Detection and Analysis on Outlier of the Average Medical Expense in China
2015-05-15YANGYangZHANGFangXIANGRongwu
YANG Yang,ZHANG Fang,XIANG Rong-wu
(School of Business Administration, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, China)
Detection and Analysis on Outlier of the Average Medical Expense in China
YANG Yang,ZHANG Fang*,XIANG Rong-wu
(School of Business Administration, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, China)
Objective To analyze 4 outlier detection methods so as to select a relatively simple and accurate one,thus to provide a reference for predicting the tendency of average medical expense in China. Methods Comparison,Dixon’s test,Hampel’s test and Grubb’s methods were used. Results and Conclusion Dixon’s and Hampel’s test methods are more convenient than T test and Grubb’s methods but they have poor sensitivity. There are many factors affecting medical expense per capita trend in China,such as the aging population and the financial crisis.
average medical expense; outlier; Grubb’s; Hampel’s; Dixon’s; T test
Since the reform and opening up,China’s economy has made remarkable achievements and national per capita income has steadily increased. China’s medical and health services have also made significant progress which improve residents’ quality of life. But the rapid growth of medical costs increases the economical burden on residents. Medical costs are related to the vital interests of the governments and people’s livelihood. The reasons that lead to the rising medical costs have become the focus of governments,health professionals,economic theorists and even ordinary people. The trend of medical costs is rising year by year,but due to the financial crisis,wealth gap and regional differences,the rise in China’s per capita health care costs may have specificity in some year,but the regularity is not significant. In addition,China’s per capita health care costs rose in the past 2 years. In this context,we made the reason by detecting the outliers of China’s per capita health care costs in recent years.
1 Material and methods
A retrospective survey of the utilization of itraconazole injection in a hospital from 2008 to 2012 was carried out. The data covered the following aspects: the patients’ name,age,and gender; admission departments,discharge diagnosis; the course of treatments,names of disease,dosage and administration,sequential therapy and combined drugs of itraconazole injection; fungal culture results,fungal infection diagnosis; liver and kidney function,adverse reactions. A total of 159 cases of hospitalized patients who used itraconazole injection and 152 copies of medical records were obtained ultimately. Ninety-seven patients were males,and 55 were females. The age ranged from 7 to 85 years old,and the average age was (58.10 ± 15.60). Capita health care costs in recent years. Outlier detection is a primary step in many datamining applications. In the process of data analysis,we find that the data often contain some sample data,and their models are different from most of other data. These data objects are called outliers. These outlier data may lead to the deviation of the data analysis results or errors. But from another perspective,these outliers may also associate with some small probability events. The outliers may contain more important information. Therefore,the detection of outliers has a very important significance to us. There are many different methods in outlier detection. Comparing the different outlier detection methods has also became a hot topic in domestic academic research. This study selected Dixon’s,T test,Grubb’s and Hampel’s test to detect relevant statistics and determined the outliers of China’s per capita health care costs from 1990 to 2013. Then we compared theresults to select a relatively reasonable detection method that could help us improve the accuracy.
2 Statistics
China Health Statistics Yearbook[1]has a detailed statistical interception to China’s per capita health care costs. We chose China’s per capita health care costs from 1990 to 2013 for research,the specific data writen in Table 1.
As can be seen from the table,China’s per capita health care costs shows a rising trend year by year in nearly 2 decades,but the regularity is not significant and the magnitude of rise is not fixed. Therefore,there is a need for us to have a simple data processing and trend prediction. First we take 3 methods of outlier detection to analyze per capita health care costs.
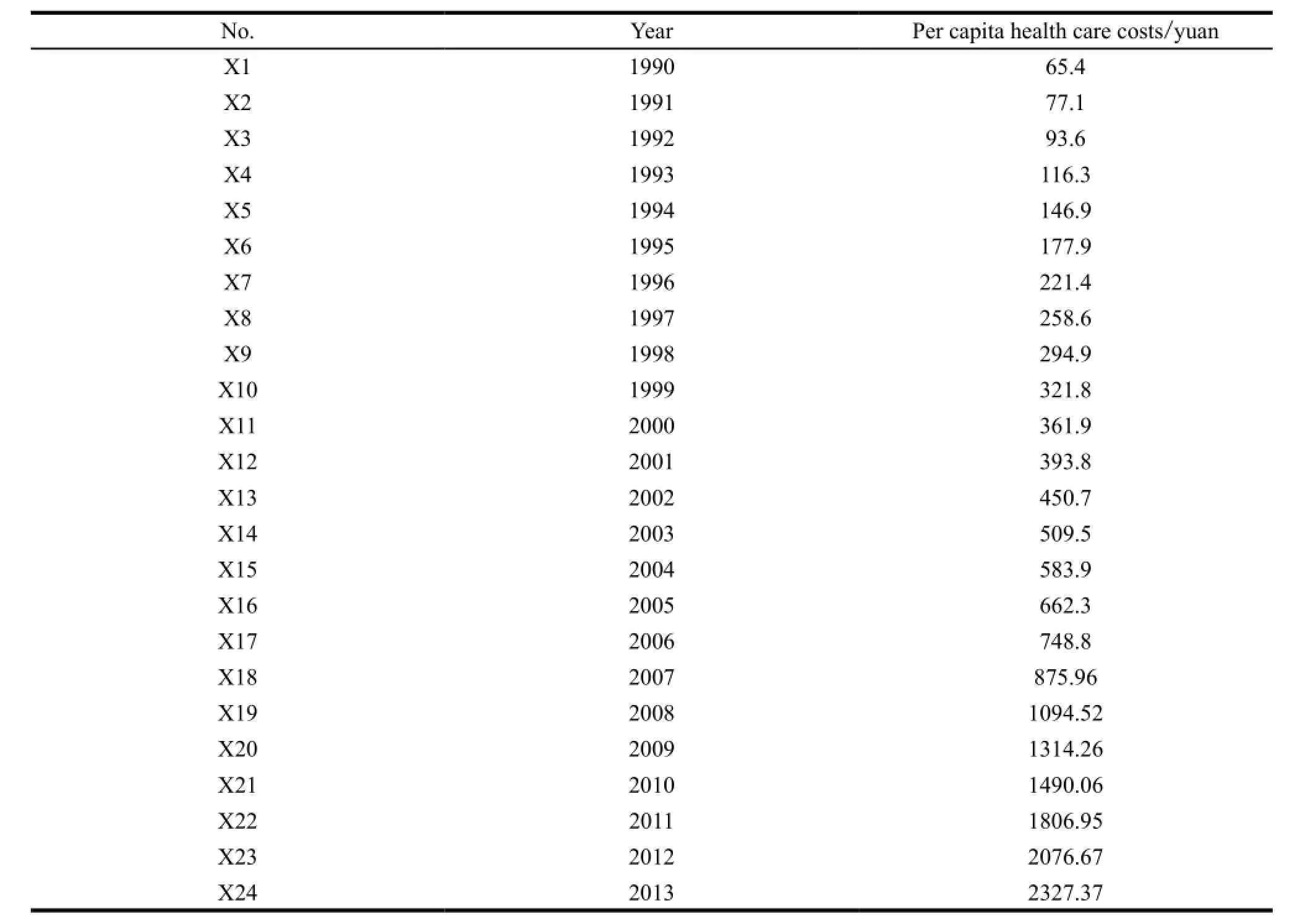
Table 1 Per capital health care costs from 1990 to 2013
3 Comparison of outlier-test procedures
3.1 The outlier tests of Grubb’s
Grubb’s detection is named after its author—Frank Guerra. Grubb’s detection[2,3]is based on a normal distribution of the test. This detection method may be used only for small sample data. As long as the abnormal value is detected,we can use this detection method. Grubb’s detection can be used to measure the mean value of multiple sets of data. In this test,we have 2 kinds of assumptions: the null hypothesis (H0) and the hypothesis assumed to be (H1).
H0: There are no outliers in the data set;
H1: There is at least one outlier in the data set.
The procedure of Grubb’s is as follows. According to the data,we calculate the mean and standard deviation:
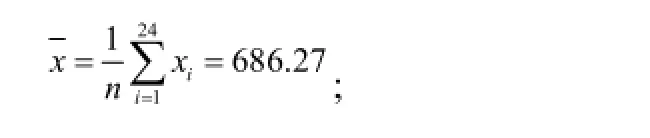


4 Test results
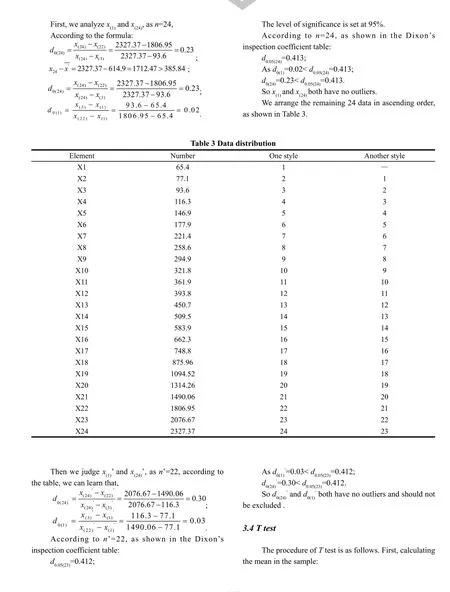
We used four outlier detection methods in this paper,and the different outlier detection sensitivity for the same set of data were different. Through the Hampel’s test and T test,we found that x(24)was the outlier and should be excluded. But the Grubb’s and Dixon’s test showed that these 24 numbers had no outliers. We used SPSS data analysis to find that x(24)was the outlier.
Same point: there are many outlier detection methods,such as Monte Carlo algorithms,data mining and so on,but all these methods require a lot of computer models to calculate. These requirements are more stringent,and they have high sensitivity. We use these four methods which only need a simple calculation and data processing. The calculation is simple,but the sensitivity is relatively lower than the computer models.
The different points are as shown in Table 4.

Table 4 Different points
5 The analysis of the reason
In this paper,we used 4 methods to detect the per capita health care costs in China. According to the result we concluded that China’s per capita health care costs showed abnormal values in 2013. This indicated that China’s per capita health care costs had a rising trend over the years. But the prices curve fluctuated in 2013. For this outlier,the increasing per capita health care costs had an important effect. We analyzed the causes briefly.
WANG Xun and LIU Guang-bin[4]used regression analysis and econometric model to analyze the impact of population aging on health care costs from towns and villages in their article named “Empirical Study of an Aging Population and Rising Health Care Costs”. According to the regression results,they concluded that income levels,mortality and aging levels were the major reasons lead to the rising health care costs. LI Lian-you and HE Pingping’s[5]study showed that the growth of China’s medical expenses was mainly affected by economic growth. There was a long-run equilibrium relationship between each other,but the short-term impact was not significant.
The international economy,market environment,domestic economy,market conditions and the degree of aging population have a inseparable effect on the outliers.
As to economic growth,health care price changeshave little effect on China’s medical expenses. From the scholars’ study in the past few years,per capita health care costs showing a rising trend each year can be roughly attributed to the rise in per capita income and enhancing the speed of aging population. In addition,people usually think the reasons of the growth in medical costs from the supply and demand aspect. In the article named “Economic Growth,Population Aging and Increasing Medical Cost”,HE ping-ping[6]found that economic growth and aging population were the main reasons lead to China’s per capita health care costs rise. In 2008,the size of pensions shrunk greatly in the world. Due to a high degree of linkage of capital market,although China’s financial markets and the world’s financial markets were not fully in line,China’s capital market had certain impact. At the end of 2007,China’s stock began to fall,which resulted in the failure of pension funds investment in the stock. As an important part of the medical expenses,pension funds have a direct impact on China’s per capita health care costs. In 2007,China’s per capita health care costs began to rise slowly. In the first half year in 2008,China was facing the risk of high inflation. In 2009,with the recovering global economy,China’s capital investment market gradually expanded,which made up the losses of China’s pension investment and the total pension also increased significantly. The curve of per capita health care costs began to rise[7].
In 2012,the outbreak of the international financial crisis had a profound impact on China’s financial and medical markets,resulting in stock market shrink and high unemployment. It also led to the decline of medical expenses. In 2013,China’s aging population reached the highest level,which affected the supply and demand of China’s medical market and the distribution of the national economy.
In the same year,China’s economy began to pick up gradually. But the investment gradually withdrew from the market. Because most people had no confidence in stock market and housing market which led to the reducing currency in circulation. All these factors can indirectly lead to the outliers of China’s per capita health care costs.
6 Conclusion
This paper adopts 4 outlier detection methods for China’s per capita health care costs. Grubbs and T-test were required to calculate standard deviation with repetitions,and they were much difficult. But their sensitivity was high. While Hampel’s and Dixon’s tests were much simple and they were conservative,but their sensitivity was low.
[1]China Statistical Yearbook [G]. 2014: 21-22.
[2]Ma,C.A. Health care payment systems: coast and quality incentive [J]. Journal of Economics and Management Strategy,1994,8 (3): 93-112.
[3]Maimon O,Rockach L. Data mining and knowledge discovery handbook: a complete guide for practitioners and researchers [M]. Norwell,Massachusetts,USA: Kluwer Academic Publishers,2005: 1.
[4]WANG Xun,LIU guang-bin. Empirical study of aging population and rising health care costs [J]. Chongqing Three Trinocular Cardiff University,2003 (6): 30-32.
[5]HE Ping-ping,LI Lian-you. Analysis of China’s medical expenses growth [J]. Statistics and Decision-making,2008 (13): 74-76.
[6]HE Ping-ping. Analysis of China’s medical cost increase factor of econometric [J]. Pacific Journal,2005 (10): 25-31.
[7]ZHAO Yu-xin. The total cost of the development of China’s health trends and influencing factors [J]. Health Economics Research,2000 (1): 24-30.
* Corresponding author: ZHANG fang,associate professor. Major research area: pharmaceutical economics. Tel: 15040165700,E-mail: xzhangf@126.com
杂志排行
亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Toxic TCM Supervision: Current Situations and Countermeasures
- WHO Prequalification of Medicines Program: Technical Assistance Effect
- Drug Registration and Approval System in China: Current Status,Controversies and Future Perspectives
- Analysis of TCM Patented Technology Based on the IPC Classification System
- A Study on the Contract Research Organization
- An Empirical Study on Model of Consumers’ Initial Trust in Online Pharmacies
