滚动轴承缺陷振动建模及冲击特征提取*
2015-02-07李祥阳陈万强西安航空学院陕西省泵类装备工程研究中心西安710077
李祥阳,陈万强(西安航空学院陕西省泵类装备工程研究中心 西安,710077)
滚动轴承缺陷振动建模及冲击特征提取*
李祥阳,陈万强
(西安航空学院陕西省泵类装备工程研究中心 西安,710077)
以SKF6205-2RS深沟球轴承为研究对象,运用Hertzian接触理论、弹性力学及滚动轴承几何学,建立了可预测滚动轴承不同损伤位置和程度的状态模型,并通过Runge-Kutta数值方法获取了系统响应。计算结果表明:径向负荷作用下,模型对内圈、外圈、钢球局部损伤所激励的频率及其谐波成分可进行良好预测;阐述不同状态下轴承振动规律,论证连续Haar小波变换周期性;利用连续Haar小波变换在时间-尺度域上所特有的周期性结合自相关消噪,提出了一种滚动轴承早期损伤特征提取的自相关连续Haar小波方法。诊断实例证明,这种方法能够有效消除信号的噪声,提取信号的弱冲击成分。
滚动轴承;预测模型;连续Haar小波;自相关消噪;弱冲击成分
引 言
航空发动机和航空燃气涡轮机等重大装备的核心技术问题之一就是轴承,它对整个飞机制造业的发展水平有着举足轻重的作用。对滚动轴承进行状态评估可以提高装备的可靠性,实现由“事后维修”到“预知维修”的转变,提高飞机设备的管理水平,保证产品质量;同时又为航空轴承可靠性增长设计和服役性能控制奠定了方法基础[1-2]。预测模型是一种有效的工具,它可以帮助深入理解产生损伤的机理,还可以用来检验各种评估方法的实效性。文献[3-4]从数字信号角度出发,用周期性脉冲序列来模拟单点和多点损伤对轴承的冲击激励,并给出了轴承损伤响应模型,在研究轴承载荷分布基础上采用脉冲序列模拟瞬态冲击力。文献[5]提出了一种数学模型,用来描述当轴承通过损伤点时内部轴承力的变化,并且采用VB编制了载荷影响及谱图分析程序。文献[6]分析了外负荷和损伤位置对振动行为的影响,确定了外载荷作用下振动的周期性与力传递的途径。文献[7]论证了滚动轴承局部损伤信号的统计量具有近似循环平稳性,指出由于离心力、陀螺力矩和润滑形态的影响,会导致接触角的不断变化和轴承部件的相对滑动,从严格意义上讲,轴承损伤信号是非平稳信号,但仍然可以将其视为近似循环平稳信号。文献[8-9]研究了球轴承的自然振动,拾取了外圈的径向、轴向的振动,对拾取信号进行FFT谱分析和模态分析,导出了外圈自然振动表达式、平面内自然振动频率表达式和平面外自然振动频率表达式,分析了3种振动频率公式的精度。研究了单个和多个缺陷对应的冲击响应特点,给出了损伤频率的计算公式,但并没有在时、频域进行分析,只是认为损伤对轴承的冲击可以用矩形波、三角波和半余弦波等脉冲序列来描述。以上研究从动力学响应的角度进行统计模拟,没有涉及轴承本身的建模问题。文献[10]提出考虑接触-变形域的轴承仿真模型,讨论了故障位置对振动的影响。文献[11]采用两自由度方程模拟了内、外圈和滚动体故障,分析了轴承周期、准周期和混沌运动。文献[12]用有限元法研究了不平衡力作用下损伤轴承的动特性。
笔者对已有的状态模型作了改进。在Fukata二自由度方程[13]基础上引入了套圈-钢球-支座的振动耦合作用,综合考虑了局部损伤的位置和程度,建立了可预测不同损伤位置和损伤程度的滚动轴承状态分析模型,揭示了不同状态下的振动规律。要获得轴承服役的准确信息,信号处理至关重要。FFT变换通过构造不同类型的滤波器来满足消噪的需要,却无法消除遍布于整个频域范围内的噪声。应用匹配滤波器时,如果输入信号的信噪比较低,滤波器将输出多峰,造成特征失效[14]。笔者在对预测响应信号处理的基础上,分析了连续Haar小波所特有的时间-尺度周期性,指出这种特性可以充分展示滚动轴承损伤振动信号中的周期性冲击成分。已有的小波技术在轴承信号处理中的应用往往从基函数相似性匹配的角度出发,笔者进一步发掘小波基函数在滚动轴承振动信号中的应用。结合自相关预处理,提出了一种自相关连续Haar小波变换方法用来识别轴承早期损伤模式。理论和实践证明,这种方法能够有效消除损伤信号中的干扰,使得在消除干扰信号的同时保留信号中的弱冲击成分。
1 滚动轴承预测模型
滚动轴承受载接触时,钢球与滚道之间将发生非线性弹性变形,由Hertzian理论,点接触弹性恢复力[15]为

其中:δ为弹性趋近量;K为总接触刚度系数。
内外圈分别为Ki,Ko,由以下两式求的

其中:∑-ρ为接触点的曲率和;γ*为变形系数,其值的计算参见文献[15]。
图1为滚动轴承坐标示意图,第i个钢球-套圈接触变形δi为内圈在x,y方向位移(xs,ys),钢球位置角θi和游隙c的函数


图1 滚动轴承示意图Fig.1 The reference axes of the rolling bearing
设(xb,yb)为钢球的坐标,由于振动传递作用,考虑到钢球自身的振动,局部接触变形为

其中:θi为轴承第i个钢球的位置角。

其中:ωc为轴承公转速度即保持器转速;N为钢球个数。

设轴的转速为ω,则,其中:Db为钢球直径;Dp为轴承节圆直径。
同理,设(xo,yo)为支座处的运动坐标,接触变形就可表示为

图2为内圈-钢球-支座振动耦合作用示意图。根据Lagrange方程,动力学方程为
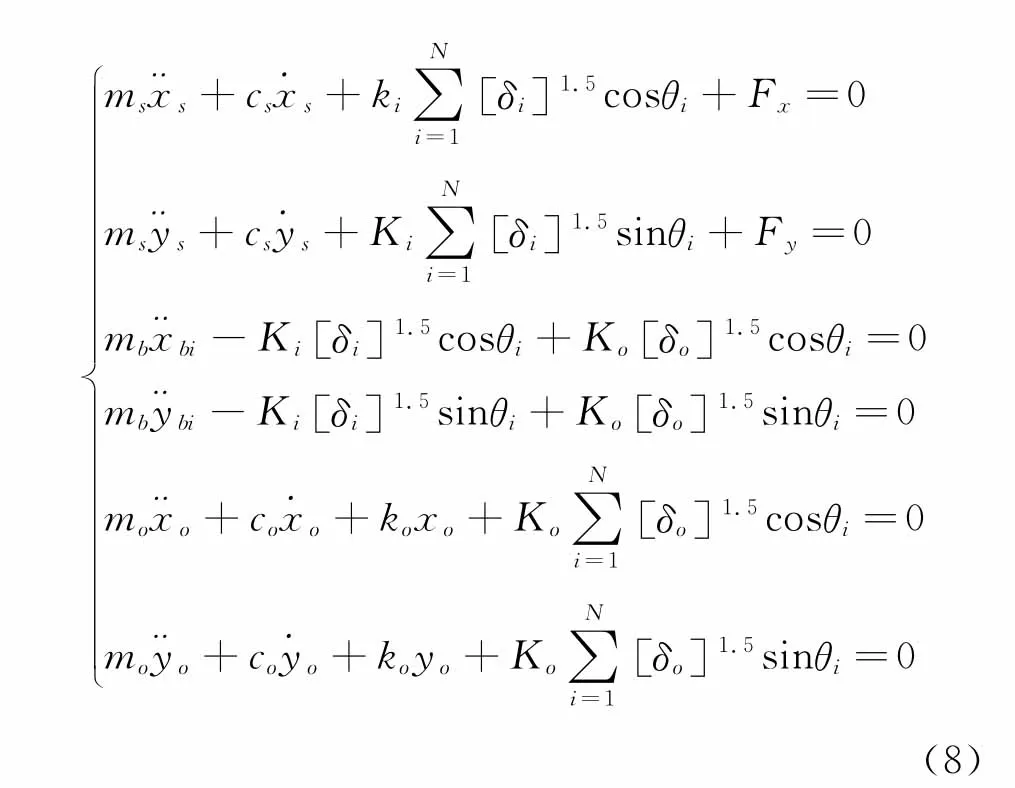
其中:ms,mb,mo分别为内圈与轴的质量、钢球质量、外圈与支座质量;cs为轴承内阻尼;ko,co为支座刚度与阻尼。

图2 滚动轴承振动系统坐标图Fig.2 The reference axes of the rolling bearing vibration system
2 局部损伤模型及响应分析
2.1 轴承损伤建模
轴承长期服役由于交互应力作用会出现疲劳剥落等局部损伤,在损伤接触域θd中,载荷作用会激发短时冲击,冲击可以表示为

对内圈处的局部损伤诱发振动可表示为

设kd为动荷系数,其大小与损伤类型、形状及尺寸等因素有关,通过调整kd的值可以模拟不同损伤程度;ε为载荷分配系数;β为外圈局部损伤角位置,根据文献[15]则有
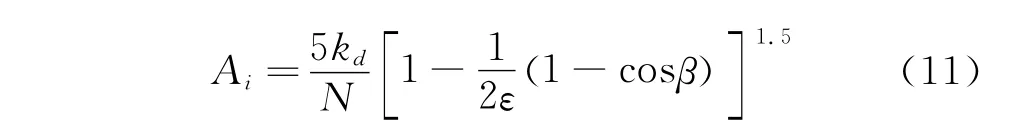
内圈接触角为

外圈处局部损伤诱发冲击序列可表示为
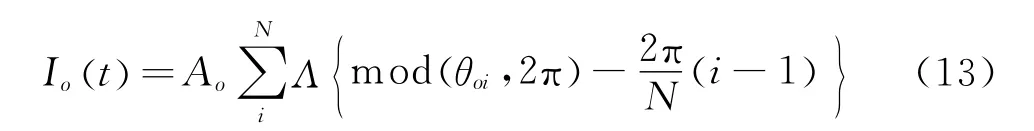

滚动体自转时损伤处会与内、外圈作用而激发两个序列,同内、外圈作用时产生的脉冲大小不同,表达式为

轴承外圈与支座固定,因此外圈接触角为

2.2 轴承预测响应分析
上述轴承损伤建模方法可以根据设计参数预测各种损伤信号,表现在模型上相当于把式(5),(7)中的游隙c增加损伤激励冲击序列,使得

钢球损伤总的振动冲击序列为
轴承诊断首要的任务是根据轴承损伤信号的特点选择可行的处理方法。预测模型从动力学角度描述了轴承损伤的内在涵义,这对时序方法的选择十分有益。以SKF6205-2RS深沟球轴承为研究对象进行算例分析,有关参数为:转轴质量ms=5.5 kg,轴承阻尼cs=877.6 Ns/m,内圈直径为25.001 mm,外圈直径为51.998 mm,厚度为0.5906 mm,钢球直径Db= 7.94 mm,节圆直径Dp=39.039 mm,支座质量mo= 12.638 kg,支座阻尼co=1796 Ns/m,支座刚度ko= 12.3×106N/m,轴承游隙e=0.1um,钢球个数N= 9,转速为1796 r/min,径向载荷Fx=650 N,Fy= 500 N,轴承为普通轴承钢制。式(8)非线性很强,难以得到解析解,通过Runge-Kutta数值方法获取系统响应。
轴承从正常演化为异常,在波形和谱图上会显示一定的规律。图3对应正常状态轴承的振动,显然从波形中看不出冲击成分,这时轴承的振动主要由转频fs和变柔度振动频率[13]及其谐波组成。这是因为在径向载荷的作用下,各钢球的受力情况是不一样的,随着钢球上的某一点的运动位置不同受力情况亦不一样。随着钢球相对于径向载荷作用线的移动,轴承刚度以数倍于钢球沿静止套圈转动的频率呈周期性变化。文献[13]研究证明,当转速远离临界转速时,轴承振动频率表现为变柔度振动频率振动和它的谐波。

图3 正常状态波形与谱图Fig.3 Waveform and spectrum of normal signal
以外圈为例进行损伤模拟,图4为模拟信号波形和功率谱图。与正常状态相比,其特点是时域为一系列有一定时间间隔的周期性冲击波形,循环周期T=1/fo与损伤频率相对应,这是由于损伤接触产生冲击能量所致。谱图主要为转频fs,损伤特征频率fo=0.5 N 1-d/D()
pfs=105.8 Hz及其高次谐波与调制成分。在承受来自钢球方向的接触载荷作用下,轴承支座处产生弯曲变形,并与滚动体一起旋转而产生振动。Fukata二自由度方程实质上描述了转轴处的运动,缺乏式(8)耦合效应,因此振动频率表现为低频成分,反映不出损伤的循环周期冲击与钢球-支座振动的高频调制。图4中,因为冲击能量较弱,低频处谱线被轴承其他振动成分压制。同时,损伤接触区产生的脉冲冲击力受到载荷分布的调制,冲击响应为一种单边振荡衰减波形,是局部化的,通过图5可以明显看出特征频率的各次谐波。

图4 外圈损伤信号波形与谱图Fig.4 Waveform and spectrum of outer ring damage signal

图5 外圈损伤信号包络谱图Fig.5 Envelope spectrum of outer ring damage signal
3 自相关Haar小波原理
使用与信号波形最相似的基函数对信号分解,提取隐含异常特征是特征波形混合基分解的精髓[16]。小波函数中Haar小波在支撑域上是单位矩形波,标准的Haar小波为

Haar小波在时域中不连续,且为方形波,如图6所示。连续Haar小波特有的时间(平移)和尺度的周期性可以充分展示信号中的周期性冲击成分及其特点,用这种小波来分析由滚动轴承局部损伤而诱发的周期性冲击振动有着其他小波不具备的特定优势。

图6 Haar小波波形Fig.6 Waveform of Haar wavelet
3.1 连续Haar小波变换周期性
与二进离散小波相比,连续小波具有以下两个方面的优势[14]:a.连续小波变换的分割是使窗长按尺度减低方向逐渐减少的,在尺度划分上比二进小波更加精细,信息冗余度高,对时间-尺度特性体现更加直观,适合瞬态成分检测;b.二进小波要求基函数正交并且不具有“时不变”特性,对不确定时刻信号检测时,则要求小波的时不变性。对于标准Haar小波,幅值变化最大倍数为2,设轴承损伤信号为s( t),因此s( t)的Haar小波变换在时间b上是以T为周期,在尺度j上以2T为周期的[17],即

其中:n为自然数。
图7为损伤信号局部放大图,可以清晰看出周期性冲击分量和轴承阻尼作用使冲击波形衰减。可见,对一个固定的尺度,当Haar小波沿时间移动整周期时,内积是不变的,形成了时间上的周期性。同理,尺度整周期变化时由于整周期部分的内积互相抵消,总的内积仍保持不变,从而形成了尺度上的周期性。对损伤信号连续Haar小波变换正是利用时间-尺度上的周期性,将滚动轴承周期冲击衰减模式提取出来。

图7 损伤信号时间周期性表示Fig.7 Time periodic expression of damage signal
3.2 连续Haar小波自相关分析及应用
诊断实践表明,滚动轴承正常信号峭度值约为3,近似为高斯信号。除了轴承自身转频和变柔度振动外,还有许多随机性干扰,有效去除可以大幅提高诊断的准确性[14-16]。利用Haar小波变换提取周期性冲击成分,利用自相关消噪可以预除噪声干扰,两者结合可对轴承早期损伤进行精确识别。
时间序列()s t按时间平均计算的各态历经随机过程的自相关函数[1]为

s( t),Rs(τ)中包含损伤信息,由于噪声与噪声之间的不相关性会随着时间延迟而很快衰减为0,并且不需要任何关于信号与噪声的谱分布和概率分布的先验知识。
自相关连续Haar小波处理流程如图8所示,对图4外圈损伤信号加强噪声干扰来模拟轴承早期损伤,图9为波形和谱图。可见,冲击成分被大量噪声掩盖,直接进行谱分析难以提取出特征谱线。将信号进行连续Haar小波变换,如图10所示。可以看出,两图中均有等间隔的脉冲成分,但是噪声干扰使图10(a)分辨率不高,自相关处理后图10(b)的等间隔冲击成分显示清晰,周期约为0.009 5 s与损伤频率一致。为了谱分析的需要,需要计算尺度与频率的对应关系[16]

图8 连续自相关Haar小波流程图Fig.8 The flow of autocorrelation-Continuous Haar wavelet

图9 模拟信号波形与谱图Fig.9 Waveform and spectrum of simulation signal
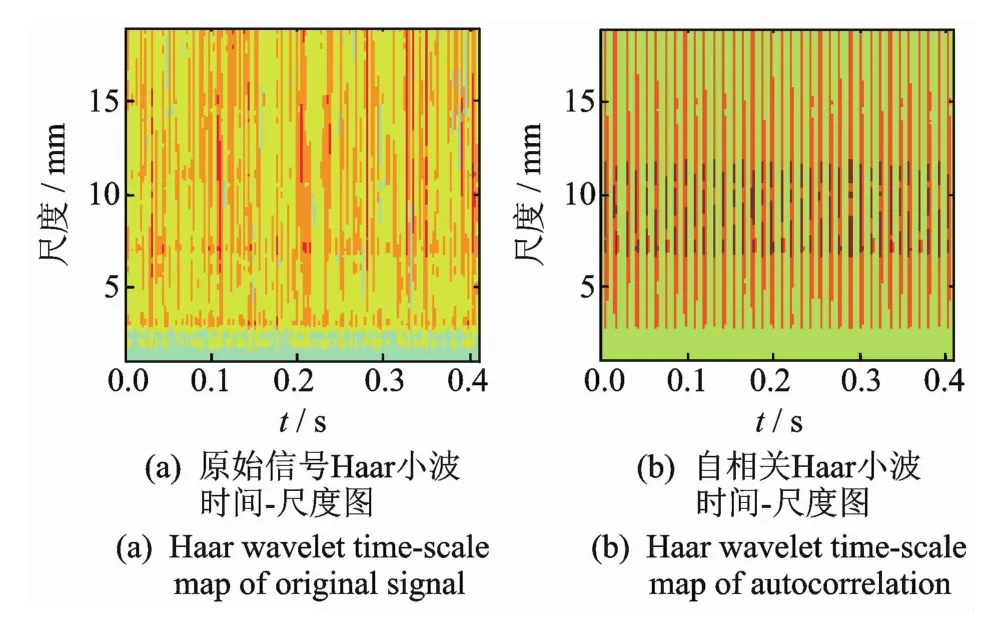
图10 模拟信号Haar小波时间-尺度图Fig.10 Haar wavelet time-scale map of simulation signal

其中:fj为尺度j对应的频率;fc为小波的中心频率;δt为采样周期。
选择冲击特征明显的尺度进行包络谱分析如图11所示。转频fs=ω/2π=29.5 Hz以及损伤频率与其高次谐波清晰可辨。可见,自相关连续Haar小波变换在提取淹没在强大背景噪声中的微弱周期性冲击成分是有效的,且Haar小波形式简单,运算方便,非常适合于基于图像的在线监测系统。
4 实 验
实验数据来源于美国凯斯西储大学轴承研究中心[18]。该中心提供了深沟球轴承正常与内外圈、钢球损伤的实验数据,并设置了轴承的不同损伤程度以供研究者使用。实验装置如图12所示,实验轴承支承电动机转轴,电动机风扇端和驱动端的轴承座上方各放置一个加速度传感器来采集轴承的振动加速度信号。分析的为6205-2RS JEM SKF深沟球轴承,转速为1 772 r/min,采样频率为12 k Hz,结构参数见文献[18]。图13为轴承早期损伤信号的时域波形。由于在确定尺度下连续Haar小波整周期移动的内积不变,对不同的信号连续Haar小波沿一个周期移动内积变化不同,因此导致不同信号在其时间-尺度图上具有不同的特征。图14为各种状态的自相关连续Haar小波时间-尺度图。可以看到,各种状态在图形中得到了明显区分,正常情况主要表现为谐波形式;损伤状态下均有等间隔的冲击产生,其余信号成分的能量在图形上产生了发散。这样利用连续Haar小波所特有的时间-尺度周期性加之自相关消噪就可以分离弱冲击。

图11 自相关连续Haar小波处理后谱图Fig.11 Spectrum of autocorrelation-continuous Haar wavelet processing
当滚动轴承在转速为1 772 r/min时,钢球内外圈损伤频率分别为139.205,159.928和105.871 Hz。从图15可以看出,表征钢球轻微故障的特征信息已被完全淹没在振动信号中,即使145.9 Hz附近都没有明显的谱峰,自相关连续Haar小波处理后选择相应尺度谱分析可以清楚地观察到轴承钢球损伤特征频率139.2 Hz。利用自相关连续Haar小波对内、外圈损伤进行识别[19-20],如图16,17所示。可见,特征频率非常明显,谱峰突出,与实际损伤类型相符。

图12 实验装置Fig.12 Experimental apparatus
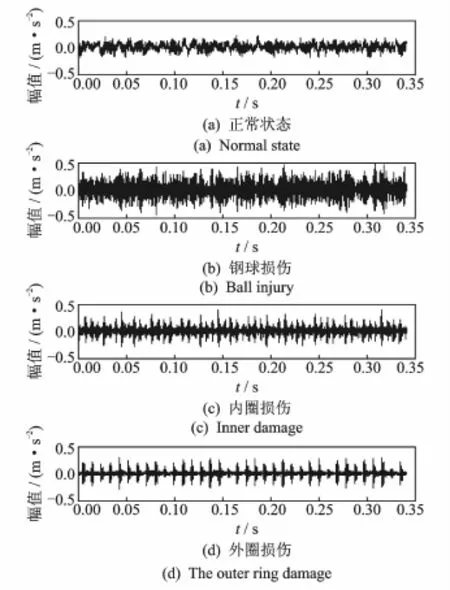
图13 典型型号时域波形Fig.13 Typical time domain waveform

图14 实验信号自相关连续Haar小波时间-尺度图Fig.14 Haar wavelet time-scale map of test signal
5 案例分析
滚动轴承的服役性能是复杂工况下运动行为的综合体现,贯穿于设计、制造、装调和服役整个寿命周期。出厂前的全寿命周期实验是轴承企业掌握轴承服役行为的重要途径。ABLT-1A型全寿命轴承实验机可以测试到轴承从正常到失效的全寿命周期振动信号,实验现场如图18所示。ABLT-1A型试验机一次能实验4个轴承,4个测试轴承都为6309深沟球轴承,实验机转速为3 kr/min,振动信号由探针传感器直接接触轴承外圈测量,采样频率为32 k Hz。

图15 钢球损伤频谱Fig.15 Spectrum of the ball damage signal

图16 内圈损伤频谱Fig.16 Spectrum of the inner ring damage signal

图17 外圈损伤频谱Fig.17 Spectrum of the outer ring damage signal
图19(a)为监测到的振动信号。由于测试过程中噪声很大,因此监测到的振动信号杂乱无章,冲击特征信号基本被完全淹没,得不到有用的失效信息。经自相关-连续Haar小波消噪后,大量噪声被剔除,可以观察到多个明显的冲击且具有一定周期,如图19(b)和(c)所示。对滤波后的信号进行包络谱分析,谱图中特征频率及其倍频分量突出,这与外圈故障频率相吻合,因此可以认定实验轴承的外圈已经损伤,结果与现场实际情况相吻合。

图18 实验现场Fig.18 Experimental site

图19 使用提取方法测得信号的消噪结果Fig.19 De-noising measured results of signal using the extraction method
6 结 论
1)在已有的二自由度方程基础上建立了滚动轴承局部损伤的预测模型,该模型可预测不同状态下轴承振动响应。分析了预测响应及其规律,指出滚动轴承正常信号是由转频和变柔度振动频率及其谐波组成,没有冲击特征;损伤振动信号本质上为循环的周期性脉冲序列,是损伤特征频率及其高次谐波的组合和调制。
2)论证了连续Haar小波变换在时间-尺度上的周期性,运用这种特定优势有效提取了滚动轴承周期性冲击模式。在基函数相似匹配的基础上揭示了小波选择深层次的理论,丰富了小波选择的思路。
3)冲击振荡信号在时间-尺度域的图形特征便于在谐波干扰下突出冲击成分。自相关处理不需要任何关于信号与噪声的谱分布和概率分布的先验知识,就能高效去除噪声,用于信号预处理,增强了连续Haar小波时间-尺度图的冲击特征。实践表明,该方法在滚动轴承弱冲击提取方面有较好的应用前景。
[1] 陈果.滚动轴承早期故障的特征提取与智能诊断[J].航空学报,2009,30(2):362-367.Chen Guo.Feature extraction and intelligent diagnosis for ball bearing early faults[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2009,30(2):362-367.(in Chinese)
[2] 陈予恕.机械故障诊断的非线性动力学原理[J].机械工程学报,2007,43(1):25-34.Chen Yushu.Nonlinear dynamic principle of mechanical fault dianosis[J].Chinese Journal of Mechanical Bngineering,2007,43(1):25-34.(in Chinese)
[3] McFadden P D,Smith J D.Model for the vibration produced by a single point defect in a rolling element bearing[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1984,96(1):69-82.
[4] Mc Fadden P D,Smith J D.Model for the vibration produced by multiple point defects in a rolling element bearing[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1985,98(2):263-273.
[5] Kiral Z,Karagulle H.Simulation and analysis of vibration signals generated by rolling element bearing with defects[J].Tribology International,2003,36:667-678.
[6] Su Y T,Lin M H,Lee M S.The effects of surface irregularities on roller bearing vibrations[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1993,163(3):455-466.
[7] Randall R B,Antoni J,Chobsaard S.The elationship between pectral correlation and envelope analysis for cyclostationary machine signals application to ball bearing diagnostics[J].Mechanical Systems and System Processing,2001,15(5):945-962.
[8] Rahnejat H,Gohar R.Vibration of radial ball bearings [J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science,1985,199:181-193.
[9] Rahnejat H.Computational modelling of problems in contact dynamics[J].Engineering Analysis,1985,2:192-197.
[10]Ashtekar A,Sadeghi F,Stacke L E.A new approach to modeling surface defects in bearing dynamics simulations[J].Journal of Tribology-Transactions of the ASME,2008,130:1-8.
[11]Rafsanjani A,Abbasion S.Anoushiravan farshidianfar nonlinear dynamic modeling of surface defects in rolling element bearing system[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2009(319):1150-1174.
[12]Kral Z,Karagulle H.Vibration analysis of rolling element bearings with various defects under the action of an unbalanced force[J].Mechanical System and Signal Processing,2006(20):1967-1991.
[13]Fukata S,Gad E H,Kondou T,et al.On the radial vibration of ball bearings(computer simulation)[J].Bulletin of the JSME,1985,28:899-904.
[14]隋文涛,张丹.总变差降噪方法在轴承故障诊断中的应用[J].振动、测试与诊断,2014,34(6):1033-1037.Sui Wentao,Zhang Dan.Total variation denoising method and its application in fault diagnosis of bearings[J].Journal of Vibration,Measurement&Diagnosis,2014,34(6):1033-1037.(in Chinese)
[15]屈梁生.机械监测诊断中的理论与方法[M].西安:西安交通大学出版社,2009:28-32.
[16]Harris T A.Rolling bearing analysis[M].3rd ed.New York:Wiley,2001:53-54.
[17]张永芳,周世生,吕延军.轴向槽气体润滑轴承-转子系统非线性行为[J].振动、测试与诊断,2013,33(2):219-223.Zhang Yongfang,Zhou Shisheng,LüYanjun,et al.Nonlinear dynamic behaviors of rotor system supported by self-acting gas-lubricated bearings with axial grooves[J].Journal of Vibration,Measurement&Diagnosis,2013,33(2):219-223.(in Chinese)
[18]何正嘉,訾艳阳,张西宁.现代信号处理及工程应用[M].西安:西安交通大学出版社,2007:33-36.
[19]程正兴.小波分析与应用实例[M].西安:西安交通大学出版社,2006:11-14.
[20]温廷新,王俊俊.滚动轴承故障诊断优化仿真研究[J/OL].[2012-06-15].http://www.eecs.case.edu/laboratory/bearing/download.html.

Abstract A cone-shaped MDOF-USM(multi-degree-of-freedom ultrasonic motor)is designed for research and application.The single-foot drive mode is adopted on the stator.A four-quadrant piezoelectric stack is employed as the exciting element to generate two-dimensional linear motion,and its movement mechanism is analyzed.The parametric model of the MDOF-USM is set up in ANSYS,and the finite element model is imported into the Optimus(a multi-disciplinary optimization software).Optimization results indicate that the design requirements of the MDOF-USM are fulfilled.Finally,a MDOF-USM is successfully manufactured and applied to an x-y platform.
Keywords ultrasonic motors;multi-degree of freedom;optimal design;Optimus;x-y platform
Abstract To provide a real loading environment for structural design,product life estimation and health assessment,it is important to correctly identify the dynamic load and its position.In this paper,the fre-
quency domain method is used to study dynamic load position determination,and an equivalent load error method based on the vibration characteristic of the linear elastic system is proposed.This method constructs an object function with equivalent load error values at the same location from different measuring points.The actual position is where the equivalent load error is the smallest.Simulation on the tablet is perfect with both single point drive and double points one,and the method is still valid when noise is added.It provides the basis for complex structures and the determination of multiple loading locations.The experimental verification on a simply supported beam shows that this method can correctly identify the dynamic load location,is not sensitive to noise,and has good prospects for engineering applications.
Keywords load identification;position determination;equivalent load;frequency domain method
Abstract The floor of a car body experiences an abnormal vibration when a metro accelerates and brakes,which significantly deteriorates riding comfort.Theoretical analysis and field experiments are conducted to study this abnormal vibration,with resolution promoted and validation measurements.The short-time Fourier transform(STFT)time-frequency method is applied to tested data.It shows that the excitation of the abnormal floor vibration comes from the twice frequency of motor rotation.A mathematical model consisting of the motor shaft and gear rotor connected by a coupler is built to study the rotary dynamics of the traction system of the railroad vehicle's powered bogie.Analysis illustrates that the dynamics in the traction system experience a shaft misalignment between the motor shaft and gear rotor.The output torque of the gear rotor is obtained and shows that this misalignment can result in even frequencies oscillation of motor shaft rotation with the twice frequency dominated.The measurement is explained by the analysis,and it is shown that the abnormal vibration can be alleviated by eliminating this misalignment.Validation measurements are conducted after eliminating the misalignment and show that the twice frequency vibration of motor rotation dropp significantly,which reduces the root mean square and amplitude of acceleration of the car body floor by 41%and 53%,respectively.The measurements agree with the theoretical analysis,and a high level of riding comfort is obtained.
Keywords metro;car body;coupler;misalignment
Abstract The dispersion and multimode nature of a guided wave makes the analysis and identification of guided wave echoes complex.This paper proposes an echo identification method based on the frequency domain phase tracking.First,the frequency domain phase of the analyzed signals is extracted and normalized to the referenced signals of the direct propagation wave-packet.Then,the normalized values are pres-ented in an order spectrum.Finally,the location and recognition of each echo is determined with the analysis of the propagation path in the propagation medium.Simulation analysis and experimental results demonstrate the applicability and effectiveness of the proposed method.
Keywords Ultrasonic guided waves;dispersion characteristic;phase shift tracking;echo identification
Abstract Aiming at the end effect and mode mixing of empirical mode decomposition(EMD)in practical applications,an improved EMD method consisting of the following techniques is proposedafter analyzing several solutions.First,short signals are extended with genetic support vector regression,then an ensemble EMD combined with an alternative envelope for the sifting procedure is employed to process the extended signals.The simulation results of two nonlinear and one simulated fault signals,as well as comparisons with other EMD methods,verify the capability of the proposed method to alleviatethe end effect and mode mixing.Applying the proposed method and envelope analysis to fault diagnosis of the ball bearing with an inner raceway defect,the results demonstrate the superiority of the method in extracting fault characteristic information for engineering applications.
Keywords empirical mode decomposition;end effect;genetic support vector regression;mode mixing;envelope fitting;fault diagnosis
Abstract Variable predictive model based class discrimination(VPMCD)is a pattern recognition method that utilizes the inner relations among characteristic values extracted from the original data.In this paper,VPMCD and independent component analysis(ICA)are combined with the correlation coefficient in order to diagnosis the rolling bearing fault.First,the ICA is used to analyze vibration signals with different fault categories,and the independent components are extracted from each category.Second,the correlation coefficients are extracted from the samples and independent components of each category.The sum of the absolute values of the correlation coefficients is used as a characteristic value.Finally,the VPMCD classifier is used to recognize and classify the faults.The experimental results show that this method can be effectively applied to rolling bearing fault diagnosis.
Keywords variable predictive model based class discriminate;independent component analysis;correlation coefficient;rolling bearing;fault diagnosis
Abstract In the fault diagnosis of a hydro-turbine generating unit(HGU),kernel clustering is a valid non-supervised learning method.In order to solve the problems of kernel parameter selection and cluster center calculation,a novel electromagnetism-like artificial bee colony weighted kernel clustering(EAWKC)is proposed.First,after considering the influence of different symptoms,the data is weighted,and the clustering model is built based on the kernel Xie-Beni clustering index.Then,the electromagnetism-like artificial bee colony(ELABC)method is proposed and introduced in order to solve the objective function to realize the synchronized optimization of the clustering center,symptom weight and kernel parameter.The classification accuracy of EAWKC is checked by three of the UCI testing data sets and the HGU fault samples,and compared with the traditional method.The experimental results show that EAWKC has higher accuracy and can effectively complete the fault diagnosis.
Keywords hydroelectric generating unit;fault diagnosis;mercer kernel;weighted kernel clustering;electromagnetism-like artificial bee colony(ELABC)
Abstract In order to diagnose the abnormal noise of a certain type of diesel generating set,a new method of empirical mode decomposition(EMD)and Hilbert transform is proposed to analyze the non-stationary vibration signals of the generator main bearing,which can effectively extract the time-frequency characteristics of main bearing vibration signals.Comprehensive analyses are made based on the signals of diesel generating set noise,generator main bearing vibration and shaft system torsional vibration.The diagnostic results show that the torsional vibration amplitude values of the shaft system are too high,with diesel engine excitation causing the relative motion of pin coupling rubber parts surfaces.This procedure can produce dry friction force,which leads to the intermittent abnormal vibration noise of the shaft system.This method has reference value for the abnormal vibration noise diagnosis caused by friction of the rotary shaft system components.
Keywords vibration noise;empirical mode decomposition(EMD);Hilbert transform;time-frequency characteristic;diagnosis
Abstract A novel method is proposed for finite element model updating and structural damage identification.The second generation wavelet is used as a platform for the multi-resolution representation of the updating information.This method reduces the uncertainty of the model updating process.At the lower level of resolution,the updating curve of stiffness is represented by a limited number of scaling and wavelet coefficients,which are realized with the generic algorithm(GA).The complex finite element model is simplified by matching a number of modal parameters for easy manipulation in the updating process.Then,damage identification is carried out based on the simplified model.An example of a box girder with variable cross-sections is given for varying sectional properties to show the effectiveness of the proposed method.The results indicate that the proposed method is stable against variations in crack depth and changes in the number of concentrated cracks.The method is also suitable for the identification of multiple groups of cracks.
Keywords model updating;damage identification;multi-resolution analysis;wavelet
Abstract The rotor inter-turn short circuit fault is one of the main electrical faults of turbo-generators.It can cause the unbalanced electromagnetic force to act on the rotor,leading to rotor vibration and even greatly affecting the security of the generator and power system.The accurate calculation of the electromagnetic force is significant for the stability of the generator and power system.By establishing the generator finite element model,the operation of the generator under a rotor winding short-circuit fault is simulated.The changes of magnetic field lines and air-gap field density are analyzed for the impacts of short position,short circuit number of turns and excitation current on the electromagnetic force.The equivalent magnetic flux method and the magnetomotive force superposition method are compared and come up with some improvements for the equivalent magnetic flux method.The calculation results of the unbalanced electromagnetic force by the two methods are compared with the results of the finite element method,and reasons for the difference are pointed out.
Keywords rotor inter-turn short circuit fault;unbalanced electromagnetic force;the finite element method;the equivalent magnetic flux method;the magnetomotive force superposition method
Abstract In order to analyze the multi-component and multi-modulation characteristics of a gearbox fault signal,an optimal wavelet demodulation method based on singular value decomposition(SVD)is proposed.In this method,Morlet wavelet transform is used as an adaptive band-pass filter to extract the impact component in the geabox vibration signal.The minimum Shannon entropy is used as the wavelet timescale resolution index to optimize the Morlet wavelet parameters.Based on SVD,the optimal wavelet coefficient is utilized to determine the parameters.The new method can extract transient information better,reduce noise,effectively extract the signal period,and assure the validity of the fault feature recognition.The experimental results show that the proposed method can more accurately and effectively extract the fault characteristic hidden in the gearbox vibration signal.
Keywords singular value decomposition;continuous wavelet transform;parameter selection;feature extraction
Abstract Shaft orbit recognition is an important approach for the vibration state judgment of steam turbines.Extracting the features of shaft orbit images is not an easy task,and the traditional feature extraction methods are not perfect in comprehensiveness,accuracy and stability.In order to overcome these problems,a feature extraction method based on imitating human eyes is proposed for the steam turbine.This method imitates human eyes to extract the most important information of the image structure,boundary and region,and realizes the shape characterization comprehensively and accurately through full integration of the information.Three intelligent classification methods are used to test the effectiveness of the proposed method,and the experimental results prove that this feature extraction method for steam turbine is simple,efficient and accurate.
Keywords steam turbine;shaft orbit;condition monitoring;feature extraction;imitating human eyes
Abstract This paper presents a neural sliding mode control method for the mechanical arm with a non-singular inversion terminal in order to realize the trajectory tracking of a multi-joint robot arm with external
interference and modeling errors.First,an inversion-sliding-mode controller with a non-singular terminal sliding surface is designed based on the inversion method and the principle of sliding mode control.Then,the radial basis function(RBF)neural network adaptive law is designed against the uncertainty in the inversion sliding mode control system due to its modeling errors and external interference.The upper bound of this uncertainty is estimated online.Finally,the stability of the control system is proved using the Lyapunov Theorem.Simulation analysis and experimental results show that the proposed method can not only eliminate the chattering phenomenon in the system,but also improve its tracking performance and robustness.
Keywords inversion of control;neural network;sliding mode control;non-singular terminal
Abstract In environmental shaker testing applications,sigma clipping of the shaker drive signal is used to protect the test system.However,the clipped signal spectrum will no longer correspond exactly to the given power spectral density(PSD).This may cause reduced vibration test reliability and even the wrong results,especially for modal tests.Both the power spectrum equalization control algorithm and PID control strategy are presented in order to compensate for the difference between certain spectra and the clipped specification.The results show that,in the case of Gaussian random signals,the two methods show almost the same compensation effect in terms of minimum error and iterative steps.For non-Gaussian random signals,however,the PID control strategy obtained fewer iterative steps and minor errors.
Keywords clipping;Gaussian signal;Non-Gaussian signal;power spectrum equalization;PID control
Abstract It is of great importance to useany prior information effectively and reasonably in the evaluation of small samples.Therefore,a new testability evaluation method based on mixed Beta prior distribution is presented,while considering both the credibility and the importance of prior information as well as the testability evaluation of complex equipment in small samples.The results show that,according to classical methods using small binomial samples,the lowerconfidence limits of product testability are conservative.Most of the measurements for the credibility of the prior information are based on data.The evaluation results are aggressive due to the missing sources of prior information.Thus,the conclusion is reasonable,and this method is promising for engineering applications.
Keywords testability evaluation;small sample;credibility;importance;mixed Beta distribution
Abstract In the processing of fault vibration signals,an improved CBI-LMD(cubic B-spline interpolation local mean decomposition)method based on self-adaptive waveform matching and an orthogonality criterion is proposed to combat the low decomposition accuracy of the cubic spline interpolation-based local mean decomposition(CSI-LMD)method.First,the raw vibration signal is extended with a self-adaptive waveform matching technique.Next,instead of CSI,the CBI is used to calculate the local means and envelope functions.Finally,the orthogonality criterion is used to set a stopping criterion for the product function.Simulation and experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively extract more accurate feature information in less time than CSI-LMD.
Keywords local mean decomposition;cubic B-spline interpolation;orthogonality criterion;fault rotor;vibration analysis
Abstract Aiming at the multi-functional properties of Pb-based lanthanumdoped zirconate titanates(PZT)sensors in concrete for structural health monitoring,which enable the sensors to simultaneously receive signals with different functions,a method for extracting the signals for variant purposes in the multi-functional PZT sensors is proposed.Because there is a difference in frequency ranges from different function signals,the vibration signal related to the overall structure performance and the acoustic emission signal associated with local damages are acquired based on the Mallat algorithm.The correctness of the extracted signals is verified by comparing with those from accelerometers and acoustic emission sensors.In addition,the proposed method is applied to the seismic damage experiment of a reinforced concrete frame-shear structure.The experimental results show that the vibration signal acquired by the proposed method can abstract the frequency of the structure.Meanwhile,the acoustic emission signal abstracted from PZT sensors can monitor the released energy caused by local damage.It can be concluded that the vibration signals and acoustic emission signals can be extracted using the proposed method,and the evaluation of the overall dynamic performance and local damage can be realized.
Keywords PZT sensors;wavelet analysis;acoustic emission;vibration test
Abstract Based on wavelet packet analysis and wavelet packet energy,the sum square of the wavelet packet energy change rate(WPERSS)damage index is proposed.The wavelet packet is applied to extract the damage index from both healthy and damaged structures for damage detection.A simply supported beam example is simulated in different damage and noise conditions.In addition,a double pylon cablestayed bridge model is tested in three damage conditions.The results are analyzed and prove the effectiveness of the WPERSS damage index.
Keywords wavelet packet;damage detection;damage index;sum square of energy change rate
Abstract To improve the impeller milling efficiency,the zero-order analytical method to construct the milling stability lobe diagram is investigated,which is used to determine parameter optimization of the FV520B material milling.The appropriate number of revolutions and the cutting depth processing can be selected,and the chatter occurrence can be avoided.By using this method,the required accuracy and surface quality for the workpiece can be achieved,and tool safety and machine reliability can be maintained.Through experimental data analysis,the parameters to construct the lobe diagram can be obtained.Different testing points in the constructed lobes are used to verify the method's correctness.This method has great significance in the actual impeller manufacturing process.
Keywords milling chatter;stability lobes;modal analysis;FV520B
Abstract A method for realizing tool wear condition monitoring using multi-feature of the cutting sound is presented.Based on empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert transformation theories,the cutting sound signal is analyzed.The energies of intrinsic modes and Hilbert spectrum in different frequency ranges are extracted as candidatefeatures of the monitoring signal.To solve the feature selection problem,the sup-port vector machine is selected as the classifier,and the multiple population genetic algorithm is used to optimize its input features.Then,the interference features are eliminated from the candidate features.After the classifier parameters are also optimized with the multiple population genetic algorithm,the test samples are classified with the optimized classifier,and the performances of the classifiers before and after optimization are compared.The results show that the performance of the optimized classifier is significantly improved,and the method can be used effectively for identification of the tool wear condition.
Keywords empirical mode decomposition;Hilbert transformation;cutting sound;support vector machine;multiple population genetic algorithm
Abstract The mode shape functions of the elastic beams with concentrated mass and stiffness and their frequency equations under typical boundary conditions are derived with Laplace transform.Using these equations,the inherent characteristics of a cantilever beam with a spring and lumped mass are obtained.Then,its modal parameters are recognized using the NEx T-ERA(eigen system realization algorithm based on the natural excitation technique)method.The analytic and experimental results show that modal parameters change with the stiffness and location of the mass and spring.
Keywords elastic beams;concentrated masses;lumped springs;NEx T-ERA;modal identification
Abstract The dynamic responses of a light-weight,high-speedplanar parallel robot are studied based on elastodynamics and experiments.First,according to the geometric and inertial nonlinearities of the mechanism,a set of linear ordinary differential equations of motion is built,and the dynamic responses of two typical configurations are analyzed.Second,an experimental setup that includes the test-bed mechanism of a 3-RRR light-weight parallel robot and a control system is developed.Finally,the experimentally measured residual vibrations of the manipulator are compared with the numerical results.It turns out that the experimental results agree with the numerical ones at configuration two,but differ at configuration one,where the experimentally measured dynamic response is self-excited vibrationand the simulation result is damped vibration.This shows that the robot has different dynamic responses at different configurations.
Keywords planar parallel robot;high-speed;elasto-dynamic;residual vibration
Abstract In order to effectively minimize the harmful vibration caused by rotor unbalance and to monitor the balance state in real time,an embedded on-line automatic balance system for a magnetic balancer is designed based on a modular design concept.First,an embedded controller is constructed using the combination of digital signal processing(DSP)and field-programmable gate array(FPGA).At the same time,a mathematical model of an adaptive control algorithm is established based on the traditional influence coefficient method.Multithreaded balance control software and a user interface are developed using C and C# language,respectively.Lastly,the experiment is conducted on a domestic electric spindle to verify the function of the whole system.The experimental results show that the unbalance-induced vibration can decrease by 43%at 3 000 r/min.
Keywords rotor unbalance;online automatic balance;embedded control system;adaptive control;digital signal processing
Abstract While the existing de-noising algorithm requires prior knowledge of vibration signals,a new adaptive de-noising algorithm is proposed based on sparse coding and dictionary learning(DLSDF).Depending on the essential attribute of different signals,the optimal dictionary of data-driving is learned from the raw data.The orthogonal matching pursuit algorithmworks out the sparsest coefficients.Then,the de-noised signal is reconstructed using sparse coding and the optimal dictionary.Simulation and experimental results show that the algorithm based on sparse coding and dictionary learning is adaptive,and denoising is stronger than the existing one.
Keywords dictionary learning;sparse coding;adaptive de-nosing;vibration signal
Abstract Multiscale entropy has begun to play an increasingly important role in the analysis of non-sta-tionary and nonlinear vibration signals.Changes in the sample entropy of different scales can reflect changes in the transformer windings of different runnings.In this paper,a novel feature extraction is proposed,and a new and effective feature parameter is provided to efficiently and quantitatively describe faulty signals of the transformer winding.The results of analyzing the experimental data of the winding vibration show that compared to sample entropy,multiscale entropy can efficiently realize the feature extraction of faulty signals.Therefore,it is feasible to introduce the effective feature parameter into the use of transformer winding vibration signal analysis.
Keywords multiscale entropy;transformer winding;vibration signal;feature extraction;effective feature parameter
Abstract To analyze milling chatter stability lobes and surface location error with worn tools,the cutting force coefficients under different worn conditions are identified using the full-discrete method.The stable critical cutting depth of the milling system increases after normal wear,and gradually declines as the work piece surface hardness increases.Then,the difference in the critical cutting depth between the normal wear tool and the wear free tool flank gradually becomes small.In addition,surface location error appears in some stable regions.Experimental results prove that the theoretical model can effectively optimize machining parameters with varying wear loss of the milling cutter.
Keywords milling cutter wear;full-discrete method;chatter stability lobes;surface location error
Abstract This paper proposes a method based on singular value decomposition technology in order to solve the hard target penetration overload signals de-noising problem.First,the signal reconstruction submatrix is established based on the principle of stability of the main singular components.Second,the″dominant of the former K singular values energy″rule is used to extract the effective order of singular value.Penetration signals are then decomposed based on the previous steps.Finally,the signal is reconstructed using the extracted effective singular values.Experiments show that the proposed method can effectively eliminate the vibration and noise hiding in the penetration process.The proposed method can get a better signal to noise ratio than when using the wavelet transform,as well as the exact penetration depths of the experiments.Ultimately,the proposed method is a feasible new method on penetration fuse signals processing.
Keywords penetration overload signals;singular value decomposition;signal reconstruction;signal to noise ratio
Abstract A method for flood discharge structure in the time domain is proposed in order to identify the operating modal parameters of high dams.First,useful information of the vibration signals is obtained by filtering the white noise and flow fluctuating noise using the wavelet threshold empirical mode decomposition filtering method.Then,the natural frequency and damping ratio of the system are identified using Hilbert-Huang transform(H HT).Finally,the modal orders and operating modal parameters of the flood discharge structure are determined using the singular entropy increment theory.Simulation results show that this method has strong robustness and superior precision,and can effectively avoid frequency confounding.Its successful use on the No.5 overflow section of the Three Gorges gravity dam provides the basis of the safe operation and online dynamic non-destruction monitoring of the high dam flood discharge structure.
Keywords flood discharge excitation;operating modal;parameter identification;wavelet threshold-empirical mode decomposition filtering;Hilbert-Huang transform
Abstract The state models of the SKF6205-2RS deep groove ball bearing are set to predict the location and degree of its damage based on the Hertzian contact deformation theory,elastic theory and the geometry of the rolling bearing.Next,the system response is obtained using the Runge-Kutta numerical method.The calculation results prove that the frequency and harmonic components of the local damages of the inner ring,outer ring and ball under radial loads are well predicted.Moreover,the bearing vibration laws under different conditions are introduced to prove the periodicity of the continuous Haar wavelet transform.Finally,an autocorrelation continuous Haar wavelet method is proposed for early damage signals exacting of rolling bearings.The proposed approach is successfully applied to noise reduction and weak impulse feature extraction of bearing signals.
Keywords rolling bearing;prediction model;continuous Haar wavelet;autocorrelation denoising;weak impulse component
Advance in Electrokinetic Phenomena and Theory
Guo Wanlin1,2,Fei Wenwen1,2
(1.State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures,Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing,210016,China)
(2.Key Laboratory for Intelligent Nano Materials and Devices of the MOE,Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing,210016,China)
Electrokinetic phenomena are a family of dynamic phenomena that occur commonly in the interfaces of solids and ionic liquids.All the electrokinetic phenomena originate from the same source of the electrical double layer formed at the interface,and are widely used in areas such as separation of mass and protein,purification of water,detection of molecules and particles and gene sequencing.A brief historical review of the discovery of electrokinetic phenomena is firstly given here,and the development of the electrical double layer theory is described in details.The important classical electrokinetic phenomena are introduced.Especially,the newly discovered electrokinetic phenomena in graphene are introduced and compared with the classical phenomena.The review is aimed to deepen our understanding of the physical mechanisms of electrokinetic phenomena and enhance their applications.
electrokinetic phenomena;solid/liquid interfaces;electrical double layer;graphene
Optimization of a Multi-degree of Freedom Ultrasonic Motor and Its Application on a x-y Platform
Zhu Hua,Wu Wencai,Liu Weidong,Pan Song
(State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures,Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing,210016,China)
The Equivalent Load Error Method of Dynamic Load Position Determination
Jiang Qi1,2,Zhang Fang1,2,Jiang Jinhui1,2,Zhu Dechun1,2,Xu Jing1,2,Pu Yuxue1,2
(1.State Key Laboratory for Strength and Vibration of Mechanical Structures,Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing,210016,China)
(2.Institute of Vibration Engineering Research,Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing,210016,China)
Car Body Vibration Analysis Subject to Coupling Misalignment in Traction System of Metro Vehicle
Shi Huailong,Wang Jianbin,Dai Huanyun,Wu Pingbo
(Traction Power Skate Key Laboratory,Southwest Jiaotong University Chengdu,610031,China)
Echo Identification of Phase Shift Tracking for Ultrasonic Guided Waves
Bo Lin,Liu Xiaofeng,Fu Libin
(The State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmission,Chongqing University Chongqing,400044,China)
Applications of Improved Empirical Mode Decomposition in Machinery Fault Diagnosis
Ma Wenpeng1,2,Zhang Junhong1,3,Ma Liang1,3,Liu Yu1,Jia Xiaojie1
(1.State Key Laboratory of Engines,Tianjin University Tianjin,300072,China)
(2.School of Mechanical Engineering,Tianjin University of Technology Tianjin,300384,China)
(3.Renai College,Tianjin University Tianjin,301636,China)
The Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Correlation Coefficient of Independent Component Analysis and VPMCD
Cheng Junsheng,Ma Xingwei,Yang Yu
(State Key Laboratory of Advanced Design and Manufacture for Vehicle Body,Hunan University Changsha,410082,China)
Fault Diagnosis for Hydroelectric Generator Unit Based
on Electromagnetism-Like Artificial Bee Colony Weighted Kernel Clustering
Xiao Han1,2,Fu Junfang1,Cai Daquan1,Zhou Jianzhong2,Xiao Jian2,Fu Wenlong2
(1.Henan Electric Power Survey and Design Institute Zhengzhou,450000,China)
(2.School of Hydropower and Information Engineering,Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wuhan,430074,China)
Abnormal Vibration Noise Diagnosis for Rubber Pin Coupling of Diesel Generating Set
Wen Huabing,Peng Zilong,Meng Fanlin
(School of Energy and Power Engineering,Jiangsu University of Science and Technology Zhenjiang,212003,China)
Finite Element Model Updating and Damage Identification Based on the Second Generation Wavelet Analysis
Zhang Xin,Liu Yang,Gao Danying
(School of Civil Engineering,Zhengzhou University Zhengzhou,450001,China)
Contrast of Calculation Method for Unbalanced Electromagnetic Force Under Rotor Inter-Turn Short Circuit Faults
Wan Shuting,Dou Longjiang,Zhang Yu,Zhang Chengjie,Zhou Guowei
(Department of Mechanical Engineering,North China Electric Power University Baoding,071003,China)
The Feature Extraction Method of Non-Stationary Vibration Signal Based on SVD-Complex Analytical Wavelet Demodulation
Zhao Ling1,Liu Xiaofeng2,Lou Lu1
(1.The College of Information Science and Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University Chongqing,400074,China)
(2.The State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmission,Chongqing University Chongqing,400044,China)
A Shaft Orbit Identification Method Imitating Human Eyes for Steam Turbine
Chen Xiaoyue1,2,Zhou Jianzhong2,Xiao Jian2,Fu Wenlong2,Zhang Weibo2,
Xia Xin2,Li Chaoshun2,Zhang Yongchuan2
(1.School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering,East China Jiaotong University Nanchang,330013,China)
(2.College of Hydropower and Information Engineering,Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wuhan,430074,China)
Manipulator Inversion of Non-Singular Terminal Neural Sliding Mode Control
Jia Yuqin1,2,Hu Xiaoxiong2
(1.Department of Mining Engineering,Lüliang University Lüliang,033001,China)
(2.School of Mechanical Engineering,Taiyuan University of Science and Technology Taiyuan,030024,China)
Power Spectral Density Compensation Algorithm for Signal Clipping in Vibration Test
Yan Lutao,Yang Zhipeng,Gao Fei,Liu Jie
(Beijing Institute of Structure and Environment Engineering Beijing,100076,China)
Evaluation of Complex Equipment Testability Based on Mixed Prior Distribution
Zhang Xishan1,Huang Kaoli2,Yan Pengcheng2,Lian Guangyao2,Wang Shaoguang2
(1.Four Department,Ordnance Engineering College Shijiazhuang,050003,China)
(2.One Research Room,Ordnance Technological Research Institute Shijiazhuang,050003,China)
Vibration Analysis of Fault Rotor Based on the Improved Local Mean Decomposition
Deng Linfeng,Zhao Rongzhen,Jin Wuyin
(School of Mechanical and Electronical Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology Lanzhou,730050,China)
The Analysis and Application of Multi-functional PZT Sensors for Health Monitoring of Concrete Structures
Li Xu1,Huo Linsheng1,Li Hongnan1,Bai Fenglong2
(1.Faculty of Infrastructure Engineering,Dalian University of Technology Dalian,116023,China)
(2.Dalian Building Scientific Research&Design Stock Co.,LTD Dalian,116021,China)
Wavelet Packet Energy Based Damage Detection Index for Bridge
Zhu Jinsong1,2,Sun Yadan1
(1.School of Civil Engineering,Tianjin University Tianjin,300072,China)
(2.The Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Coast Civil Structure Safety,Tianjin University Tianjin,300072,China)
Milling Stability Lobe Diagram Construction on FV520B Stainless Steel and Experimental Testing Investigation
Li Hongkun,Zhao Pengshi,Li Jingzhong,Dong Lei
(School of Mechanical Engineering,Dalian University of Technology Dalian,116023,China)
Tool Wear Condition Monitoring Based on Cutting Sound Signal and Optimized SVM
Zhang Kaifeng1,2,Yuan Huiqun1,Nie Peng2
(1.School of Mechanical Engineering&Automation,Northeastern University Shenyang,110819,China)
(2.School of Mechanical&Electrical Engineering,Shenyang Aerospace University Shenyang,110136,China)
Analytical Study and Modal Identification Experiment on Free Vibration of Beams Carrying Concentrated Masses and Springs
Wang Zhuang1,2,Hong Ming2,Xu Junchen2,Cui Hongyu2
(1.China Ship Development and Design Center Wuhan,430064,China)
(2.School of Naval Architecture Engineering,Dalian University of Technology Dalian,116024,China)
Dynamic Analysis and Experiment of High-Speed Planar Parallel Robots
Gao Mingwang1,Zhang Xianmin2
(1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Shandong University of Technology Zibo,255049,China)
(2.School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,South China University of Technology Guangzhou,510641,China)
Development and Validation of Embedded Control System for Rotor Online Automatic Balance
Fan Hongwei1,2,Jing Minqing1,Zhi Jingjuan1,Xin Wenhui3,Li Meng1,Liu Heng1
(1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Xi'an Jiaotong University Xi'an,710049,China)
(2.School of Mechanical Engineering,Xi'an University of Science and Technology Xi'an,710054,China)
(3.School of Mechanical and Precision Instrument Engineering,Xi'an University of Technology Xi'an,710048,China)
Adaptive De-noising for Vibration Signal Based on Dictionary Learning and Sparse Coding
Guo Liang1,Yao Lei2,Gao Hongli1,Huang Haifeng1,Zhang Xiaochen1
(1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Southwest Jiaotong University Chengdu,610031,China)
(2.Air-Breathing Hypersonic Technology Research Center,China Aerodynamics Research and Development Center Mianyang,621000,China)
Feature Research of Vibration Signal of Power Transformer Using Multiscale Entropy
Li Li1,Zhu Yongli2,Song Yaqi1
(1.School of Control and Computer Engineering,North China Electric Power University Baoding,071003,China)
(2.State Key Laboratory of Alternate Electrical Power System with Renewable Energy Sources,North China Electric Power University Beijing,102206,China)
The Influence of Wear Loss of Milling Cutter on Milling Stability and Surface Location Error
Wu Shi,Liu Xianli,Song Shenggang,Qu Da
(School of Mechanical and Power Engineering,Harbin University of Science and Technology Harbin,150080,China)
Research of the Penetration Overload Signals De-noising Method Based on Singular Value Decomposition
Zhao Haifeng1,2,3,Zhang Ya1,Li Shizhong1,Guo Yan1,2
(1.Faculty of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,North University of China Taiyuan,030051,China)
(2.School of Mechatronics,Nanjing College of Information Technology Nanjing,210023,China)
(3.Department of Mechanical Engineering,University of Ottawa Ottawa,K1N 6N5,Canada)
Research on Operating Modal Parameter Identification for High Dam Discharge Structure Based on the Hilbert-Huang Transform
Zhang Jianwei,Zhu Lianghuan,Jiang Qi,Zhao Yu,Guo Jia
(College of Water Conservancy,North China University of Water Conservancy and Electric Power Zhengzhou,450011,China)
Vibration Modeling of Rolling Bearing Defect and Impulse Feature Extraction
Li Xiangyang,Chen Wanqiang
(Pump Equipment Engineering Research Center of Shaanxi Province,Xi'an Aeronautical College Xi'an,710077,China)
TB17;TH133.3
10.16450/j.cnki.issn.1004-6801.2015.04.030
李祥阳,男,1972年10月生,讲师。主要研究方向为机械设计及理论。曾发表《Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on physical model and one-class support vector machine》(《ISRN Mechanical Engineering》2014,No.4)等论文。
E-mail:lxygyl@163.com
*科技部创新基金资助项目(13C26216105730);陕西省自然科学基础研究计划资助项目(2014JM2-5069)
2014-12-03;
2015-03-01
