西格列汀与其他降糖药物对照治疗2型糖尿病的Meta分析
2015-03-05梁菁菁陈静芸夏文明吕耀欣
梁菁菁,陈静芸,杨 艳,夏文明,吕耀欣
(解放军第八一医院医务处,南京210000)
西格列汀与其他降糖药物对照治疗2型糖尿病的Meta分析
梁菁菁,陈静芸,杨艳,夏文明,吕耀欣※
(解放军第八一医院医务处,南京210000)
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2015.05.045
2型糖尿病是一组由于胰岛素分泌不足伴胰岛素抵抗的代谢性疾病,随着现代人们生活水平的不断提高、人口老化、生活方式的改变以及诊断技术的进步,糖尿病患者人数也随之而迅速增加。据国际糖尿病联合会和世界卫生组织统计,全球约有2.85亿糖尿病患者,预计2025年将超过3.3亿人口[1-2]。长期的血糖控制不佳可引起患者的眼睛、肾脏、神经、心脏等的慢性损害,使其功能减退和衰竭,严重者可引起急性代谢紊乱,如酮症酸中毒、高渗性昏迷等[3]。目前常用的治疗2型糖尿病口服药物包括磺脲类、双胍类、α糖苷酶抑制剂、噻唑烷二酮类药物、二肽基肽酶4(dipeptidylpeptidase-4,DPP-4)抑制剂,注射类药物包括胰岛素、胰高血糖素样肽1(glucagon like peptide-1,GLP-1)受体激动剂。西格列汀是最早应用于临床的DPP-4抑制剂,其通过抑制α细胞分泌胰高血糖素,促使胰岛β细胞产生胰岛素,从而降低血糖[4]。本研究采用系统评价法探讨西格列汀治疗2型糖尿病的疗效和安全性。
1资料与方法
1.1纳入与排除标准
1.1.1研究类型随机对照试验(randomized controlled trial,RCT),文种限英文和中文。
1.1.2研究对象诊断标准符合美国糖尿病协会或世界卫生组织标准的成年2型糖尿病患者。
1.1.3干预措施西格列汀与其他降糖药对照,合并用药不限,疗程不少于3个月,入组总人数不少于100例,剂量不少于50 mg/d。
1.1.4结局指标主要结局指标为糖化血红蛋白(glycosylated hemoglobin,HbA1c),次要结局指标为低血糖发生率和不良反应。
1.2文献检索计算机检索Cochrane图书馆(2012年第2期),PubMed(1978年至2012年10月),CNKI(1978年至2012年10月),EMBASE(1974年至2012年10月),VIP(1989年至2012年10月),CBI(1978年至2012年10月)。英文检索词包括sitagliptin、JANUVIA、 randomized controlled trial等;中文检索词包括西格列汀、随机、对照等。
1.3数据提取及方法质量学评价由2名研究者独立进行文献筛选、数据提取和质量评价,并进行核对讨论。文献质量评价包括随机序列的产生、随机化隐藏、盲法、撤出与退出4个方面,按照改良Jadad计分标准评估临床试验质量。试验质量评分0~7分,1~3分为低质量,4~7分为高质量[5]。
1.4统计学方法应用RevMan 5.0软件进行Meta 分析。纳入研究的异质性检验采用χ2检验,若P<0.1采用随机效应模型;反之采用固定效应模型。区间估计采用95%置信区间(confidence inteval,CI),连续变量结果采用均数差(MD)表示,非连续性变量结果采用OR或RR表示。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
2.1文献检索结果初检出1052篇文献,均为英文文献。通过阅读题目、摘要及全文后排除重复或不符合纳入标准的文献,符合纳入标准的RCT文献20篇[6-25]。纳入研究的基本特征详见表1。
2.2方法质量学评价纳入的研究设计均为RCT,质量均较高,Jadad评分均在4分以上,均为双盲RCT,采用意向性分析。
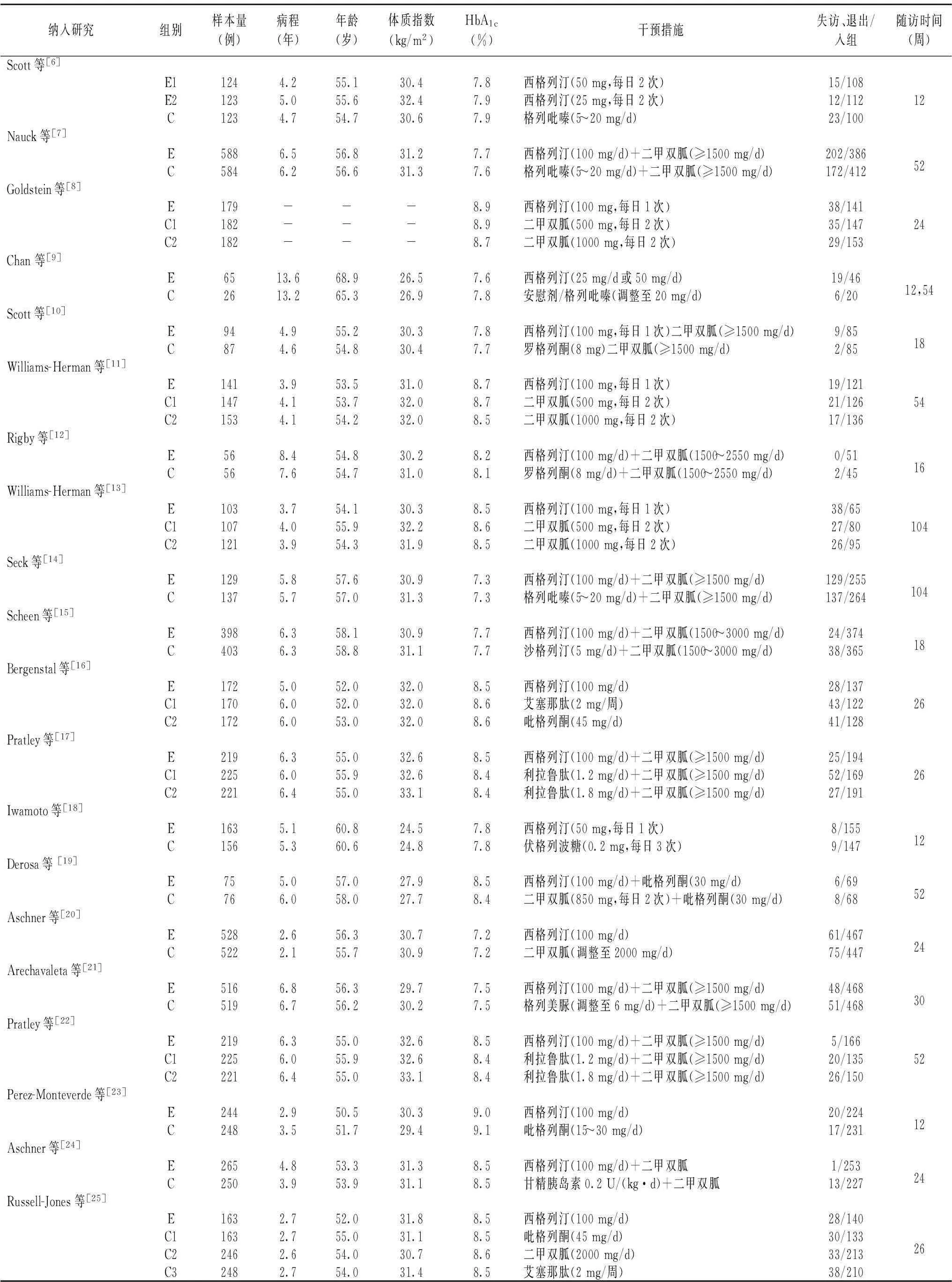
表1 纳入研究的基本信息
E:试验组;C:对照组; HbA1c:糖化血红蛋白;“-”文献中未提供
2.3Meta分析结果
2.3.1HbA1c纳入20篇文献均比较了西格列汀与阳性药物在降低患者HbA1c方面的疗效,但Chan 等[9]的数据不全,不能纳入进行Meta分析。Williams-Herman等[11]、Williams-Herman等[13]是Goldstein等[8]的扩展试验,Seck等[14]是Nauck等[7]的扩展试验,Pratley等[22]是Pratley等[17]的扩展试验。Scheen等[15]比较了另一种DPP-4抑制剂沙格列汀与西格列汀的疗效,结果显示沙格列汀与西格列汀降低 HbA1c疗效相似,差异无统计学意义,不进行Meta分析。Meta分析显示,在降低HbA1c水平方面,西格列汀优于α糖苷酶抑制剂,不劣于噻唑烷二酮类组、磺脲类组,但是不及二甲双胍组、GLP-1受体激动剂组与胰岛素组,见图1。

图1 西格列汀与其他降糖药物降低糖化血红蛋白有效性的森林图
2.3.2不良反应发生率纳入11个研究进行Meta分析,比较西格列汀和其他降糖药物治疗2型糖尿病时不良反应的发生率。治疗过程中出现的不良反应有上呼吸道感染、腹痛、尿路感染和头痛,鼻咽炎,低血糖,高血压,背痛,咳嗽等。Meta分析结果显示,西格列汀的不良反应发生率与噻唑烷二酮组类似,显著低于二甲双胍组、磺脲类组、α糖苷酶抑制剂组、GLP-1受体激动剂组,但是高于甘精胰岛素,见表2。
2.3.3低血糖发生率纳入11个研究的数据进行Meta分析,比较西格列汀和其他降糖药物治疗2型糖尿病时低血糖事件的发生率。结果显示,治疗过程中,西格列汀与二甲双胍,噻唑烷二酮类和伏格列波糖,GLP-1受体激动剂的低血糖发生率类似,低于磺脲类组与甘精胰岛素,见表3。

表2 不良反应发生率的Meta分析结果
GLP-1:胰高血糖样肽1
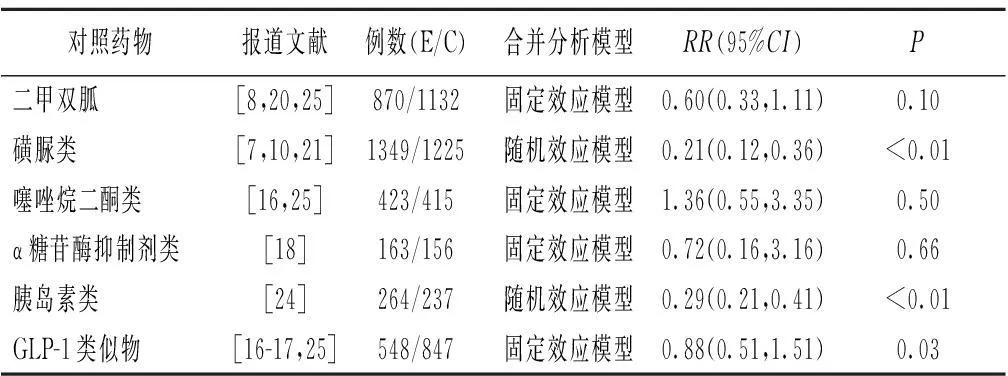
表3 低血糖发生率的Meta分析结果
GLP-1:胰高血糖样肽1
3讨论
本研究结果显示,西格列汀可以有效控制2型糖尿病患者的血糖,疗效不逊于传统降血糖药物。治疗过程中,西格列汀的不良反应均较轻微可以耐受,其不良反应发生率及低血糖的发生率均较低。
GLP-1被认为是促胰岛素作用最强的肠促胰岛素,而DPP4是促使GLP-1降解、失活的关键酶之一,DPP-4抑制剂通过抑制DPP-4的活性,增加GLP-1的血浆水平,通过葡萄糖依赖性促进胰岛素分泌,抑制胰高血糖素分泌,起到降低血糖的作用,还通过促进胰岛β细胞增殖,抑制其凋亡,保护胰岛β细胞功能[4]。目前DPP-4抑制剂作为新型抗糖尿病药物已被国际糖尿病联盟[26]、中华医学会糖尿病学分会[27]和美国内分泌医师学会[28]纳入2型糖尿病的治疗路径中。西格列汀是最早上市的DPP-4抑制剂,其可对DPP-4的活性产生至少80%的抑制作用,这种抑制作用可持续24 h,是一种安全、方便、有效的药物。目前对于其的临床研究也是DPP-4抑制剂中最多的。
本研究客观评价了西格列汀治疗2型糖尿病的疗效及安全性,为西格列汀的应用提供了一定的临床依据。本系统评价纳入的20个研究均为多中心研究,研究质量较高。但本系统评价仍然存在以下局限性:①α糖苷酶抑制剂类药物及胰岛素均仅纳入1篇随机对照研究,存在缺陷。②对照组为磺酰脲类、噻唑烷二酮类、GLP-1类似物时均存在合并用药的情况,需考虑到可能存在的药物相互作用。③检索文种仅为中文和英文,可能存在发表偏倚。
综上所述,西格列汀能安全有效地控制 2型糖尿病患者的血糖,与其他降糖药物相比,在有效性和安全性方面取得较好的平衡。
参考文献
[1]King H,Aubert RE,Herman WH.Global burden of diabetes,1995-2025:prevalence,numerical esrimates and projection[J].Diabetes Care,2008,21(9):1414-1431.
[2]Zhang P,Zhang X,Brown J,etal.Global healthcare expenditure on diabetes for 2010 and 2030[J].Res Clin Pract,2011,92(2):301.
[3]Ryden L,Standl E,Bartnik M,etal.Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases:executive summary.The Task Force on Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD)[J].Eur Heart J,2007,28(1):88-136.
[4]Neumiller JJ,Wood L,Campbell RK.Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Pharmacotherapy,2010,30(5):463-484.
[5]刘亮,林国生,李绪勇,等.西罗莫司洗脱支架与裸金属支架治疗CHD的系统评价[J].临床荟萃,2011,26(4):301-306.
[6]Scott R,Wu M,Sanchez M,etal.Efficacy and tolerability of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy over 12 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Int J Clin Pract,2007,61(1):171-180.
[7]Nauck MA,Meininger G,Sheng D,etal.Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor,sitagliptin,compared with the sulfonylurea,glipizide,in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin alone:a randomized,double-blind, non-inferiority trial[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2007,9(2):194-205.
[8]Goldstein BJ,Feinglos MN,Lunceford JK,etal.Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin,a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and metformin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes Care,2007,30(8):1979-1987.
[9]Chan JC,Scott R,Arjona Ferreira JC,etal.Safety and efficacy of sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic renal insufficiency[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2008,10(7):545-555.
[10]Scott R,Loeys T,Davies MJ,etal.Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2008,10(10):959-969.
[11]Williams-Herman D,Johnson J,Teng R,etal.Efficacy and safety of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin and metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes:a 54-week study[J].Curr Med Res Opin,2009,25(3):569-583.
[12]Rigby SP,Handelsman Y,Lai YL,etal.Effects of colesevelam, rosiglitazone,or sitagliptin on glycemic control and lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled by metformin monotherapy[J].Endocr Pract,2010,16(1):53-63.
[13]Williams-Herman D,Johnson J,Teng R,etal.Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin and metformin as initial combination therapy and as monotherapy over 2 years in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2010,12(5):442-451.
[14]Seck T,Nauck M,Sheng D,etal.Safety and efficacy of treatment with sitagliptin or glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin:a 2-year study[J].Int J Clin Pract,2010,64(5):562-576.
[15]Scheen AJ,Charpentier G,Ostgren CJ,etal.Efficacy and safety of saxagliptin in combination with metformin compared with sitagliptin in combination with metformin in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Diabetes Metab Res Rev,2010,26(7):540-549.
[16]Bergenstal RM,Wysham C,Macconell L,etal.Efficacy and safety of exenatide once weekly versus sitagliptin or pioglitazone as an adjunct to metformin for treatment of type 2 diabetes(DURATION-2):a randomised trial[J].Lancet,2010,376(9739):431-439.
[17]Pratley RE,Nauck M,Bailey T,etal.Liraglutide versus sitagliptin for patients with type 2 diabetes who did not have adequate glycaemic control with metformin:a 26-week,randomised,parallel-group,open-label trial[J].Lancet,2010,375(9724):1447-1456.
[18]Iwamoto Y,Tajima N,Kadowaki T,etal.Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin monotherapy compared with voglibose in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes:a randomized, double-blind trial[J].Diabetes Obes Metab, 2010,12(7):613-622.
[19]Derosa G,Maffioli P,Salvadeo SA,etal.Effects of sitagliptin or metformin added to pioglitazone monotherapy in poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus patients[J].Metabolism,2010,59(6):887-895.
[20]Aschner P,Katzeff HL,Guo H,etal.Efficacy and safety of monotherapy of sitagliptin compared with metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2010,12(3):252-261.
[21]Arechavaleta R,Seck T,Chen Y,etal.Efficacy and safety of treatment with sitagliptin or glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy:a randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2011,13(2):160-168.
[22]Pratley R,Nauck M,Bailey T,etal.One year of liraglutide treatment offers sustained and more effective glycaemic control and weight reduction compared with sitagliptin,both in combination with metformin, in patients with type 2 diabetes:a randomised,parallel-group,open-label trial[J].Int J Clin Pract,2011,65(4):397-407.
[23]Perez-Monteverde A,Seck T,Xu L,etal.Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin and the fixed-dose combination of sitagliptin and metformin vs.pioglitazone in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Int J Clin Pract,2011,65(9):930-938.
[24]Aschner P,Chan J,Owens DR,etal.Insulin glargine versus sitagliptin in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus uncontrolled on metformin (EASIE):a multicentre,randomised open-label trial[J].Lancet, 2012,379(9833):2262-2269.
[25]Russell-Jones D,Cuddihy RM,Hanefeld M,etal.Efficacy and safety of exenatide once weekly versus metformin,pioglitazone,and sitagliptin used as monotherapy in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (DURATION-4):a 26-week double-blind study[J].Diabetes Care,2012,35(2):252-258.
[26]Ceriello A,Colagiuri S.International Diabetes Federation guideline for management of postmeal glucose:a review of recommendations[J].Diabet Med,2008,25(10):1151-1156.
[27]中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2010年版)[M].北京:北京大学医学出版社,2011:16-17.
[28]Rodbard HW,Jellinger PS,Davidson JA,etal.Statement by an American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists American College of Endocrinology consensuspanel on type 2 diabetes mellitus:an algorithm for glycemic control[J].Endocr Pract,2009,15(6):540-559.
摘要:目的系统评价西格列汀治疗2型糖尿病的疗效及安全性。方法检索Cochrane图书馆,PubMed,EMBASE,CBM,VIP,CNKI数据库。根据Cochrane手册对纳入的随机对照试验(RCT)进行质量评价,并用RevMan 5.0软件进行Meta分析。结果共纳入20个研究,Meta分析结果显示,在降低糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)水平方面,西格列汀优于α糖苷酶抑制剂。在控制患者体质量方面,西格列汀的疗效优于磺酰脲类、噻唑烷二酮类和胰岛素,西格列汀不良反应发生率明显低于双胍组、磺脲类组、α糖苷酶抑制剂组、胰高血糖素样肽1 (GLP-1)受体激动剂组。西格列汀与二甲双胍、噻唑烷二酮类、伏格列波糖、GLP-1受体激动剂的低血糖发生率差异无统计学意义。结论西格列汀治疗2型糖尿病患者疗效可靠且安全,可以用来治疗2型糖尿病。
关键词:糖尿病,2型;西格列汀;Meta分析;系统评价
A Meta-analysis on Sitagliptin and Other Antidiabetic Drugs in the Treatment of Type 2 DiabetesLIANGJing-jing,CHENJing-yun,YANGYan,XIAWen-ming,LVYao-xin.(DepartmentofMedicalAffairs,NO.81Hospital,Nanjing210000,China)
Abstract:ObjectiveTo systematically review the efficacy and safety of sitagliptin for type 2 diabetes mellitus.MethodsRandomized controlled trials(RCTs)were retrieved from the Cochrane Library,PubMed,EMBASE,CBM,VIP and CNKI.We used the method recommended by the Cochrane Collaboration to perform a meta-analysis of RCTs.ResultsAltogether 20 studies were included.The meta-analysis showed that sitagliptin provided greater reductions in HbA1c than α-glycosidase inhibitors. In weight control,sitagliptin showed greater reductions compared with sulfonylureas,thiazolidinedione and insulin.Lower incidence of overall adverse events(AEs) was observed in Sitagliptin than in metformin,sulfonylureas, α-glycosidase and glucagon like peptide-1(GLP-1) receptor agonist.The incidence of hypoglycemia in sitagliptin, metformin,sulfonylureas,voglibose and GLP-1 receptor agonist had no statistically significant difference.ConclusionSitagliptin is effective and safe for type 2 diabetes.
Key words:Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Sitagliptin; Meta-analysis; Systematic review
收稿日期:2013-01-24修回日期:2014-08-15编辑:伊姗
中图分类号:R977
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1006-2084(2015)05-0886-05
