能量来源,在调节肠道功能中发挥重要作用。之前的临床试验表明[38],粪便中的水分、大便次数及大便体积的增加,与粪便中丁酸盐的浓度增加成正相关。
同样,临床试验也表明,服用格氏乳杆菌CECT5714可使[3-12]儿童粪便乳酸菌数量增加。同一研究显示,对于服用益生菌的儿童来说,粪便的细胞毒比对照组儿童低[39]。另一项临床试验表明,含鼠李糖乳杆菌LGG的婴幼儿配方奶粉可以促进新生儿的生长发育,提高婴儿对营养的生物利用率[40]。
6 结论
研究显示,母乳喂养是新生儿肠道定植的主要决定因素。除了对胃肠道的有益作用外,通过益生菌调节微生物菌群,近而可调控免疫功能,提高对肠道病原体的抵抗能力。因此,在婴幼儿配方奶粉中添加母乳益生菌,可达到在某种程度上模拟人乳对儿童的功效,提高婴幼儿的健康。
参考文献:
[1]Lopez-Alarcon M,Villalpando S,Fajardo A.Breastfeeding lowers the frequency and duration of acute respiratory infection and diarrhea in infants under six months of age[J].Nutr,1997,127(3):436-443
[2]Wright AL,Bauer M,Naylor A,et al.Increasing breastfeeding rates to reduce infant illness at the community level[J].Pediatrics,1998, 101(5):837-844
[3]Boehm G,Borte M,Bellsted K,et al.Protein quality of human milk fortifier in low birth weight infants:effects on growth and plasm amino acid profiles[J].Eur J Pediatr 1993,152(12):1036-1039
[4]Isaacs CE.Human milk inactivates pathogen individually,additively and synergistically[J].Nutr,2005,135(5):1286-1288
[5]Hekkila¨MP,Saris PEJ.Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus by the commensal bacteria of human milk[J].Appl Microbiol,2003,95(3): 471-478
[6]Martin R,Langa S,Reviriego C,et al.Human milk is a source of lactic acid bacteria for the infant gut[J].Pediatr,2003,143(6):754-758
[7]Ford JE,Law BA,Marshall VME,et al.Influence of the heat treatment of human milk on some of its protective constituents[J].Pediatr,1977,90(1):29-35
[8]Cesar JA,Victoria CG,Barros FC,et al.Impact of breast feeding on admission for pneumonia in postneonatal period in Brazil:nested case-control study[J].BMJ,1999,318(5):1316-1320
[9]Victoria CG,Smiyh PG,Vaughan JP,et al.Evidence for protection by breast-feeding against infant deaths from infectious diseases in Brazil[J].Lancet II,1987,330(8554):319-322
[10]Duncan B,Ey J,Holberg CJ,et al.Exclusive breast-feeding for at least 4 months protects against otitis media[J].Pediatrics,1994,91 (5):867-871
[11]Pisacane A,Graziano L,Mazzarella G,et al.Breast-feeding and urinary tract infections[J].Pediatr,1992,120(1):331-332
[12]Silfverdal AS,Olcen P.Protective effect of breastfeeding:an ecologic study of Haemophilus influenzae meningitis and breastfeeding in a Swedish population[J].Int J Epidemiol,1999,28(1):152-156
[13]Grazioso CF,Werner AL,Alling DW,et al.Antiinflammatory effects of human milk on chemically induced colitis in rats[J].Pediatr Res, 1997,42(5):639-643
[14]Garofalo RP,Goldman AP.Expression of functional immunomodulatory and antiinflammatory factors in human milk[J].Clin Perinatol, 1999,26(2):361-367
[15]Hahn-Zoric M,Fulconis F,Minoli L,et al.Antibody response to parenteral and oral vaccines are impaired by conventional and low protein formulas as compared to breast-feeding[J].Acta Paediatr Scand,1990,79(12):1137-1142
[16]Harmsen HJM,Wildeboer-Veloo ACM,Raangs GC,et al.Analysis of intestinal flora development in breast-fed infants by using molecular identification and detection methods[J].Pediatr Gstroenterol Nutr,2000,30(1):61-67
[17]Kunz C,Rudloff S.Biological functions of oligosaccharides in human milk[J].Acta Paediatr,1993,82(12):903-912
[18]Gilliland SE,Speck ML.Antagonistic action of lactobacillus acidophilus toward intestinal and food borne pathogens in associative cultures[J].Food Prot,1977(4):820-823
[19]Conway PL.Selection criteria for probiotic microorganisms[J].Asia pacific J Clin Nutr,1996,5(1):10-14
[20]Kalliomaki M,Salminen S,Arvilommi H,et al.Probiotics in primary prevention of atopic disease:a randomized placebo-controlled trial [J].Lancet,2001,357(9262):1076-1079
[21]Hoyos AB.Reduced incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis associated with enteral administration of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium infantis to neonates in an intensive care unit[J].Int J Infect Dis,1999,3(4):197-202
[22]Gavin A,Ostovr K.Microbiological characterization of human milk [J].J Food Prot,1977(3):614-616
[23]Martin R,Olivares M,Marin ML,et al.Probiotic potential of 3 lactobacilli strains isolated from breast milk[J].Hum Lact,2005,21(1): 8-17
[24]Martin R,Jimenez E,Olivares M,et al.Lactobacillus salivarius CECT5713,a potential probiotic strain isolated from infant feces and breast milk of a mother-child pair[J].Int J Microbiol,2006,112 (1):35-43
[25]Conway PL,Gorbach SL,Goldin BR.Survival of lactic acid bacteria in the human stomach and adhesion to intestinal cells[J].J Dairy Sci,1987,70(1):1-12
[26]Fons M,Gomez A,Karjalainen T.Mechanisms of colonization and colonization resistance of the digestive tract[J].Microb Ecol Health Dis,2000,12(2):240-246
[27]Olivares M,Diaz-Ropero MP,Martin R,et al.Antimicrobial potential of four lactobacillus strains isolated from breast milk[J].J Appl Microbiol,2006,101(1):72-79
[28]Talarico TL,Dobrogosz WJ.Chemical characterization of an antimicrobial substance produced by Lactobacillus reuteri[J].Antimicrob Agents Chemother,1989,33(5):674-679
[29]Martin R,Olivares M,Marin ML,et al.Characterization of a reuterin-producing Lactobcillus coryniformis strain isolated from a goat’s milk cheese[J].Int J Food Microbiol,2005,104(3):267-277
[30]Diaz-Ropero MP,Martin R,Sierra S,et al.Two Lactobacillus strains,isolated from breast milk,differently modulate the immune response[J].J Appl Microbiol,2006,102(2):337-343
[31]Senok AC,Ismaeel AY,Botta GA.Probiotics:facts and myths[J]. Clin Microb Infect,2005,11(12):958-966
[32]Bjo¨rksten B,Naaber P,Sepp E,et al.The gut microflora in allergic Estonian and sweedish 2-year-old children[J].Clin Exp Allergy, 1999,29(3):342-346
[33]Olivares M,Dl'az-Ropero MP,Lara-Villoslada F,et al.Effectiveness of probiotics in allergy:child’s game or adult affair[J].Nutr foods,2005(4):59-64
[34]Peran L,Sierra S,Comalada M,et al.A comparative study of the preventative effects exerted by two probiotics,Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus fermentum,in the trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid model of rat colitis[J].Br J Nutr,2007,97(1):96-103
[35]Olivares M,Diaz-Ropero MP,Gomez N,et al.The consumption of two new probiotic strains,Lactobacillus gasseri CECT5714 and Lactobacillus coryniformis CECT5711,boost the immune system of healthy adults[J].Int Microbiol,2006,91(1):47-52
[36]Olivares M,Dl'az-Ropero MP,Sierra S,et al.Oral intake of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 enhances the effect of influenza vaccination[J].Nutrition,2007,23(3):254-260
[37]Peran L,Camuesco D,Comalada M,et al.Preventative effects of a probiotic,Lactobacillus salivarius ssp salivarius,in the TNBS model of rat colitis[J].World J Gastroenterol,2005,11(33):5185-5192
[38]Olivares M,Dl'az-Ropero MP,Gomez N,et al.Oral administration of two probiotic strains,Lactobacillus gasseri CECT5714 and Lactobacillus coryniformis CECT5711,enhances the intestinal function of healthy adults[J].In J Microbiol,2006,107(2):104-111
[39]Lara-Villoslada F,Sierra S,Boza J,et al.Beneficial effects of consumption of a dairy product containing two probiotic strains,LactobacilluscoryniformisCECT5711andLactobacillusgasseri CECT5714ninhealthychildren[J].NutrHosp,2007,4(22):496-502
[40]Vendt N,Gru¨nberg H,Tuure T,et al.Growth during the first 6 months of life in infants using formula enriched with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG:doble-blind,randomized trial[J].J Hum Nutr Dietet, 2006,19(1):51-58
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2015.20.049
收稿日期:2015-06-09
基金项目:河北省教育厅项目(ZD2015122);河北省自然科学基金项目(C2015209288);唐山市应用基础研究计划项目(14130254B);河北联合大学培育基金项目(SP201309,GP201524)
作者简介:刘海燕(1977—),女(汉),讲师,博士研究生,研究方向:食品营养与安全。
Beneficial Effects of Probiotic Bacteria Isolated from Breast Milk
LIU Hai-yan1,ZHANG Jian-wei2
(1.School of Public Health,North China University of Science and Technology,Tangshan 063000,Hebei,China;2.Department of Physical Education,Tangshan Normal University,Tangshan 063000,Hebei,China)
Abstract:Breast milk is the best food for the neonate because it provides a unique combination of proteins,carbohydrates,lipids,minerals and vitamins that ensures the correct growth and development of the infant.In addition,it also contains bioactive compounds responsible for a wide range of beneficial effects such as the promotion of immune system maturation and the protection against infections.Among these bioactive agents,probiotic bacteria have been recently isolated from human milk.The present work reviews the beneficial effects of these bacteria both in animal models and in clinical trials.The promotion of immune system maturation and defence against infections as well as the anti-inflammatory properties are among the main healthy effects of these bacteria.The isolation of probiotic bacteria with beneficial effects for the host provides scientific support for the supplementation of infant formula with these bacteria,in order to advance the pursuit of the main goal of formula:to mimic breast milk and its functional effects as closely as possible.
Key words:human milk;human milk bacteria;probiotics;probiotic effect;infant nutrition
