竹叶中黄酮类化合物丰度的文献调研
2015-01-09楚秉泉庞美蓉
楚秉泉,庞美蓉,张 英
浙江大学生物系统工程与食品科学学院 馥莉食品研究院 浙江省农产品加工技术研究重点实验室 浙江省食品加工技术与装备工程中心,杭州 310058
竹为禾本科(Gramineae)竹亚科(Bambusoideae Nees)多年生草本植物,全世界约有70 多属、1200多种。全球竹林总面积达2200 万公顷,主要分布在亚洲、拉丁美洲、非洲等地[1]。我国拥有世界上最丰富的竹类资源和最为悠久的竹文化史,素有“竹子王国”之称。据统计,我国竹类资源有39 属、500余种,竹林面积约为720 万公顷,主要分布在闽浙、两广及云贵川等地区[2]。
(淡)竹叶在我国具有悠久的药用和食用历史。近20年来,竹叶有效成分及其生物学功效的研究和开发正成为一个热点领域。大量的研究表明,竹叶提取物含有丰富的黄酮、酚酸、内酯、蒽醌、多糖、特种氨基酸等生物活性成分[3,4],具有抗氧化[5-8]、抑菌[8-12]、抗衰老[13,14]、调节血脂[15,16]、保护心脑血管[17]、抗抑郁[18]、抑制食品内源性化学污染物[19]等多重功效。2002年(淡)竹叶被卫生部列入“既可用于食品也可用于药品的物品”名单,以竹叶提取物为主成分的功能性食品、饮品、保健品、日化产品不断涌现。早在2004年,竹叶抗氧化物被批准列入《中华人民共和国食品添加剂使用卫生标准》(国标GB-2760),最近(2013年底)国家食品安全标准《食品添加剂 竹叶抗氧化物》通过审定。一旦此国标正式颁发,无疑将迎来一个竹叶资源开发利用的新高潮。
黄酮类化合物是竹叶中最具代表性的活性组分[2],特征性成分为竹叶碳苷黄酮[20-23],如荭草苷(Orientin)、异荭草苷(Isoorientin)、牡荆苷(Vitexin)和异牡荆苷(Isovitexin)等[2,24]。目前,测定竹叶总黄酮含量的方法主要采用分光光度法,通常采用硝酸铝-亚硝酸钠比色法、以芦丁为对照品[35-44];测定竹叶碳苷黄酮含量的方法则多采用反相高效液相色谱法 (RP-HPLC) 以及高效薄层色谱法(HPTLC)[3,30,31]。本文综述了自1994~2013年间国内外公开发表的58 篇文献,对涉及竹亚科18 个属、91 种竹叶的黄酮类化合物含量水平进行统计分析,以期为竹叶黄酮的开发利用提供帮助和指导。
1 材料与方法
作者研读了近20年来国内外有关竹子有效成分研究的文献894 篇,其中包括SCI 收录的英文文献149 篇、中文文献745 篇,并对检测方法欠妥或有明显错误的文献进行剔除,最终选出了有关竹叶黄酮含量研究的文献58 篇。九成以上发表于2000年以后,涉及竹亚科(Bambusoideae Nees)的18 个属、91 个种(详见表1)。表1 中属和种的拉丁名均参考《中国竹类植物图志》[25],但个别竹种由于该图志中未收录,故采用原文献中的拉丁名,如烂头苦竹(Pleioblastus sp.)[26]等。

表1 竹叶黄酮研究所涉的竹种Table 1 Bamboo species related with bamboo-leaf-flavonoid studies

从表1 可见,竹叶黄酮研究涉及较多的竹种依次为箣竹属(Bambusa Retz.corr.Schreber)、刚竹属(Phyllostachys Sieb.et Zucc.)、大明竹属(Pleioblastus Nakai)和箬竹属(Indocalamus Nakai)的品种,如箣竹属(Bambusa Retz.corr.Schreber)有27 个竹种、刚竹属(Phyllostachys Sieb.et Zucc.)有17 个竹种、大明竹属(Pleioblastus Nakai)和箬竹属(Indocalamus Nakai)分别有14 个和8 个竹种被报道;而巴山木竹属(Bashania Keng f.et Yi)、筱竹(Thamnocalamus Munro)、唐竹属(Sinobambusa Makino ex Nakai)和井冈寒竹属(Gelidocalamus Wen)等则仅有个别种出现。除了竹林的分布、叶片的大小、采样的难易程度等因素的局限外,对不同地区、不同竹种开发价值的期待也会影响研究工作的倾向性。
除了对竹叶总黄酮含量进行梳理外,本文还分析了竹叶中主要黄酮类化合物的含量数据,包括荭草苷、异荭草苷、牡荆苷、异牡荆苷、槲皮素(Quercetin)、苜蓿素(Tricin)、芦丁(Rutin)和木犀草素(Luteolin)(结构如图1 所示)。
几乎所有公开发表的文献中,用于分析测试的竹叶试样均为干燥粉末,鲜叶的干燥方法略有差异。竹叶黄酮的提取多采用乙醇-水溶液、超声辅助提取和热回流提取等,但乙醇浓度、提取时间、提取功率、提取温度等则存在较大差异[26-29]。总黄酮含量测定多以芦丁为对照品,采用硝酸铝-亚硝酸钠比色法测定,黄酮类化合物含量的测定多采用反相高效液相色谱法(RP-HPLC),也有部分文献采用高效薄层色谱法(HPTLC)[3,30,31]。
本文在数据汇总处理中,未考虑立竹条件、采样季节、样品预处理、提取和测定方法等因素差异。每篇文献所报道的单个竹种的竹叶黄酮含量数据的均值即作为一个有效样本数。对于同一作者的学位论文及其发表的学术论文中的相同数据不重复统计与分析;部分文献将竹类的老叶与新叶、上部叶与下部叶分开测定,本文将其合并处理分析;少量文献将同一品种的叶样按不同竹龄进行采集,本文按不同竹龄的样品个数作为有效样本数。同时,将不同文献来源的竹叶黄酮含量的数据单位进行统一,均以干竹叶的质量分数(mg/g)计。
利用Excel 2010 软件进行数据录入,采用SPSS 19.0(SPSS Inc.Chicago)进行统计分析,黄酮含量的统计结果以5 个参数指标呈现,分别是:平均值(Mean)、标准差(SD)、中值(Median)、含量范围(Range)和有效样本个数(n)。
2 结果与讨论
统计分析的数据汇总见表2。有关刚竹属(Phyllostachys Sieb.et Zucc.)叶片总黄酮的研究最多,本文引用了30 篇文献,有效样本数达45 个;其次对箬竹属(Indocalamus Nakai)、大明竹属(Pleioblastus Nakai)、慈竹属(Neosinocalamus Keng f.)和箣竹属(Bambusa Retz.corr.Schreber)也有较多研究,而思簩竹属(Schizostachyum Nees)、巴山木竹属(Bashania Keng f.et Yi)、唐竹属(Sinobambusa Makino ex Nakai)、井冈寒竹属(Gelidocalamus Wen)和筱竹属(Thamnocalamus Munro)则均仅有1 篇文献报道。同样,在刚竹属(Phyllostachys Sieb.et Zucc.)和箬竹属(Indocalamus Nakai)叶片中,有7 种黄酮类化合物的含量被涉及。
竹叶总黄酮含量除香竹属(Chimonocalamus Hsueh et Yi)未见报道外,其余17 个属的含量范围为4.60~25.43 mg/g,其中倭竹属(Shibataea Makino ex Nakai)含量最高,思簩竹属(Schizostachyum Nees)最低。而对于竹叶中黄酮类化合物的研究,共有14 篇文献报道,涉及12 个属(见表2)。检出的黄酮化合物包括4 种主要的竹叶碳苷黄酮,其中有关荭草苷的文献10 篇,涉及6 个属,含量变化在0.30(倭竹属)~0.54 mg/g(赤竹属)之间;有关异荭草苷的文献9 篇,涉及7 个属,含量变化在0.16(倭竹属)~1.39 mg/g(箣竹属)之间;有关异牡荆苷的文献9 篇,涉及6 个属,含量变化在0.20(刚竹属)~0.65 mg/g(箬竹属)之间;有关牡荆苷的文献11 篇,涉及7 个属,含量变化在0.06(箣竹属)~0.65 mg/g(赤竹属)。且仅在箬竹属(Indocalamus Nakai)、刚竹属(Phyllostachys Sieb.et Zucc.)、赤竹属(Sasa Makino et Shibata)和大明竹属(Pleioblastus Nakai)中,4 种碳苷黄酮同时被检出,含量合计为1.23(大明竹属)~2.49 mg/g(箬竹属)。其它黄酮类化合物如芦丁、槲皮素、苜蓿素和木犀草素等也有少量报道,其中,芦丁在慈竹属(Neosinocalamus Keng f.)和箣竹属(Bambusa Retz.corr.Schreber)叶片中含量较丰富,分别为1.64 mg/g 和1.53 mg/g(详见表2)。
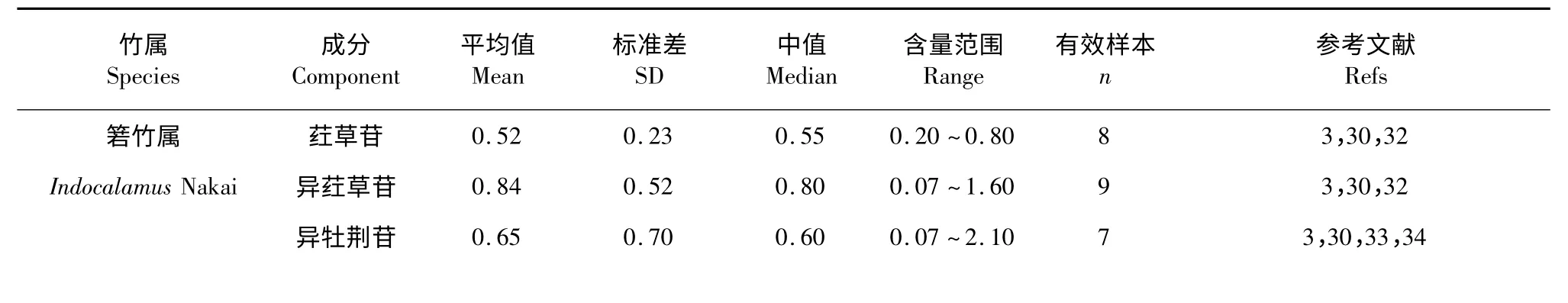
表2 竹叶中黄酮类化合物的含量水平分析(mg/g,以干竹叶计)Table 2 Analysis on flavonoid contents in bamboo leaves(mg/g·d.w)

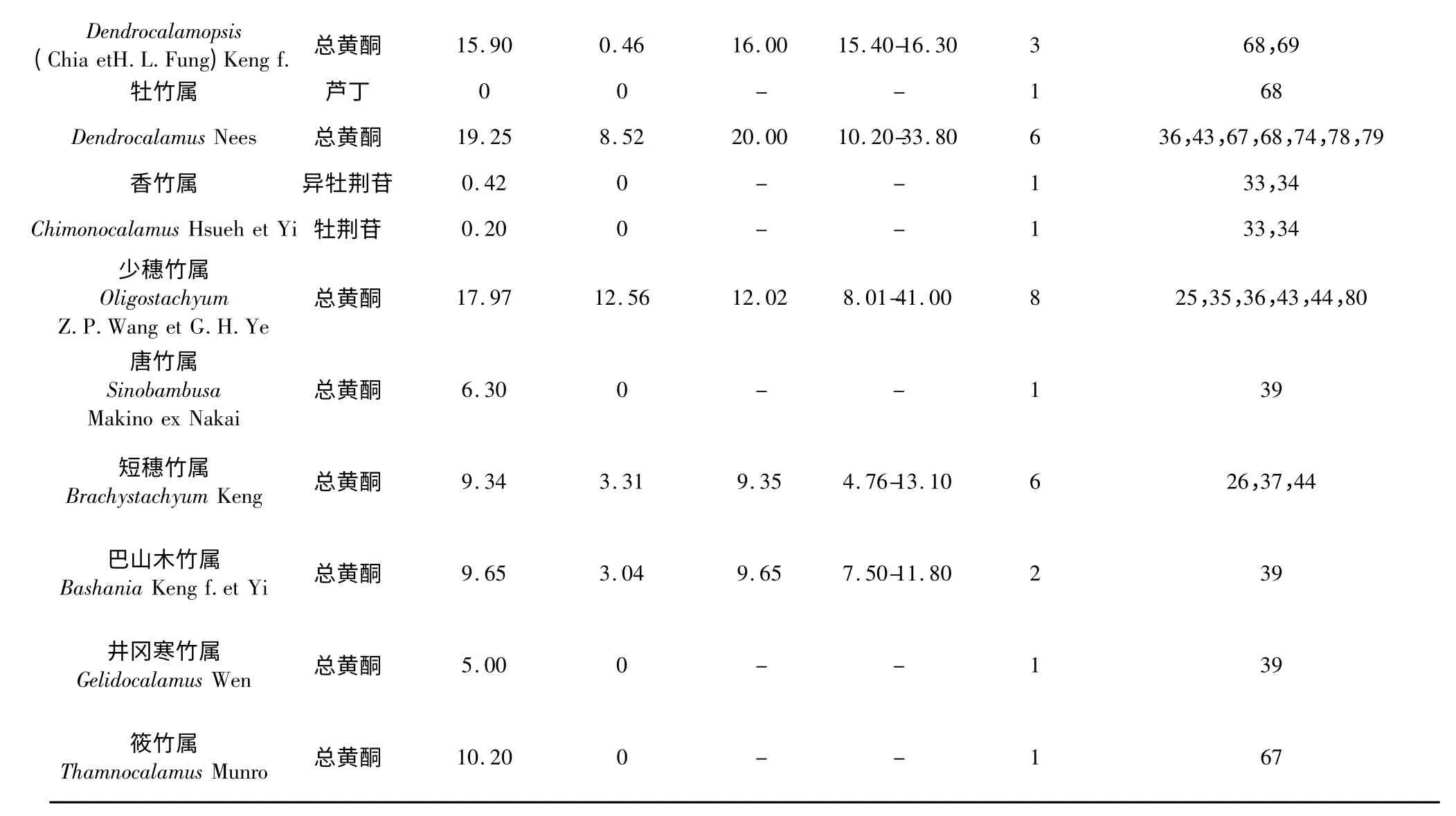
刚竹属(Phyllostachys Sieb.et Zucc.)的代表种毛竹[P.heterocycla var.pubescens (Nazel)Ohwi]是我国最重要的经济竹种,约占竹林总面积的70%[59]。关于毛竹叶黄酮的研究文献最多,涉及面最广,数据最全,一定程度上反映出科研工作者对毛竹叶黄酮开发利用的迫切愿望。表2 数据显示,刚竹属叶片的总黄酮平均含量为16.34 mg/g,四种碳苷黄酮的含量合计为1.38 mg/g,其中异荭草苷含量最高(0.55 mg/g)。
除刚竹属(Phyllostachys Sieb.et Zucc.)外,箬竹属(Indocalamus Nakai)、箣竹属(Bambusa Retz.corr.Schreber)和大明竹属(Pleioblastus Nakai)竹叶黄酮的研究文献较多。其中,箬竹属(Indocalamus Nakai)叶片中,总黄酮平均含量为17.25 mg/g,高于刚竹属(Phyllostachys Sieb.et Zucc.),四种碳苷黄酮中也是异荭草苷含量最为丰富(0.84 mg/g),合计碳苷黄酮总量为2.49 mg/g;箣竹属(Bambusa Retz.corr.Schreber)叶片中,总黄酮平均含量为16.27 mg/g,与刚竹属(Phyllostachys Sieb.et Zucc.)接近,值得注意的是,其叶片中异荭草苷和芦丁的含量处于较高水平,分别为1.39 mg/g 和1.53 mg/g,但荭草苷含量未见报道;大明竹属(Pleioblastus Nakai)叶片中,总黄酮平均含量为12.63 mg/g,低于刚竹属(Phyllostachys Sieb.et Zucc.),四种碳苷黄酮总量为1.23 mg/g,其中荭草苷最高(0.41 mg/g)。
表2 数据还显示,竹亚科不同属间竹叶黄酮的含量范围波动大,差距可达数十倍。除了种间差异带来的遗传因素外,立竹条件、采样季节、鲜叶干燥方式、提取和分析方法等的差异都可能对结果造成一定的影响[26-29,72]。
1 Jiang ZH(江泽慧).Bamboo and Rattan in the World(世界竹藤).Beijing:China Forestry Publishing House,2002.3-5.
2 Yin LR(尹利端),et al.Research progress in industrial preparation and efficacy of extracts of bamboo leaves.Sci Tech Food Ind(食品工业科技),2012,33:383-386.
3 Cui J(崔健).Flavonoids and volatile components from Indocalams leaves.Beijing:China Academy of forestry(中国林业科学研究院),PhD.2011.
4 Zhang Y(张英).Natural functional extract of bamboo leaves——bamboo leaf anthoxanthin.Chin Food Add (中国食品添加剂),2002,3:54-58,66.
5 Guo XF(郭雪峰),et al.Detection of antioxidative capacity of bamboo leaf extract by scavenging superoxide anion free radical.Spectrosc Spect Anal(光谱学与光谱分析),2008,28:1823-1826.
6 Lee HJ,et al.The compound isolated from the leaves of Phyllostachys nigra protects oxidative stress-induced retinal ganglion cells death.Food Chem Toxicol,2010,48:1721-1727.
7 Hu C,et al.Evaluation of antioxidant and prooxidant activities of bamboo Phyllostachys nigra var.Henonis leaf extract in vitro.J Agric Food Chem,2000,48:3170-3176.
8 Zhang Y(张英).Studies on functional factors in bamboo leaves.Wuxi:Jiangnan University,(无锡轻工大学,现江南大学),PhD.1995.
9 Wang HB,et al.Flavone glucosides with immunomodulatory activity from the leaves of Pleioblastus amarus.Phytochemistry,2004,65:969-974.
10 Ni XM(倪向梅),Cao GQ(曹光群).In vitro antibacterial and antioxidant activity of bamboo leaves extract.Nat Prod Res Dev (天然产物研究与开发),2011,23:717-721.
11 Wu YH(吴耀辉),et al.Study on antimicrobial effect of the extracts from Bambusa vulgaris cv.Wamin leaf.Food Sci Tech(食品科技),2010,35:218-221.
12 Xia HJ(夏海军).Antimicrobial activities of extracts from Bambusa multiplex leaves.Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University(安徽农业大学),MSc.2009.
13 Zhang Y(张英),et al.Primary studies on bamboo-leaf-flavonoids used as anti-aging factor for skin protection.Chem Ind Forest Prod(林产化学与工业),2004,24:95-100.
14 Zhang Y(张英),Tang LL(唐莉莉).Experimental studies on anti-aging effect of the leaf extract of Ph.nigra var.henonis.J Bam Res(竹子研究汇刊),1997,6(4):62-67.
15 Shen J(沈健),Feng L(冯磊).Effects of extraction of bamboo-leaf on metabolism of blood lipid in rat.Mod Rehab(现代康复),1999,3:549-551.
16 Liu LL(刘连亮),et al.Experimental study of compound tablets of Bamboo-leaf-flavonoids on hyperlipidimia of rats.Food Drug(食品与药品),2012:395-398.
17 Lu BY(陆柏益),et al.Advances in studies on antioxidative activity and cardio-cerebrovascular pharmacology of bambomleaf-flavonoids.Chem Ind Forest Prod(林产化学与工业),2005,25:120-124.
18 Zhao N(赵楠),et al.Antidepressant effect of bamboo-leaves-flavonoids on mice behavior model.Chin Pharm Commun(中国药理通讯),2008,25(3):47.
19 Zhang Y,et al.New research developments on acrylamide:analytical chemistry,formation mechanism,and mitigation recipes.Chem Rev,2009,109:4375-4397.
20 Xu BQ(许宝泉),et al.Bamboo leaves flavanone physiological function research progresses.Jiangxi Forestry Sci Tech(江西林业科技),2006,1:37-39.
21 Sun CH(孙长花),et al.Research headway in physiological activity and application of bamboo leaf flavone.Sichuan Food Ferm(四川食品与发酵),2006,1:13-16.
22 Lv Z,et al.Rapid identification and detection of flavonoids compounds from bamboo leaves by LC-(ESI)-IT-TOF/MS.Biol Res,2012,7:1405-1418.
23 Zhang Y(张英).Bamboo leaves flavone physiology and pharmacological activity.World Bam Rattan(世界竹藤通讯),2004,2(2):1-11.
24 Zhang Y(张英).Application of bamboo leaves antioxidants in food industry.Chin food add lett (中国食品添加剂,专家论坛),2006:59-62.
25 Zhu SL(朱石麟),et al.China Bamboo(中国竹类植物图志).Beijing:Science Press,1994.
26 Yu ZY(俞卓裕).Technologic studies on the effective fraction of bamboo leaves.Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,MSc.2003.
27 Chen Y(陈宇),et al.Studies on the extraction process of total flavonoids in bamboo leaves.J Putian Univ(莆田学院学报),2012,19(2):38-41.
28 Yang P(杨萍),et al.A comparative study of total flavone contents in ku bamboos.J Zhejiang Forest Coll (浙江林学院学报),2005,22:24-27.
29 Li P(李鹏),et al.Studies on the extraction process of total flavonoids in bamboo leaves.Food Eng·Agric Mach(食品工程·农业机械),2011,10:151-153.
30 Cui J,et al.HPTLC analysis of the flavonoids in eight species of Indocalamus leaves.JPC-J Planar Chromat,2011,24:394-399.
31 Sun J,et al.Simultaneous HPTLC analysis of flavonoids in the leaves of three different species of bamboo.JPC-J Planar Chromat,2010,23:40-45.
32 Ni QX(倪勤学),et al.Active components in six kinds of ground bamboo leaves and their anti-oxidant activities.Chin Trad.Herb Drugs(中草药),2011,42:2317-2321.
33 Wang H(王慧),et al.Preparation and comparative analysis of antioxidant activity of bamboo leaf extracts from different varieties.J Anhui Agric Univ(安徽农业大学学报),2012,39:540-544.
34 Wang H(王慧).Antioxidant activity of bamboo leaf extracts from varieties and extraction process optimization.Beijing:China Academy of Forestry,MSc.2012.
35 Wu JM(邬建敏),Jia ZS(贾之慎).Analysis of total flavonoid and rutin content in bamboo.J Zhejiang Agric Univ(浙江农业大学学报),1998,24:425-428.
36 Lu ZK(陆志科),Xie BX(谢碧霞).Analysis of the active components in bamboo leaves and the anti-microbial effect of their extracts.J Central South Forestry Univ(中南林学院学报),2004,24(4):70-73.
37 Yuan XF(袁晓峰).Extraction and analysis of flavonoids in several bamboo leaves and branches.Nanjing:Nanjing Forestry University,MSc.2006.
38 Lu ZK(陆志科),Xie BX(谢碧霞).A study of chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of different extracts in different kinds of bamboo leaves.J Northwest Forestry Univ(西北林学院学报),2005,20:49-52.
39 Chen WY(陈文英),et al.Screening of high quality bamboo leaf flavonoids and comparison of its determination methods.Mod Chem Ind(现代化工),2008,28:355-358.
40 Su CH(苏春花),et al.Seasonal changes of Indocalamus leaf active ingredients contents.Chin J App Eco(应用生态学报),2011,22:2471-2476.
41 Li SF(李水芳).The research on chemical components in Indocalamus leaves.Changsha:Central South University of Forestry and Technology,MSc.2006.
42 Xiang TY(向天勇),et al.The separation and purification of the bioactive substances of Indocalamus leaves.J Hubei Ins Nationalities(Nat Sci Edit)(湖北民族学院学报·自然科学版),2002,20(3):70-74.
43 Lu ZK(陆志科).Extraetion & isolation of bio-actviated constituents in bamboo leaves and its antifungi actviities.Zhuzhou:Cenrtal-South Foerstyr Unlversyity,PhD.2004.
44 Jia ZS(贾之慎),et al.Study on flavonoid content in bamboo.J Bamboo Res(竹子研究汇刊),1995,14(2):39-45.
45 Pan N(潘娜).Study on the anti-oxidizing action of flavonoids from bamboo leaves and the inhibition action on acrylamide of fried potatoes.Beijing:Beijing Forestry University,MSc.2010.
46 Wang J(王进).Screening and determination of active components and analysis of volatile compounds from bamboo leaves of the Genus Bambusa.Beijing:China Academy of forestry,PhD.2012.
47 Tang F(汤峰),et al.Chemical constituents of leaves of Phyllostachys heteroclada Oliver.J Jilin Univ,Sci Edi(吉林大学学报·理学版),2013,51:724-726.
48 Li HY(李洪玉),et al.Determination of orientin,isoorientin,isovitexin in bamboo leaf from different sources by HPLC.Chin Trad Pat Med(中成药),2004,26:208-210.
49 Liu X(刘璇).Antioxidant and effect on the cell apoptosis phenomenon on bamboo,vaccinium vitis idaea extracts.Beijing:Capital Normal University,MSc.2009.
50 Zhang Y(张英),et al.Comparison study on total flavonoid content and anti-free radical activity of the leaves of bamboo,Phyllostachys nigra,and Ginkgo bilabo.China J Chin Mat Med(中国中药杂志),2002,27:254-257.
51 Xue YQ(薛月芹).Study on compositions of bamboo leaf and correlated foundation research.Hangzhou:Zhejiang Forestry University,MSc.2008.
52 Li D(李栋).Study on bamboo leaf flavone extraction,purification,identification and its antioxidant and antibacterial activity.Wuhan:Central China Agricultural University,MSc.2008.
53 Han ZC(韩正春).Study for the technology of extraction,purification and quality criteria of the bio-active constituents from bamboo leaves.Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,MSc.2002.
54 Liu X(刘璇),et al.Anti-oxidative of Extract of north Ph.Praecox leaves.J Environ Health(环境与健康杂志),2009,26:239-241.
55 Li YF(李悦丰).Comparison of bamboo leaf flavone and Vc content in different species bamboo.Hunan Agric Sci(湖南农业科学),2009,2:37-38.
56 Zhang SS(张珊珊),Zhao XH(赵晓红).Ultrasonic-assisted extraction process of flavones from north Ph.praecox Leaf.Food Sci(食品科学),2007,28:147-151.
57 Zhang SS(张珊珊),et al.Flavones extraction from north Ph.Praecox leaf by ethanol.Acad Period.Farm Prod Proc(农产品加工·学刊),2010,11:33-36.
58 Chen Y(陈雅),et al.Comparison of the contents of total flavonoids in the bamboo leaves from different regions in wuling moutain area of the northwestern Hunan province.J Jishou Univ,Nat Sci(吉首大学学报·自科版),2012,33(5):85-87.
59 Lu ZK(陆志科),Liao W(廖威).Preliminary determination of chemical components for leaves of phllostachys Pubescens.J Shanxi Univ,Nat Sci(山西大学学报·自科版),2003,26(1):46-48.
60 Yao ZR(姚志蕊),et al.Research on extraction of anti-microbial active components from Phyllostachys pubescens Mazel exH.de Lehaie leaves.Chem Ind Forest Prod(林产化学与工业),2008,28(5):51-54.
61 Yao ZR(姚志蕊).Extraction and analysis of the Antimicrobial ingredient of Phyllostachys pubescens leaves.Wuxi:Jiangnan University,MSc.2008.
62 Zhang YX(张颖心).Separation of total flavonoids from Phyllostachys pubescens leaves and design of product chain for Phyllostachys pubescens based on circular economy.Wuxi:Jiangnan University,PhD.2008.
63 Wu HY(吴华勇),et al.Optimization of total flavonoids extraction from bamboo leaves by response surface methodology.Food Sci(食品科学),2008,29:196-200.
64 Tong XB(童晓滨),et al.The study pick up the total flavanone in the lei-bamboo leaves and determination.J Nanping Teach Coll (南平师专学报),2007,26(4):19-23.
65 Zhang Y(张英),et al.Studies on seasonal variation of flavonoids and lactones in bamboo leaves.Chem Ind Forest Prod(林产化学与工业),2002,22(2):65-69.
66 Tong XB(童晓滨).Technique of combined extraction of polysaccharide and flavanone from cv.Ventricousinte-mode leaves.Mod Chem Ind(现代化工),2009,29(11):53-55.
67 He CL(何春雷),et al.Study on technologic parameters in extracting flavonoids from bamboo leaves.J Sci Agric Univ(四川农业大学学报),2006,24:409-412.
68 Zheng DY(郑德勇),An XN(安鑫南).Study on the compositions of cluster-bamboo’s leaf extractives and its DPPH free radical scavenging ability.J Fujian Coll Forest(福建林学院学报),2004,24:193-196.
69 Wu YH(吴耀辉),et al.Preliminary study of extracting flavonoids from leaves of powdery bamboo.J Cent South Univ Forestry Tech(中南林业科技大学学报),2010,30:123-126.
70 Gong YF(龚燕飞),et al.Research on extraction technology of the flavonoids in Bambusa Ventricosa Mcclure leaf.J Cent South Univ Forestry Tech(中南林业科技大学学报),2010,30:119-122.
71 Nakajima Y,et al.Six new flavonolignans from Sasa Veitchii(Carr.)Rehder.Tetra.2003,59:8011-8015.
72 Ni QX(倪勤学),et al.Effects of different drying methods on the effective component and antioxidant capability of bamboo leaves.J Chin Inst Food Sci Tech(中国食品学报),2012,12(12):84-90.
73 Li H,et al.Ultrasonically assisted simultaneous extraction of isoorientin,orientin and vitexin from leaves of Neosinocalamus Affinis (Rendle)Keng F.(N.Affinis).Sep Sci Technol,2013,48:1987-1997.
74 Ye L(叶玲).Analysis of bamboo extracts and their calcium antagonistic effects.Chengdu:Sichuan University,MSc.2006.
75 Yu W(余 文),et al.Techniques flavone extraction from leaves and differences of flavone content in Neosinocalamus Affinins from different regions of Sichuan province.J Northwest A&F Univ,Nat Sci(西北农林科技大学学报,自科版),2008,36:143-148.
76 Wang Q(王琼),Su ZX(苏智先).Changes of total flavonoids content at the module and ramet levels in Neosinocalamus affinis.Acta Bot Yunnanica(云南植物研究),2004,26:458-464.
77 Jiang JB(蒋剑波),et al.Extraction and determination of flavonoids from Sinocalamus affinis leaves in Xiangxi.Chin Wild Plant Res (中国野生植物资源),2011,30(2):46-50.
78 Jiang HT(蒋和体),Tu DW(屠大伟).A preliminary study on biochemmical appraisal and extracting process of flavonoids from Dendrocalamus yunnanicus leaves.J Southwest Agric Univ,Nat Sci(西南农业大学学报,自科版),2006,28:809-812.
79 Xie BX(谢碧霞),Lu ZK(陆志科).The separation and identification of antimicrobial active substances in Sinoealamus latiflorus McClure leaves.J Cent South Forestry Univ(中南林学院学报),2005,25(5):10-14.
80 Xu G(许钢),Zhang H(张虹).Leaching method study of flavone from bamboo leaves.Food Mach(食品与机械),1999,6:23-24.
