肱骨近端锁定内固定系统治疗肱骨近端骨折中肱骨头螺钉分布分析
2015-06-24周靖黄伟林维成王天兵
周靖 黄伟 林维成 王天兵
·论著·
肱骨近端锁定内固定系统治疗肱骨近端骨折中肱骨头螺钉分布分析
周靖 黄伟 林维成 王天兵
目的 分析肱骨近端锁定内固定系统(proximal humerus internal locking system,PHILOS)中肱骨头螺钉的分布。讨论该固定系统应用中存在的不足。方法 2007年12月至2014年8月,接受PHILOS治疗的41例肱骨近端骨折患者,其中男性15例,女性26例,平均年龄67.7岁(42~89岁)。进行术前健侧肩关节CT测量。测量指标为肱骨头螺钉的理想中心分布线(标记为a)与实际中心分布线(标记为a′)的夹角α。计算其范围及平均值。结果 a′线与冠状面的夹角均小于a线与冠状面的夹角,即a线比a′线更远离冠状面。a线与a′线的夹角α范围为0°~54.3°,平均为20.8°。结论 PHILOS治疗肱骨近端骨折时,螺钉在肱骨头内的分布是整体偏向前方,存在固定螺钉在肱骨头内分布不均匀的现象,有进一步改良空间。
肱骨骨折,近端;锁定内固定系统;螺钉
肱骨近端骨折较为常见,属关节周围骨折,治疗上有一定特殊性。随着老龄化社会的加剧,骨质疏松人群逐渐增多,骨质疏松性骨折已逐渐成为创伤骨科临床治疗中面临的重要问题,如何在骨质疏松性骨折中增加固定的稳定性,确保骨折能够在固定稳定的前提下达到骨性愈合,已成为创伤骨科医师的难题。肱骨近端骨折也属于此类骨折,肱骨近端锁定内固定系统(proximal humerus internal locking system,PHILOS)因其锁定螺钉的成角稳定性及肱骨头内多个方向螺钉的组合排列,增加了固定的稳定性,因而广泛应用于临床。本文就PHILOS治疗肱骨近端骨折患者中肱骨头螺钉的分布进行研究分析。
资 料 与 方 法
一、一般资料
选取病例标准:(1)肱骨近端骨折;(2)术前进行肩关节CT检查;(3)接受PHILOS手术治疗。2007年12月至2014年8月符合上述标准的病例41例,其中男性15例,女性26例,平均年龄67.7岁(42~89岁),均为新鲜骨折。
二、治疗方法
所有患者术前均进行肩关节CT检查。麻醉方式为全身麻醉,手术体位为沙滩椅位,切口选择三角肌胸大肌入路,内固定装置选择辛迪思公司PHILOS。
三、数据测量
选取健侧肩关节CT横断面作为测量资料,测量指标为肱骨头螺钉的理想中心分布线(标记为a)与实际中心分布线(标记为a′)的夹角α。a线即肱骨头的垂直线,a′线即PHILOS板的垂直线,考虑到PHILOS板常规放置于大结节处,a′线也就是大结节的垂直线。于每个病例健侧肩关节CT横断面标记上述两线,并测量其夹角。
四、统计方法
统计各病例的夹角α范围,并计算平均值。
结 果
定义身体冠状面为基准线,在所有病例的健侧肩关节CT横断面上观察到,a′线与冠状面的夹角均小于a线与冠状面的夹角,即a线比a′线更远离冠状面。a线与a′线的夹角α范围为0°~54.3°,平均值为20.8°(图1)。
讨 论
肱骨近端骨折属于常见骨折之一,临床上约占所有骨折的5%[1]。据北京大学人民医院创伤骨科姜保国教授领衔开展的“十一五”国家科技支撑计划课题报道,共在全国5所大学的附属医院收集到有完整随访资料的关节周围骨折患者2 338例,其中肱骨近端骨折315例,占13.5%。其在发病年龄上有两个高峰:一个是30岁左右,此类患者骨折多为高能量损伤,常常合并有其他类型的骨折或脏器损伤;另外一个年龄高峰是60岁以上,尤以老年女性为多[2]。本组病例女性占63.4%(26/41),平均年龄67.7岁。而老年女性是骨质疏松的好发人群,本身肱骨近端位于长骨干骺端,因此这一区域的骨折常为骨质疏松性骨折,对于骨折固定的稳定性上提出了更高的要求。近年来随着PHILOS在临床上的广泛使用,很多研究都报道了良好的临床效果,但不可否认的是仍然存在固定松动导致退钉、断钉等并发症[3-7]。因此如何进一步提高内固定系统的稳定性是摆在创伤骨科医师面前的一个重要问题。
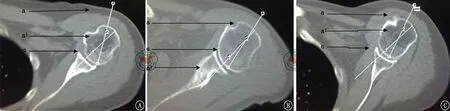
图1 术前健侧肩关节CT横断面。A、B、C图分别示肱骨头螺钉的理想中心分布线a线、肱骨头螺钉的实际中心分布线a′线及二者之间的夹角α
PHILOS采用了锁定接骨板的原理,锁定螺钉可提供成角稳定性,多组螺钉呈不同角度置入肱骨头内,起到内固定支架的作用,从而增加了固定的稳定性,为肱骨近端骨质疏松性骨折的固定提供了一种良好的方法[8-9]。但不可忽视的是,肱骨头骨质属于松质骨,把持螺钉的能力有限,为了增强螺钉固定的整体稳定性,理想的肱骨头内螺钉的分布应是以肱骨头轴心线为中心而分布于其周围,从而起到稳定维持复位、避免肱骨头前后倾、内外翻等并发症存在。因此内固定系统的肱骨头螺钉中心分布线应与肱骨头的轴心线相重合。而PHILOS的肱骨头螺钉中心分布线是与接骨板相垂直的,因此接骨板的放置位置在一定程度上决定了其肱骨头螺钉的中心分布线。鉴于PHILOS常规放置于结节间沟后缘0.5~1.0 cm处[10-11],即覆盖于大结节处,因此其肱骨头螺钉的中心分布线应大致与大结节相垂直。而事实上,人体在进化发育过程中,随着上肢从负重中的解放,肱骨头存在着一个相对于颈干部的生理性后倾角度,因此PHILOS的肱骨头螺钉中心分布线可能并不与理想的肱骨头轴心线相重合。根据笔者的测量结果可以看到,41例患者中,肱骨头螺钉的理想中心分布线a线(即肱骨头的轴心线或垂直线)与实际中心分布线a′线(即PHILOS板的垂直线或大结节的的垂线)只在一个病例中是重合的,而在其他40例病例中,两线并不重合,都呈一夹角α(图1)。这表明事实上PHILOS的肱骨头螺钉并不是在肱骨头内呈中心分布,而是整体偏向前方或后方。在本组病例中其偏离角度为0°~54.3°,平均为20.8°。再结合测量结果a线比a′线更远离冠状面,表明实际上肱骨头螺钉是整体偏向前方的(图2),这一结果可以用肱骨头生理性后倾进行理解。PHILOS板基于放置位置的限制,已不能再向前侧放置,这样会干扰结节间沟内的结构。因此其肱骨头螺钉的整体偏前方置入难以通过改变接骨板的放置位置来进行调整,而偏离中心分布的肱骨头螺钉势必会影响螺钉的置入深度,对复位的维持、固定的稳定性、螺钉穿入关节面等方面带来一定的影响。因此临床中在使用PHILOS板时应充分考虑到这一因素,在置入螺钉时应多方向X线投照,避免螺钉穿入关节面。同时如何在设计上调整PHILOS是一个需要临床考虑的问题。多向锁定螺钉的引入可以为PHILOS的改进提供一些思考,而多向甚至万向锁定螺钉的使用已在桡骨远端骨折等部位得到了实现。
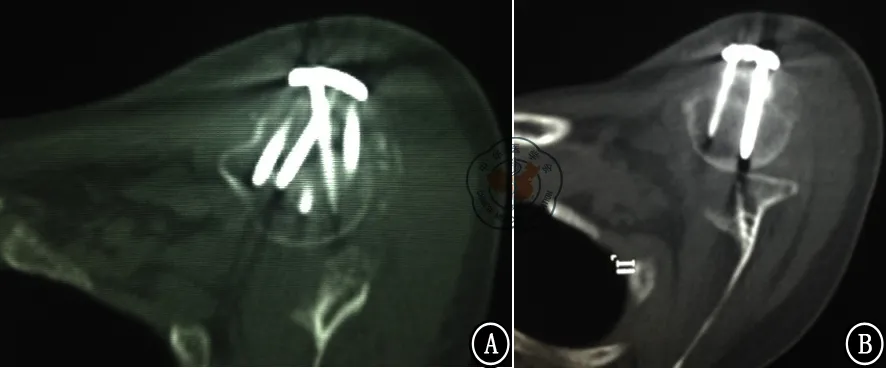
图2 术后患侧肩关节CT横断面。A、B图示术后螺钉在肱骨头的分布总体偏向前方
本组病例属于回顾性临床研究,限于样本量的大小,可能在结果上存在一些偏倚。需要大样本的回顾性研究结合尸体标本研究来进一步支持。以期达到完善肱骨近端骨折固定方法,解决固定方面问题的目的。
[1] Kristiansen B,Barfod G,Bredesen J,et al.Epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures[J].Acta Orthop Scand,1987,58(1):75-77.
[2] 姜保国,陈建海.肱骨近端骨折的治疗[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2012,44(6):821-823.
[3] Südkamp N,Bayer J,Hepp P,et al.Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with use of the locking proximal humerus plate.Results of a prospective,multicenter,observational study[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2009,91(6):1320-1328.
[4] 付中国,邓磊,白露,等.肱骨近端骨折锁定接骨板治疗术后并发症分析[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2011,43(5):666-670.
[5] Sproul RC,Iyengar JJ,Devcic Z,et al.A systematic review of locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures[J].Injury,2011,42(4):408-413.
[6] Kumar GN,Sharma G,Sharma V,et al.Surgical treatment of proximal humerus fractures using PHILOS plate[J].Chin J Traumatol,2014,17(5):279-284.
[8] Königshausen M,Kübler L,Godry H,et al.Clinical outcome and complications using a polyaxial locking plate in the treatment of displaced proximal humerus fractures.A reliable system?[J].Injury,2012,43(2):223-231.
[9] Barco R,Barrientos I,Encinas C,et al.Minimally invasive poly-axial screw plating for three-part fractures of the proximal humerus[J].Injury,2012,43(Suppl 2):S7-S11.
[10] 黄磊,李广旭,李波,等.PHILOS锁定加压接骨板与肱骨近端锁定加压接骨板治疗肱骨近端骨折[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(52):9861-9864.
[11] 蔡俊丰,李旭,刘林,等.肱骨近端骨折内固定相关应用解剖学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2011,29(3):268-271.
(本文编辑:李静)
周靖,黄伟,林维成,等.肱骨近端锁定内固定系统治疗肱骨近端骨折中肱骨头螺钉分布分析[J/CD].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2015,3(2):81-84.
Analysis of Screw Distribution in the Humerus Head in Proximal Humerus Fracture Treated with Proximal Humerus Internal Fixation Locking System
ZhouJing,HuangWei,LinWeicheng,WangTianbing.
DepartmentofTraumaandOrthopedics,PekingUniversityPeople′sHospital,PekingUniversityTrafficMedicineCenter,Beijing100044,China
WangTianbing,Email:wangtianbing@medmail.com.cn
Background Proximal humerus fracture is one of the fractures that easily occur in human body.It is a fracture around joints so there are specific treatment ways.As the aggravation of aging society,the osteoporosis population is getting larger.Osteoporosis has become an important issue in the traumatic orthopedics treatment.How to increase the stability of fixation in osteoporosis fracture and how to make sure stability of the bony union in fracture are becoming challenges for traumatic orthopedists.Proximal humerus fracture is one kind of osteoporosis fractures.Proximal Humerus Internal Locking System (PHILOS) has a stable angulation of screws locking as well as assembly of multi-directions of screws inside the humerus heads.These characteristics increase the stability of fixation and lead to the wide clinical application.This research analyze the humerus head screws distribution in proximal humerus fracture treated by PHILOS.Methods General data:inclusion criteria of cases:(1) proximal humerus fracture; (2) CT on the shoulder joints before operation;(3) accept the PHILOS operation.From December 2007 to August 2014,41 patients who reached the above-mentioned criteria were selected as the study subjectives.They were patients with fresh fractures and 15 were males and 26 were females.And their average age was 67.7 years old (from 42-89 years old).All patients should have CT of the shoulder joints before the operation.They will get general anesthesia and the operation position is beach chair position.The incision will be performed from the deltopectoral approach.PHILOS from Synthes is selected as the internal fixation device.Date measurements:The contralateral shoulder joint cross section on the CT was selected as the measurement data.The measurement index was the included angle α between the ideal center distribution lines in the humeus head screws (mark as "a") and the real center distribution line (mark as "a′").Line a is the perpendicular line of humerus head,line a′ is the perpendicular line of PHILOS board.And given that the PHILOS plate usually is placed on the greater tuberosity,line a′ is also the perpendicular line of the greater tuberosity.Each contralateral shoulder joint cross section on the CT is marked with the above-mentioned two lines,and their included angle is measured.Statistical method:The included angle α in each case was set and the average value was calculated.Results The body coronal plane was defined as the datum line which can be observed in the contralateral shoulder joint cross section on the CT.The included angle between line a′ and the coronary plane were all smaller than the included angle between line a and the coronary plane.Namely,line a is further away to the coronary plane than line a′.The included angle α between line a and line a′ was from 0°to 54.3°,and the average value was 20.8°.Conclusion When PHILOS treating proximal humeral fracture,the distribution of screws inside the humerus head overall toward the front side,and the distribution of fixed screws inside the humerus head is uneven,which needs to be improved.
Humerus fracture,proximal;Internal locking system;Screw
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2015.02.003
国家自然科学基金资助(31371210);教育部创新团队资助(IRT1201);卫生公益性行业科研专项资助(201002014)
100044北京大学人民医院创伤骨科 北京大学交通医学中心
王天兵,Email:wangtianbing@medmail.com.cn
2014-04-08)
