基于全变分原理的多震源混合数据直接偏移方法
2015-04-17卢昕婷韩立国张盼孙宏宇
卢昕婷, 韩立国, 张盼, 孙宏宇
吉林大学地球探测科学与技术学院, 长春 130026
基于全变分原理的多震源混合数据直接偏移方法
卢昕婷, 韩立国*, 张盼, 孙宏宇
吉林大学地球探测科学与技术学院, 长春 130026
多震源混合地震采集技术,即将多个震源以一定编码方式连续地激发,得到多炮混合的地震数据.该技术能减少地震采集时间,节约采集成本,但是混合数据的直接偏移会在成像剖面中引入严重的串扰噪声,影响成像效果.从数学上看,地震成像属于典型的数学物理反问题,可以采用线性反演方法求解一个正则化约束的最小二乘(LS)优化问题,获得更高质量的成像结果.全变分(TV)正则化方法是图像去噪和复原领域中广泛应用的热点技术,其能在去除噪声的过程中保留图像的边缘信息和不连续性.在对TV图像去噪复原方法原理分析的基础上,本文将多震源混合数据直接偏移成像问题转换成图像复原的极小化能量泛函问题,用TV正则化代替传统最小二乘偏移(LSM)中的L2范数正则化,提出基于全变分原理的混合数据直接偏移方法.该方法使用基于梯度的快速迭代收缩阈值与快速梯度投影组合算法——FISTA/FGP求解最优化问题,能有效压制串扰噪声,增强同相轴连续性,提高成像分辨率.理论模型测试结果表明:将本方法应用于混合数据,无论是去噪效果还是成像精度都得到显著改善.
多震源混合采集; 混合数据; 直接成像; 串扰噪声; 全变分
1 引言
多震源混合采集(blended acquisition)是近年来兴起的一种新型地震采集技术,该技术由Berkhout(2008)和Berkhout等(2009)在多震源同时采集技术 (simultaneous acquisition)(Silverman,1979; Beasley et al., 1998; Bagaini, 2006; Beasley, 2008)的基础上发展而来.在混合采集系统中,不同空间位置的多个震源以一定的编码方式连续激发,得到的地震记录为波场混叠的多炮混合数据.由于震源之间的激发时间间隔很小,这种采集方式极大地提高了数据的获取量和采集效率.
目前,针对混合数据的偏移成像方法可分为两类:一是直接对混合数据进行偏移成像,不做任何预处理.该方法具有较高的处理效率,但是由于波场数据相互混叠干扰,直接偏移的成像剖面上会出现串扰噪声(crosstalk),严重降低成像质量;二是先将多炮混合记录进行炮分离处理(deblending),对得到的单炮数据进行常规偏移成像.该方法处理效率较低,炮分离的效果将影响偏移成像结果.综合比较,直接偏移方法将是未来混合数据成像的主要发展方向,其研究重点在于如何有效地压制串扰噪声.
Tang和Biondi(2009)在其论文中首次提出使用最小二乘偏移(LSM)来压制混合数据直接成像的串扰噪声.LSM可以使用多种偏移算子,具有较高灵活性,同时能很好地适应混合采集技术的处理要求.以上性质使得该方法成为现阶段混合数据直接偏移的主流方法,近年来也陆续涌现出成功的应用实例(Schuster and Dai, 2010; Verschuur and Berkhout,2011; Dai et al., 2011, 2012; Huang and Schuster, 2012).
LSM属于数学上的病态问题,需要引入正则化约束来确保求解过程的稳定.传统的Tikhonov正则化(Tikhonov and Arsenin, 1977)采用光滑性约束如L2范数约束,具有良好的算法稳定性,但它对目标模型有平滑滤波效应,容易导致模型过度光滑,边缘模糊,不连续信息不能被精确重构.为了减弱这种平滑效应,提高成像质量,本文提出基于全变分(TV)(total variation)原理的TV范数约束偏移算法.
全变分(Rudin et al., 1992)是图像去噪和复原领域的研究热点技术之一,其基本原理是将图像去噪/复原问题转换成图像模型的能量泛函最小化问题.全变分原理在地震图像去噪(屈勇等,2011;公成敏,2014)、地震反演(Askan et al., 2007; Burstedde and Ghattas, 2009; 毛衡等, 2012)以及地震偏移速度模型重建(Anagaw, 2009; Anagaw and Sacchi, 2012)方面已经得到应用.地下介质大多是不规则的,并且具有明显的成层性,全变分模型采用非光滑性约束,在去噪时能够不平滑目标边界保留图像的不连续性特征.因此,为了在压制串扰噪声的同时最大限度地还原地下介质的真实信息,本文将全变分应用到多震源地震数据直接偏移成像中,建立全变分地震偏移成像模型,提出基于TV范数约束的混合数据直接偏移方法.考虑计算成本,本方法采用快速迭代收缩阈值与快速梯度投影组合算法——FISTA/FGP(Fast Iterative Shrinkage-Thresholding Algorithm/Fast Gradient Projection)(Beck and Teboulle, 2009)求解目标函数的最优化问题.理论模型的测试结果表明:TV范数约束的混合数据直接偏移能有效压制噪声,保护地震剖面的边缘信息,增强剖面的结构特征,提高成像精度.
2 混合采集与直接偏移成像
在波动方程波恩近似的条件下,地震数据d和地下反射系数m有如下线性关系:
d=Lm,
(1)
其中,L为正演模拟算子.
混合采集数据是来自多个震源的炮集叠加记录,即超级炮,这种混合过程可表示如下:
(2)
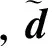
将式(1)代入式(2)中有:
(3)
(4)
同常规单炮偏移算子一致,超级炮偏移算子也可以用正演算子的伴随矩阵表示,即
(5)
(6)
将式(3)代入式(6)有:
(7)
由(7)式可以看出偏移成像相当于地下真实反射系数的模糊表示.
3 全变分多震源地震数据偏移成像
3.1 全变分偏移成像数学模型
二维地震图像的TV范数有两种表示方法:
(1)基于L2范数的各向同性扩散模型(Chambolle, 2004):
(8)
式中,n1和n2为m的维数.
(2)基于L1范数的各向异性扩散模型,即经典的ROF模型:
(9)
各向同性扩散模型在重构时会增加多余的光滑作用,模糊图像边缘;各向异性扩散模型具有良好的边缘保持特性,但是该模型可能会将噪声处理成假边缘,在平滑区出现阶梯效应.由于地震图像具有不连续性,通常表现为分段光滑的曲线或者直线奇异性,各向异性扩散模型在不同图像特征区域内扩散特性不一样,有利于保持地震图像的不连续性特征.特别说明一点,各向异性扩散模型在某种程度上可以看作特殊的L1范数稀疏约束,其本质就是图像梯度的L1范数,对于稀疏度比较高的模型,它能更好地保留解的内在稀疏性.
本文将式(9)定义的TV范数约束应用到混合数据直接偏移成像中以达到减弱串扰噪声,提高成像精度的目的.
偏移成像的TV范数约束最优化问题如下所示:
min‖m‖TV, subject toLm=d.
(10)
根据正则化理论,将上述优化问题转化为最小化成本函数J(m):
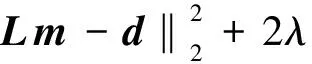
(11)
式(11)右边由两项组成:第一项为数据项,又叫保真项,反映了近似解与测量数据之间的误差,其作用是在去噪过程中保留原始图像特性,确保解的真实性;第二项为平滑项,即正则项,λ为正则化参数,用来调节数据项与平滑项的相对贡献量.在全变分模型中,λ的取值对计算结果起着十分重要的影响:λ取值越大,TV范数占的权重越大,图像去噪效果更好,但解可能会和测量数据有较大差异;若λ取值过小,会导致图像边缘比较模糊,得不到理想的去噪效果.在实际应用中,λ的选取和图像噪声水平有关.
3.2 全变分快速组合算法
本文采用Beck和Teboulle提出的快速组合算法FISTA/FGP求解式(11).该算法结合FISTA和FGP二者优点,实现简单,稳定性好,有较高的计算效率.具体操作如下.
首先考虑L=I时的特殊情况,即
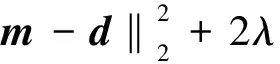
(12)
在FISTA/FGP中,FGP算法求解TV约束最优化问题的基本思路是先构造式(12)的对偶问题,然后基于梯度类方法求解.该对偶问题解的形式如式(13)所示:
m=PBl,u(d-λY(p,q)).
(13)
所需参数定义如下:
(1)Φ为矩阵对(p,q)的集合,其中p∈R(n1-1)×n2,q∈Rn1×(n2-1)且满足:
(14)
(2)Y为线性运算符,其将矩阵对(p,q)映射为一个n1×n2的矩阵:
(Y(p,q))i,j=pi,j-pi-1,j+qi,j-qi,j-1,
i=1,…,n1-1,j=1,…,n2-1,
(15)
其中p0,j≡pn1,j≡qi,0≡qi,n2≡0.
(3)PBl,u为正交投影算子:
(16)
FGP算法实现流程如下:
初始赋值:
(r1,s1)=(p0,q0)=(O(n1-1)×n2,On1×(n2-1)),t1=1. 第k步迭代:
(pk,qk)=
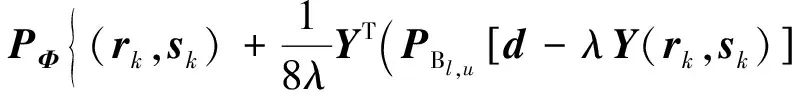
(17a)

(17c)
(17d)
经典的梯度方法中,关于式(11)的第k阶迭代优化公式为:
(18)
式中,α为迭代步长,控制收敛速度.FISTA/FGP中,确保迭代收敛需要保证α≥max eig(LHL),即α的值必须大于LHL的最大特征值.
如果定义:
(19)
(20)
对比式(20)与式(12),我们可以使用FISTA和FGP组合算法求解式(20).
FISTA的计算过程如下所示:
初始赋值:y1=m0,t1=1.
第k步迭代:
mk=DL(yk),
(21a)
(21b)
(21c)
其中,DL是算法的核心,以FGP替换DL,就成为FISTA/FGP算法.
4 理论模型测试
本文通过层状介质模型,SEG/EAGE断层模型与Marmousi模型测试方法的准确性和适应性.其中,层状模型主要测试方法的有效性,SEG/EAGE断层模型主要测试方法的抗噪性和正则化参数选择对偏移结果的影响,最后通过Marmousi模型测试方法在复杂介质条件下的适应性.
4.1 层状介质模型偏移
层状介质模型如图1所示.模型纵横向网格点数均为100,纵横向网格间距均为10 m,背景速度为2500 m·s-1.检波器和单震源个数均为100个,时间采样间隔为1 ms,震源子波为主频30 Hz的雷克子波.通过正演模拟得到100个单炮记录,使用随机时间间隔编码算子,每5个单炮合成一个混合炮(图2).数值试验中所有偏移均采用克希霍夫偏移算子,其对观测系统适应性强,对速度模型敏感度比较低.

图1 层状模型(反射系数)Fig.1 Layered model (reflectivity)
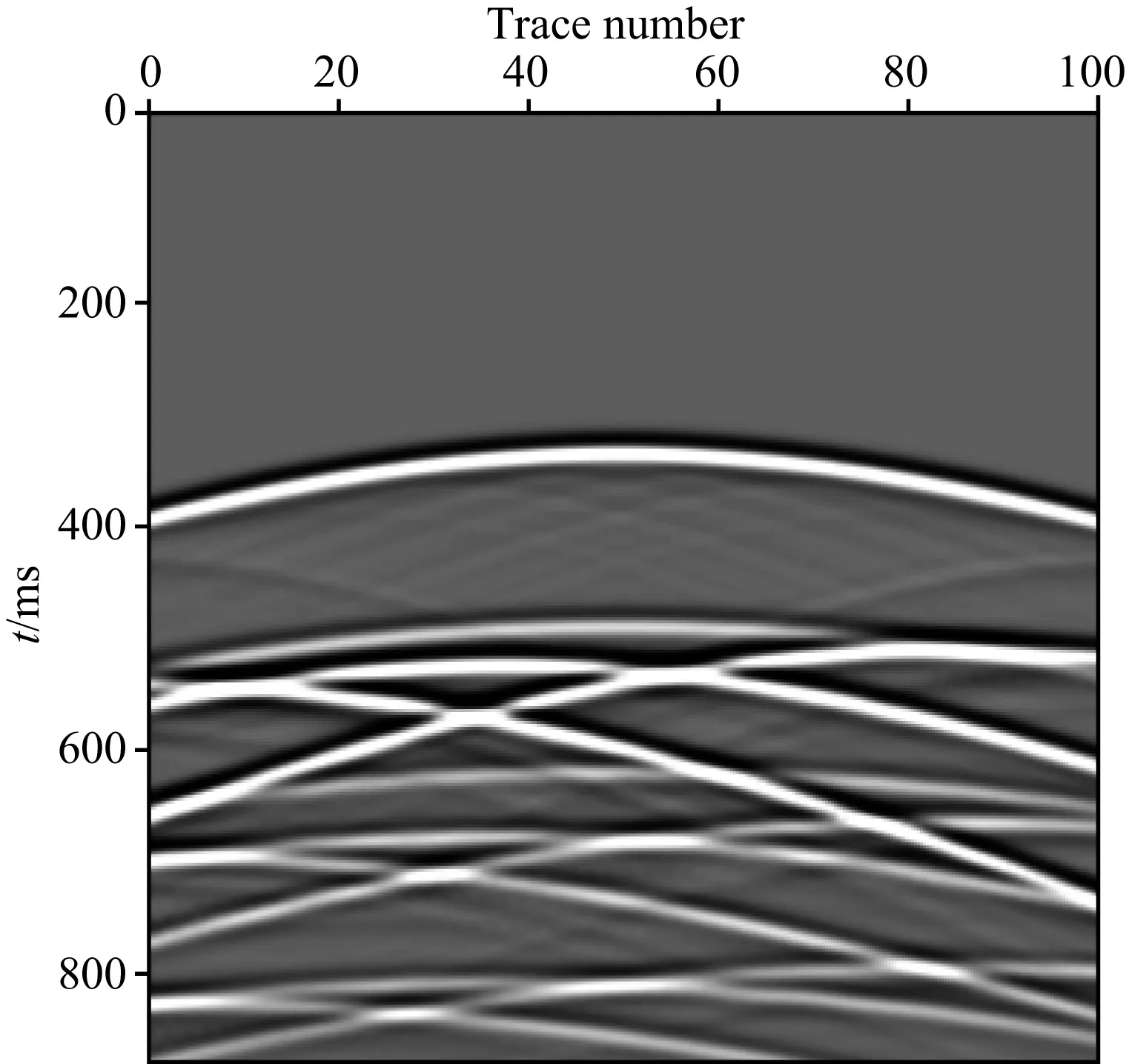
图2 层状模型混合炮记录Fig.2 A blended shot gather of layered model
图3a为混合数据常规克希霍夫偏移成像剖面,图3b为混合数据L2范数约束LSM成像剖面,图3c为混合数据TV范数约束偏移成像剖面.从图3可以看出,和常规偏移成像相比,LSM能有效去除一部分串扰噪声(图3矩形框内所示)和偏移画弧(图3箭头所示),但在最终成像剖面上还有明显的噪声残留,反射能量聚集也不够集中.而TV范数约束偏移对串扰噪声和偏移画弧的压制效果非常显著,成像剖面变得干净,并且偏移能量聚焦更佳,同相轴变清晰,更加接近真实反射系数.由此验证了TV范数约束在分层模型成像上的优势.
4.2 断层模型偏移
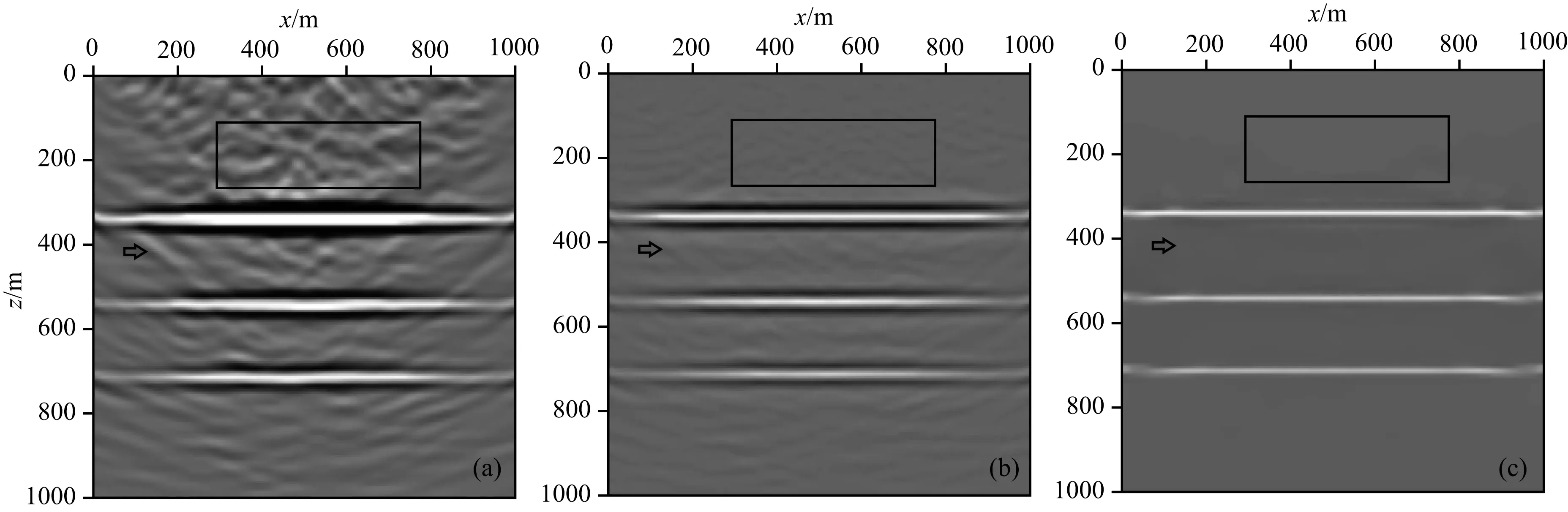
图3 混合数据(a)克希霍夫偏移结果,(b) LSM结果,(c) TV范数约束偏移结果Fig.3 Imaging results from (a) Kirchhoff migration, (b) LSM, (c) TV norm constrained migration for blended data
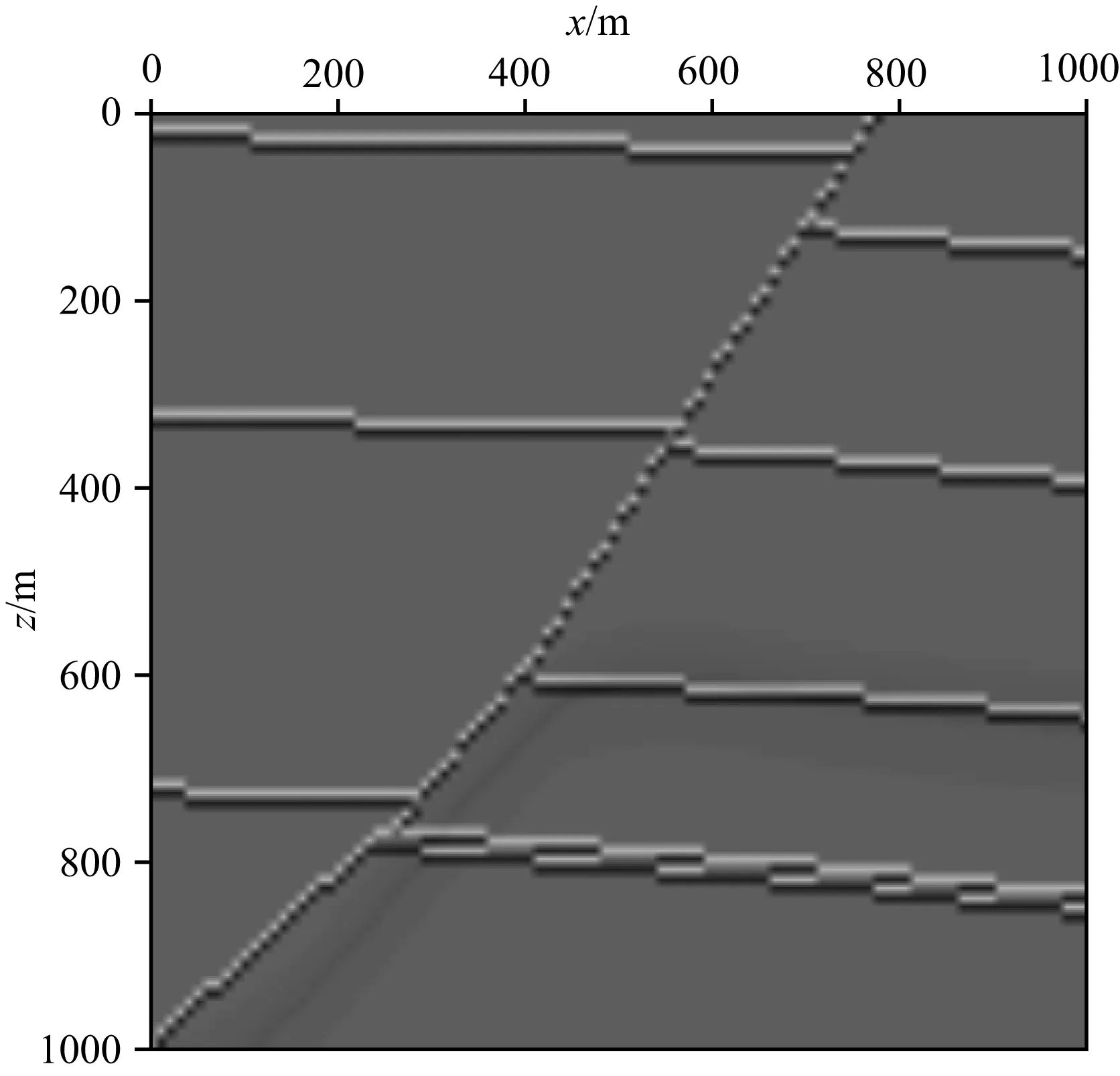
图4 SEG/EAGE断层模型(反射系数)Fig.4 SEG/EAGE fault model (reflectivity)
由于实际地震数据中通常包含有一定程度的噪声,本文接下来使用SEG/EAGE断层模型的含噪数据进行数值试验.为了减轻计算负担,在不降低计算精确度和模型复杂性的前提下,将原有速度模型抽稀(图4).重采样之后模型的横向和纵向网格点数均为100,网格间距均为10 m,背景速度为2500 m·s-1.检波器和单震源个数均为100个,从模型网格的起始点依次排列.时间采样间隔为2 ms,震源子波为主频30 Hz的雷克子波,每5个单炮合成一个混合炮(图5a).单炮混合之后,在数据中加入15%的高斯白噪声(图5b),使用不同取值的λ进行混合数据TV范数约束偏移(图6).
图6a为混合数据克希霍夫偏移成像结果,图6b,6c,6d分别为λ=0.00001,0.0001,0.001时的TV范数约束偏移成像结果.如图所示,混合数据常规偏移成像剖面上,噪声影响严重,成像质量差.当λ=0.0001时,TV范数约束偏移能较为理想的完成对串扰噪声、偏移噪声和随机噪声的衰减处理,同时成像结果贴近真实模型.当λ=0.00001时,方法去噪力度不够.随着λ取值增大,去噪能力增强,但是当λ=0.001时,深层的一部分真实信息也被去除.因此参数λ的取值,需要综合考虑偏移成像的去噪效果和数据保真度.
4.3 复杂模型偏移
最后使用垂直射线和常密度假设下的局部Marmousi模型(图7)考察本方法对复杂地质构造的成像效果.模型横向和纵向网格点数分别为551和221,纵横向网格间距均为10 m,背景速度为3000 m·s-1.检波器和单震源个数均为276个,炮间距和道间距均为20 m.时间采样间隔为1 ms,震源子波为主频30 Hz的雷克子波.通过正演模拟得到276个单炮记录,每4个单炮合成一个混合炮.
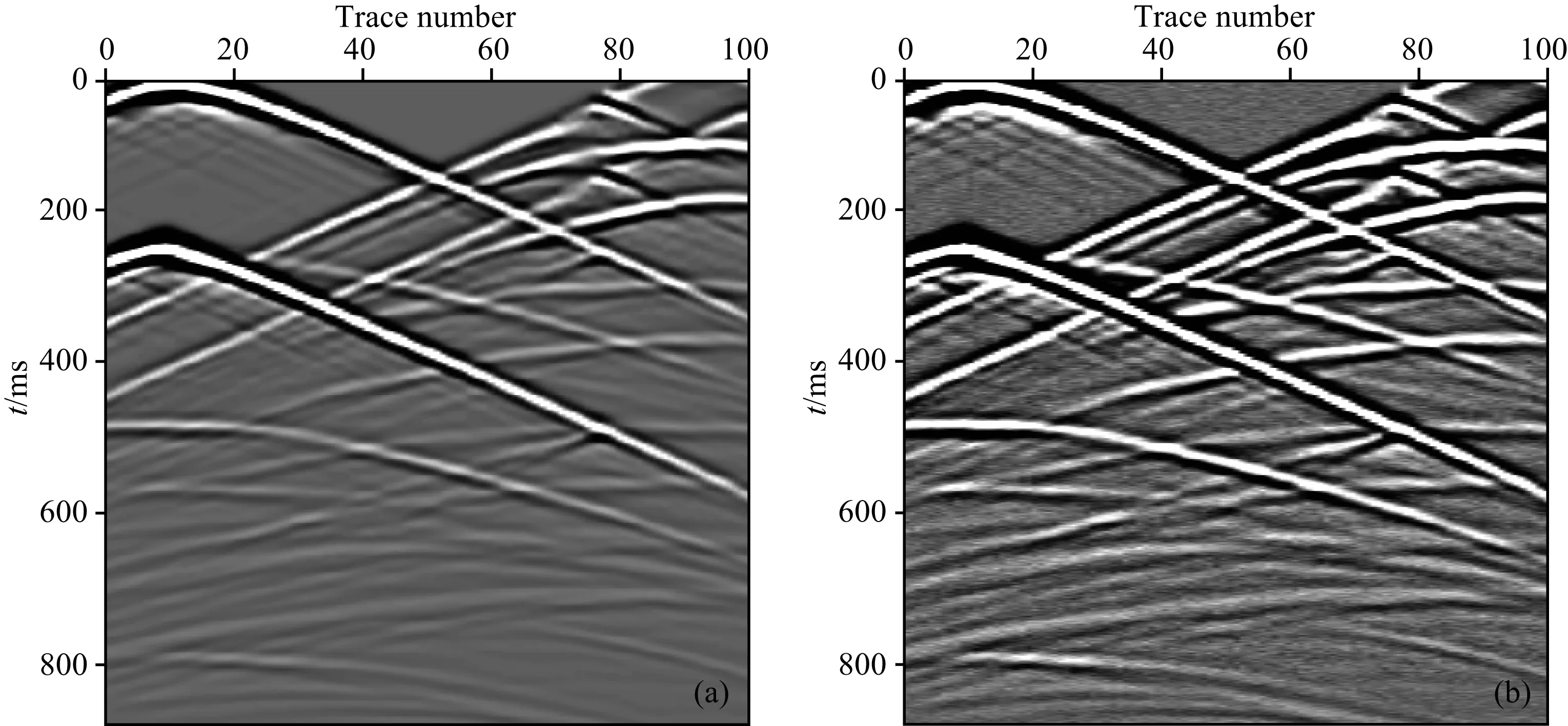
图5 (a)混合炮记录;(b)含信噪比15%高斯白噪的混合炮记录Fig.5 (a) is the blended shot gather. (b) is the blended shot gather that is added with white Gaussian noise (SNR=15%).
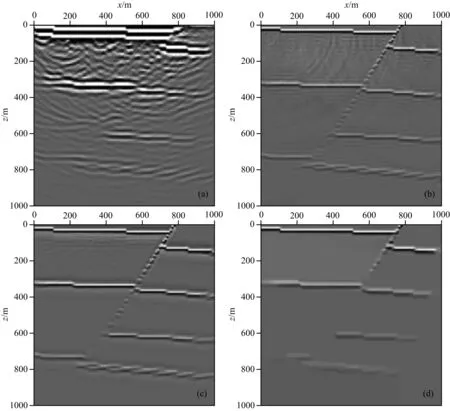
图6 混合数据(a)克希霍夫偏移结果,(b) λ=0.00001时TV范数约束偏移结果,(c) λ=0.0001时TV范数约束偏移结果,(d) λ=0.001时TV范数约束偏移结果Fig.6 Imaging results for blended data from (a) Kirchhoff migration, (b) TV norm constrained migration (λ=0.00001), (c) TV norm constrained migration (λ=0.0001), (d) TV norm constrained migration (λ=0.001)

图7 Marmousi模型(反射系数)Fig.7 Marmousi model (reflectivity)
混合数据常规偏移成像如图8a所示,图8b和图8c分别为常规单炮数据和混合数据TV范数约束偏移成像.由图可以看出,混合数据常规偏移成像效果差,剖面上存在严重的串扰噪声和偏移噪声污染,成像精度低.TV范数约束偏移通过多次迭代对绕射点能量反复聚焦,使绕射波的归位更准确,串扰噪声和偏移噪声得到有效压制.同时,整个成像剖面上粗糙的同相轴变得清晰,连续性增强,背斜、断层、薄互层等复杂地质构造都达到了很好的成像效果与精度,成像分辨率显著提高.
取图7和图8中方框1和方框2内的图像放大显示(图9和图10),能更明显地看出TV范数约束偏移的成像效果.图11为Marmousi模型偏移成像和反射系数任意两道数据的波形对比图.相比较之下,TV范数约束偏移的成像结果和真实反射系数有较高相似度,波峰波谷吻合度较好.
5 计算速率分析
对于多震源混合数据直接偏移成像,TV范数约束偏移每次迭代都需要进行1次正演和1次偏移.因此N次迭代,其计算成本大约是常规偏移的2N倍,计算量十分巨大.
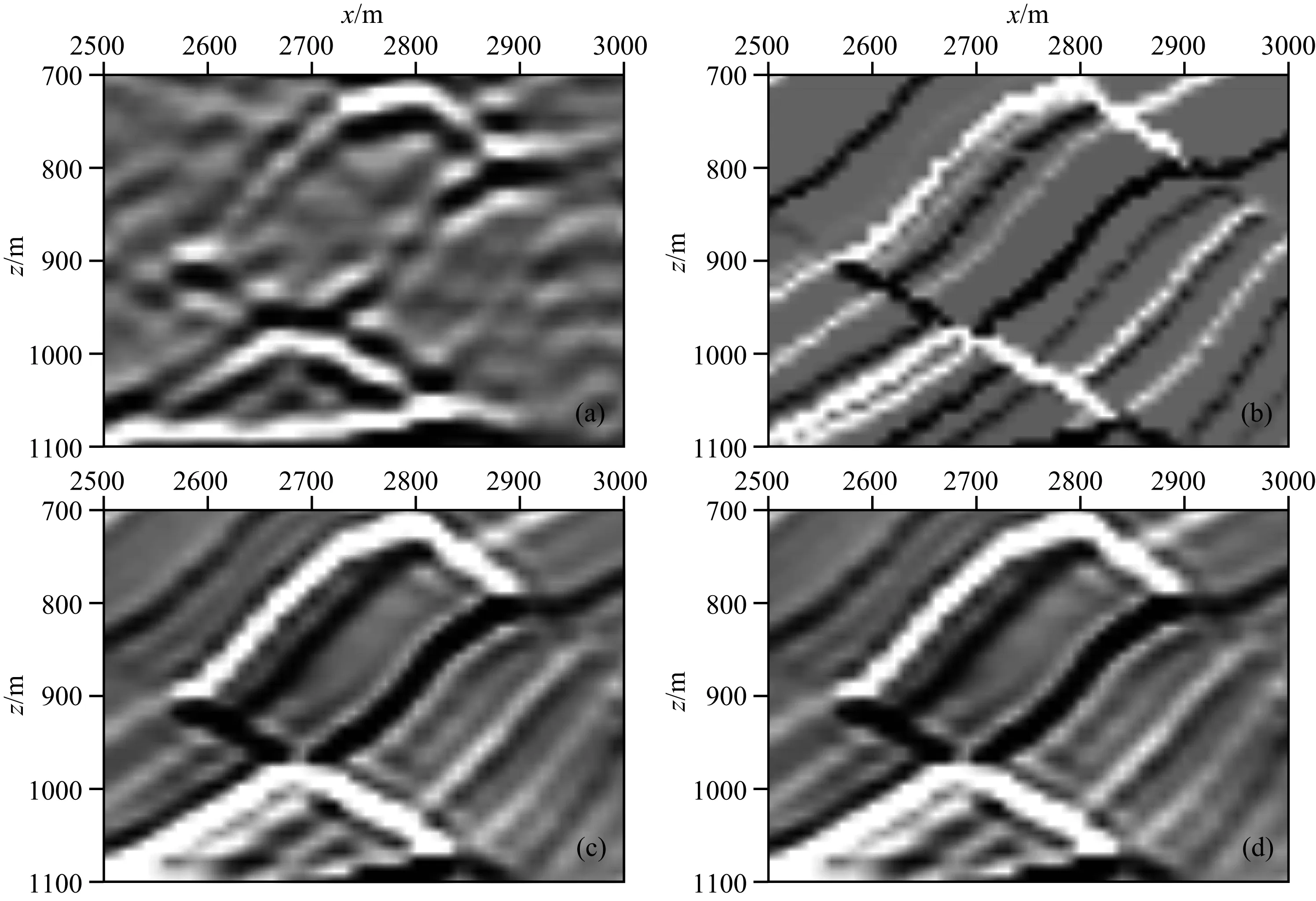
图10 方框2内数据对比(a) 混合数据克希霍夫偏移; (b) 反射系数; (c) 常规单炮数据TV范数约束偏移; (d) 混合数据TV范数约束偏移.Fig.10 The data in rectangle 2(a) Kirchhoff migration for blended data; (b) Reflectivity; (c) TV norm constrained migration for conventional sources data; (d) TV norm constrained migration for blended data.
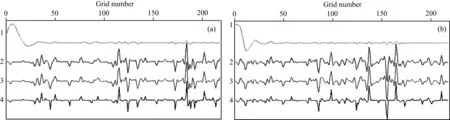
图11 偏移数据与反射系数波形对比图1号线为混合数据克希霍夫偏移,2号线为混合数据TV范数约束偏移,3号线为常规单炮数据TV范数约束偏移,4号线为真实反射系数.(a)第300道的数据;(b)第450道的数据.Fig.11 The waveform comparison of migration data and reflectivityThe first line is Kirchhoff migration for blended data, the second line is TV norm constrained migration for blended data, the third line is TV norm constrained migration for conventional sources data, the fourth line is reflectivity. (a) is the 300th traces, (b) is the 450th traces.
此类迭代偏移方法以计算成本换取成像精度,实际使用时,最终迭代次数需要权衡这两方面的影响,兼顾方法的有效性和实用性.随着计算机计算性能提高,GPU等快速计算设备的应用以及并行编程技术的发展,有望解决计算效率难题,使本方法对二维乃至三维大规模多震源混合数据的处理成为可能.
6 结论
多震源混合地震采集技术是对传统单炮地震采集技术的重大革新,而混合数据直接成像处理将是支撑该技术的发展方向之一.针对混合数据直接偏移所引起的串扰噪声,本文提出基于全变分原理的混合数据TV范数约束偏移.使用TV范数作为正则化约束项可以测度图像的跳跃性,不需要强制要求解的平滑性,图像的边缘纹理在成像过程中能够得到保存.
本方法属于混合数据直接偏移,无需炮分离处理,提高了数据处理效率.利用FISTA/FGP快速算法求解优化问题,实现方便,有较高收敛速度.层状介质模型,SEG/EAGE断层模型和Marmousi模型的TV范数约束偏移试算都获得理想的成像结果:在最终成像剖面上,随机噪声、偏移弧状噪声和串扰噪声都得到有效压制;偏移能量正确归位;各尺度地质构造都有较好的成像精度,成像分辨率明显提高.TV范数约束偏移适用于常见的偏移算法(波动方程偏移,逆时偏移等),计算效率和结果精度因所选偏移算子而有一定的差异.
最后需要注意,TV范数约束偏移是基于最小二乘优化的迭代偏移算法,通过增加偏移迭代次数来达到去噪和提高成像分辨率的目的.本算法能改善传统偏移成像方法的成像效果,但是计算耗时也相应增加,因此迭代次数的选择要综合考虑计算成本和成像精度.随着计算机运行速度的提升以及并行编程技术的发展,计算时间存在大量减少的可能,为本方法的实际应用提供了有希望的前景.
Anagaw A Y. 2009. Total variation and adjoint state methods for seismic wavefield imaging [Master′s thesis]. Alberta: Physics Department of University of Alberta.
Anagaw A Y, Sacchi M D. 2012. Edge-preserving seismic imaging using the total variation method.JournalofGeophysicsandEngineering, 9(2): 138-146.
Askan A, Akcelik V, Bielak J, et al. 2007. Full waveform inversion for seismic velocity and anelastic losses in heterogeneous structures.BulletinoftheSeismologicalSocietyofAmerica, 97(6): 1990-2008.
Bagaini C. 2006. Overview of simultaneous vibroseis acquisition methods. ∥ 76th Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, 70-74. Beasley C J, Chambers R E, Jiang Z R. 1998. A new look at simultaneous sources. ∥ SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 133-135.
Beasley C J. 2008. Simultaneous sources: A technology whose time has come. ∥ 78th Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, 2796-2800.Beck A, Teboulle M. 2009. Fast gradient-based algorithms for constrained total variation image denoising and deblurring problems.IEEETransactionsonImageProcessing, 18(11): 2419-2434.
Berkhout A J. 2008. Changing the mindset in seismic data acquisition.TheLeadingEdge, 27(7): 924-938.
Berkhout A J, Blacquière G, Verschuur D J. 2009. The concept of double blending: Combining incoherent shooting with incoherent sensing.Geophysics, 74(4): A59-A62.Burstedde C, Ghattas O. 2009. Algorithmic strategies for full waveform inversion: 1D experiments.Geophysics, 74(6): WCC37-WCC46.
Chambolle A. 2004. An algorithm for total variation minimization and applications.JournalofMathematicalImagingandVision, 20(1): 89-97.
Dai W, Wang X, Schuster G T. 2011. Least-squares migration of multisource data with a deblurring filter.Geophysics, 76(5): R135-R146.
Dai W, Fowler P, Schuster G T. 2012. Multi-source least-squares reverse time migration.GeophysicalProspecting, 60(4): 681-695. Gong C M. 2014. Application of variational principle in seismic data denoising.Computer&DigitalEngineering(in Chinese), 42(7): 1271-1274.
Huang Y S, Schuster G T. 2012. Multisource least-squares migration of marine streamer and land data with frequency-division encoding.GeophysicalProspecting, 60(4): 663-680.
Mao H, Wang W, Han B. 2012. Seismic waveform inversion based on Bayesian-sparsity constraint regularization method.CommunicationonAppliedMathematicsandComputation(in Chinese), 26(3): 285-297.
Qu Y, Cao J X, Zhu H D, et al. 2011. An improved total variation technique for seismic image denoising.ActaPetroleiSinica(in Chinese), 32(5): 815-819.
Rudin L I, Osher S, Fatemi E. 1992. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms.PhysicaD:NonlinearPhenomena, 60(1-4): 259-268.Schuster G T, Dai W. 2010. Multi-source wave equation least-squares migration with a deblurring filter. ∥ 72nd EAGE Conference & Exhibition, Extended Abstracts, 276-279. Silverman D. 1979. Method of three dimensional seismic prospecting. U. S. Patent 4, 159, 463, 1979.Tang Y X, Biondi B. 2009. Least-squares migration/inversion of blended data. ∥ SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 28: 2859-2863.
Tikhonov A N, Arsenin V Y. 1977. Solutions of Ill-Posed Problems. Washington, DC: V. H. Winston and Sons.
Verschuur D J, Berkhout A J. 2011. Seismic migration of blended shot records with surface-related multiple scattering.Geophysics, 76(1): A7-A13.
附中文参考文献
公成敏. 2014. 全变分原理在地震数据去噪中的应用. 计算机与数字工程, 42(7): 1271-1274.
毛衡, 王薇, 韩波. 2012. 基于贝叶斯-稀疏约束正则化方法的地震波形反演. 应用数学与计算数学学报, 26(3): 285-297.
屈勇, 曹俊兴, 朱海东等. 2011. 一种改进的全变分地震图像去噪技术. 石油学报, 32(5): 815-819.
(本文编辑 何燕)
Direct migration method of multi-source blended data based on total variation
LU Xin-Ting, HAN Li-Guo*, ZHANG Pan, SUN Hong-Yu
CollegeofGeo-explorationSciencesandTechnology,JilinUniversity,Changchun130026,China
In acquisition of multi-source blended data, multiple sources are continuously shot and geophones continuously receive seismic signals to acquire blended shot records overlapping in both the spatial and temporal domains. Relative to the traditional seismic acquisition, blended acquisition can decrease the effective survey duration and reduce the cost of surveys. However, this continuously shooting and recording strategy can lead to complex blended wave fields and create great difficulties to the following migration imaging. There are two migration imaging methods about the blended data at this stage: to perform the migration processing directly on the blended data without any pre-separation, or recovery the blended data to individual shot data, which is called “deblending”, then conduct standard migration processing to these deblended data. The first method has a high processing efficiency, but the multi-source direct migration is usually not satisfactory because of the crosstalk contamination. The second method has low efficiency and the source separation has serious influence on imaging quality. All things considered, the direct migration method has a better prospect of application, so this article studies a direct migration method of blended data which can effectively remove the crosstalk.Mathematically, the seismic imaging can be regarded as a typical mathematical and physical inverse problem and a better imaging result can be obtained by solving a regularized least-squares (LS) problem with a linear inversion method. The total variation (TV) regularization method is widely used in image denoising and restoration fields. It can produce a denoised image where edges and discontinuities are preserved. On the basis of analyzing the principles of TV image denoising and restoration method, in this paper, we formulate the direct migration of multi-source seismic data as a problem of minimizing the energy functional of image restoration, use the TV regularization to replace the L2 norm regularization in the traditional least-squares migration (LSM) and propose a TV norm constrained migration method. The proposed method employs a gradient-based algorithm—a combination of fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm and fast gradient projection method (FISTA/FGP) to solve the optimization problem. It combines the advantages of FISTA and FGP, which is simple in algorithm, convenient to realize and stable.To test the validity and adaptability of our migration method, numerical experimentations are carried out on a horizontally-layered medium model, SEG/EAGE fault model and 2D Marmousi model, respectively. First, we compute the prestack Kirchhoff migration, the L2 norm constrained LSM and TV norm constrained migration for the horizontally-layered medium model. The results show that the TV norm constrained migration can effectively suppress the migration artifacts and crosstalk and the image quality is better than the other two. For the case of data containing noise, this article adds 15% Gauss white noise into the synthetic blended data of the SEG/EAGE fault model and applies the TV norm constrained migration with different values of the optimization parameters. The results indicate that our algorithm has good anti-noise performance and point out that there is influence of the selection of regularization parameters on the imaging results. So considering the denoise effect and fidelity of migration imaging, an assigned range of these optimization parameters is proposed. For the complex medium case, we compute the standard migration and TV norm constrained migration for the blended data of the 2D Marmousi model and use the conventional data TV norm constrained migration as a reference. The imaging results and waveform comparison both indicate that our method can yield desired migration imaging of complex geological structures.For the crosstalk noise caused by direct imaging of blended data, we propose a direct migration method based on TV regularization. The results of theoretical model experiments show that our method can effectively suppress the random noise, migration artifacts and crosstalk noise, enhance the continuity of seismic events and improve the imaging resolution. TV norm constrained migration belongs to an iterative migration algorithm based on least-square optimization and has a prominent imaging effect. However, it is also a computing-expensive algorithm. With the development of the computer performance and the parallel programming technology, the computational cost can be reduced, which can enable our method to practical applications.
Multi-source blended acquisition; Blended data; Direct imaging; Crosstalk noise; Total variation
卢昕婷, 韩立国, 张盼等. 2015. 基于全变分原理的多震源混合数据直接偏移方法.地球物理学报,58(9):3335-3345,
10.6038/cjg20150926.
Lu X T, Han L G, Zhang P,et al. 2015. Direct migration method of multi-source blended data based on total variation.ChineseJ.Geophys. (in Chinese),58(9):3335-3345,doi:10.6038/cjg20150926.
10.6038/cjg20150926
P631
2014-12-31,2015-09-01收修定稿
国家自然科学基金项目(41374115),国家高技术研究发展计划(863计划)重大项目课题(2014AA06A605)联合资助.
卢昕婷,女,1988年生,博士生,主要从事混合震源数据处理.E-mail:luxt13@mails.jlu.edu.cn
*通讯作者 韩立国,男,1961年生,教授,博士生导师,主要从事地震数据处理解释工作.E-mail:hanliguo@jlu.edu.cn
