莲心碱对氯化锂-匹鲁卡品癫痫模型大鼠皮层脑电图的影响
2014-09-13范崇桂刘照
范崇桂,刘照
(1.南阳市中心医院神经内科,河南南阳473000;2.浙江大学临床内科,浙江杭州310027)
莲心碱对氯化锂-匹鲁卡品癫痫模型大鼠皮层脑电图的影响
范崇桂1,刘照2
(1.南阳市中心医院神经内科,河南南阳473000;2.浙江大学临床内科,浙江杭州310027)
目的本实验旨在探讨莲心碱对氯化锂-匹鲁卡品致癫大鼠皮层脑电图的影响,进一步研究莲心碱的抗癫痫作用谱。方法32只雄性SD大鼠随机分为4组:低剂量莲心碱组(2.5mg/mL)、高剂量莲心碱组(5mg/mL)、生理盐水组作为阴性对照组、左乙拉西坦组(100mg/mL)作为阳性对照组,每组8只。建立氯化锂-匹鲁卡品癫痫模型。行为学确定建模成功后,将大鼠麻醉固定于立体定位仪,根据George Paxions图谱将套管针插入左侧侧脑室,留置套管针备用。安置皮层脑电图记录电极。记录脑电图30min后,各组大鼠分别用微量注射器沿留置管缓慢注射不同浓度的莲心碱、左乙拉西坦和生理盐水各10μL,之后继续记录脑电图150min。分别观测给药前30min与给药后每30min癫痫样放电次数的变化。记录同组内单位时间癫痫样放电次数,并进行前后比较,以及比较同时段癫痫样放电次数变化。结果低剂量莲心碱组、高剂量莲心碱组和左乙拉西坦组注射后单位时间癫痫样放电次数呈下降趋势,其中低剂量莲心碱组注射60min后下降具有显著统计学差异(P<0.01)、高剂量莲心碱组30min后下降有显著性差异(P<0.01);左乙拉西坦组注射30min内即有明显降低(P<0.01);生理盐水组注射后单位时间癫痫样放电次数变化无统计学差异。莲心碱组单位时间癫痫样放电次数与同时段左乙拉西坦组进行比较,高剂量莲心碱组注射后各时段癫痫样放电次数变化与左乙拉西坦组比较均无统计学差异;低剂量莲心碱组注射后30~60min时间段癫痫样放电次数没有左乙拉西坦组减少明显(P<0.05),其余各时段2组癫痫样放电次数变化无统计学差异。结论莲心碱对氯化锂-匹鲁卡品癫痫模型大鼠急性期皮层脑电图癫痫样放电具有抑制作用。
莲心碱;氯化锂;匹鲁卡品;癫痫模型;皮层脑电图
癫痫是一种古老而常见的脑部疾病,公元前400年希腊内科医师希波克拉底就首次对癫痫进行了描述。19世纪末英国神经病学家Jackson等指出癫痫是一种神经细胞对肌肉冲动的发作性过度释放,由此进入了癫痫学的新纪元。目前人们认识到癫痫包括多组疾病和综合征,是由多种原因引起的一种慢性脑功能障碍性疾病[1]。本实验继续探讨莲心碱对氯化锂-匹鲁卡品癫痫模型大鼠皮层脑电图癫痫样放电的影响,并以明确对氯化锂-匹鲁卡品癫痫模型癫痫样放电具有抑制作用的左乙拉西坦作为阳性对照,进一步深入研究莲心碱的抗癫痫作用谱。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料 实验动物:健康雄性Sprague-Dawley(SD)大鼠32只,SPF级,实验起始体质量(210±30)g,由华中科技大学同济实验动物中心提供[许可证号:SCXK(鄂)2004-0007]。
实验药品:匹鲁卡品(pilocarpine,Pilo)美国FLUKA公司生产,临用前用生理盐水配成1%溶液;氯化锂(lithium chloride,LiCl2,武汉亦新生物技术有限公司生产)临用前用生理盐水配成1%溶液;硫酸阿托品(芜湖康奇制药有限公司生产,批号YCY078);乌拉坦(国药集团化学试剂有限公司生产,51-79-6),临用前用生理盐水配成10%溶液;莲心碱(liensinine,武汉李时珍药业公司制备,5088-90-4)临用前用生理盐水稀释成2.5、5 mg/mL,2种浓度的溶液;左乙拉西坦(levetiracetam tablets,Keppra比利时UCB公司生产,H20110409)临用前用生理盐水配成10%溶液;生理盐水华北制药股份有限公司生产实验仪器:RM6240生物信号采集处理系统,成都仪器厂生产;江湾Ⅱ型立体定向仪,第二军医大学器材处生产;微量进样器,上海安亭微量进样器厂生产;不锈钢套管针,武汉大学生理教研室提供,内径0.5mm,内置硅胶管。
1.2 方法 32只雄性SD大鼠随机分为4组:低剂量莲心碱组(2.5mg/mL)、高剂量莲心碱组(5 mg/mL)、生理盐水组作为阴性对照组、左乙拉西坦组(100 mg/mL)作为阳性对照组,每组8只。建立氯化锂-匹鲁卡品癫痫模型,实验中严格遵循《实验动物保护条例》。行为学确定建模成功后,将大鼠麻醉固定于立体定位仪,根据George Paxions图谱将套管针插入左侧侧脑室,留置套管针备用。安置皮层脑电图记录电极。记录脑电图30min后,各组大鼠分别用微量注射器沿留置管缓慢注射不同浓度的莲心碱、左乙拉西坦和生理盐水各10μL,之后继续记录脑电图150min。分别观测给药前30 min与给药后每30 min癫痫样放电次数的变化。
1.3 统计学方法 实验数据均采用SPSS 13.0软件进行统计学处理。正态计量数据用“±s”表示,多样本均数采用单因素方差分析;以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 正常大鼠皮层脑电图和氯化锂-匹鲁卡品致癫大鼠皮层脑电图 正常大鼠皮层脑电图以α、θ波为主要波形,波幅小于75μV。氯化锂-匹鲁卡品致癫大鼠皮层脑电图表现为成簇性发放的棘波、尖波节律以及棘-慢、尖-慢复合波等多种形式的癫痫样放电(波幅100~1000μV,见图1)。
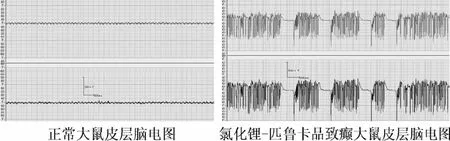
图1 大鼠皮层脑电图Fig.1 Cortical EEG in rats
2.2 莲心碱对癫痫模型皮层脑电图癫痫样放电的影响低剂量莲心碱组和高剂量莲心碱组注射后单位时间内癫痫样放电次数呈下降趋势(见图2),其中低剂量莲心碱组注射60 min后下降具有显著统计学差异(P<0.01)、高剂量莲心碱组注射30min后下降有显著统计学差异(P<0.01);左乙拉西坦组注射30min内下降即有显著统计学差异(P<0.01);生理盐水组注射后单位时间癫痫样放电次数变化无统计学意义(见图3、表1)。高剂量莲心碱组注射后各时段癫痫样放电次数变化与左乙拉西坦组比较均无统计学差异;低剂量莲心碱组注射后30~60 min时间段癫痫样放电次数没有左乙拉西坦组下降明显(P<0.05),其余各时段2组癫痫样放电次数变化无统计学差异(见表1)。
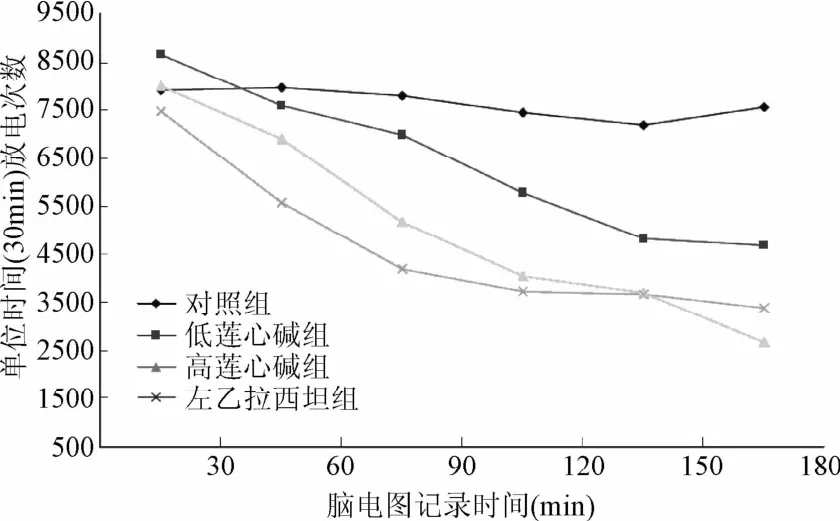
图2 各组大鼠处理前后癫痫样放电次数变化趋势图Fig.2 Change trend chart of epileptic discharge frequency of rats in each group before and after processing
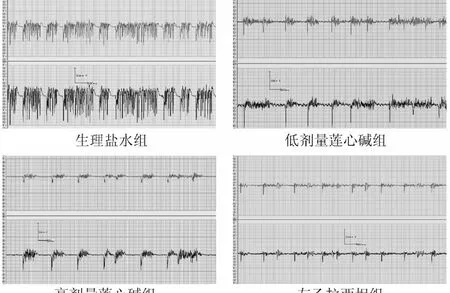
图3 4组大鼠注射后皮层脑电图Fig.3 Cortical EEG of rats in four groups after injection
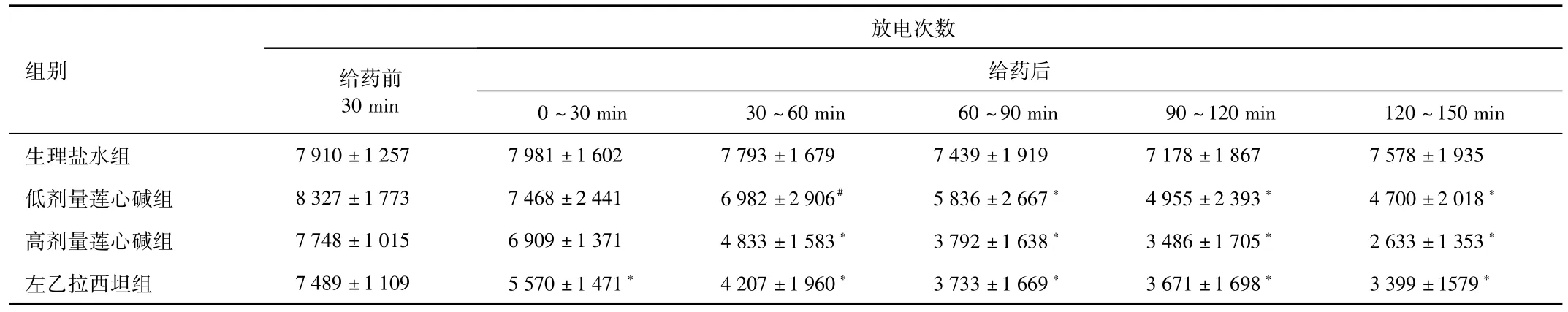
表1 4组大鼠皮层脑电图单位时间癫痫样放电次数变化(次)Tab.1 Epileptic discharge frequency changes of rats cortical EEG in unit time of four groups(times)
3 讨论
癫痫是一组由于大脑神经元过度异常放电所引起的以中枢神经系统短暂性功能失常为特征的慢性脑部疾病。其发病机制非常复杂,目前较一致的观点认为是中枢神经系统兴奋与抑制不平衡所致,而这种不平衡主要与离子通道、突触传递及神经胶质细胞的改变有关。
莲心碱是从中药莲子心中提出的一种双苄基异喹啉单醚键型生物碱,首先在器官水平发现其具有广泛的试验性抗心律失常作用,进一步在细胞及分子水平研究表明莲心碱对心肌慢反应动作电位及慢内向电流有影响,可降低离体兔窦房结(SAN)起搏细胞慢反应动作电位幅度(APA)及零相最大上升速率(Vmax),延长窦性心动周期时长(SCL);并可明显拮抗Bayk8644增大SAN起搏细胞及高K+诱发的豚鼠乳头肌慢反应动作电位的APA和Vmax作用,抑制犬浦肯野纤维慢向内流;莲心碱还能使大鼠心肌细胞钠内流及L型钙内流降低,抑制钠内流、稳态外向K+电流和L型钙内流的I-V曲线,并使后者的峰值电流电位略右移,从而提示莲心碱对Na+、K+、Ca2+的跨膜转运有抑制作用[13-14]。
本实验设计2个倍数剂量梯度的莲心碱溶液侧脑室注射,连续记录150min,结果显示莲心碱组皮层脑电图单位时间癫痫样放电次数呈下降趋势(图3),并且脑电图上可见到癫痫样放电的波幅亦较注射前有所下降;生理盐水组注射后单位时间癫痫样放电次数无明显变化。其中低剂量莲心碱组注射60min后单位时间癫痫样放电次数减少,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.01),高剂量莲心碱组30min后减少,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)(表1)。实验结果表明莲心碱可以抑制氯化锂-匹鲁卡品癫痫大鼠模型急性期的癫痫样放电,并且在一定浓度范围内随着剂量增大,莲心碱的作用时间提前。
左乙拉西坦是一种新型的抗癫痫药物,已经被美国和欧盟批准用于部分性发作和继发性全身性发作的难治性癫痫的辅助治疗[6]。左乙拉西坦对氯化锂-匹鲁卡品癫痫模型癫痫样放电有明显的影响,所以我们选用左乙拉西坦作为本实验的阳性对照。实验结果显示除了低剂量莲心碱组注射后30~60min时间段癫痫样放电次数没有左乙拉西坦组减少明显以外(P=0.03),低剂量莲心碱组其余时段与高剂量莲心碱组所有时段与左乙拉西坦组相比均无统计学差异。进一步说明莲心碱可以抑制氯化锂-匹鲁卡品模型急性期皮层脑电图的癫痫样放电,作用类似于左乙拉西坦。
综上所述,在先前发现莲心碱可以明显抑制青霉素癫痫大鼠模型皮层脑电图癫痫样放电的基础上,又证实了莲心碱对氯化锂-匹鲁卡品癫痫大鼠模型皮层脑电图癫痫样放电具有抑制作用,功效同左乙拉西坦相当,进一步证明莲心碱具有抗癫痫作用。依据莲心碱能够抑制Na+、K+、Ca2+的跨膜转运,而阻滞电压依赖性钠、钙离子通道是抗癫痫药物的最重要机制之一,推测莲心碱的抗癫痫作用机制可能与阻滞中枢神经系统细胞膜上的离子通道有关,其具体途径有待于下一步研究。
[1] Perucca E,French J,Bialer M.Development of new antiepileptic drugs:challenges,incentives,and recentadvances[J].Lancet Neurol,2007,6(9):793-804.
[2]John RP,Jacqueline F.Antiepileptic drugs in development[J].Lancet Neurol,2006,5(12):1064-1066.
[3]Piotr C,Barbara B,Stanislaw J,et al.Mechanisms of action of antiepileptic drugs[J].Medicinal Chemistry,2005,5:3-14.
[4]Racine R,Okujava V,Chipashvili S.Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulationⅡ[J].Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol,1972,32(3):281-294.
[5]Wallace RH,Wang DW,Singh R,et al.Febrile seizures and generalized epilepsy associated with amutation in the Na+channelβ1 subunit gene SCN1B[J].Nat Genet,1998,19(4):366-370.
[6]Singh NA,Charler C,Stauffer D,et al.A novel potassium channel gene,KCNQ2,imunated in an inherited epilepsy of new-borns[J].Nat Genet,1998,18(1):25-29.
[7]Guerrini R,Bonanni P,Nardocci N,et al.Autosomal recessive rolandic epilepsy with paroxysmal exercise-induced dystonia and writer's cramp:delineation of the syndrome and genemapping to chromosome 16p12-11.2[J].Ann Neurol,1999,45(3):344-345.
[8]Yang XF,Weisenfeld A.Prolonged Exposure to Levetiracetam Reveals a Presynaptic Effect on Neurotransmission[J].Epilepsia,2007,48 (10):1861-1869.
[9]Zhou H,Jiang H,Yao T,et al.Fragmentation study on the phenolic alkaloid neferine and its analogues with anti-HIV activities by electrospray-ionization tandem mass spectrometry with hydrogen/ deuterium exchange and its application for rapid identification of in vitro microsomal metabolites of neferine[J].Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom,2007,21(13):2120-2128.
[10] Lynch BA,Lambeng N,Nocka K,et al.The synaptic vesicle protein SV2A is the binding site for the antiepileptic drug levetiracetam[J]. Proc Natl Acad SciUSA,2004,101(26):9861-9866.
[11]Oliveira AA,Nogueira CRA,et al.Evaluation of levetiracetam effects on pilocarpine-induced seizures:Cholinergic muscarinic system involvement[J].Neuroscience letters,2005,05(48):184-188.
[12]Klitgaard H,Matagne A,Grimee R,et al.Electrophysiological,neurochemical and regional effects of levetiracetam in the rat pilocarpinemodel of temporal lobe epilepsy[J].Seizure,2003,12 (2):92-100.
[13]Maike G,Claudia B.Efects of the novel antiepileptic drug levetiracetam on spontaneous recurrent seizures in the rat pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy[J].Epilepsia,2002,43(4):350-357.
[14]Liu CP,TsaiWJ,Lin YL,et al.The extracts from Nelumbo nucifera suppress cell cycle progression,cyto-kine genes expression,and cell proliferation in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells[J].Life Sci.2004,75(6):699-716.
[15]Luo X,Chen B,Liu J,etal.Simultaneous analysisof N-nornuciferine,O-nornuciferine,nuciferine,and roemerine in leaves of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn by high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detectionelectrospray mass spectrometry[J].Anal Chim Acta,2005,538(5):129-133.
(编校:谭玲)
Effect of liensinine on cortical EEG of epileptic rats induced by lithium chloride-pilocarpine
FAN Chong-gui1,LIU Zhao2
(1.Department of Neurology,Nanyang Central Hospital,Nanyang 473000,China;2.Department of Clinical Medicine,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310027,China)
ObjectiveTo explore the effect of liensinine on cortical EEG of epileptic rats induced by lithium chloride-pilocarpine,and investigate the effective spectrum of liensinine on epilepsy.Methods32 SD ratswere random ly divided into four groups:low dose of liensinine group(2.5mg/mL,10μL),high dose of liensinine group(5mg/mL,10μL),the normal saline group(10μL)which was negative control group,levetiracetam group(100 mg/mL,10μL)which was positive control group,8 rats in each group.Electrocorticogram of rats was recorded after chloride lithium-pilocarpinemodel was induced.The anesthetic ratswere fixed on stereotaxic apparatus after the epilepsy model was confirmed by ethology.A trochar was put into the left lateral ventricle.Rats were implanted with epidural recording electrodes.After the cortical EEG was recorded about 30 minutes,liensinine(at concentration of 2.5,5mg/mL),levetiracetam and 0.9%sodium chloride was injected into lateral ventricle.Electrocorticogram was recorded about150 minutes again.The frequency of epileptic discharge was observed every 30 minutes.The differences of frequency in the same group and the different change of frequency between groups at the same period were compared.ResultsThe frequency of epileptic discharge decreased in low dose of liensinine group,high dose of liensinine group and levetiracetam group after administration,there was significantly statistical difference in low dose of liensinine group after administration about60 minutes(P<0.01),there was significant statistics difference in high dose of liensinine group after administration about 30 minutes(P<0.01),and the same change in levetiracetam group within 30 minutes after administration(P<0.01);the change of frequency of epileptic discharge was no significantly statistical difference between pro-and post-administration in the normal saline control group.The difference of the frequency change in epileptic discharge at the same period between liensinine group and levetiracetam group was observed,therewas statistic difference between low dose of liensinine group and levetiracetam group at the period of thirty to sixtyminutes after administration,there was no statistic difference at other periods;there was no statistic difference between high dose of liensinine group and levetiracetam group at every period.ConclusionLiensininecould inhibit the epileptic discharges in acutemodel of epileptic rats induced by chloride lithium-pilocarpine.
liensinine;lithium chloride;pilocarpine;epilepsymodel;electrocorticogram
R724.1
A
1005-1678(2014)07-0049-04
高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金(20090101120121)
范崇桂,男,硕士,主治医师,研究方向:神经内科,E-mail:qch1821460127@163.com。
